Introduction to Race and Ethnicity in Sociology
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the main difference between race and ethnicity?
Race is a socially constructed category based on physical characteristics, while ethnicity refers to shared cultural heritage.

Why are race and ethnicity considered social constructions?
They are defined and maintained through social interaction and do not exist biologically.
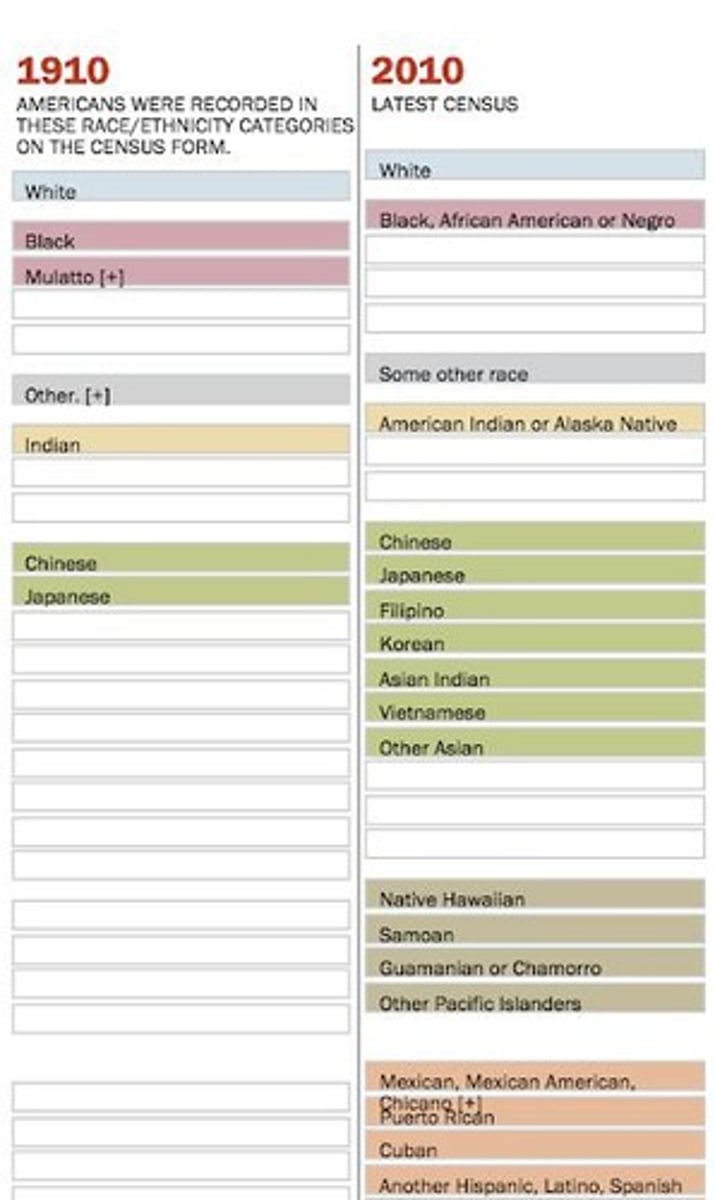
What is the definition of race?
A socially constructed category of people who share physical characteristics that distinguish them from other groups.
What is ethnicity?
A shared cultural heritage or characteristics, typically involving common language, religion, nationality, or history.
What is the concept of 'white privilege'?
The social advantages that white people enjoy relative to those in minority categories.
What does the term 'minority group' refer to?
People who are singled out for unequal treatment and regard themselves as objects of collective discrimination.
What is racism?
Prejudice and discrimination based on race, often rooted in beliefs of racial superiority.
What is the difference between prejudice and discrimination?
Prejudice is a negative attitude towards a group, while discrimination is the unfair treatment of individuals based on their group membership.
What is institutional discrimination?
Discrimination carried out systematically by social institutions affecting all members of a group.
What is individual discrimination?
Discrimination carried out by one person against another.
What is the Contact Theory?
The idea that prejudice decreases when people from different racial-ethnic backgrounds interact frequently as equals.
What are the consequences of race and ethnicity?
They influence health, education, work, family, and interactions with the criminal justice system.
What historical event is associated with the forced removal of Native Americans?
The Trail of Tears.
What landmark case affirmed that slaves were not citizens entitled to rights?
The Dred Scott case (1857).
What was the significance of the Emancipation Proclamation?
It declared the freedom of all slaves in Confederate states.
What is the 'model minority' stereotype?
The perception that Asian Americans are successful due to cultural commitment to study and hard work.
What is the largest U.S. minority group?
Hispanic Americans/Latinos.
