3.4 Price Ceilings and Price Floors
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Assuming a market is currently at the equilibrium price and quantity, when a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, ______________.
the quantity demanded will rise and the quantity supplied will fall, causing a shortage
there is nothing preventing the price from falling to its equilibrium level
there is nothing preventing the price from rising to its equilibrium level
the quantity supplied will rise and the quantity demanded will fall, causing a surplus
the quantity demanded will rise and the quantity supplied will fall, causing a shortage
When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded will rise and the quantity supplied will fall, causing a shortage.
A price floor will usually tend to create ___________ when the price floor is set above the market price.
a shortage
excess demand
excess supply
an equilibrium
excess supply
A price floor will tend to create conditions of excess supply as a result of the misalignment in the market forces of more supply produced than demanded at this higher price. If price is set above equilibrium, quantity demand decreases while quantity supplied increases, causing a shortage to exist in the market.
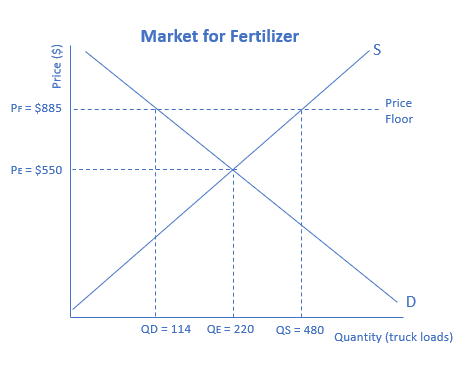
The graph below represents the fertilizer market. Calculate the surplus caused by the price floor.
366 truckloads of fertilizer
A price floor keeps the price for a good from falling below a set minimum. An effective price floor is set above the equilibrium price. To calculate the surplus caused by the price floor, subtract the quantity demanded from the quantity supplied. In this case, the surplus is equal to 480−114, or 366 truckloads of fertilizer.
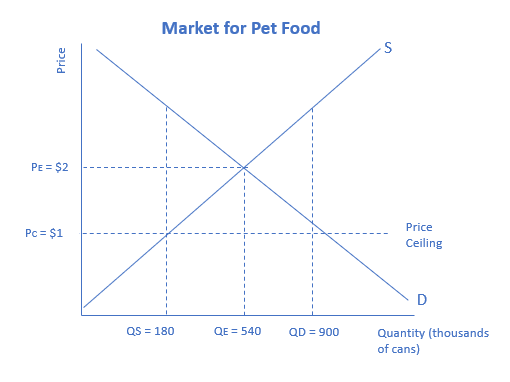
Price controls are set on pet food. Calculate the shortage caused by the price ceiling.
720 thousands of cans of pet food
A price ceiling keeps the price for a good from rising above a set maximum. An effective price ceiling is set below equilibrium price. To calculate the shortage caused by the price ceiling, subtract the quantity supplied from the quantity demanded. In this case, the shortage is equal to 900−180, or 720 thousands of cans of pet food.
Assuming a market is currently at the equilibrium price and quantity, what happens when a price ceiling is set above the equilibrium price?
There is nothing preventing the price from reaching its equilibrium level.
The quantity demanded will rise and the quantity supplied will fall, causing a shortage.
The quantity supplied will rise and the quantity demanded will fall, causing a surplus.
The price will rise to the price ceiling level.
There is nothing preventing the price from reaching its equilibrium level.
When a price ceiling is set above the equilibrium price, there is nothing preventing the price from reaching equilibrium and staying there. Since a price ceiling is a level above which price cannot rise and the equilibrium price is below that level, the price ceiling will not have any real effect on the market.
A price floor will affect both the price charged for a good and the quantity supplied if ________________.
it is set below the equilibrium price
it is set above the equilibrium price
it is set at the equilibrium price
it equals zero
it is set above the equilibrium price
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price, the quantity supplied will rise and the quantity demanded will fall, causing a surplus. When a price floor is set below the equilibrium price, there is nothing preventing the price from rising to its equilibrium level. Only when the price floor is above the market equilibrium will in influence the market quantity and price.
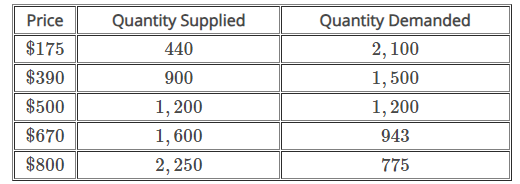
The table below represents the market for livestock. Suppose there is a price floor set at $500 for a cow. Calculate the surplus caused by the price floor.
0 cows
A price floor keeps the price for a good from falling below a set minimum. An effective price floor is set above equilibrium price. To calculate the surplus caused by the price floor, subtract the quantity demanded from the quantity supplied. In this case, the surplus is equal to 1,200−1,200, or 0 cows. Because this price floor was set at equilibrium price, there is no surplus or shortage.