landscape test 2
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
what are the basis of design
ideas (clients + designer)
canvas (the site)
materials (plants)
what can basis designs do
attraction
noise reduction
entrance
green infrastructure
property screen
outdoor living
hort. therapy
livable spaces and recreation
what are the "bones" of the garden
1. enclosure
2. form
3. Framing the view
4. entry
5. focal point
6. structures
enclosure meaning
frames the space and a sense of enclosure or background
form definition
outline of a plant (silhouette), needs balance
symmetrical form
mirror image
asymmetrical form
visual weight on either side balances each other
framing the view def
The use of plant material to direct the eye
primary axis def
a line in the landscape, usually framed with plants, off which other design elements are based
allee def
walkway lined with trees and shrubs planted in a repeating pattern
entry def
creates a break for a change in the garden; can elicit mystery
focal point def
stimulates the eye and moves the viewer from one location to another in the landscape
structure def
adds permanence to the garden
what is considered the meat of the garden
7. color
8. texture and rhythm
9. abundance
10. whimsy
11. mystery
12. time
hue def
pure color, containing no white, black, or gray
value def
the colors luminous, or the light reflected from it.
shade def
a type of value, but if it contains more black, it is lower value
tint def
a type of value but if it contains more white it is a higher value
intensity def
the brightness of a color
monochromatic
plants share the same hue, can be with similar value and intensity
analogous colors
adjacent to each other on the color wheel
analogous
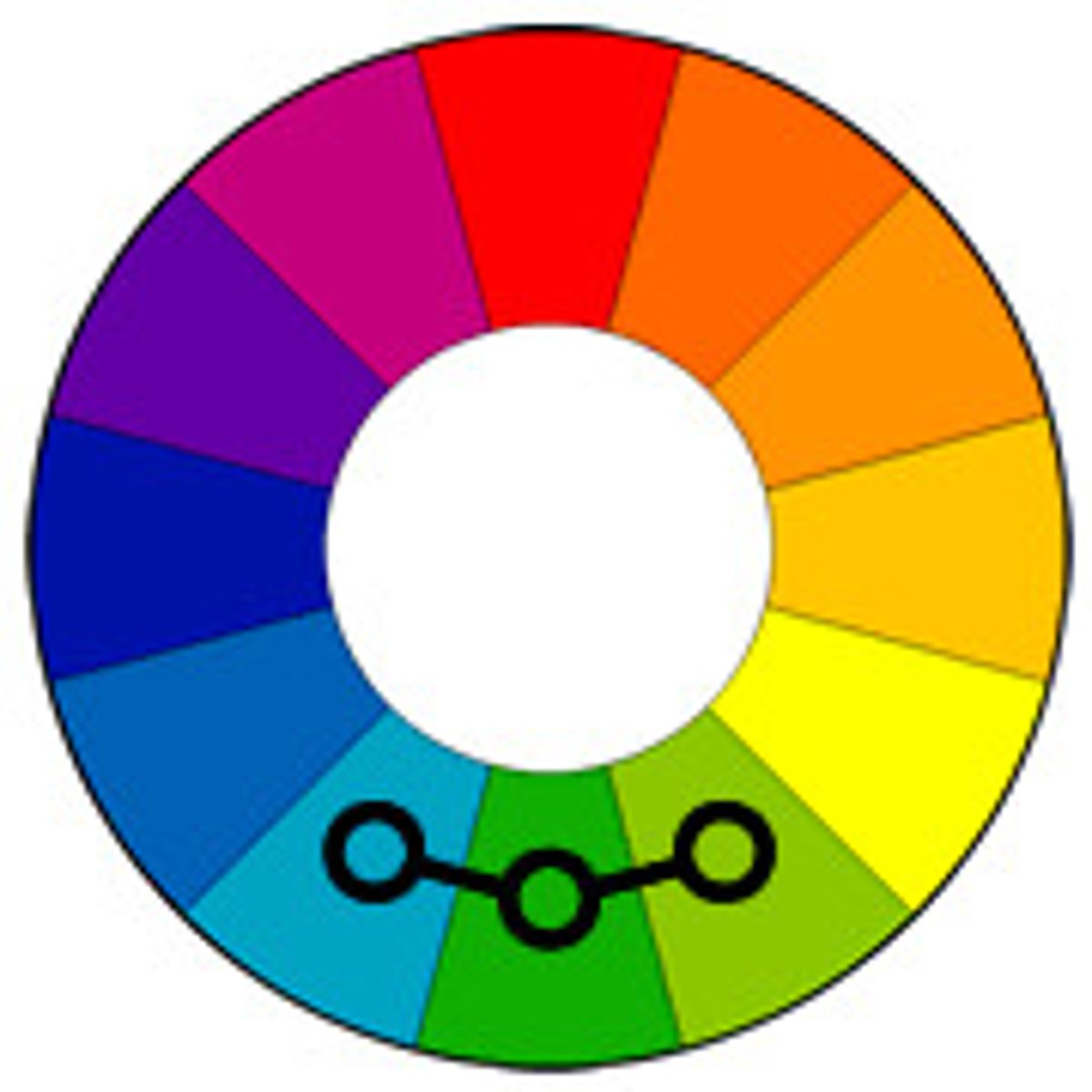
complementary/contrast
colors that are opposites on the color wheel that provide high contrast
more saturation =
more contrast
