BCS 111 Unit 6.2
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
An overview of our memory system
-
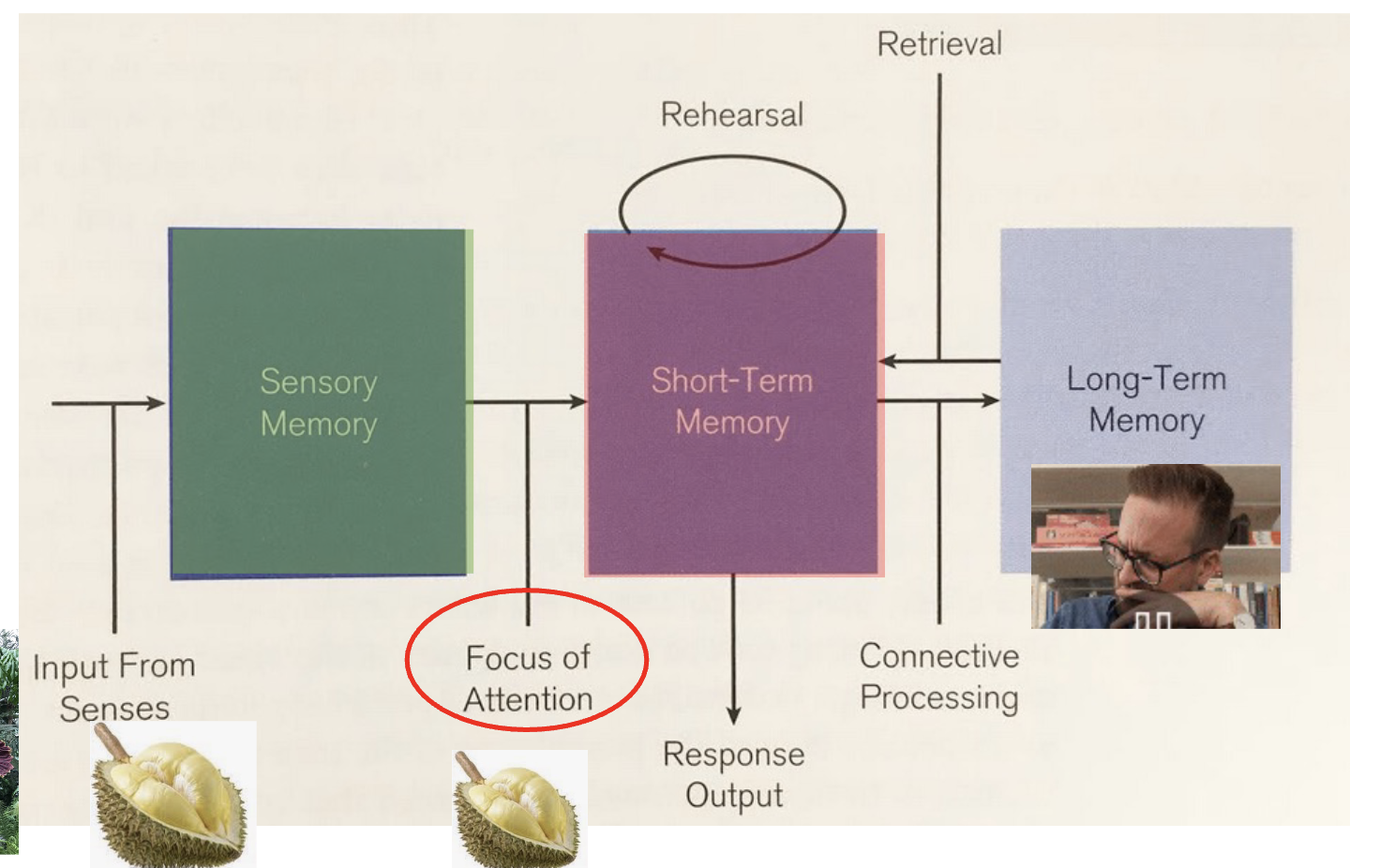
Testing processing and short-term storage capacity
Free-recall experiment
Listen carefully. Memorize as many words as you can
Testing processing and short-term storage capacity
What factors may affect your recall?
