muscles
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Surrounded by a connective tissue called fascia
Contains muscle bundles (fascicles)
Muscle (whole)
A bunch of muscle fibers (cells)
Fascicle (muscle bundle)
Long, cylindrical, multi-nucleated cell
Surrounded by sarcolemma (plasma membrane)
Inside is sarcoplasm (cytoplasm)
Contains myofibrils
Muscle Fiber (Muscle Cell)
Made up of repeating units called sarcomeres
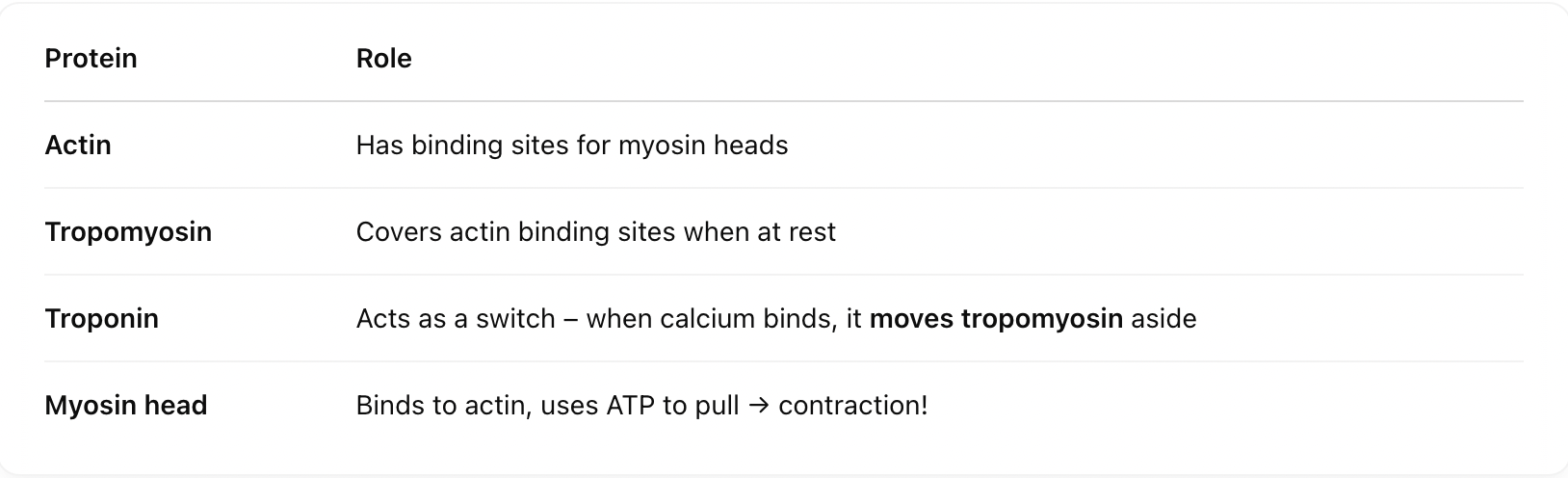
Contain actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments
Myofibrils
Light band → has only actin (thin) filaments
Center has Z-line
I-band (Isotropic Band):
Dark band → has myosin (thick) filaments
May overlap with actin
A-band (Anisotropic Band):
Zigzag line in the center of the I-band
Anchors actin filaments
Two Z-lines form a sarcomere
Z-line:
Central part of A-band with only myosin, no overlap with actin
Gets smaller during contraction
H-zone:
Runs through the center of H-zone
Holds myosin filaments together
M-line:
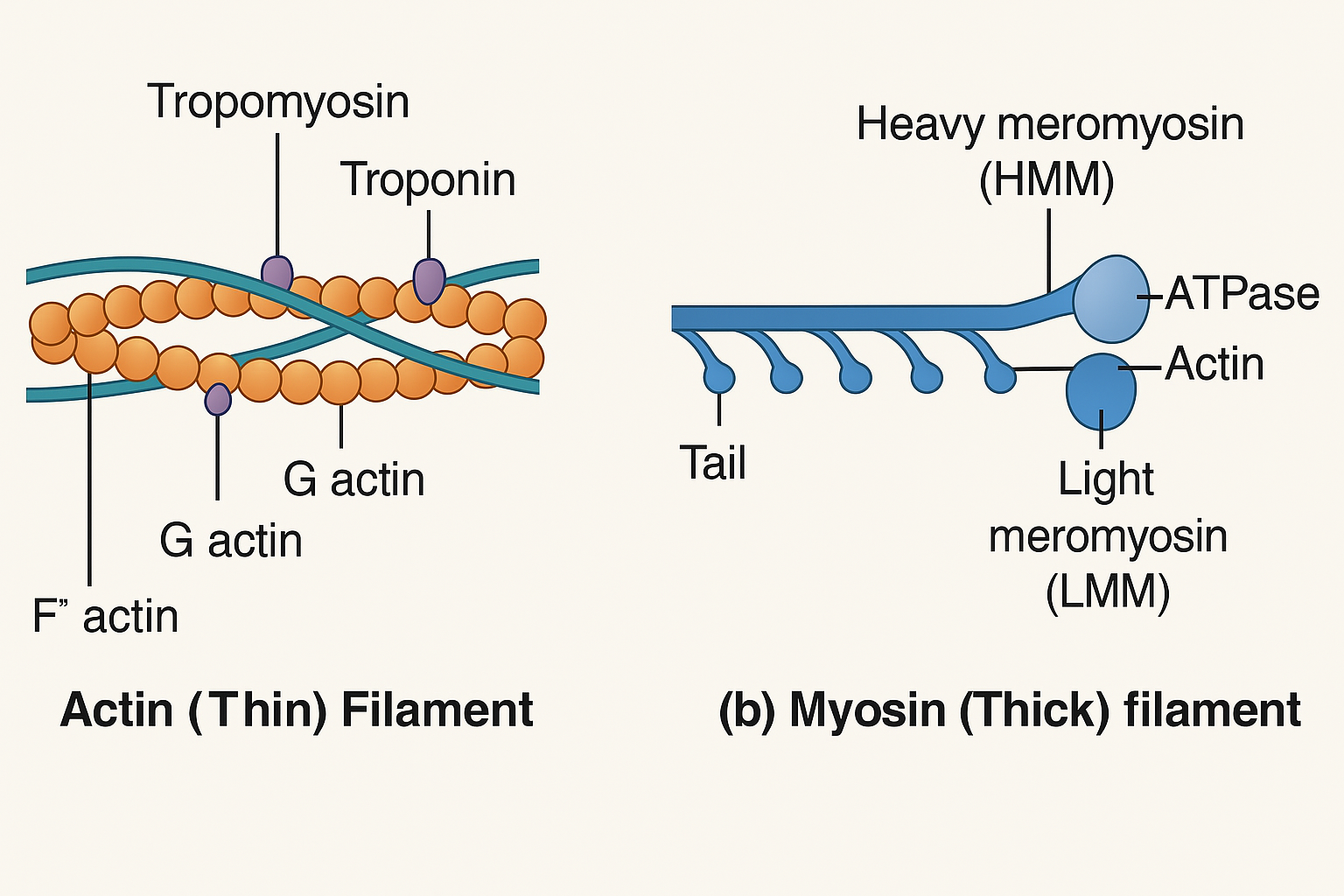
Actin is the thin filament in the sarcomere. It looks like 2 pearl chains twisted together:
🧩 What is it made of?
G-actin (Globular actin) = Single round protein unit (like a pearl)
F-actin (Filamentous actin) = A long chain of G-actins
Two F-actin strands twist together to form the thin filament
🌊 What else is attached?
Tropomyosin – A ribbon-like protein that lies along the F-actin chain
Troponin – A complex of 3 proteins attached to tropomyosin at intervals
⛔ At rest, one subunit of troponin blocks the binding sites on actin so myosin can't bind. This is a safety lock until contraction is needed!
Actin (Thin Filament)
Meromyosin = Building block of myosin
Heavy Meromyosin (HMM) = Head + short arm
Light Meromyosin (LMM) = Long tail
🔧 Special features of the myosin head:
ATPase activity – Breaks down ATP to release energy ⚡
Has binding sites for ATP and actin
These heads are called cross-arms, and they reach out to the actin like little grabbing hands during contraction.