more muted =
less contrast
color warmth
a term used to convey the emotions that colors evoke
warm color ex
red, orange, yellow
cool colors ex
blue and purple
neutral colors ex
green, brown, white, black, gray/silver
texture def
refers to the surface quality of an object. helps to do if changing the color of the image to black and white
rhythm def
repetition of colors, shapes, and plants in a landscape to unite it
abundance def
The same plant used in large plantings
whimsy def
having your own personality added
mystery def
cant see behind the hedge/hidden
time def
buildings that look old and arent actually old (more of a stylistic choice)
what should you consider when planting
-avoid powerlines and utility lines
-woody plants need more consideration as they live longer
-annuals and perennials less consideration as they can be moved easier
how big should a hole be
2-3x the size of root ball
what does planing too deep do
slow growth
thinning canopy
dieback
trunk decay
what does planting to high do
stability issues
not absorbing nutrienst
correct depth should be
2-3'' above grade
when planting make sure to remove
twine and strapping
top 1/3 to 2/3 of wire basket
only _________ what you can _________
water, maintain
lack of water can lead to
poor establishment
gradual decline of health
Nutrient defiencies
root rot issues
weak or stunted growth
what are antitranspirants
foilage sprays that reduce water loss through leaf surface (transpiration)
-can be toxic
-use at right time
what does mulch do
ensure absorbing and good drainage
avoids competition with turf
staking
only when necessary! in extremely windy sites or bare root trees
proper staking
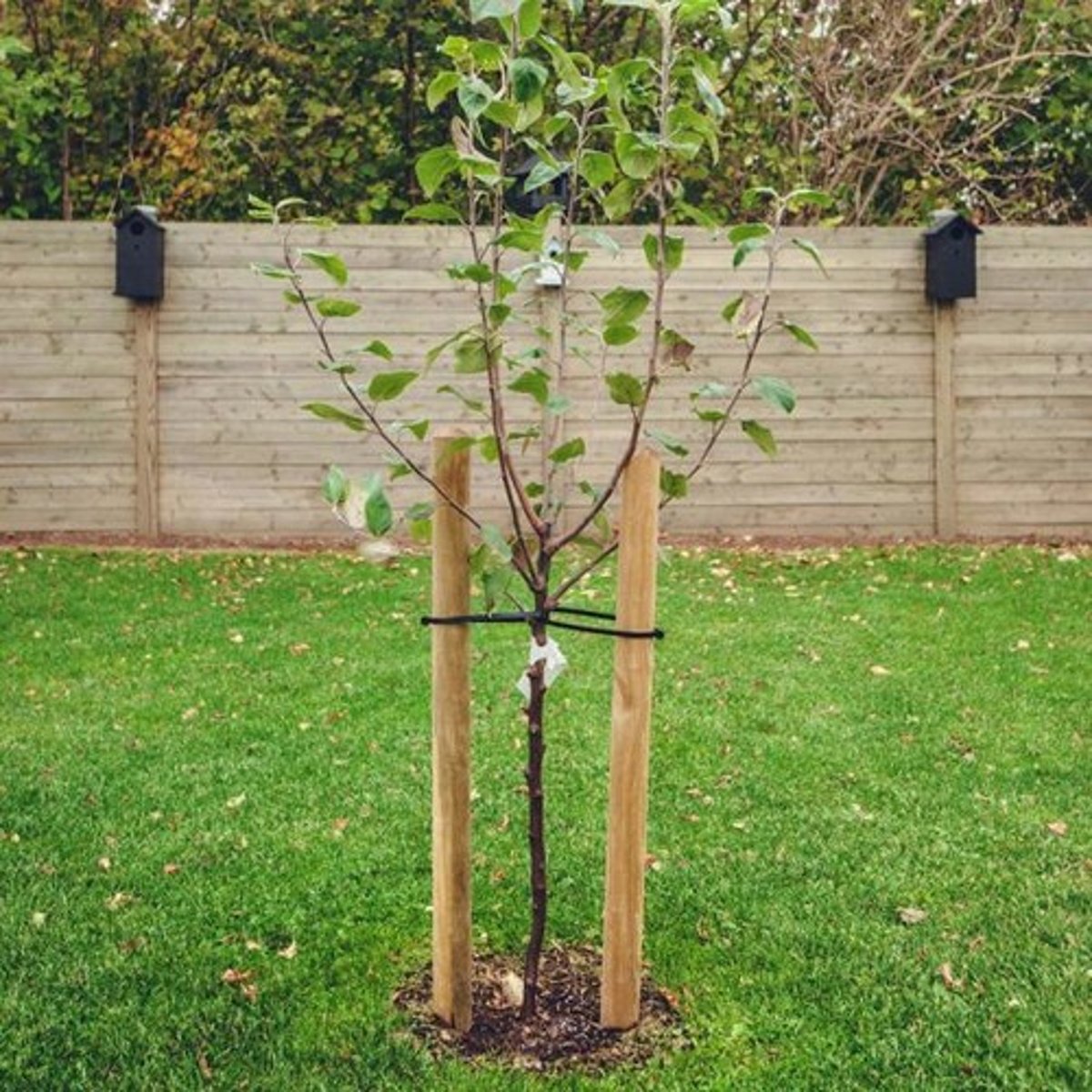

5 procedures to encourage establishment
1. loose soil
2. proper irrigation management
3. mulch ring of 8' around planting hole
4. root flare slightly above garde
5. leaving top unpruned
