Neuro 3000 MT3
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
contralateral
the opposite side of the brain
Contralateral processing occurs in the cerebrum
ipsilateral
same side of the brain
ipsilateral processing occurs in the cerebellum
decussation
the crossing over of nerve fibers from one side of the CNS to the other
allows integration of sensory/motor info from both sides of body
pyramidal decussation
descending tract from cortex (medulla) to the spinal cord
motor fibers from the cortex cross over the midline at the lower medulla and go into the spinal cord
allows for contralateral processing (occurs on both sides of the brain)
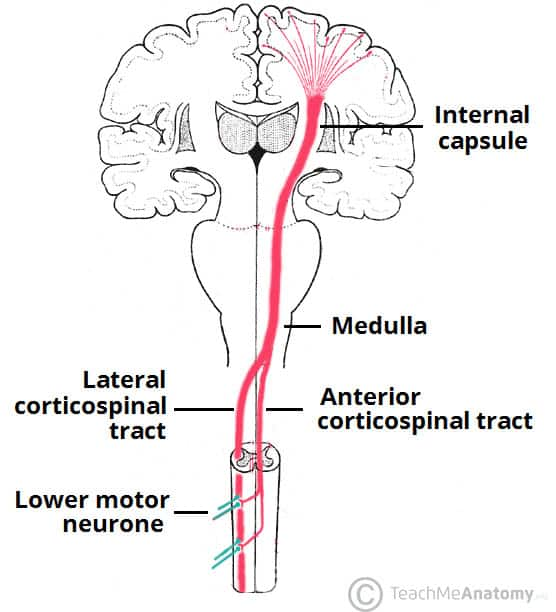
internal capsule
white matter tract in brain; carries outgoing fibers from cortex and incoming fibers from thalamus to cortex (beginning part of corticospinal tract)
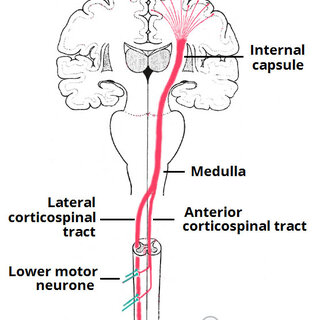
corticospinal tract
consists of long pyramidal neurons that extend from cortex to spinal cord
allows for direct movement control
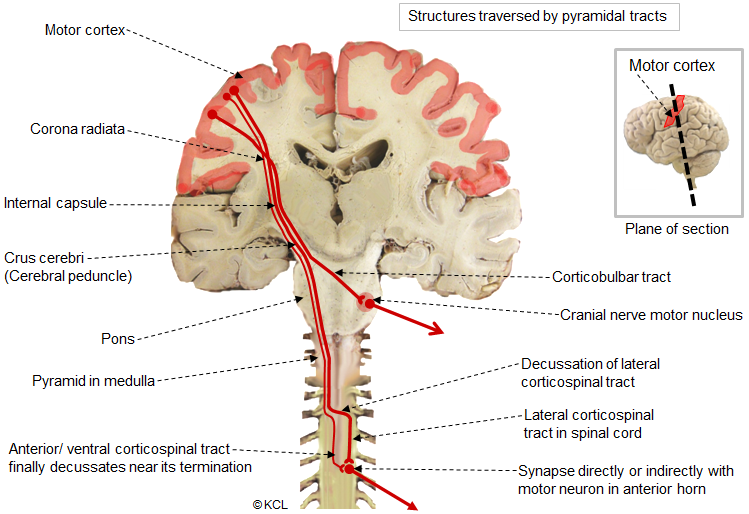
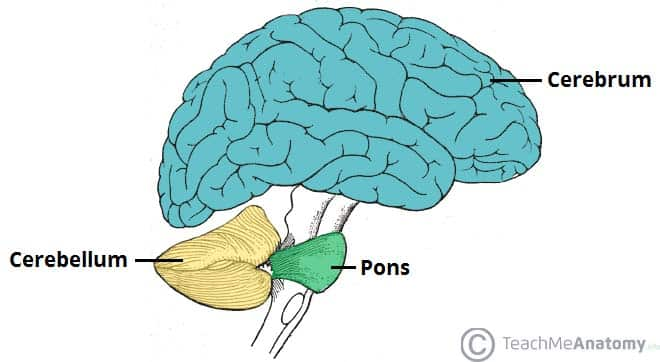
cerebrum
has two hemispheres that each get input from and control motor function for the contralateral side
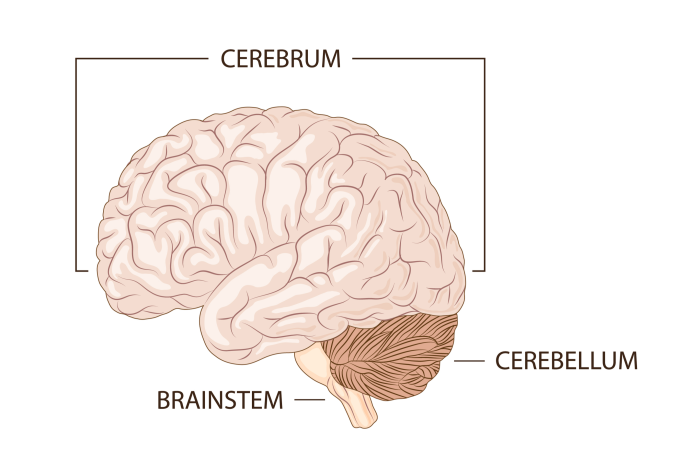
cerebellum
ipsilateral movement control
has many connections to spinal cord/cerebellum
despite smaller size, has same number of cells as cerebrum (higher conc.)
