TALENT MANAGEMENT - PRELIMS
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
CORPORATE CULTURE
Is the combination of the values and characteristics that define an organization
CORPORATE CULTURE
It influences the way employees relate to each other, to customers, to shareholders, and to business partners
CORPORATE CULTURE
reflected through its practices, dress code, business hours, office space and setup, benefits, and other aspects of its operations
CORPORATE CULTURE
It drives behaviors and unite employees around a shared set of values
CULTURE
Refers to the beliefs, traditions, and norms that are followed by a group of people (usually of a certain geographic area or a country)
1950s
The term of culture in a corporate context was first introduced by Dr. Elliot Jaques in his book The Changing Culture of a Factory
Rigid hierarchies
Dr. Elliot Jaques
The term of culture in a corporate context was first introduced by
1970s
Opened up communication channels between the bottom and the top of the organization
Women rise in the workplace
Dress code loosen up
1990s
Relationships between workers and bosses fray
2000s
Tech startup culture revolutionizes the workplace
Communication channels continue to be developed as companies realize the competitive advantages that these bring to them
PRESENT
The era of human-focused company culture begins
It is important to understand what today’s working population is looking for in their employers
DOMINANT CULTURE
Expresses the core values a majority of members share and that give the organization its distinct personality.
SUBCULTURES
Are unique patterns of values and philosophies within a group that are consistent with the dominant culture of the larger organization or social system.
COUNTERCULTURES
Are the patterns of values and philosophies that outwardly reject those of the large organization or social system
VISION
A __ statement is a simple but foundational element of culture.
Good __statements can even help orient customers, suppliers, and other stakeholders
VALUES
the core of the company’s culture.
Many companies find their values revolve around a few simple topics (employees, clients, professionalism, etc.), but the originality of those values is less important than their authenticity.
PRACTICES
Values are of little importance unless they are enshrined in the ___ of the company.
Regardless of the company’s values, those must be reinforced in review criteria and promotion policies, and considered into the operating ___ .
PEOPLE
No company can build a coherent culture without ___ who either share its core values or possess the willingness and ability to embrace those values.
The best firms are “fanatical about recruiting new employees who are not just the most talented but also the best suited to a particular corporate culture
NARRATIVE
Any organization has a unique history — a unique story.
The ability to unearth that history and craft it into a ___ is a core element of culture creation.
PLACE
whether geography, architecture, or aesthetic design — impacts the values and behaviors of people in a workplace.
Peter Drucker
CULTURE EATS STRATEGY FOR BREAKFAST
Culture
Driver of the business
Strategy
Road map
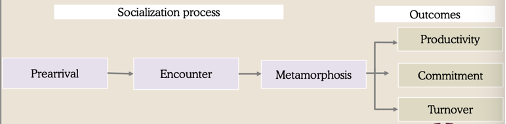
How organization culture forms
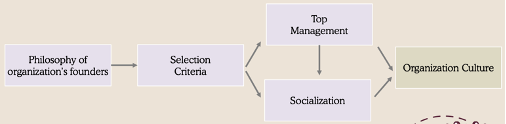
Socialization Model
FILIPINO CULUTRE IMPACTS ON HRM PRACTICES
· High-absenteeism = lacks pakikisama
· Helpful cooperation or pagtutulungan
· Camaraderie and loyalty of pakikisama within the group
· Palakasanor kakilala system
· Filipino cultural values of utang na loob and hiya
WORKFORCE PLANNING
Ensuring that the right people with the right skills are in the right place at the right time to meet an organization’s goals.
WORKFORCE PLANNING
A systematic process of identifying, acquiring, developing, and retaining employees to meet the needs of an organization.
WORKFORCE PLANNING
The “strategic” element denotes the integration between workforce planning and an organization’s strategic plan—its mission, goals, and objectives.
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Outlines the hierarchy within an organization and describes the roles, responsibilities and lines of command that exist to achieve the organization's business goals
FUNCTIONAL ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
People are grouped according to their area of professional competence and specialization.
Very bureaucratic and has a top-down approach
FUNCTIONAL ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Based on the Company’s key functions
FUNCTIONAL ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Establishing clearly defined roles and expectations
Facilitating Improved performance and productivity
Allowing for skill development and specialization
FUNCTIONAL ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Creating barriers, or silos, between functions
Limiting employees’ communication and knowledge with other departments
Inhibiting collaboration and innovation
DIVISIONAL ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Groups are organized according to the projects, or products the company focuses on.
Structure is more flexible to the hierarchical organization
DIVISIONAL ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Based on the Company’s key products
DIVISIONAL ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Allowing divisions to work independently
Meeting individual divisions' needs more quickly and specifically
Promoting focus on specific products or services
DIVISIONAL ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Duplicating resources or activities
Decentralizing decision-making
MATRIX ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Blends elements of a functional and divisional structure
Resembles a grid in which employees with similar skills are grouped together and report to more than one manager
MATRIX ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Based on the cross-functional teams and functions
MATRIX ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Enabling a flexible work environment
Fostering a balanced decision-making process
Promoting open communication and shared resources across the business
MATRIX ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Creating confusion about authority
Tracking budgets and resources can be difficult
Limiting efficiency of key performance indicators (KPIs)
FLATARCHY ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Born from the startup way of acknowledging more independence and autonomy to employees.