5 factors that limit growth
1. compacted soil
2. little or no irrigation
3. Grass or weeds growing too close to the trunk
4. planting too deep or high
5. Pruning at planting
5 factors that have little or no impact
1. peat/om added to backfill
2. root stimulant products
3. Fertilizer at planting
4. adding mycorrhizae spores
5. water-absorbing gels
what is a hazard tree
structural defect that may cause a tree or a portion of a tree to fall on someone or something of value
what is the tree hazard checklist
large dead branches?
detached branches?
cavities or rotten wood?
fungal fruting bodies present?
root damage?
relevant site changes?
unusual changes in leaf color or size/ early leaf drop?
has the tree been topped or heavily pruned?
if a defective tree in a remove setting is not frequent by people it is a hazard true
false
it is not a hazard tree, if no damage to someone or something of value
what type of trees are more prone to be hazrad trees
edge trees
lone trees
high traffic and new development
wet sites and shallow soils
why are edge trees more prone to be hazard trees
-exposed to greater stress during storms
-potential root damage during clearing
why are lone trees more prone to be hazard trees
-prone to lighting strikes
-undersized root system or low live crown ratios
top and crown problems
species differences
tree health
higher susceptibility
branch conditions
branch structures
unbalanced crowns
trunk symptoms
codomiant stems
wounds and cracks
leaning
decay indicators
root symtpoms
root failure
soil failure
root severance
root collar disorders
root disease
how does decay move
from tips to root collar
what are the roots symptoms in hazard trees
-dead/loose bark
-bleeding or ooze
-fungal fruiting structures
-cracks or seams in bark
-missing roots
signs of trunk decay
loose bark
cankers
swelling
stump sprouts
branch stubs
knots
cavities
abdnormal swellings