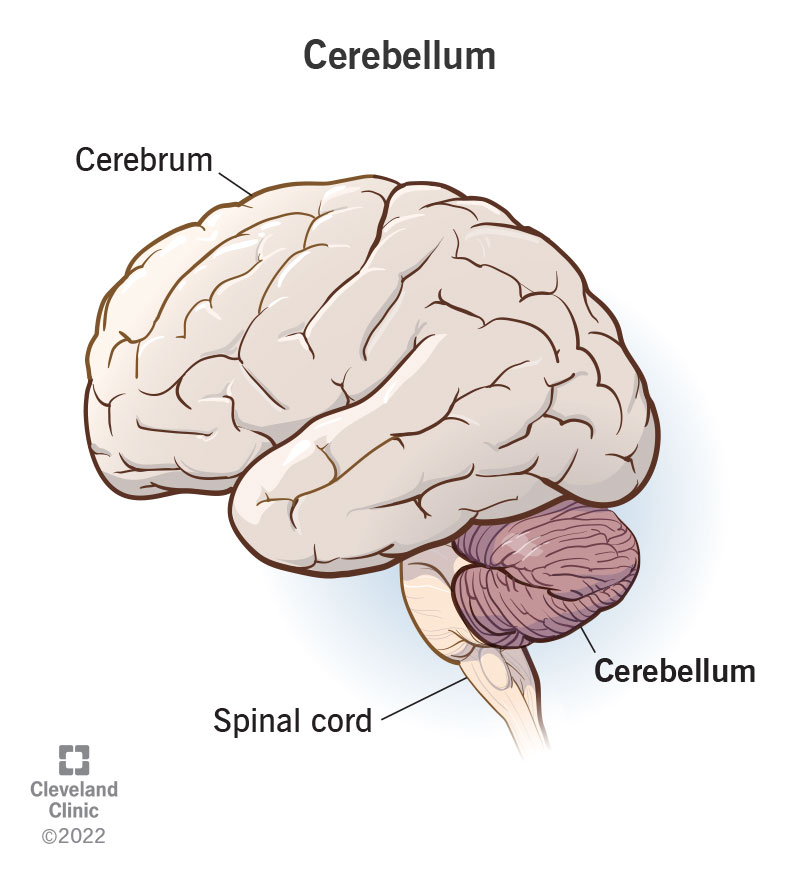
CNS
brain and spinal cord; functions in info processing and distribution
dorsal root
sensory processing; root enters into the spinal cord and runs up
protected by meninges
ventral root
motor information; root exits the spinal cord and goes down into body part
protected by meninges
PNS
Everything out of the CNS; transmits sensory and motor info to/from the CNS
Motor nervous system
divided into autonomic (glands, adipose tissue, smooth/cardiac muscle) and somatic (skeletal muscle) nervous systems
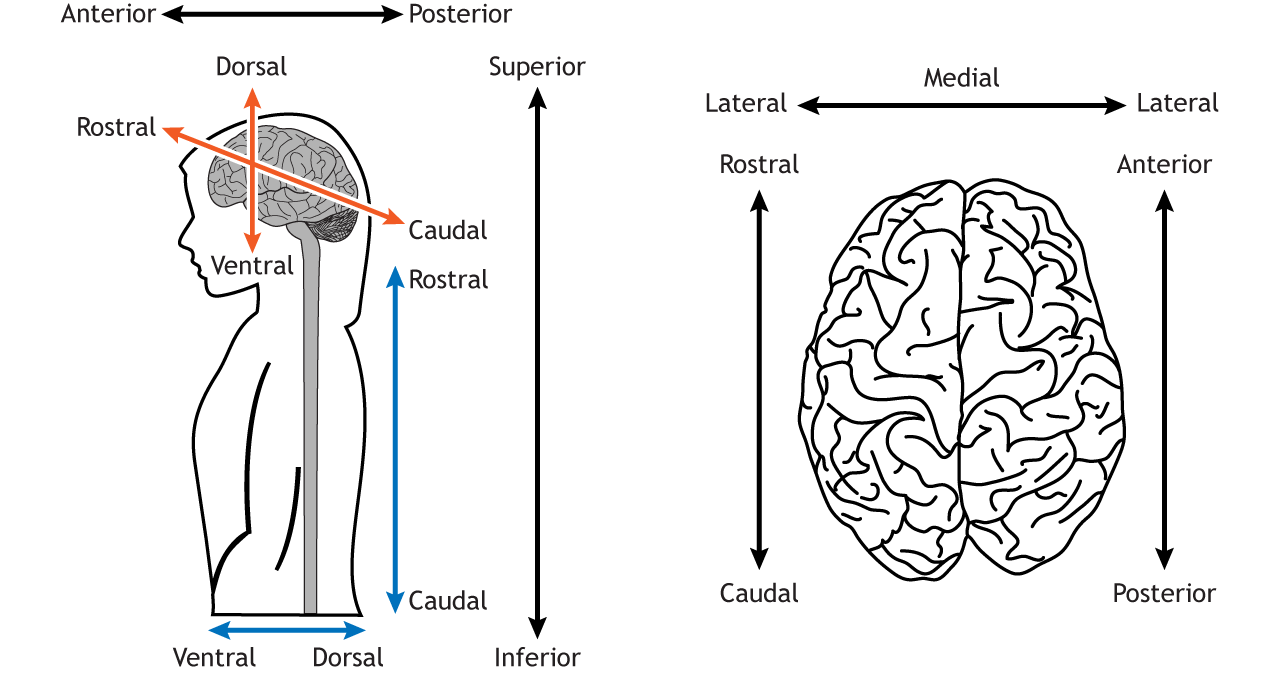
anterior/rostral
front of brain
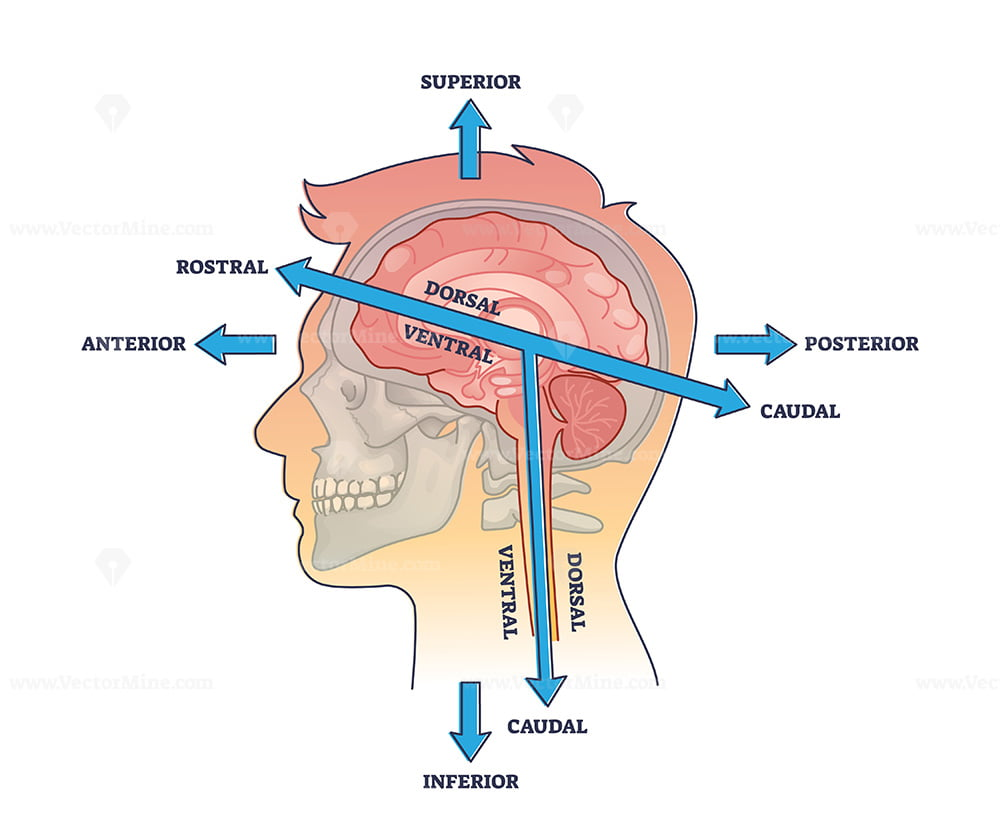
posterior/caudal
back of brain
lateral
far from midline
medial
near midline
dorsal
top of brain (mouse’s back)
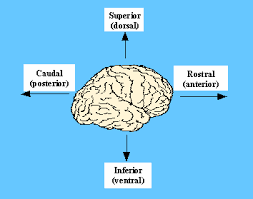
ventral
bottom of brain (mouse’s belly)
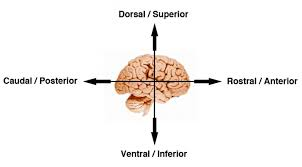
superior (to)
found above a certain structure
inferior (to)
below a certain structure
superficial
closer to surface
deep
far from surface
sagittal plane
cuts into left/right halves along midline
no bilateral symmetry
coronal/transverse plane
cuts into front/back halves
bilateral symmetry visible
horizontal plane
cuts into top/bottom halves
bilateral symmetry visible
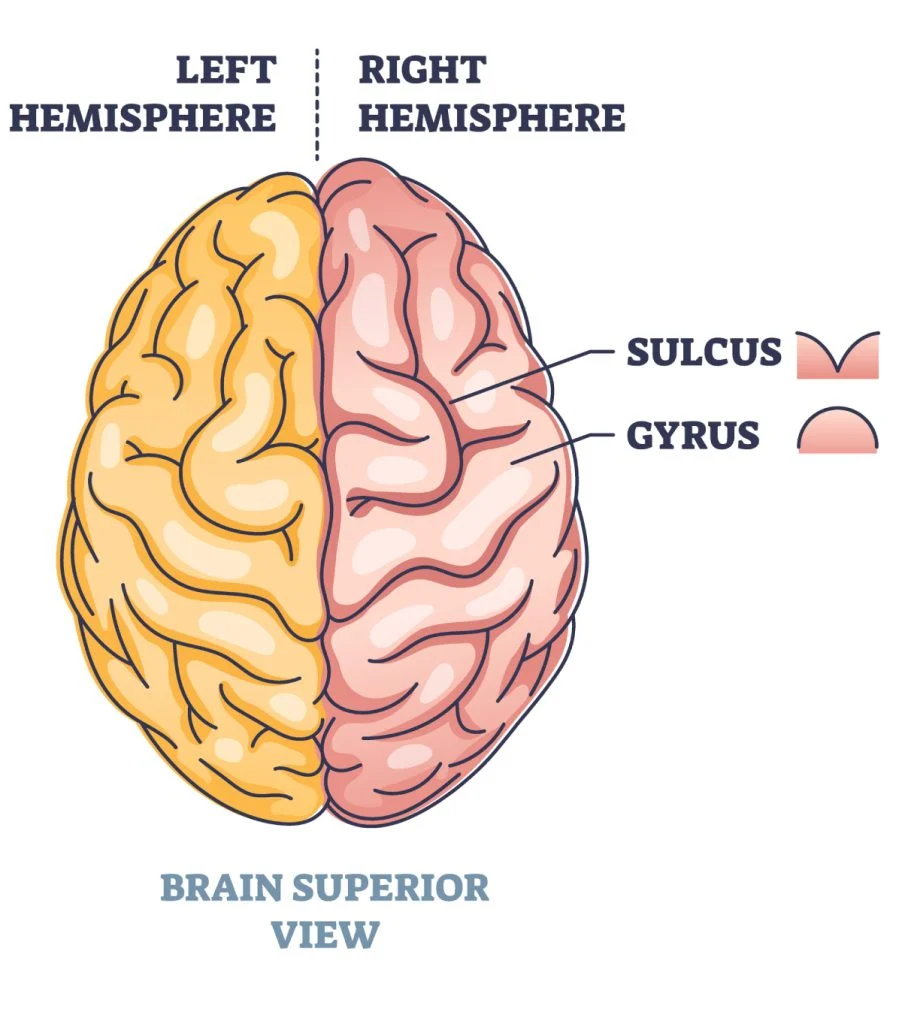
gyri
sulci
brain ridges
spaces in between the ridges
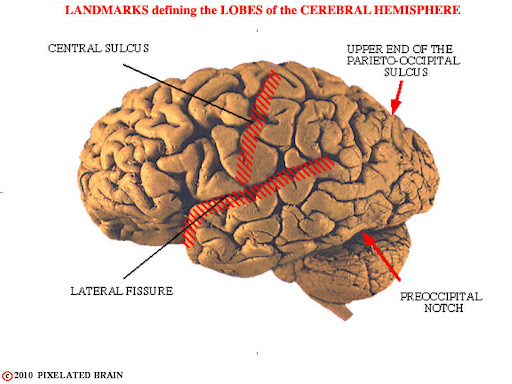
bounds frontal lobe
lateral sulcus, central sulcus
bounds parietal lobe
