Development and Selection of B and T Lymphocytes in Immunology
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
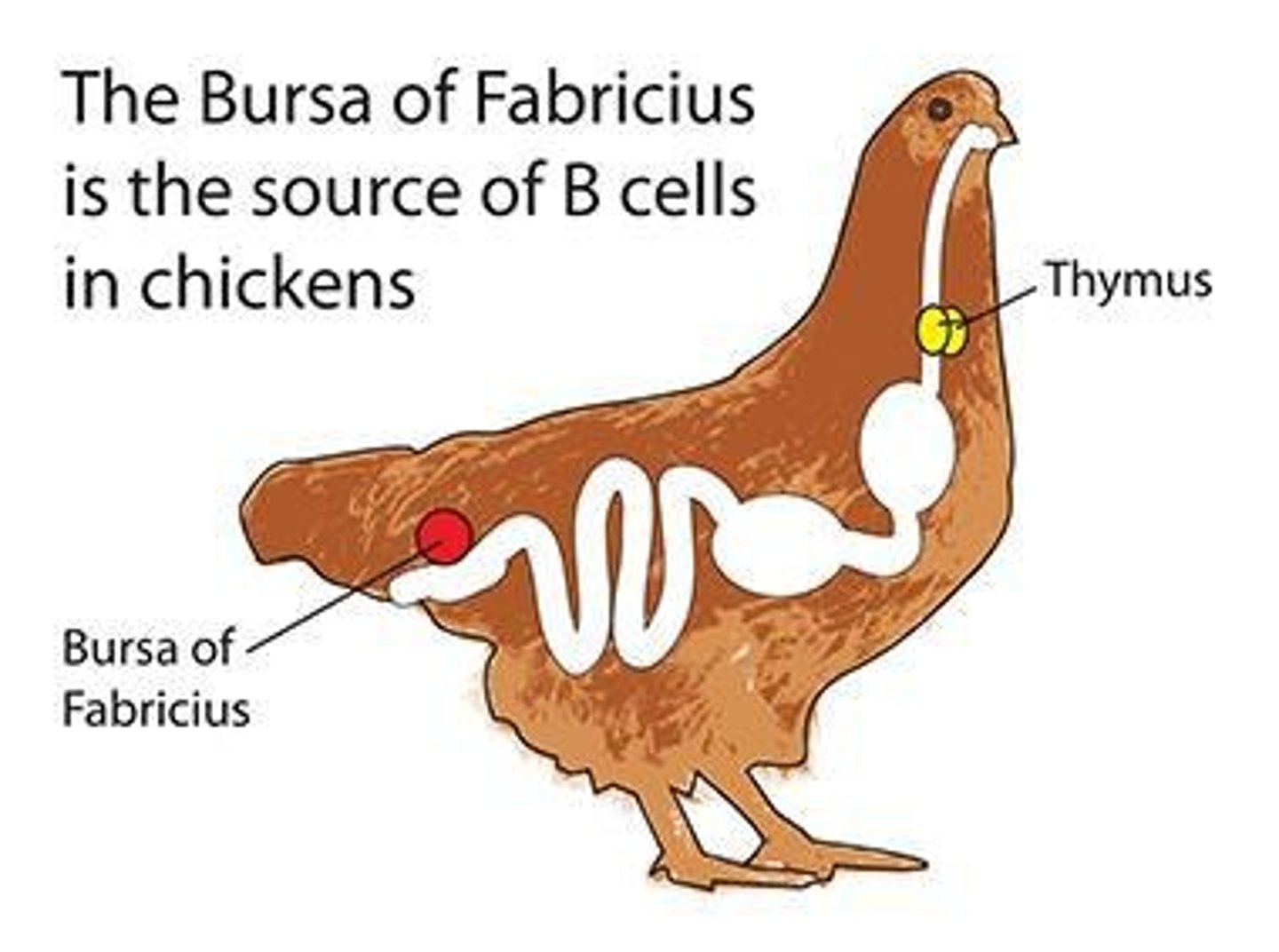
Where do B cells develop in birds?
In the Bursa of Fabricius.
Who discovered B cells and T cells?
Max Cooper and Jacques Miller in the 1960s.
What is the first stage of B cell development in the bone marrow?
Common lymphoid progenitor.
What marks successive stages of B cell differentiation?
Rearrangement of immunoglobulin (Ig) genes.
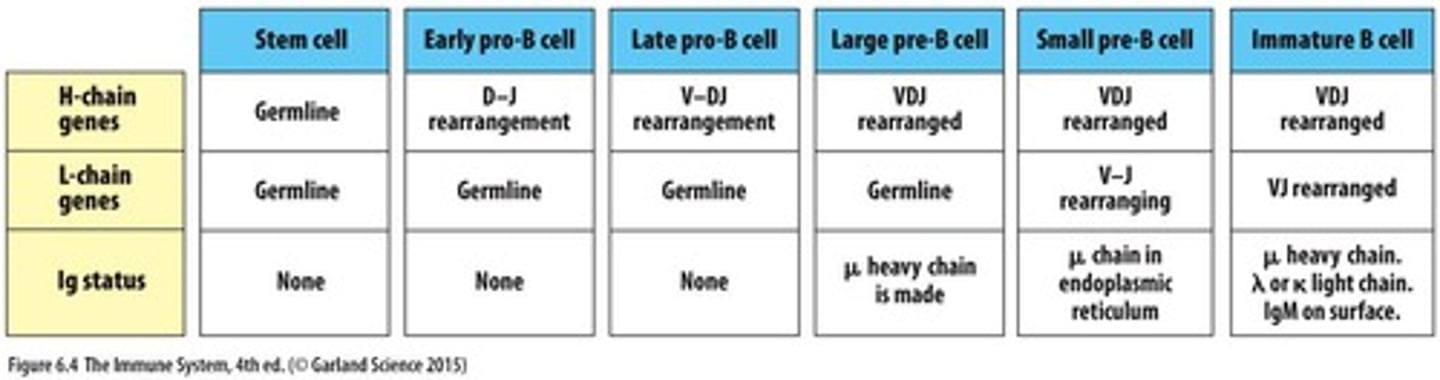
What is the first heavy chain component expressed during B cell development?