Employees are given more responsibility and decision-making power without the usual hierarchical pressures or supervision and can often be more productive
FLATARCHY ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Based on the self-management or lack of management structures
FLATARCHY ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Reducing budget costs due to lack of middle management
Building relationships between staff and superiors
Facilitating a quicker, easier decision- making process
FLATARCHY ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
Requiring extensive planning to be effective
Causing confusion over who makes decisions
Requiring contingency plans to resolve conflicts
IMPORTANCE OF AN ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
1. Definition and clarity of roles within the organization.
2. Goals alignment that makes groups of people work in coordination to achieve common business objectives.
3. Culture development based on the shape of the organization.
4. Productivity through a system meant to use the people part of the organization in the best possible way.
5. Efficiency in the use and allocation of resources within the organization.
6. Better decision-making process by allowing the flow of information within and across several departments.
IMPACT OF ORGANIZATIONAL SIZE ON STRUCTURE AND DESIGN
Work Specialization
Departmentalization
Formalization
Steps in Workforce Planning
Supply Analysis → Demand Analysis → Gap Analysis → Solution Analysis → Monitoring and Evaluation
TALENT INVENTORY
To assess the current available resources and analyze current role of employees
HR FORECAST
To predict HR requirements considering the following:
Headcount
skills mix
internal versus external labor supply
ACTION PLANNING
To enlarge the pool of qualified individuals by recruitment, selection, training, placement, transfer, promotion, development and compensation
BENEFITS OF WORKPLACE PLANNING
Strategic basis for decision making.
Enables an organization to anticipate workforce needs rather than react to surprises.
Involve contingency planning for potential future circumstances and consider options that mitigate risk.
Provides a better understanding of the areas of the workforce that need to be strengthened and facilitates the development of plans for staffing levels, succession planning, and skill development.
Creates a connection between mission, strategic plans, and human resource needs that maximizes operational effectiveness.
Talent
consists of those individuals who can make a difference to organizational performance either through their immediate contribution or, in the longer-term, by demonstrating the highest levels of potential
Talent
An individual with special competencies. In a business or other context, these competencies are strategic importance to the organization. The absence of these competencies would pose an actual situation of crisis for the organization
TALENT MANAGEMENT
Systematic attraction, identification, development, engagement, retention and deployment of those individuals who are of particular value to an organization, either in view of their “high potential” for the future or because they are fulfilling business/operation-critical roles”
TALENT MANAGEMENT
the full scope of HR processes to attract, develop, motivate and retain high-performing employees
TALENT MANAGEMENT
Process of finding, developing, training, and keeping employees whose skills best align with the needs and objectives of the company
TALENT MANAGEMENT
The goal of ____ is to hire the best employees the business can afford so that the company reaches its maximum potential for success.
Prepare - Know challenges - Search - Select - Train - Keep - Follow-up - Further preparation - Completion
Standards Steps in Talent Management
HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT
To hire great talents and make the best out of it to achieve organizational goals
HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT
Keeps the “people” function up and running
HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT
Productivity and business success
TALENT MANAGEMENT
Focuses more on the “make the most out of them” part
TALENT MANAGEMENT
Identify potential and constantly work on making them better
TALENT MANAGEMENT
Build progressive and motivating career paths for people to be their best
EMPLOYEE LIFE CYCLE
A model that shows the different stages that an employee will go through as a part of an organization
Seeking Employment
Recruitment
Pre & Onboarding
Engagement
Development & Training
Talent Retention
Offboarding
Step in the Employee Life Cycle
EMPLOYEE LIFE CYCLE
serves as a guide in better understanding the needs of employees for every stage that they undergo
EMPLOYEE LIFE CYCLE
a very important factor in retention
EMPLOYEE LIFE CYCLE
· It is an area of concern if a company is good on sonboarding but lacks development and retention programs for employees
Recruitment - Onboarding - Development - Retention
KEY METRICS IN THE EMPLOYEE LIFE CYCLE
Recruitment
time to hire
offer acceptance rate
quality of hire
cost to hire
Onboarding
ramp time
new hire engagement
training effectiveness
Development
productivity
360 feedback
promotion rates
Retention
employee engagement
attrition rate
6 months
90% of employees are deciding if they will stay or leave
3 years
69% of employees are more likely to stay with a company for years if they experienced great onboarding ; · New employees who went through a structured onboarding program were 58% more likely to be with the organization after _ years
VISION
Describes the long-term results of the company’s efforts
VISION
What an organization hopes to be and what it wants to achieve in the long-term
VISION
Helps an organization align everyone to head in the right direction
VISION
Gives a purpose to what the employees do
VISION
Using your imagination & foreseeing your company’s future
MISSION
The reason for existence of the organization
MISSION
What needs to be done to turn the vision into reality
MISSION
“Rolling up your sleeves” and putting in the work
PERSONAL VALUES
The worth or importance you attach to different factors in your life
PERSONAL VALUES
These factors are defined as any objects, activities, or frames of mind that you consider very important
PERSONAL VALUES
Interpreted differently by people from different generations religions, political systems, cultures around the globe.
ORGANIZATIONAL VALUES
The root values and beliefs which form the basis on which the organization and its employees operate from
ORGANIZATIONAL VALUES
Ultimately serve as the “guiding light” that steers the company’s attitude and behavior towards others
CORE VALUES AND COMPANY PERFORMANCE
· Help attract the right kind of talent for your brand
· Drive innovation and ambition within the company
· Help customers understand the identity of your business
VALUES CONFLICT
Conflict that occurs when one set of values clashed with another, and a decision has to be made.
STRATEGIC
Supports the organization's vision and mission statements by outlining the high-level plan to achieve both
STRATEGIC
Top management uses reports on finances, operations and the external environment to project future actions
TACTICAL
Answers "how do we achieve our strategic plan?"
TACTICAL
Outlines actions to achieve short-term goals, generally within a year or less
STRATEGIC
plan
large scale
why
difficult to copy
long time frame
TACTICAL
doing
smaller scale
how
easy to copy
short time frame