Protein Production
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
The framework describing the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to proteins.
Transcription
The process of synthesizing mRNA from a DNA template.
Translation
The process where ribosomes synthesize proteins based on the encoded mRNA sequence.
mRNA
Messenger RNA, responsible for carrying genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosomes.
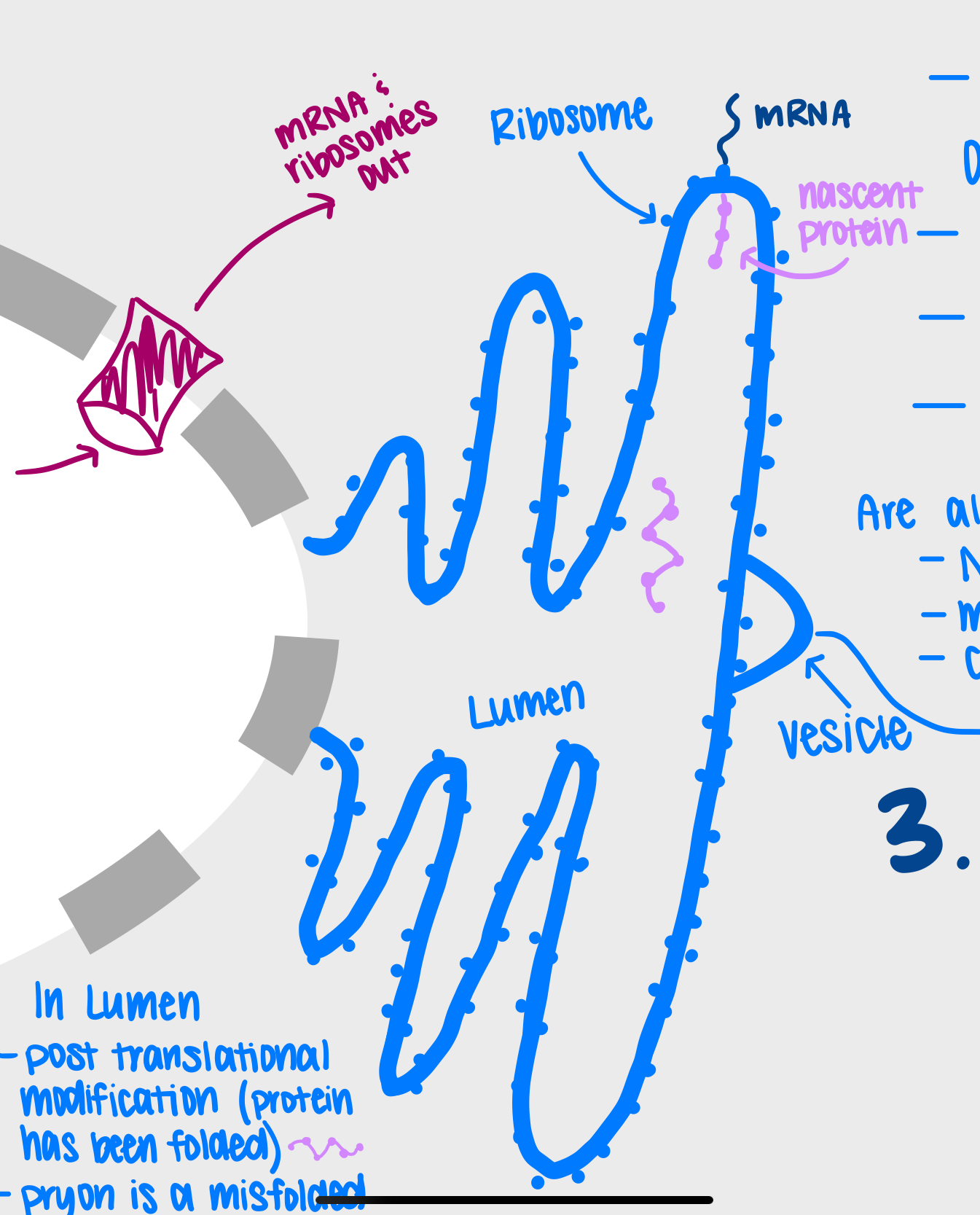
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (rER)
A cellular organelle involved in the synthesis and processing of proteins, studded with ribosomes.