The heavy chain V region is assembled first and expressed with the Cµ chain.
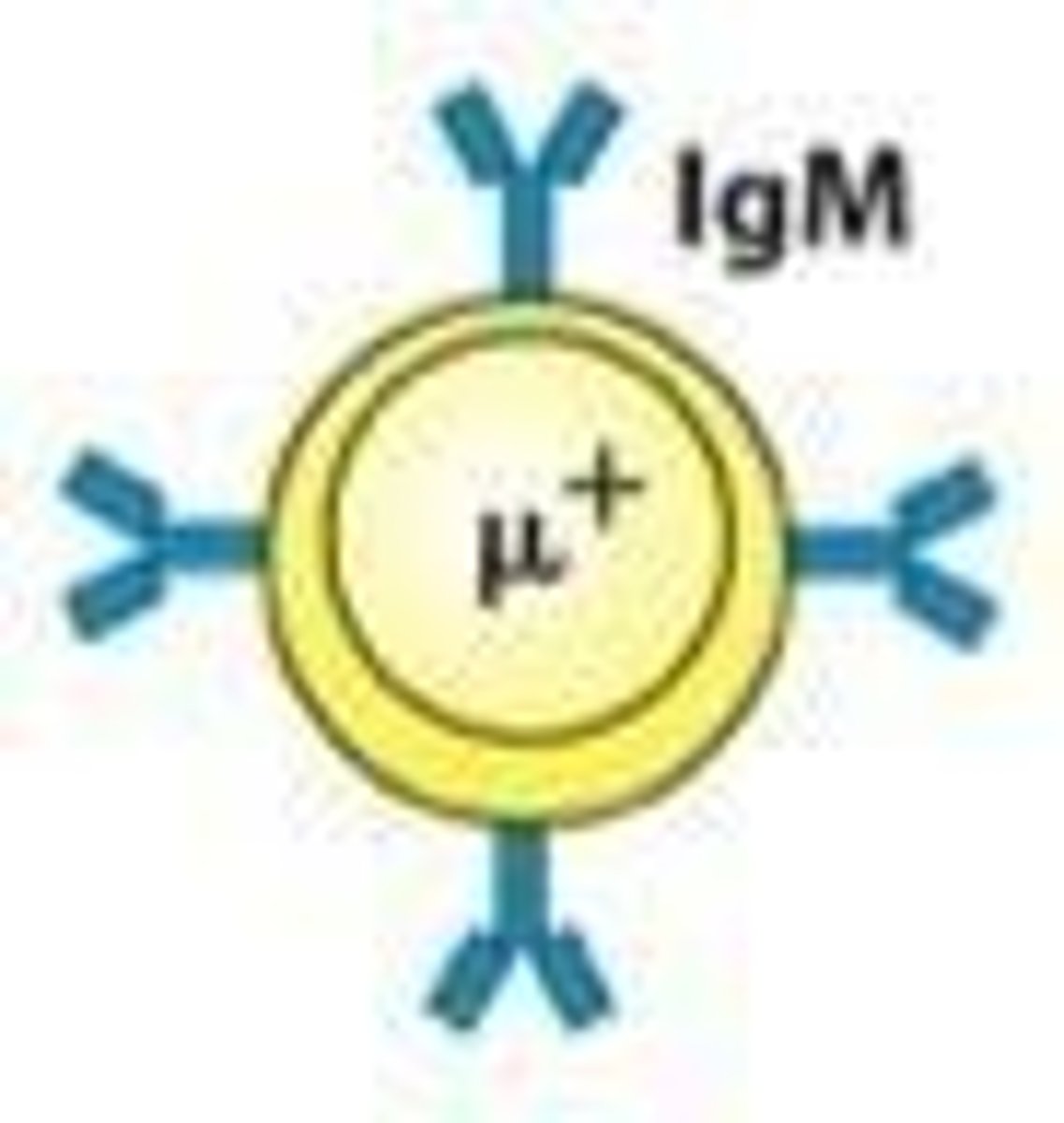
What is expressed on the cell surface as the B cell leaves the bone marrow?
IgM.
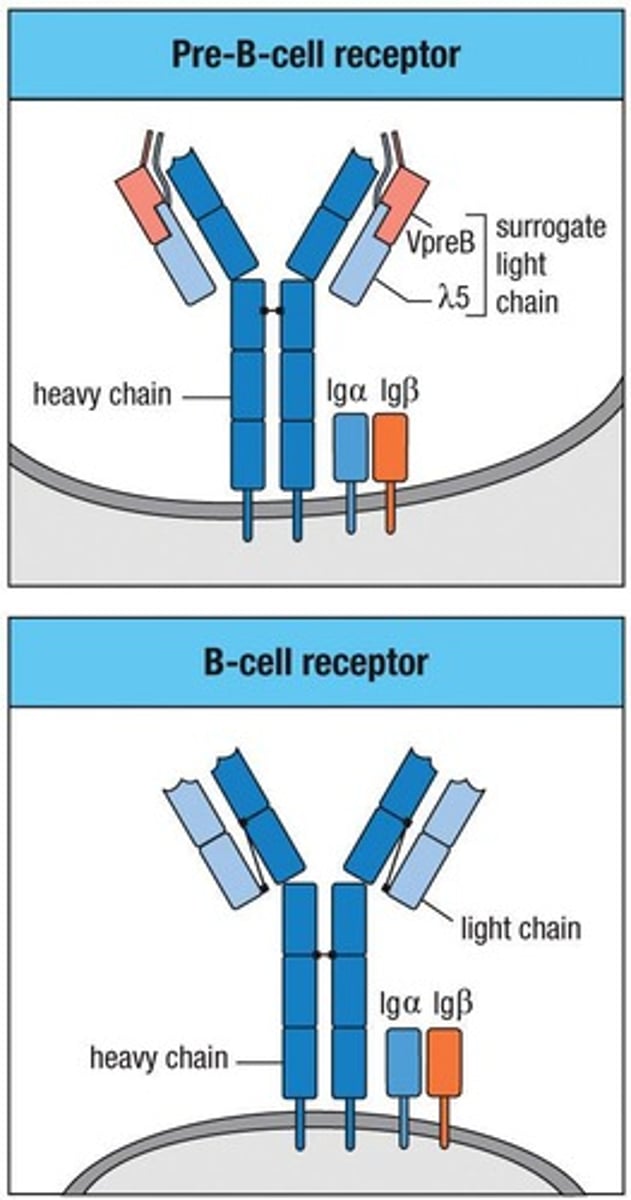