Meromyosin
how it works
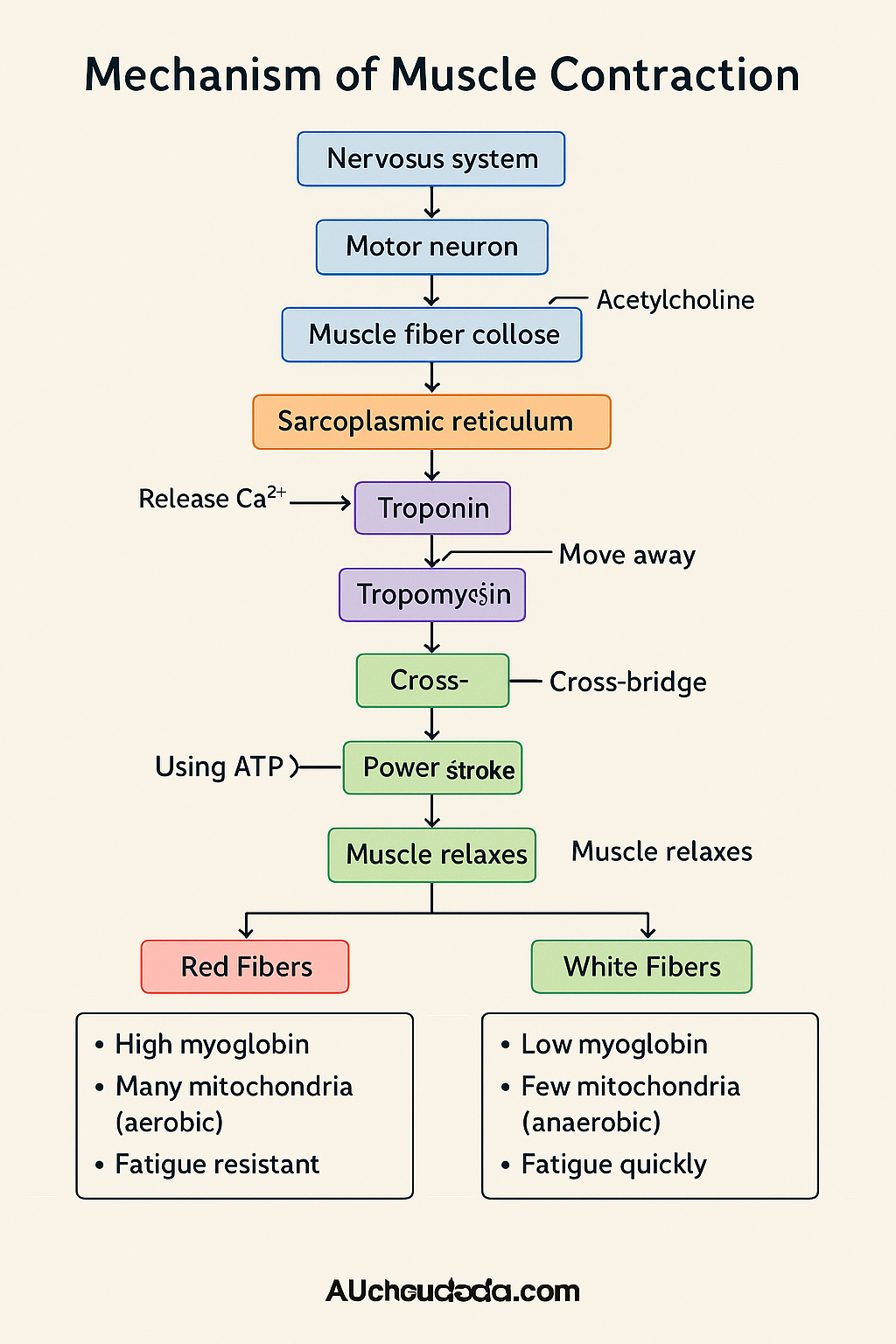
A motor neuron sends an electrical signal to the neuromuscular junction.
It releases a chemical messenger: Acetylcholine (ACh).
This creates an action potential in the sarcolemma (muscle membrane).
The Signal Arrives (Nervous system → Muscle)
The signal spreads and triggers the sarcoplasmic reticulum (Ca²⁺ storehouse) to release Calcium ions into the muscle cell (sarcoplasm)
Calcium Floods In 🚿
Calcium binds to troponin (on the actin filament).
This moves tropomyosin away from the binding sites on actin — now the myosin can attach.
Roadblocks Removed 🚧
Myosin (engine) uses ATP to get "cocked" and attaches to actin → cross-bridge is formed.
4. Cross-Bridge Formation 🪝
The myosin head pulls the actin filament towards the center of the sarcomere → contraction!
ADP + Pi (used-up ATP) are released.
5. Power Stroke 🚂
A new ATP molecule binds to myosin → cross-bridge breaks.
Myosin resets, hydrolyzes the new ATP, and reattaches to actin → the cycle continues.
Reset and Repeat 🔁
When the signal stops, Ca²⁺ is pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Troponin and tropomyosin block actin again → no binding → muscle relaxes.
Z-lines return to their original position → sarcomere lengthens.
7. Relaxation 😴
A band = myosin (thick filament) — doesn't change during contraction.
I band = actin (thin filament) — shortens during contraction.
H zone = only myosin (no overlap) — becomes smaller or disappears.