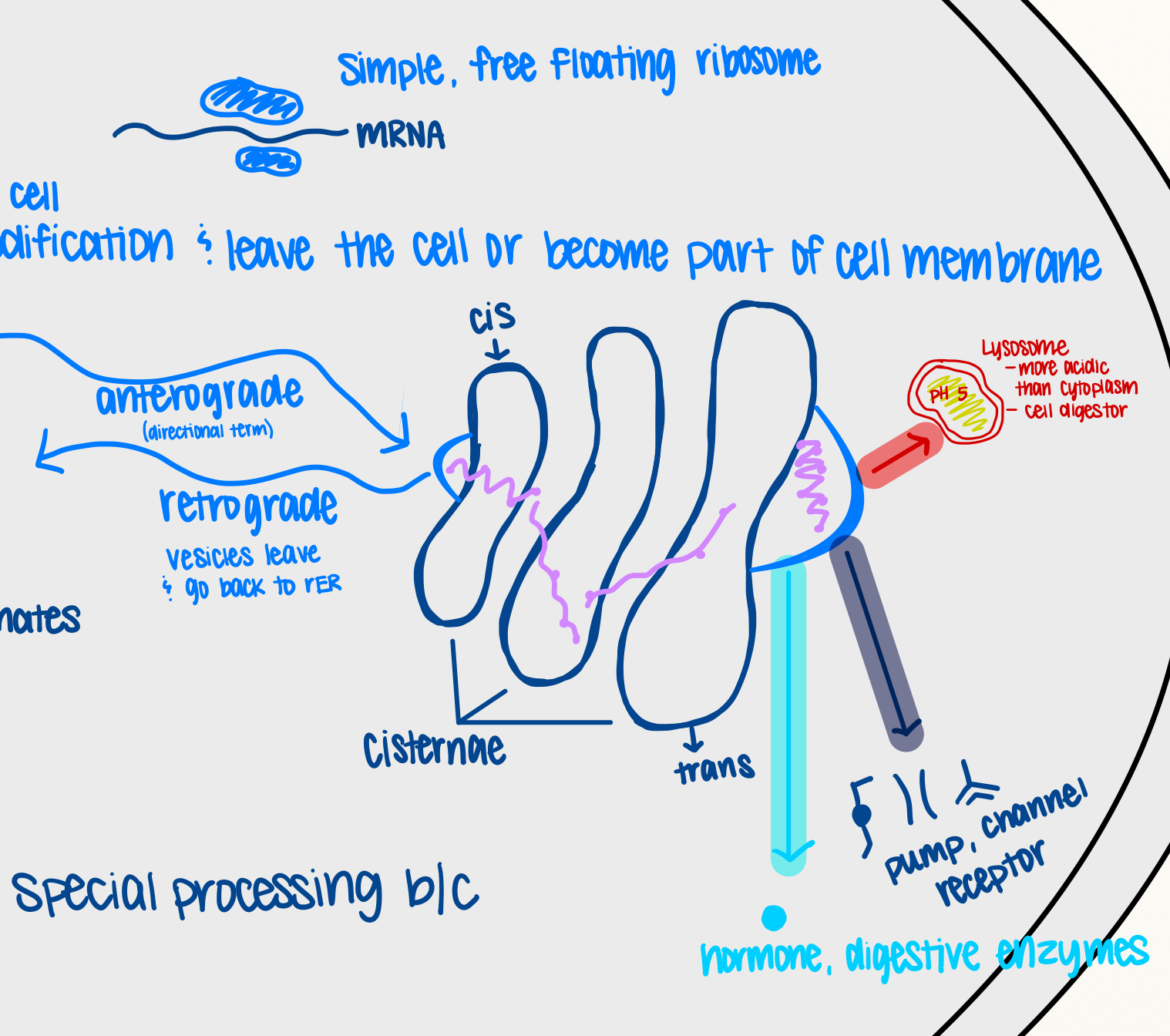
Golgi Apparatus
An organelle that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
Post-Translational Modification
Chemical changes to a protein that occur after it is synthesized, affecting its function and destination.
Vesicle
A membrane-bound sac that transports substances within a cell.
Cis Face of Golgi
The side of the Golgi apparatus that receives vesicles containing proteins from the rough ER.
Lumen
The interior space of the rough endoplasmic reticulum where protein folding and modifications occur.
Protein Secretion
The process by which proteins produced within the cell are transported out of the cell.
Nuclear Pores
Protein complexes that regulate the transportation of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm.
Amino Acids
The building blocks of proteins, of which there are about 20 different types.
Phospholipid Bilayer
The structure forming the cell membrane, composed of two layers of phospholipids.
Ribosome
A cellular structure that synthesizes proteins by translating mRNA.
Chromatin
A complex of DNA and protein found in the nucleus, which condenses to form chromosomes during cell division.