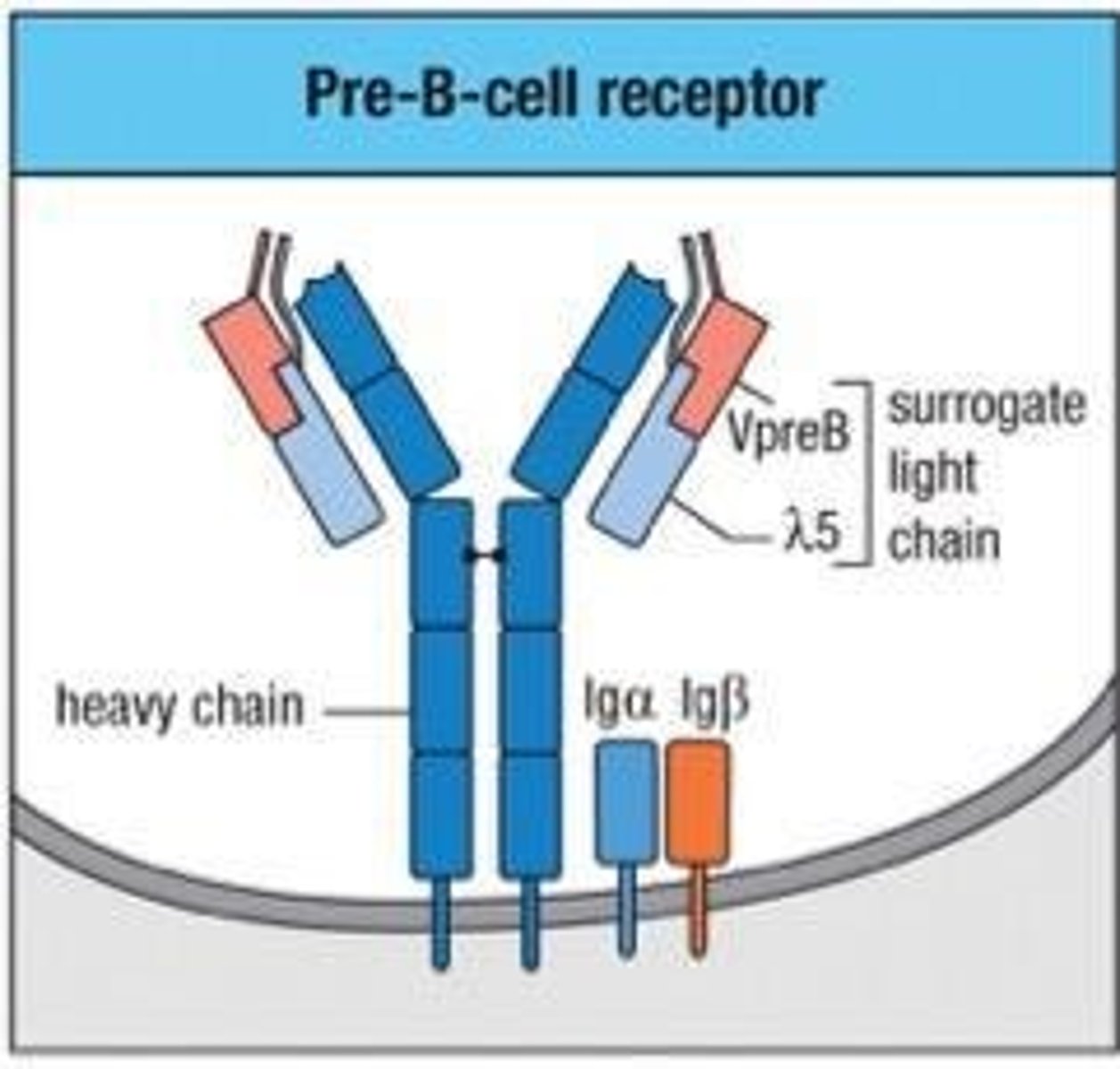
What is the role of the pre-B cell receptor?
It monitors the quality of the antibody heavy chain.
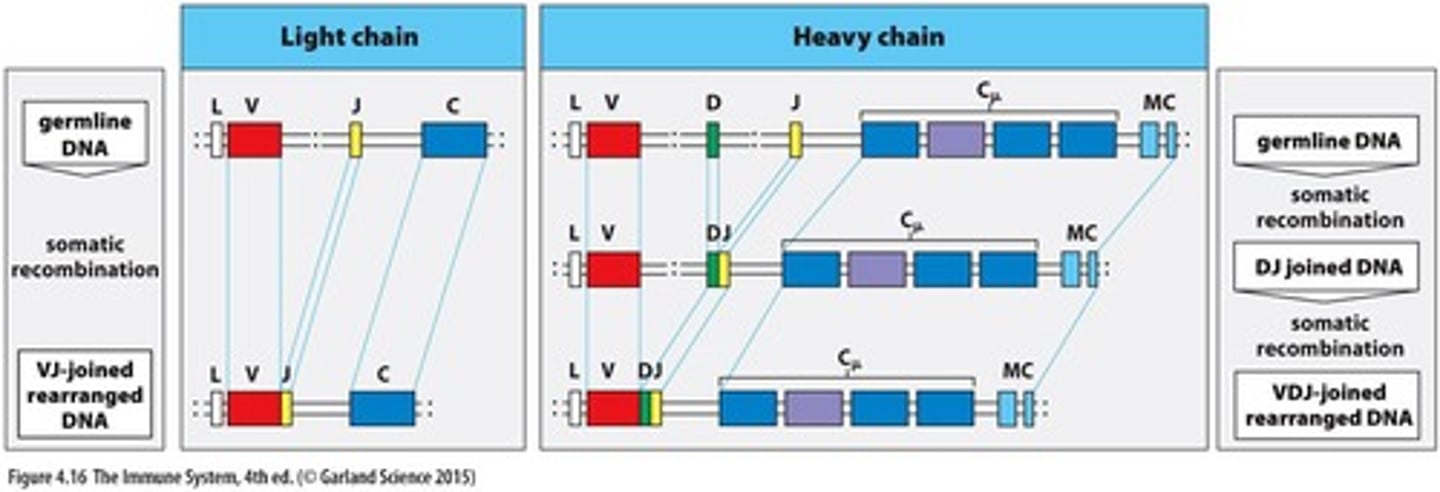
What occurs during VDJ recombination?