lateral sulcus, central sulcus, parieto-occipital sulcus
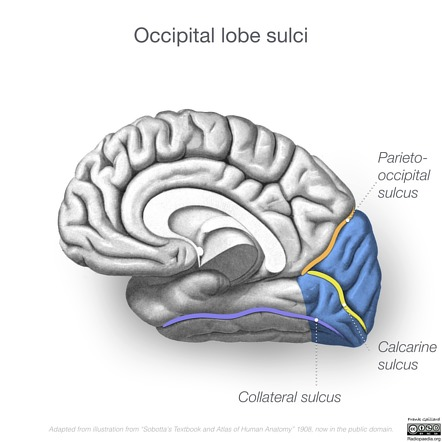
bounds occipital lobe
parietal-occipital sulcus, transverse fissure
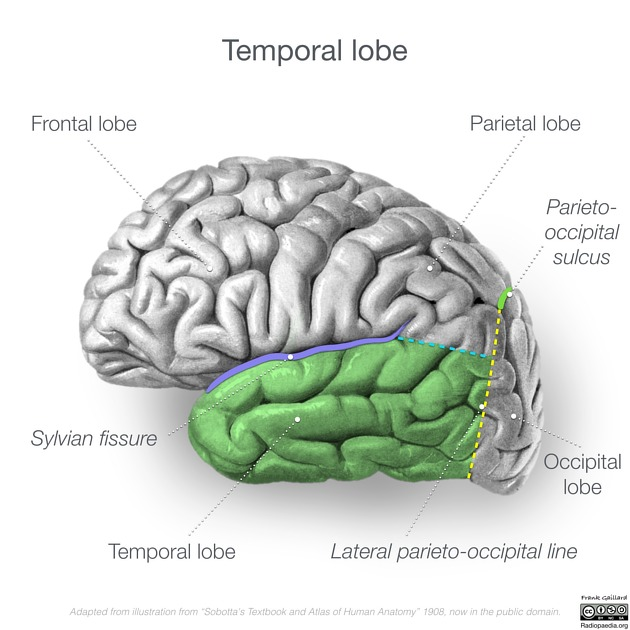
bounds temporal lobe
lateral sulcus, parieto-occipital sulcus
fissures
deeper than sulci; mark major brain divisions
longitudinal fissure
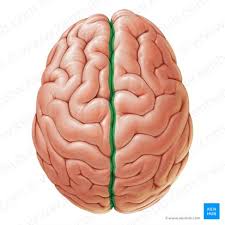
separates left and right hemispheres
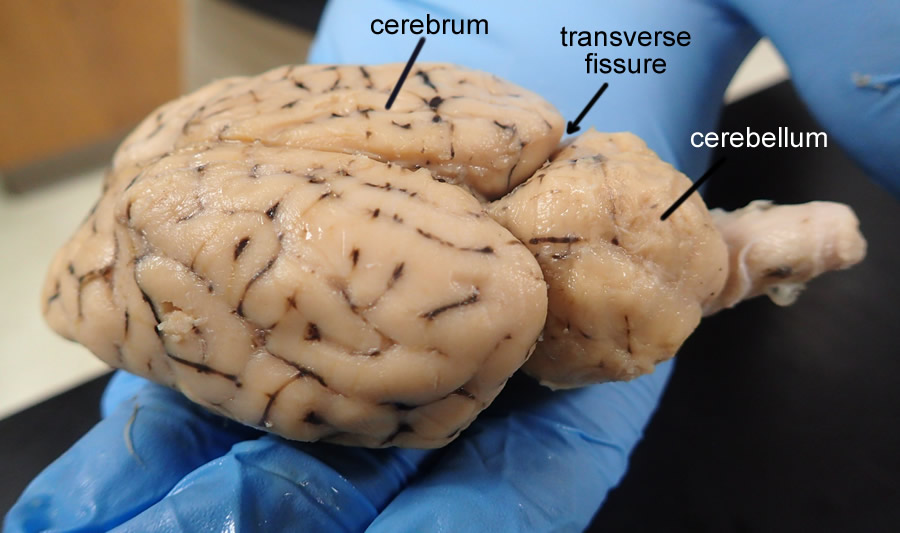
transverse fissure
separates cerebrum and cerebellum
grey matter (cortex)
cell bodies; appear grey
white matter
myelin sheaths from axons
PNS
myelination occurs through Schwann cells
somatic NS
voluntary movements by skeletal muscles
Motor neurons: their cell bodies are located in CNS, axons in PNS
autonomic NS
unconscious movements (smooth muscle, heart muscle, glands)
sympathetic and parasympathetic
sympathetic NS: driven by norepinephrine
activates fight or flight response
dilates pupils, heart races, digestion slows
parasympathetic NS: driven by ACh
calms fight or flight response
breathing slows, digestion resumes, heart slows down
ganglion
collection of neuron soma in the PNS
ex: dorsal root ganglia, basal ganglia
preganglionic neuron
soma in CNS; innervate postganglionic neurons
in sympathetic NS: come from thoracic and lumbar spinal cord
parasympathetic NS: come from cranial nerves and sacrum
cranial nerves
12 total; relay info from brain to head, neck, GI tract
pseudo-unipolar neurons
