Unit 14: Waves, Sound, and Physical Optics
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Waves transfer ______ between two locations.
Energy
Wave Pulse
A single disturbance that transfers energy without transferring matter
How does a wave move?
By propagating (to move through)
Mechanical Waves
Requires a medium to move through
Electromagnetic Waves
Doesn’t require a medium to move through
Longitudinal Waves
The motion of the medium is parallel to the wave
Transverve Waves
The motion of the medium is perpendicular to the wave
____________ waves only happen in mechanical waves.
Longitudinal
Parts of a Longitudinal Wave
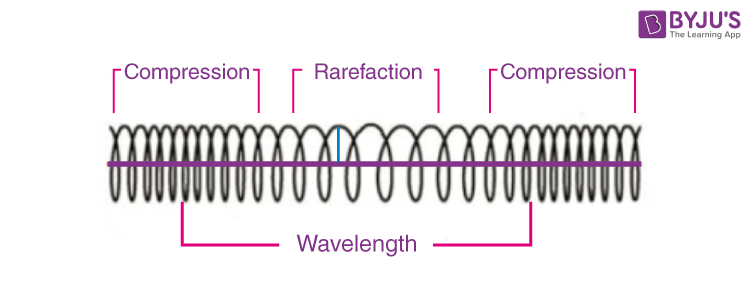
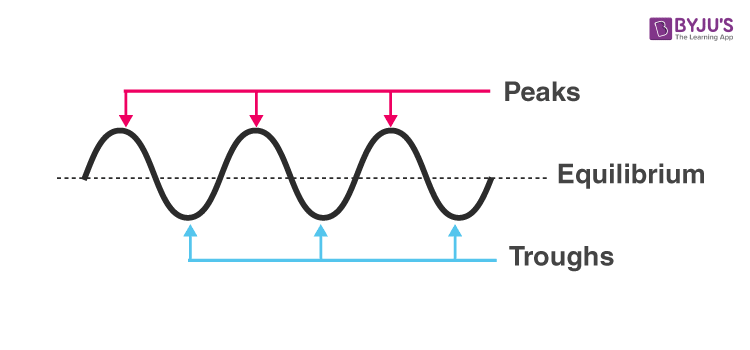
Parts of a Transverse Wave
What does the speed of a wave depend on?
Tension (FT) - increasing tension increases speed
Linear density (kg/m) - decreasing linear density increases speed
Sound waves travel fastest when in a ____ climate not a ____ climate.
Warm; Cold
Amplitude
Maximum displacement of a wave, wave pulse, or oscillation from its equilibrium position
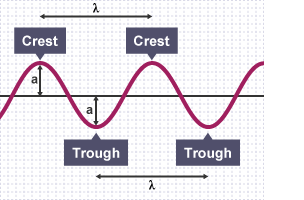
Amplitude is based off of ________.
Pressure
The higher the amplitude, the ______ the sound in a sound wave.
Louder
The higher the amplitude, the ______ of light in a light wave.
Brighter
The speed of a wave depends on the _______.
Medium
A single point on a periodic wave moves a distance of ____ amplitudes.
Four (4)
Does amplitude affect wave speed?
No
How are energy (E) and amplitude (A) related?
E = A2
Period
Number of seconds it takes for a wave or oscillation to happen
Period (seconds) = total # of sec/# of oscillation
Frequency
Number of times a wave or oscillation happens every second
Frequency (Hertz) = total # of oscillation/# of seconds
Higher frequency means ______ periods.
Shorter
How is frequency related to pitch?
A higher frequency is equal to a higher pitch
Higher pitch means a ______ period and a _______ frequency.
Shorter; Higher
What does frequency tell us about a light wave?
Tells us what type of wave it is (or what color it is)
A greater frequency means that I have _______ energy.
Greater
Is amplitude related to the period and frequency of a wave?
