9.2 (phloem transport)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
1
New cards
Active transport
a transport mechanism where ions or molecules move against a concentration gradient, this movement requires energy.
2
New cards
Hydrostatic pressure gradient
the stress that develops when solutions containing different concentrations of solute in a common solvent are separated by a membrane that is permeable to the solvent, but not the solute.
3
New cards
Incompressibility of water
the incapability of water to lose volume in response to pressure.
4
New cards
Osmosis
the diffusion of fluid through a semi-permeable membrane from a solution with a low solute concentration to a solution with a higher solute concentration until there is an equal concentration of fluid on both sides of the membrane.
5
New cards
Phloem
the food-conducting tissue of vascular plants that conducts synthesized nutrients to different parts of the plants.
6
New cards
Sieve tubes
an element of phloem tissue consisting of a longitudinal row of thin-walled elongated cells with perforations in their connecting walls through which food materials pass.
7
New cards
Reduced organelles in sieve elements
Absence of cell structures (including nucleus, cytoskeleton, golgi, ribosomes and vacuole) frees the lumen to conduct a large volume of sap
8
New cards
Companion cells
Metabolic support cells (containing all the standard organelles) provide biomolecules (e.g. enzymes) necessary to maintain life functions in the sieve elements
9
New cards
Plasmodesmata
Openings between the sieve elements and companion cells allow communication and support from companion cells
10
New cards
Sieve plate
Pores through the horizontal cells that join sieve elements allow sap to flow freely
11
New cards
Cell membrane
Presence of a fully functional cell membrane in sieve elements that contains specialised protein pumps provides the structures needed to control the composition of sap
12
New cards
Sources
photosynthesising tissues and storage organs that are exporting sugars to other parts of the plant.
13
New cards
Sinks
organs that cannot produce (sufficient) sugars and need them for respiration or storage.
14
New cards
phloem loading
The process by which soluble carbohydrates (sugars) enter the phloem. Requires active transport.
15
New cards
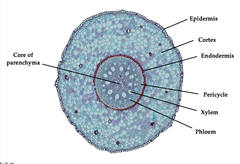
Transverse section of a young dicot stem (shoot)
16
New cards
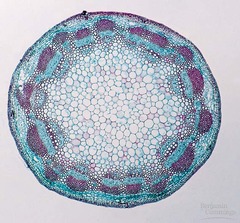
Transverse section of a dicot root
17
New cards
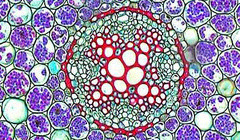
Transverse section of monocot root.