Stages of neurodevelopment (post-fertilization)
Cleavage to blastocyst
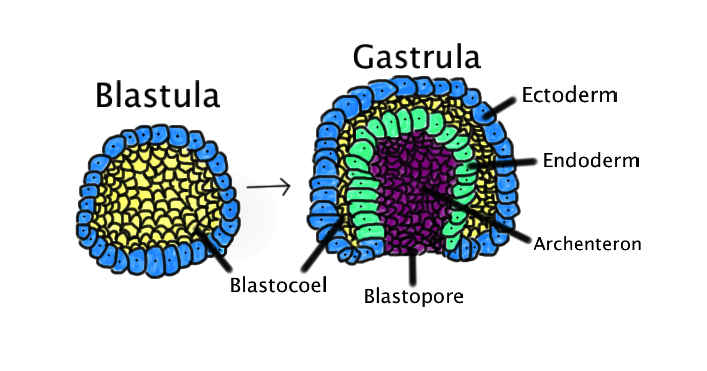
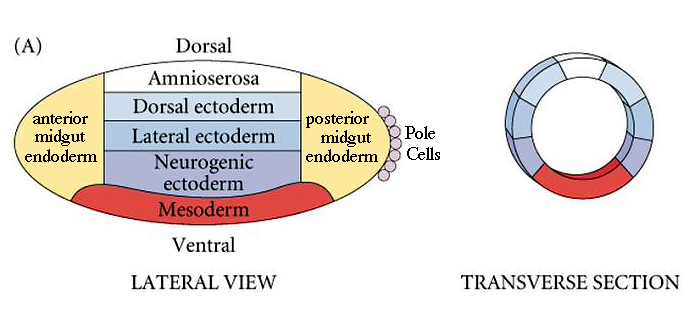
Gastrulation and neural induction; formation of 3 germ layers
Neurulation, formation of neural tube
Organogenesis, brain patterning
Cleavage to blastocyst (days 2-10)
where ESCs come from
1. Neural induction (days 11-15)
occurs during gastrulation
formation of 3 germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm
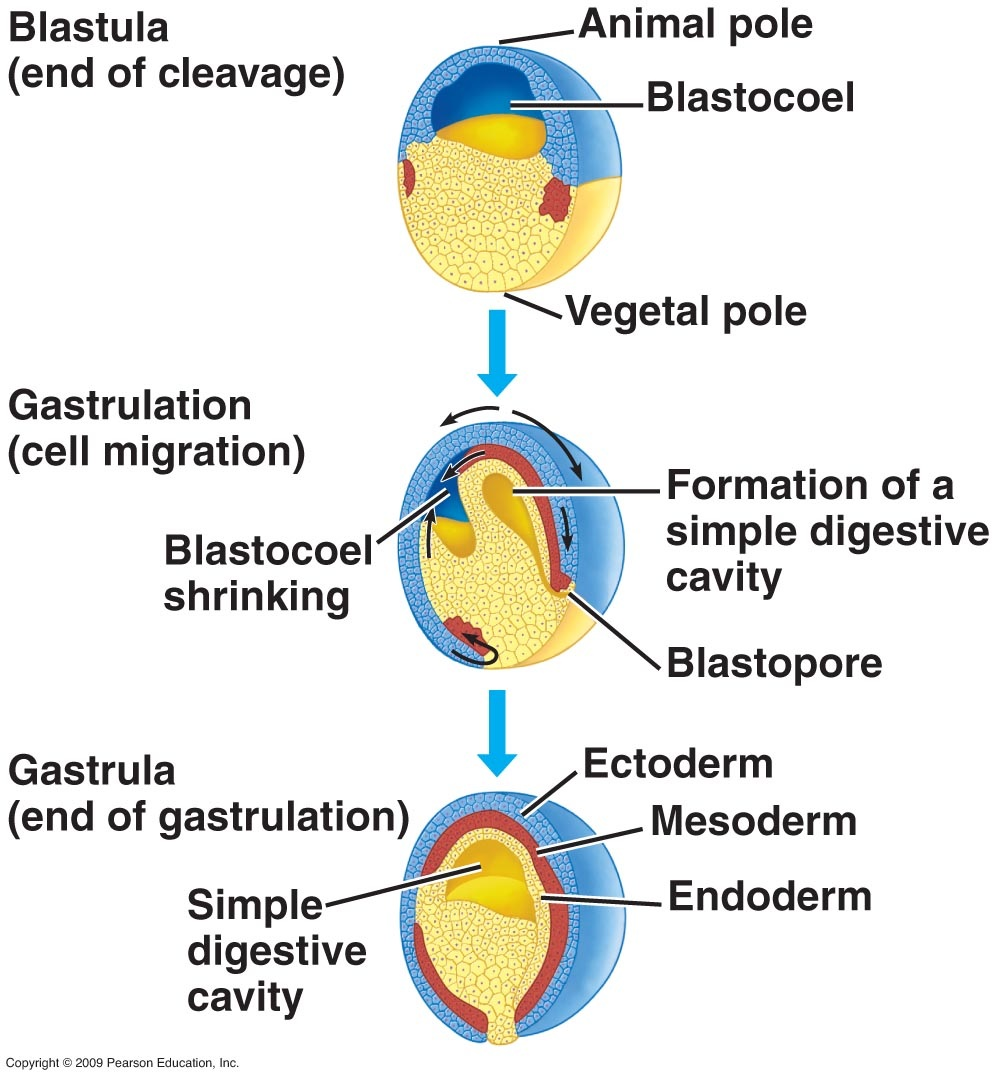
ectoderm
nervous system, skin
endoderm
internal organs
mesoderm
muscle and skeleton; becomes bone/muscle around spine
produces the neural inducer noggin
noggin
neural inducer; makes the ectoderm become neural (otherwise, would just become skin)
generates neural tube from ectoderm
used to convert ESCs to neurons
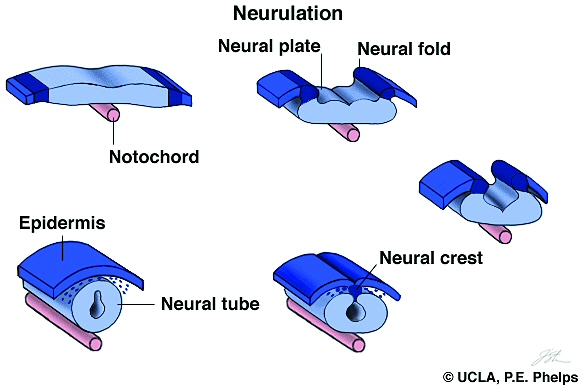
Neurulation/neural tube formation (days 16-25)
neural tube becomes brain and spinal cord; closes off
neural crest develops and becomes sensory/autonomic neurons
still part of the neuroectoderm
endoderm becomes internal organs
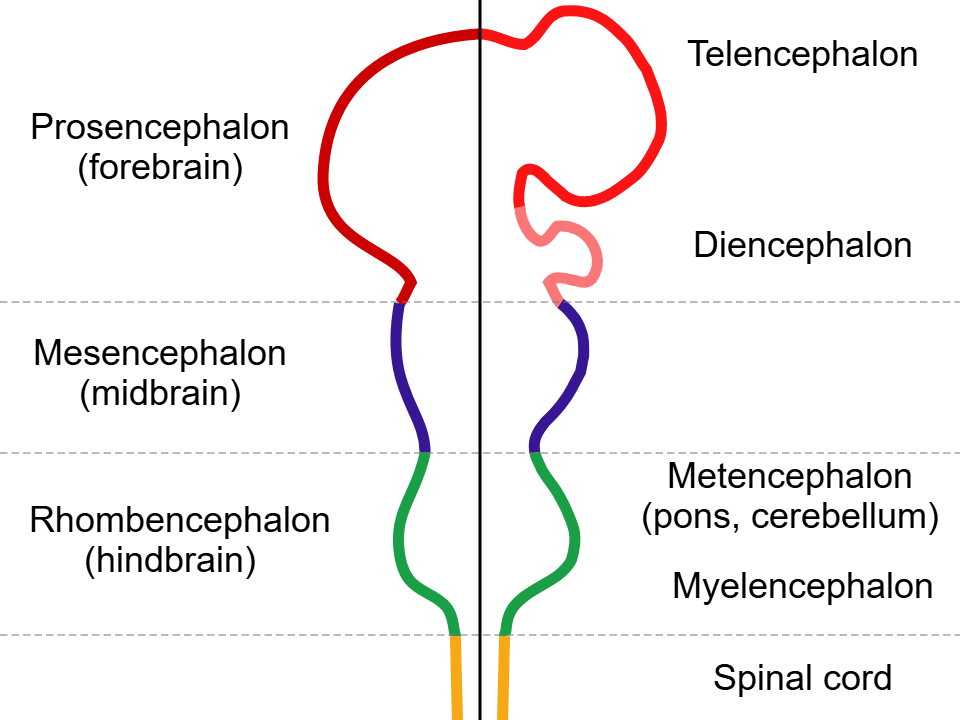
Regionalization and patterning (days 28+): anterior-posterior patterning
controlled by RA, lipophilic molecule
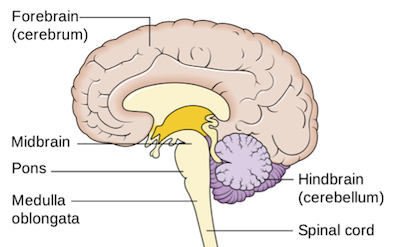
3 brain vesicles appear: prosencephalon (forebrain), mesencephalon (midbrain), and rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
development goes from posterior to anterior; hindbrain first