No, it is completely independent
Y = Asin((2π)(X)/T)
Y = y-axis variable (pressure)
A = amplitude
sin = can be sin, cos, - sin, or -cos depending on the shape of the wave
T = period
X = x-axis variable (time)
B = Asin((2π)(X)/𝜆)
B = y-axis variable (magnetic field)
𝜆 = wavelength
X = x-axis variable (time)
Medium
A substance through which a wave may travel
When a wave travels from a low-mass string to a high-mass string, part of the wave energy is
Reflected back while some is transmitted into the new medium
Frequency of transmitted and reflected waves is the same as the rate at which
The wave created in the new medium is
The rate at which the wave would be reflected
If the wave speed decreases in the new medium, the reflected wave will be ________
Inverted
If the wave speed increases in the new medium, the reflected wave maintains its _________ __________
Original orientation
When wave speed changes so does _________
Wavelength
Nearly all light waves are ____________
Unpolarized
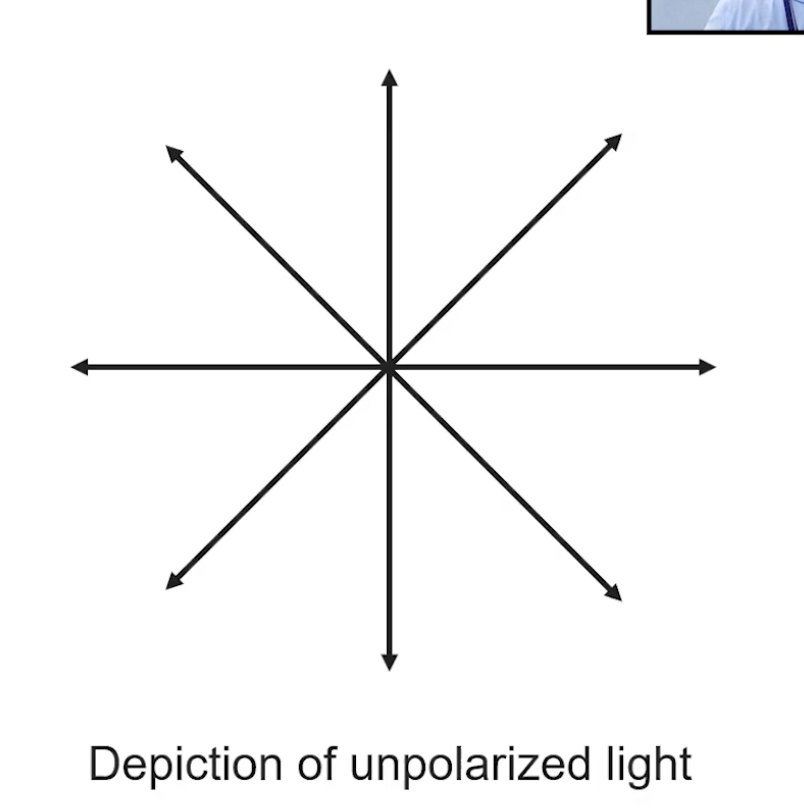
How does polarized light look like?

A)
When unpolarized light passes through a polarizing filter, approximately 50% of the original intensity is transmitted
How many filters do we need to completely block out light?
Two and the intensity (I) will drop to 0
Intensity
Measure of amount of power transferred per unit area
I = Power/Area or I = (Energy/Time)/Area
After a wave is polarized, _____ is decreased, which means that intensity also decreases.
Power
A polarized wave will have a lower _________.
Intensity
The speed of a wave depends on what?
The medium and type of wave moving through the medium.
What affects the wave speed of an electromagnetic wave?
It depends on the materials electric permittivity and magnetic permeability.
Electromagnetic Waves
A combination of transverse electric and magnetic waves that oscillate at right angles to each other
When a wave source is moving just as fast as the observer, the observed frequency is
equal to the rest frequency
When a wave source is moving toward an observed, the observed frequency is
Greater than the rest frequency
When a wave source is moving away from an observed frequency is
Less than the rest frequency
When a light source is moving toward a viewer, the observed color is
Shifted towards the blue end of the visible light spectrum
When a light source is moving toward a viewer, the observed color is
Shifted toward the red end of the visible light spectrum compared to the rest color
Constructive Interference
When amplitudes add together
Destructive Interference
When two waves add together to produce a wave with 0 amplitude
Beat Frequency
When two waves with slightly different frequencies interfere, they create a phenomenon
Nodes
Where the medium never moves from equilibrium
Antinodes
Points where the medium oscillates with a maximum amplitude
Diffraction
The spreading of a wave around the edges of an obstacle and through an opening