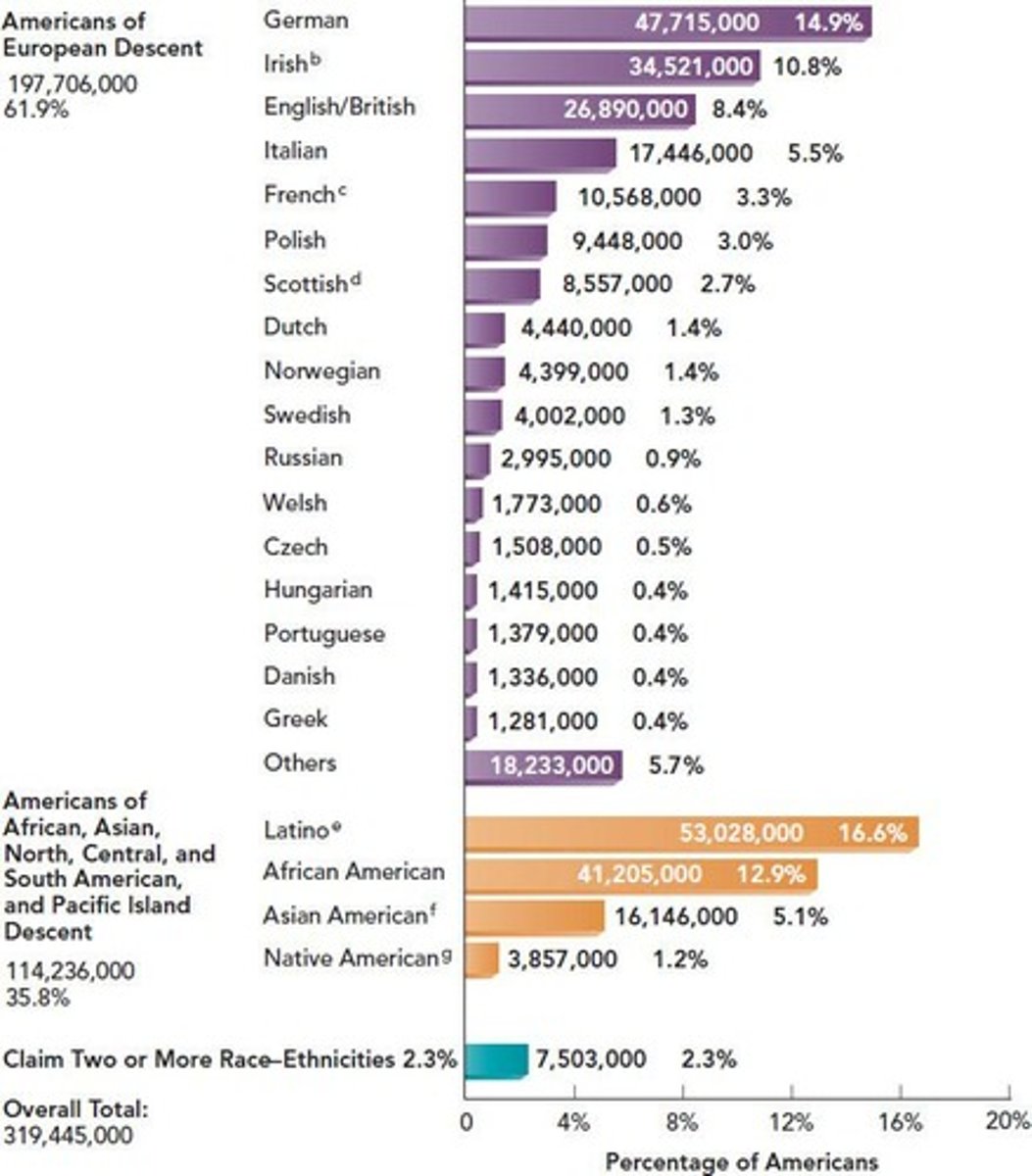
What are Jim Crow laws?
State laws that enforced racial segregation in the Southern United States.
What does the term 'invisible knapsack' refer to?
The unearned resources and privileges that white people carry, which are not visible or intended to be seen.
What is the significance of the Fourteenth Amendment?
It grants citizenship to everyone born in the United States.
What was the Great Migration?
The movement of thousands of African Americans to the North after World War I.
What does the term 'genocide' mean?
The annihilation or attempted annihilation of a people based on their presumed race or ethnicity.
What is the role of sociologists in studying race and ethnicity?
To analyze how race and ethnicity are constructed and their impact on social inequality.
What are some examples of characteristics that can lead to discrimination?
Age, sex, weight, skin color, sexual orientation, disability.
What is the significance of the Civil Rights Acts?
They aimed to end legal discrimination against African Americans.
How do sociologists view the boundaries of race and ethnicity?
They see them as fluid and changing over time.
What is the Authoritarian Personality theory?
A psychological perspective suggesting that people with high conformity and intolerance are more likely to hold prejudiced views.
What is the impact of race and ethnicity on life chances?
They affect individuals' opportunities and outcomes in various aspects of life.