All other D segments are deleted, and only one attempt at VDJ recombination is possible on each chromosome.
What are nonproductive rearrangements?
They result in the generation of STOP codons and the creation of nonfunctional proteins.
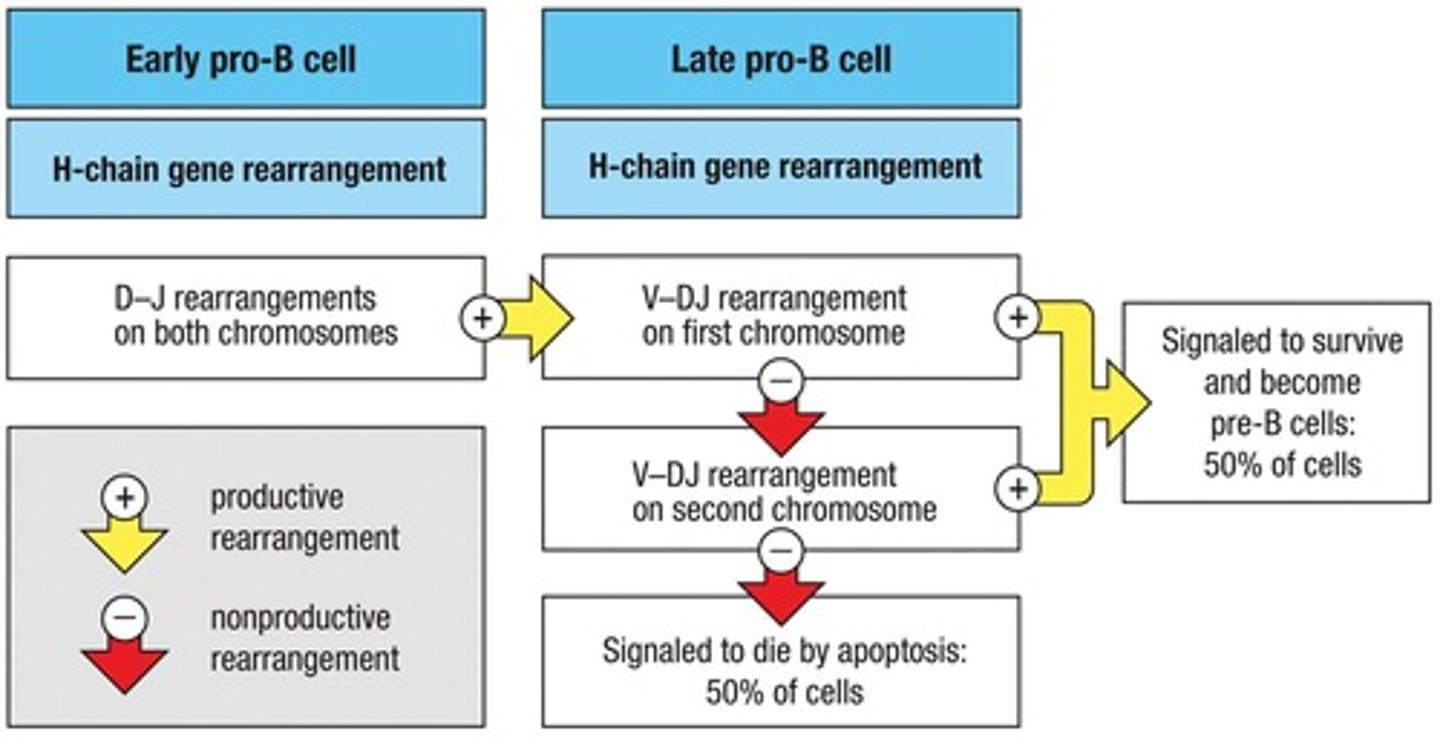
What happens if the assembly of the pre-B cell receptor is unsuccessful?
The late pro-B cell dies by apoptosis.
What is the success rate of light chain rearrangement in small pre-B cells?
85% success rate.
What are the two requirements to pass the first checkpoint in B cell development?
1. Successful heavy chain rearrangement yielding a functional protein sequence. 2. Successful light chain rearrangement.
What happens after the large pre-B cell undergoes mitosis?
It gives rise to small pre-B cells and initiates light chain rearrangement.
What is the significance of the surrogate light chain in pre-B cells?
It tests the ability of the heavy chain to interact with the light chain to form an antibody.
What is the role of cytokines in B cell development?
They guide development through cell-cell interactions.