default fate is forebrain; RA helps develop posterior fates
Regionalization and patterning (days 28+): dorsal-ventral patterning
controlled by Shh, protein
development goes from bottom up
initiates formation of nervous system
used to induce neurogenesis in iPSCs
Expansion of forebrain: day 36
prosencephalon expands and adds telencephalic vesicles
later becomes telencephalon and diencephalon
rhombencephalon begins to develop
Expansion of forebrain: days 49-90
forebrain develops into telencephalon and diencephalon
telencephalon covers diencephalon
optic cup
develops from the optic vesicle, which originates in the diencephalon (prosencephalon)
later becomes the retina
dorsal telencephalon becomes:
neocortex
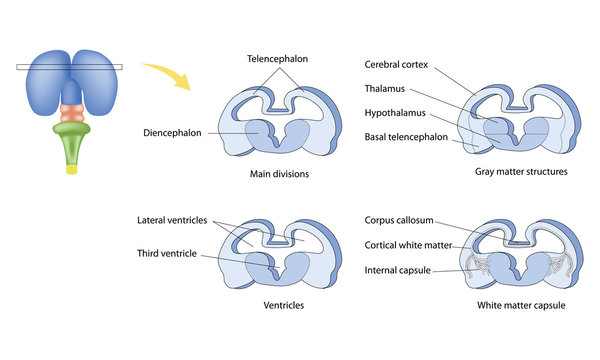
basal telencephalon becomes:
amygdala, basal ganglia (striatum)
diencephalon (ventromedial forebrain) becomes:
thalamus, hypothalamus
forebrain
seat of perception, cognition, and voluntary action
thalamic axons:
project from the thalamus (CNS) via the internal capsule
ex: if you are hurt on your right foot, the pain signals go to your left cortex
corpus callosum
white matter tract; allows communication between hemispheres
cortical neurons (which project downward) can project to:
corticospinal tract (all the way down the spinal cord)
basal ganglia for movement control
includes striatum (basal telen) and substantia nigra (midbrain)
takes in dopamine input
dorsal midbrain (mesencephalon)
Becomes the tectum