Bones: Hard due to calcium salts
Cartilage: Softer, slightly bendy due to chondroitin salts
🧍♀ Humans have 206 bones, divided into:
The skeletal system is like your body’s scaffolding—it gives shape, protection, support, and helps with movement. It is made of:
This is the central axis of the body—head to tail.
a. Skull (22 bones)
8 Cranial bones: Protect the brain (cranium)
14 Facial bones: Make up your face
Hyoid: U-shaped bone at the base of the mouth (helps in speech)
Ear ossicles (3 per ear): Malleus, Incus, Stapes → smallest bones in your body
1. Axial Skeleton (80 Bones)
⚠ The skull joins the spine at the occipital condyles, so it’s a dicondylic skull
Protect the brain (cranium)
8 Cranial bones:
Make up your face
14 Facial bones:
U-shaped bone at the base of the mouth (helps in speech)
Hyoid:
Ear ossicles (3 per ear):
Ear ossicles (3 per ear): Malleus, Incus, Stapes → smallest bones in your body
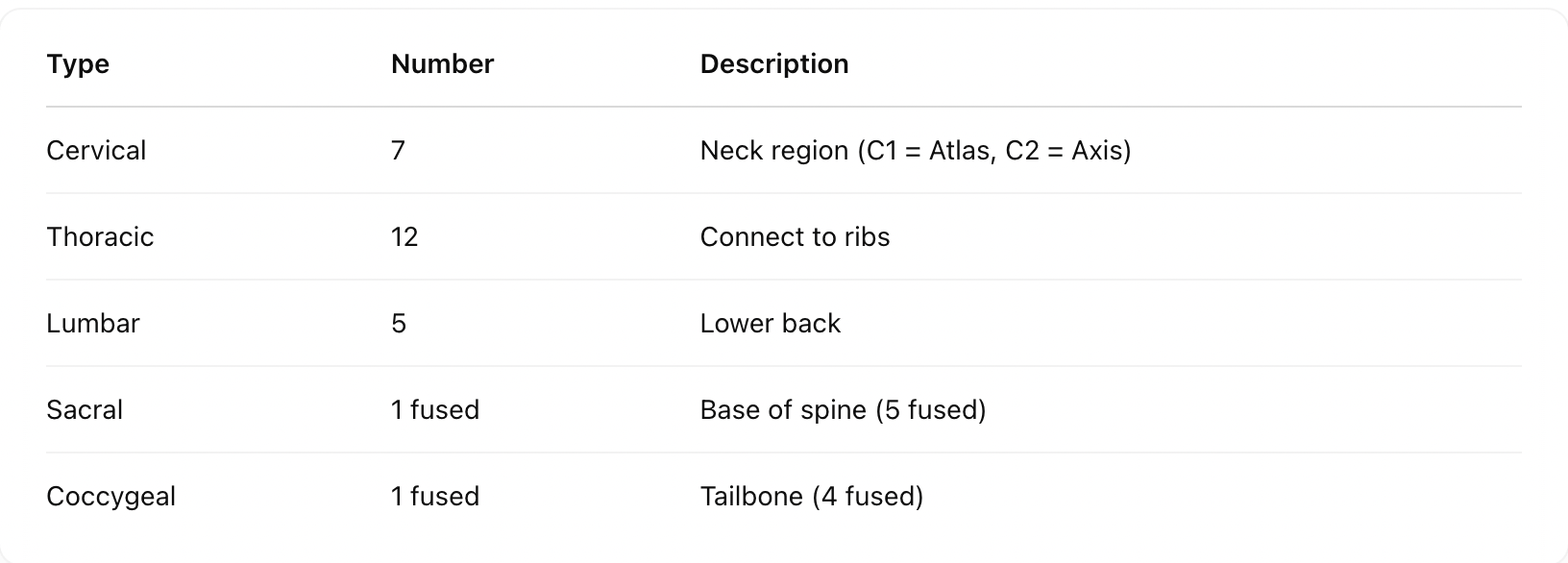
Has a neural canal through which the spinal cord passes
Vertebral Column (26 vertebrae)
Sternum: Flat bone at the center of the chest Ribs: 12 pairs
🛡 Together, thoracic vertebrae + ribs + sternum = rib cage
Sternum and Ribs (1 + 24 = 25 bones)
these are your limbs and girdles—the parts that move.
Appendicular Skeleton (126 Bones)
Humerus (upper arm)
Radius & Ulna (forearm)
Carpals (8) – Wrist bones
Metacarpals (5) – Palm bones
Phalanges (14) – Fingers
Forelimbs (Arms - 30 bones each)
Femur – Thigh bone (longest bone in body)
Tibia & Fibula – Lower leg
Tarsals (7) – Ankle bones
Metatarsals (5) – Foot bones
Phalanges (14) – Toes
Patella – Knee cap
Hindlimbs (Legs - 30 bones each)
Link Limbs to Axial Skeleton 1. Pectoral Girdle (Shoulder)
Each half has:
Clavicle (collar bone)
Scapula (shoulder blade): Has
Acromion (ridge for clavicle)
Glenoid cavity (socket for humerus)
🪶 Girdles –
Each half is one coxal bone formed by:
Ilium
Ischium
Pubis
All 3 fuse at a socket called acetabulum (for thigh bone).
The two halves join at the front to form pubic symphysis.
2. Pelvic Girdle (Hip)