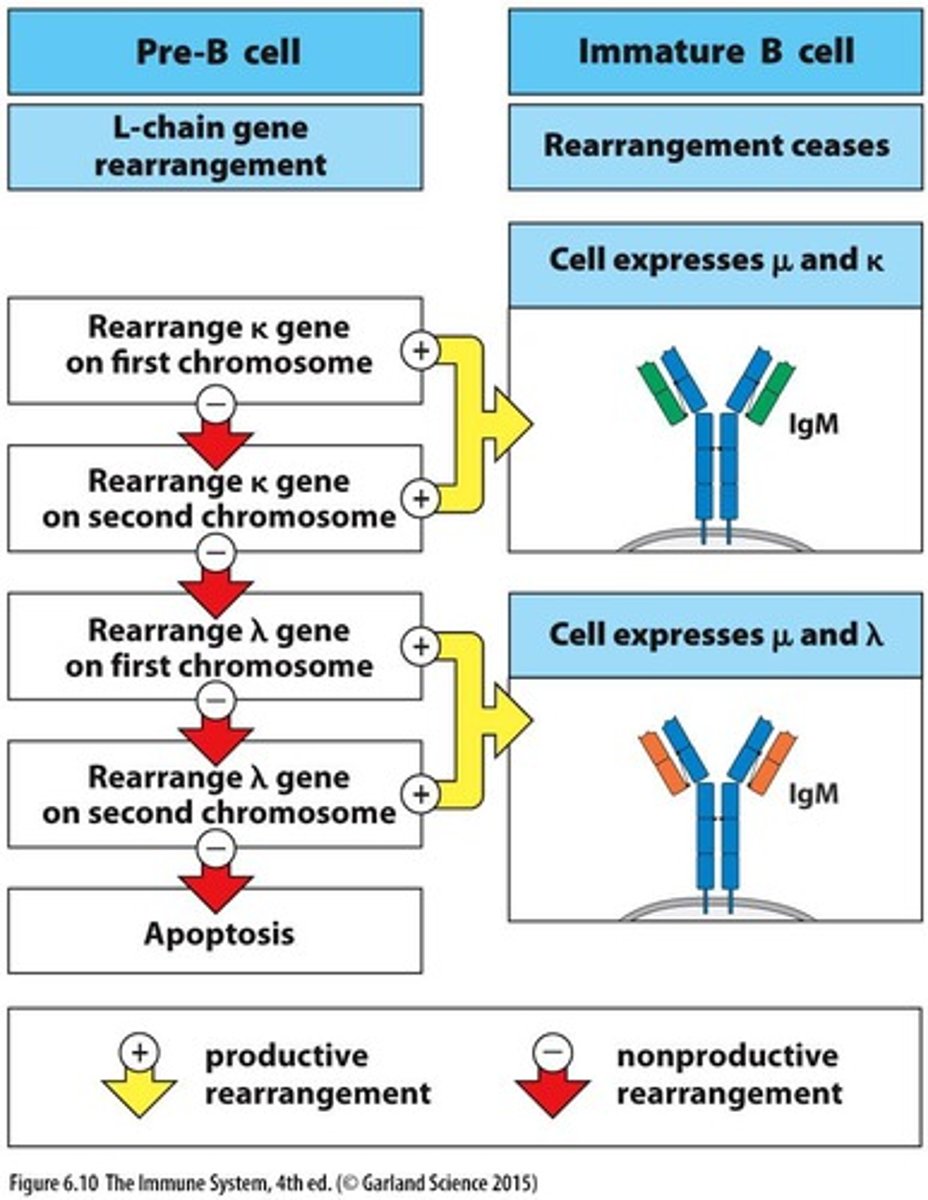
What is the first step in light chain rearrangement?
Rearrangement occurs on one chromosome at a time, beginning with the kappa locus.
What is the outcome of successful assembly of the pre-B cell receptor?
It signals through Igβ to turn off gene rearrangements at the other chromosome.
What is a small pre-B cell?
A population of cells with the same heavy chain but different light chains.
What problem arises from antibody gene rearrangement?
It generates random specificities, many of which may bind to self antigens.
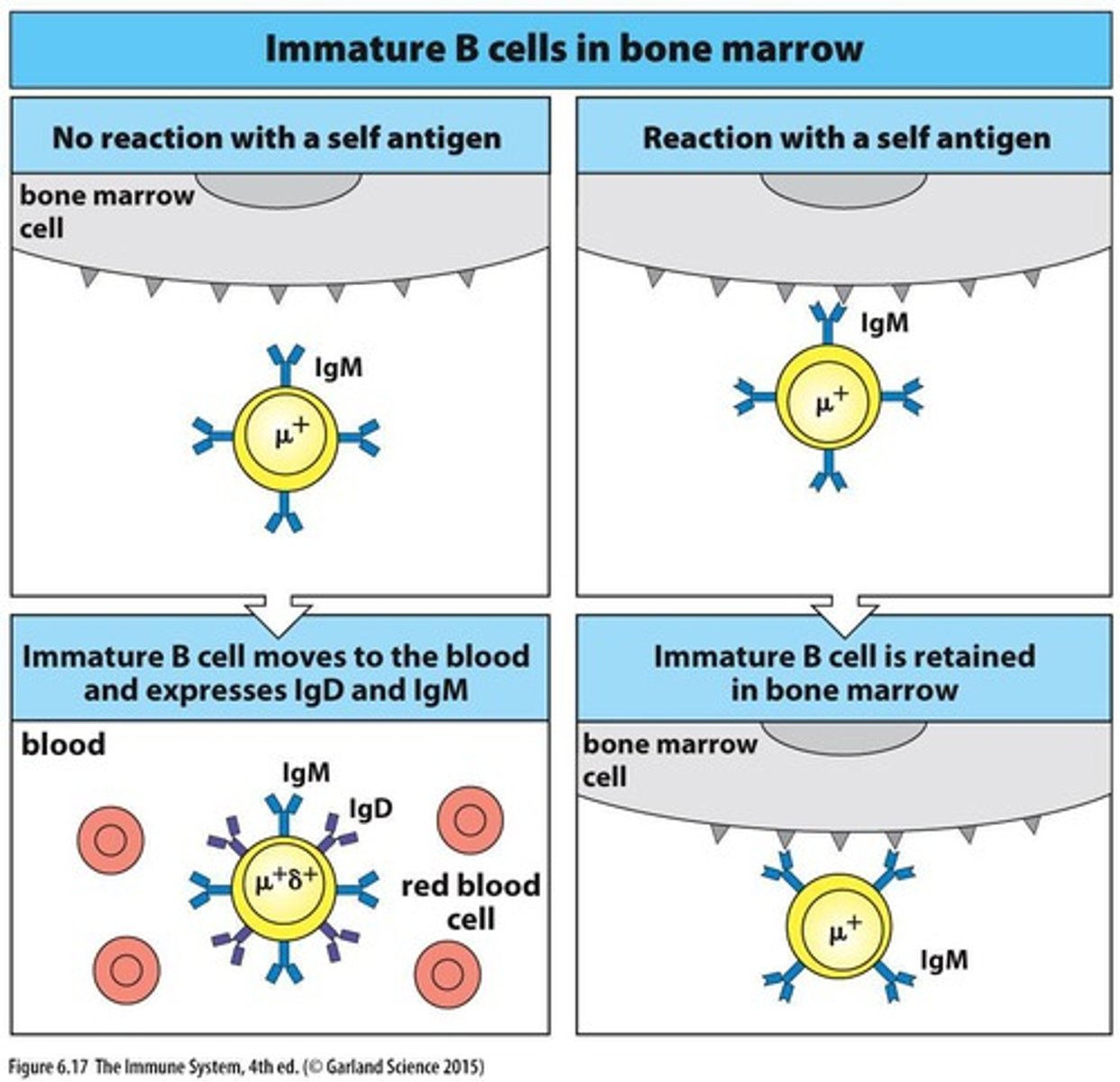
What happens to B cells that bind to self antigens?