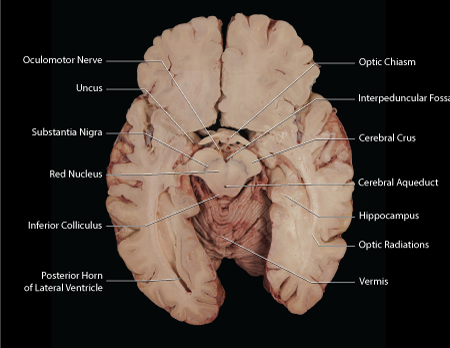
superior colliculus: visual processing
inferior colliculus: auditory processing
ventral midbrain
becomes tegmentum
cerebral aqueduct
connects diencephalon and hindbrain
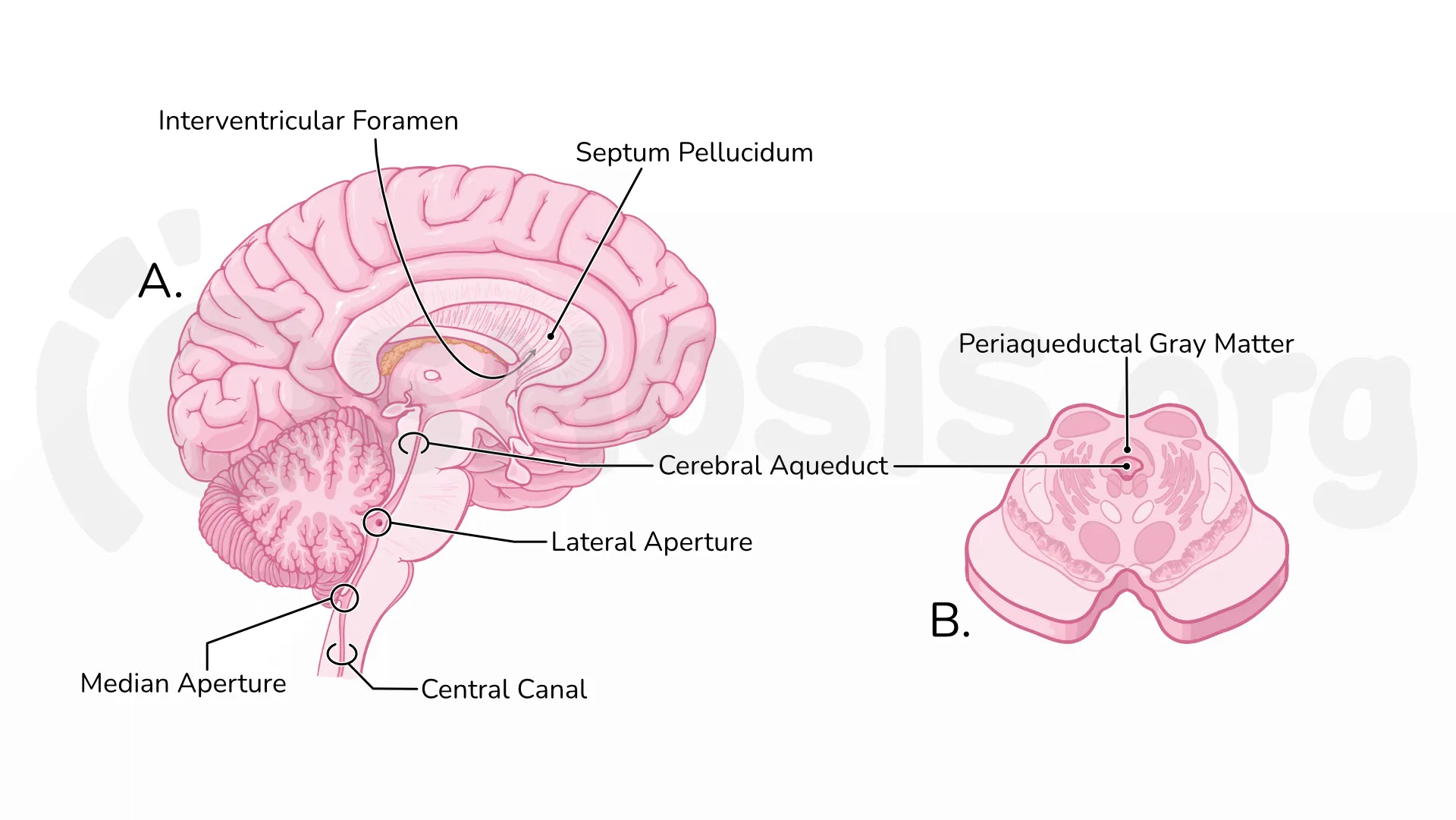
dorsal rostral hindbrain
becomes cerebellum
ventral rostral hindbrain
becomes pons, pontine nuclei
pons connects cerebral cortex and cerebellum using mossy fibers
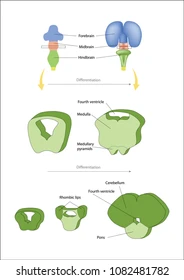
medullary pyramids (caudal hindbrain)
carry corticospinal projection axons going to the spinal cord (corticospinal tract)
pyramidal decussation
neurogenesis
neurons, astrocytes, glia, etc are generated
proliferation, migration, differentiation
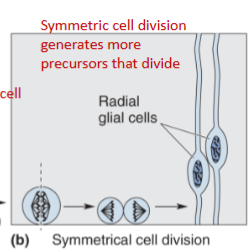
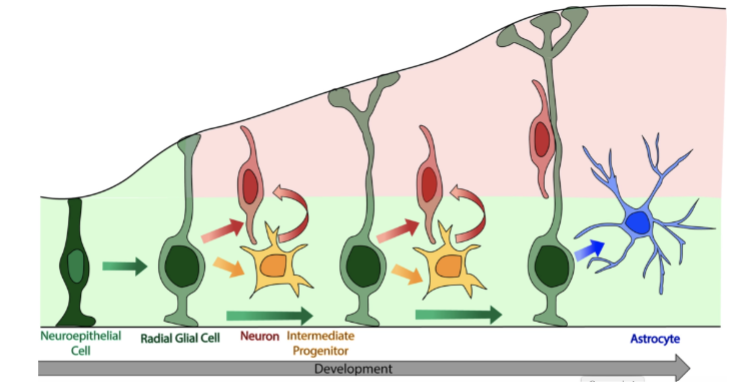
proliferation:
to start, the brain’s vesicles only have 2 layers: ventricular zone and marginal zone
contain radial glia (neuron/glia precursors)
at first, cell division is done symmetrically to generate more radial glia
note that the nuclei initially move up into the marginal zone before coming back down
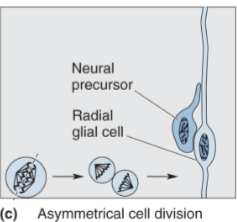
migration:
later in development, some cells develop asymmetrically; the daughter cell further from the ventricle migrates along a radial glia to reach its spot in the cortex
this cell becomes a neuron/glia
final result: one postmitotic cell, one premitotic cell
once the postmitotic cell reaches its destination, only then does it differentiate