What are some possible confounding variables?
Did you use any kind of strategy to help you recall?
Testing processing and short-term storage capacity
What factors may affect your recall (possible confounds)?
To name just a few:
Length of the list
Whether you can see the actual object
Speed of presentation
Word length
Concreteness of words
Word frequency
Testing processing and short-term storage capacity
Serial position effect: the first few words (Primacy effect) and the last few words (Recency effect) on the list are typically recalled better.
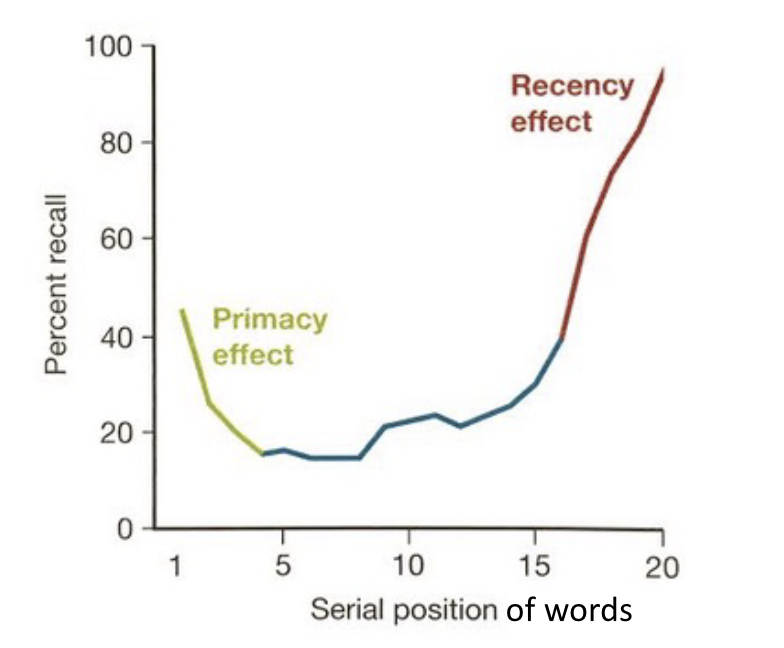
Serial position effect: Primacy vs. Recency effect
How do we disrupt primacy effect?
How do we disrupt recency effect?
Effect of presentation speed
Fast presentation yielded a weaker primacy effect than slow
No diff. in recency effect between fast and slow
Short term memory
Capacity
Magic Seven (plus or minus two)
One strategy for improving storage capacity: chunking
How would you remember the following letter string?
M L B O N C B S N N F L O N E S P N
top-down process
Short term memory: retention
The longer you count (i.e., recall interval), the poorer the recall performance
Probability of recall as a function of recall interval
Encoded info decays in about 20 s
Short term memory - retrieval
In terms of order:
Serial search: one-by-one search by order
Parallel search: scan from multiple rows/columns; not by order
In terms of when to stop search:
Self-terminating search: search stops when target detected
Exhaustive search: scan through the entire display even if target already found
How do we scientifically test forgetting in short term memory?
Two competing hypotheses: Decay vs. Interference
Probe digit task (Waugh & Norman 1965)
16-digit number
Fast vs. Slow presentation → to test “decay” theory
The number of interfering items (ranging from 1 to 12) → to test “interference” theory
Short term memory: Forgetting
Two competing theories: Decay vs. Interference
Probe digit task (Waugh & Norman 1965)
Hypotheses:
1. If poorer recall in slow presentation than fast → the claim of decay is valid.
2. If no diff between slow and fast, then interference is valid
Two competing theories: Decay vs. Interference
Hypotheses:
1. If poorer recall in slow presentation than fast → the claim of decay is valid.
2. If no diff between slow and fast, then interference is valid