They receive a negative signal and further development is stopped.
What is the role of multivalent self antigens in B cell development?
They provide a strong signal that leads to the negative selection of self-reactive B cells.
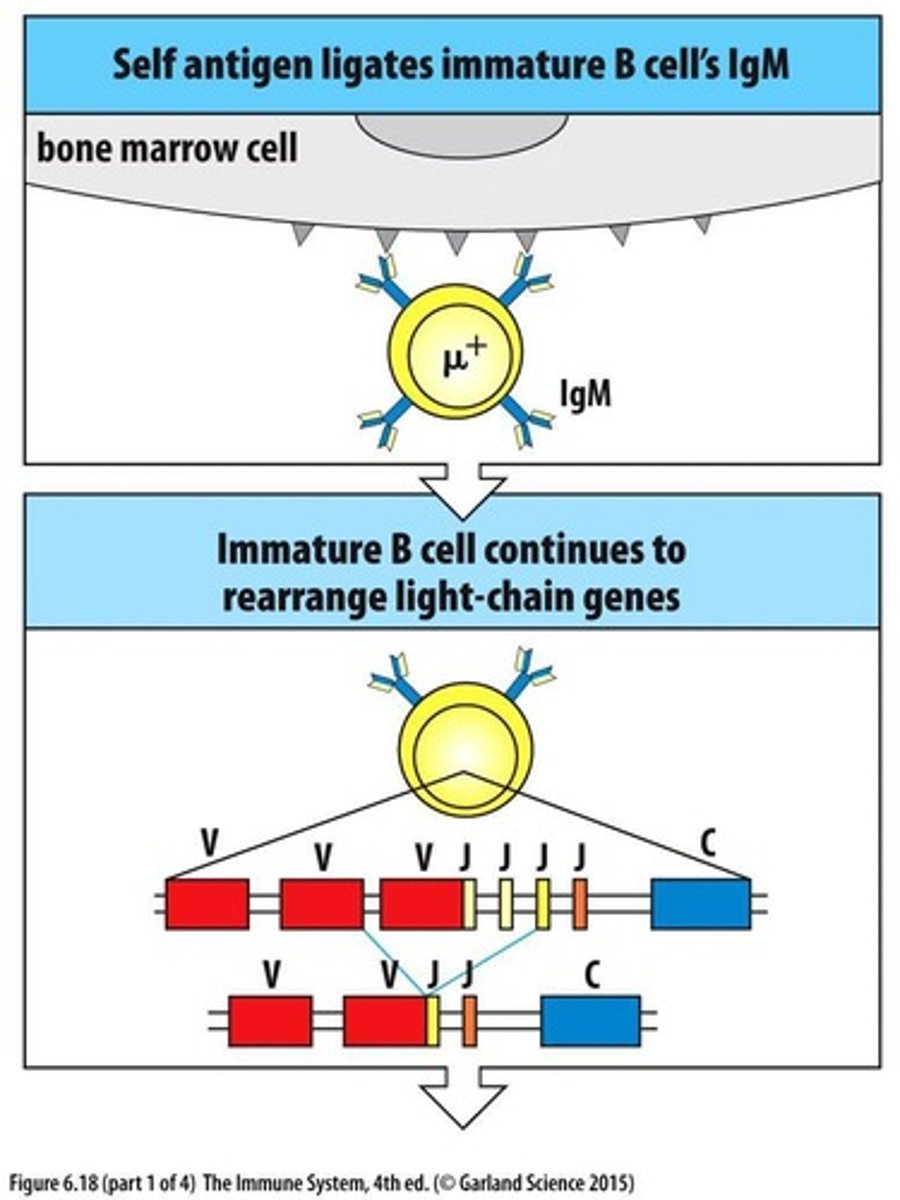
What is receptor editing in B cells?
A process where autoreactive receptors on immature B cells are modified by further rearrangement of light chain genes.
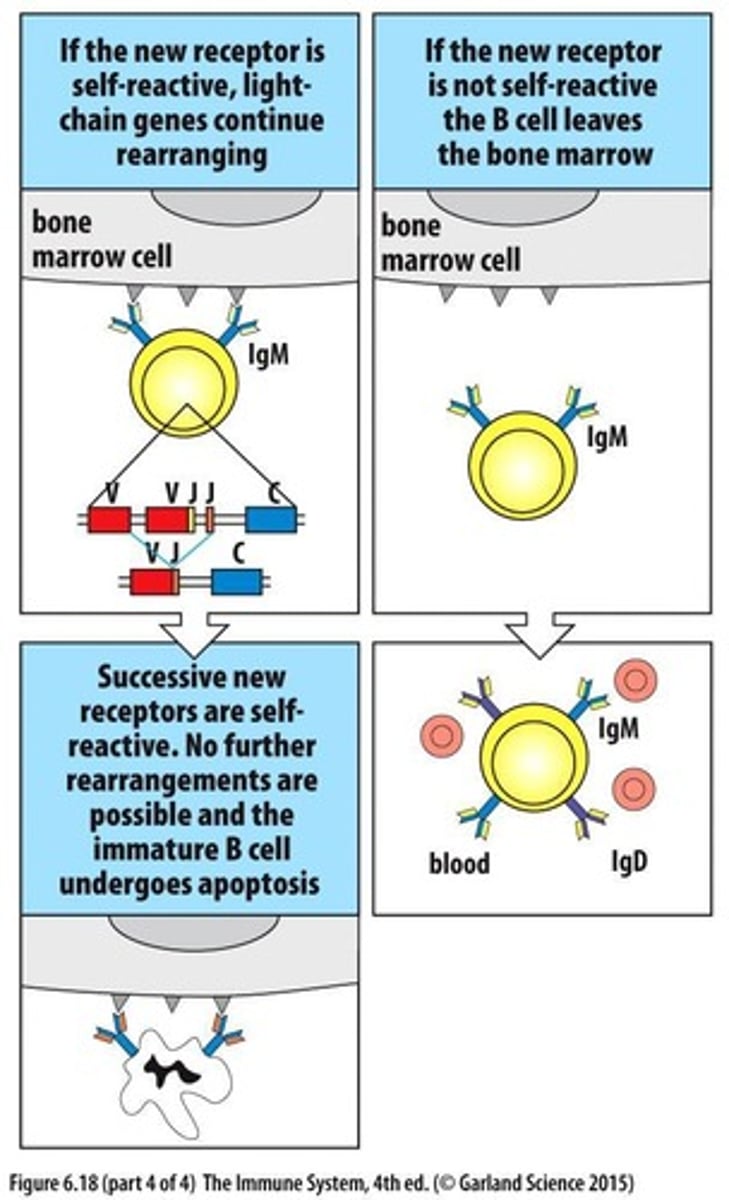
What occurs if a B cell runs out of J genes during receptor editing?