order of differentiation (after migration is finished):
pyramidal neurons are made first, then astrocytes
inhibitory interneurons and oligodendrocytes come from somewhere else
cell fate
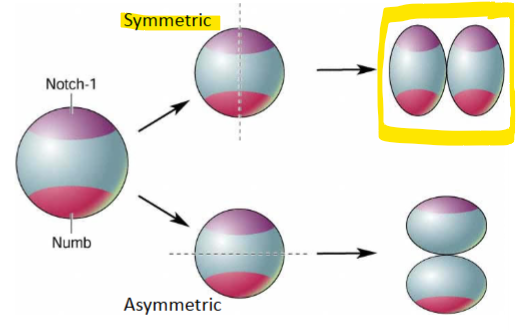
driven by gene expression in development (daughter cells have certain genes turned on/off); depends on what plane the cells are cleaved
vertical cleavage
parent cell is cleaved symmetrically
daughter cell has both Notch 1 and Numb expression; continues to differentiate
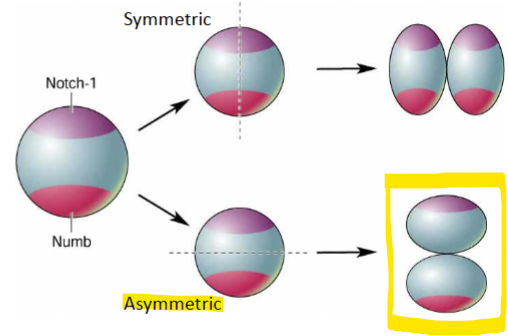
horizontal cleavage
one daughter cell only has Notch 1; this migrates to MZ and differentiates
other daughter cell only has Numb; stays behind and continues to proliferate
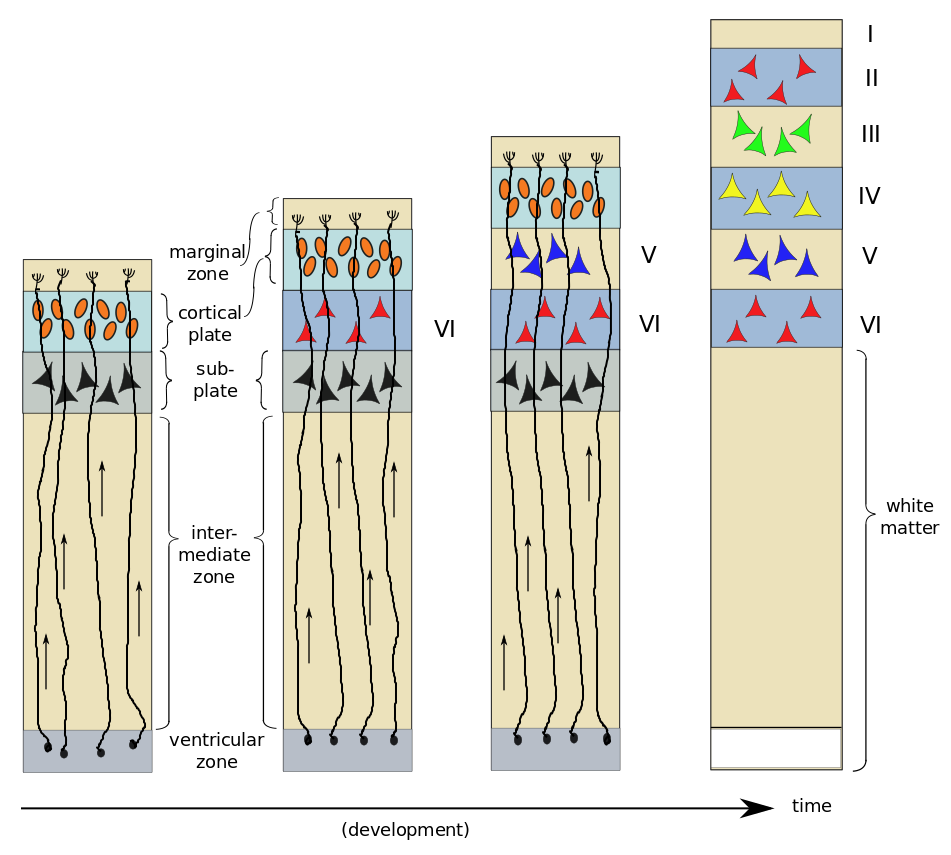
cortical layers are developed inside out
layer VI forms first, then layer V, etc
differentiation only starts once the cells have reached their location and stop migrating
once one layer is finished, then the cells will migrate up from the VZ to the next layer
differentiation
once a cell has reached its final destination, it becomes a specialized neural cell
attracted to cortical surface by semaphorin 3A, which determines axon polarity
chemoattraction, chemorepulsion
semaphorin 3A: drives pyramidal polarity
high concentration in the marginal zone, but low expression in deeper layers
axons repulsed by sema3A, which is why they extend down from the cell body
synaptogenesis
formation of synapses
target-dependent cell death (apoptosis?)