The cell dies through apoptosis.
What is clonal deletion in B cell development?
The death of developing B cells in the bone marrow expressing autoreactive antibodies.
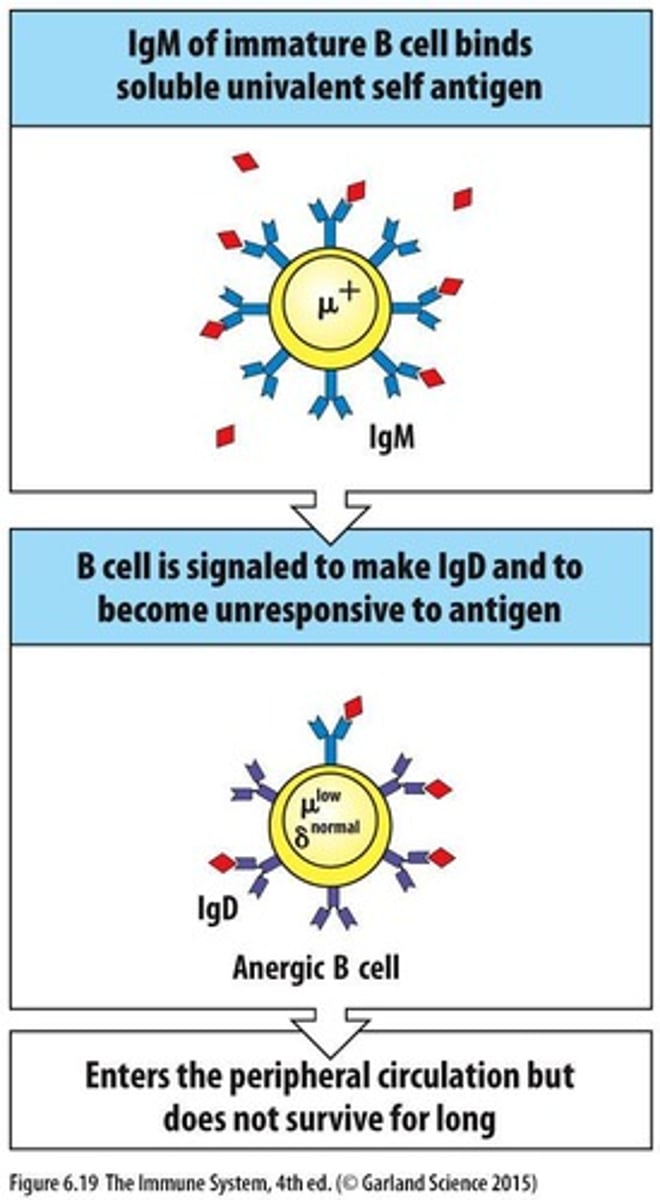
What happens to immature B cells that are reactive with monovalent self antigens?
They become nonresponsive, entering a state of anergy.
What are the three mechanisms that prevent autoreactive B cells?
1. Successful receptor editing, 2. Death by apoptosis, 3. Induction of anergy.
What is central tolerance?
Mechanisms operating in primary lymphoid organs to prevent autoreactivity.
What is peripheral tolerance?
Mechanisms that operate after B cells leave primary lymphoid organs.
What is required for the transition from immature to mature B cells?
Entry into secondary lymphoid tissues, such as lymph nodes.
How do immature B cells enter lymph nodes?
Through high endothelial venules (HEV).
What happens to B cells that do not encounter specific antigens in lymph nodes?
They leave via efferent lymphatic vessels.
What autoimmune disease is associated with antibodies to DNA?
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
What are common symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
Fatigue, joint pain, kidney issues, skin rashes, and brain involvement.
What is the significance of the 6 x 10^9 developing B cells in the bone marrow?
They die daily through inability to make functional antibodies or through clonal deletion.
What is the role of soluble proteins in B cell tolerance?
They tend to be monovalent and induce a state of nonresponsiveness in immature B cells.
What is the outcome of B cells leaving the bone marrow with self-antigen recognition?
They become tolerant through anergy or apoptosis.
What are the three T cell lineages derived from lymphoid precursors?
CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, and γδ T cells.
Where do T cell precursors migrate to from the bone marrow?
The thymus.
What type of T cell receptor (TCR) do both CD4 and CD8 T cells express?
αβ TCR.
What is MHC restriction in T cells?
T cells recognize a combination of peptide and self-MHC.
What happens to autoreactive T cells during development?
They must be removed to avoid autoimmune disease.
What is thymic involution?
The gradual degeneration of the thymus that begins one year after birth.
What is the significance of thymic involution?
It may help avoid the generation of autoimmune cells later in life.
What are the stages of T cell development in the thymus?
Double negative (DN), double positive (DP), and single positive T cells.
What characterizes double negative (DN) T cells?
They do not express CD4 or CD8.