more neurons are generated than actually needed
to determine which are lost, a limited amount of NGF/BDNF (growth factors) is produced; neurons need to compete
synaptic pruning
eliminates uneeded circuits
synaptic plasticity
learning and memory; related to synaptogenesis
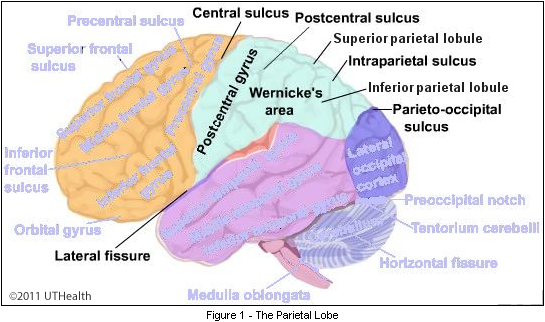
frontal lobe
complex human behavior
prefrontal cortex, primary motor cortex
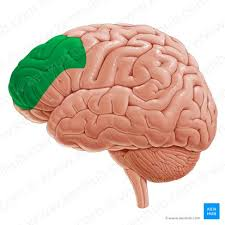
prefrontal cortex
planning, organizing, impulse control, learning, decisions
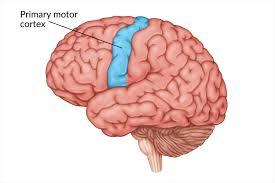
primary motor cortex
voluntary movement
primary motor/somatosensory cortex
primary motor: caudal frontal lobe
somatosensory: rostral parietal
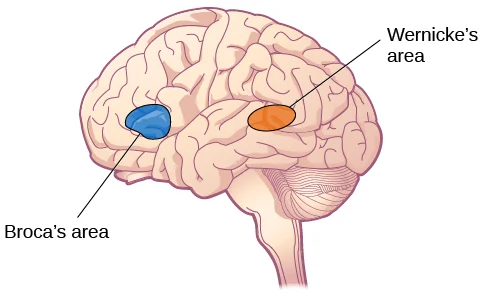
frontal lobe and language
broca’s area: language-related motor functions
wernicke’s area: language comprehension
temporal lobe
language, hearing, memory
auditory cortex, wernicke’s area
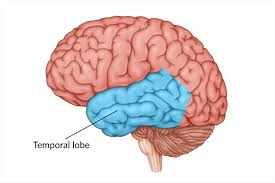
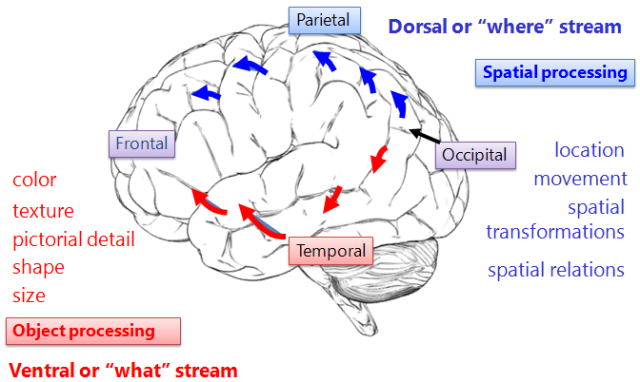
ventral stream (temporal lobe)
“what” pathway
lets you identify and recognize *what* an object is
originates in occipital lobe
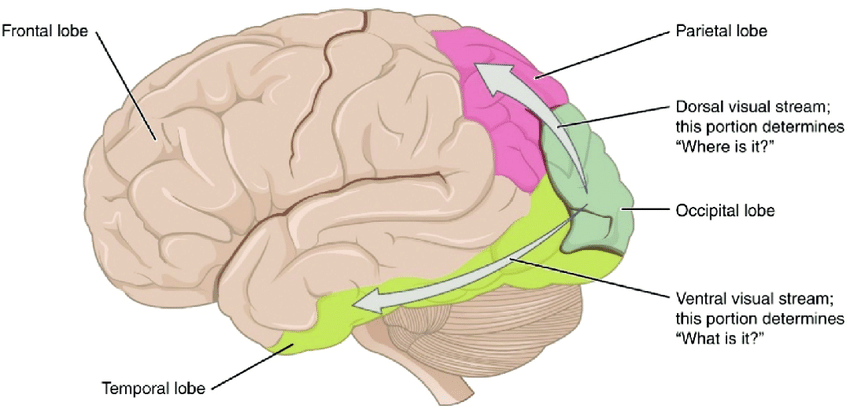
parietal lobe
sensation, spatial awareness
receives sensory input from the body
identify objects by touch; body’s position in space
primary somatosensory cortex, dorsal stream
sensorimotor cortex
primary somatosensory cortex
skin senses (touch, warmth, cold, pain)
inform about body position/movement
dorsal stream
“where” pathway
visual-motor control
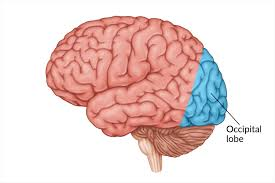
occipital lobe
processes visual info
detects individual parts of a scene (color, movement, etc)
afterward, puts them together and sends them to be processed in temporal/parietal lobes
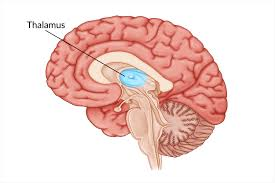
thalamus
sensory relay center
hypothalamus
controls emotion and motivated behaviors (eating, drinking, sex)
maintains homeostasis through control of autonomic NS
links endocrine and nervous systems (HPA axis)
midbrain
contains structures with secondary roles in: vision (superior colliculum/optic tectum), hearing (inferior colliculum/auditory tectum), and movement/motivation (tegmentum, VTA)
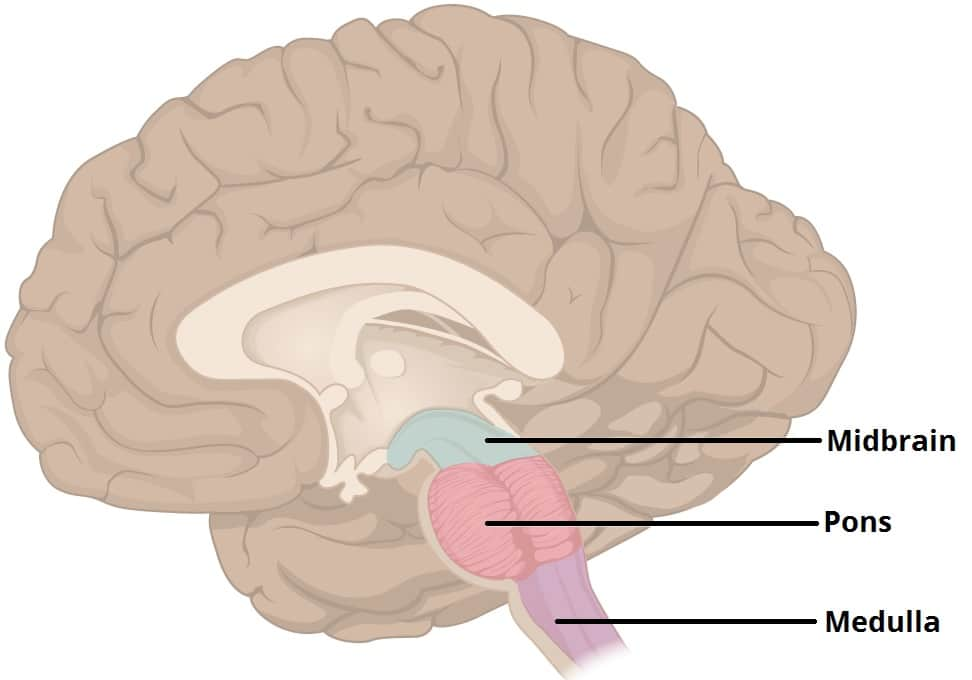
hindbrain
made of pons (motor/sensory function, corticopontocerebellar tract, sleep/arousal), medulla, cerebellum
cerebellum
refines movements from the motor cortex (coordination)
motor learning
non-motor cognition and emotion