What characterizes double positive (DP) T cells?
They express both CD4 and CD8.
What is the first checkpoint in T cell development?
The successful assembly of a functional pre-TCR.
What is the role of pTα in T cell development?
It is the functional equivalent of the surrogate light chain in B cell development.
What happens after successful β chain rearrangement in T cells?
Cells start to express CD4 and CD8.
What is the developmental pathway for T cells in the thymus?
Bone marrow → Precursor T cells → Thymic cortex → Thymic medulla → Exit to blood as differentiated T cells.
What is the difference between T cells and B cells regarding lifespan?
T cells are long-lived and self-renew, while B cells are short-lived and continually differentiate from bone marrow precursors.
What occurs during TCR gene rearrangement in DN thymocytes?
More frequent rearrangement occurs as cells develop.
What is the significance of the thymus in T cell development?
It is where T cell receptor gene rearrangement occurs and autoreactive T cells are removed.
What is the common progenitor for αβ and γδ T cells?
They develop from a common T cell progenitor.
What is the role of CD3 in T cell development?
CD3 is expressed during the rearrangement of TCR genes and is part of the pre-TCR complex.
What is the importance of the thymic cortex and medulla in T cell development?
The cortex is where early development occurs, while the medulla is involved in the final maturation of T cells.
What is the evolutionary hypothesis regarding thymic involution?
It may help avoid the generation of autoimmune T cells as pathogens accumulate with age.
What is the role of the pre-T cell receptor?
It serves as both receptor and ligand, signaling to stop rearrangement of β, γ, δ chains, initiate CD4 and CD8 production, and start cell division.
What happens immediately after successful TCR β chain rearrangement?
RAG complex proteins are turned off, allelic exclusion occurs, and the pre-T cell undergoes proliferation, creating a clone expressing the same Vβ chain.
What marks the second checkpoint in T cell development?
Successful expression of the α chain and β chain, leading to the assembly of a functional TCR.
What are the two types of T cells that can develop from a T cell expressing both CD4 and CD8?
Class I-restricted CD8 T cells and class II-restricted CD4 T cells.
What is positive selection in T cell development?
It is the process where CD4+CD8+ pre-T cells that recognize MHC with self peptide are selected for survival.
What occurs during negative selection of T cells?
T cells that bind too strongly to self-MHC + self-peptide are eliminated to avoid autoimmunity.
What is the role of the AIRE protein in T cell selection?
AIRE induces transcription of various tissue-specific self antigens in thymic medulla epithelial cells to test T cell autoreactivity.
What is the significance of VDJ recombination in T cell development?
It is essential for the rearrangement of TCR genes, and failure to complete this process leads to high rates of cell death in the thymus.
What happens to T cells that fail to pass through positive and negative selection?
They undergo apoptosis and are phagocytosed by thymic macrophages.
What is the outcome of successful α and β chain rearrangement in T cells?
It results in the expression of a functional TCR.
How do CD4 and CD8 T cells differentiate based on TCR binding?
TCR binding to MHC1 recruits CD8, while binding to MHC2 recruits CD4, driving differentiation into single positive T cells.
What is the fate of T cells that recognize self-MHC with self-peptide?
They receive a survival signal through TCR engagement during positive selection.
What is the role of dendritic cells and macrophages in T cell selection?
They interact with DP cells through self MHC + self peptide, facilitating negative selection.
What is APECED?
Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis ectodermal dystrophy, a condition resulting from lack of functional AIRE, leading to widespread autoimmune disease.
What percentage of developing T cells fail to complete differentiation?
98-99% of developing T cells fail to complete differentiation.
What is the significance of receptor editing in T cell development?
It allows for modification of the TCR α-chain if positive selection is unsuccessful, similar to antibody light chain genes.
What does it mean for T cells to undergo double-negative, double-positive, and single-positive stages?
These stages represent the progression of T cell development in the thymus, leading to functional T cells ready for circulation.
What is the role of thymic cortical epithelial cells in T cell selection?
They express both MHC1 and MHC2, presenting self peptides for T cell recognition during positive selection.
What is the significance of TCR/MHC interaction in T cell lineage commitment?
It determines whether a DP cell becomes a CD4 or CD8 T cell based on the type of MHC it interacts with.
What is the difference between αβ T cells and γδ T cells in terms of selection?
αβ T cells undergo positive and negative selection, while γδ T cells likely do not bind to MHC and may not go through these selection processes.
What happens to T cells that bind too weakly to MHC during selection?
They do not receive a survival signal and are eliminated.
What is the importance of TCR specificity in T cell development?
TCR specificity influences the survival and differentiation of T cells, ensuring proper immune responses.
Who discovered B and T cells, and when?
Max Cooper and Jacques Miller, in the 1960s.
What role do bone marrow stromal cells play in B cell development?
They provide survival and differentiation signals (e.g., IL-7, SCF) and adhesion molecules that guide B cell development.
At which stage is the αβ vs. γδ T cell lineage decision made?
At the DN3 stage.
What percent of thymocytes die during T cell development, and why?
95% die, because they fail positive or negative selection.
What is the structure of the thymus lobule, and where do selection events occur?
Cortex (dense thymocytes, positive selection by cortical epithelial cells) and Medulla (fewer thymocytes, negative selection by dendritic cells, macrophages, and medullary epithelial cells).
Which signaling molecules transmit survival/proliferation signals in pre-BCR and pre-TCR complexes?
Igβ (for pre-BCR) and CD3 (for pre-TCR).
What ensures only one heavy or β chain is expressed per lymphocyte?
Allelic exclusion (enforced by pre-BCR or pre-TCR signaling).
Why is thymic involution thought to occur?
To conserve energy once a diverse T cell repertoire is established.
What is allelic exclusion, and why is it important?
ensures only one heavy or β chain gene is expressed per cell, maintaining antibody or TCR specificity.
What is the role of IL-7 and SCF in B cell development?
They’re cytokines from stromal cells that promote proliferation and differentiation of early B cells.
checkpoint 1 in T cell development and what do they test for
tests for successful rearrangement of the β chain gene, ensuring the production of a functional pre-TCR.
checkpoint 2 in T cell development and what do they test for
tests for the successful rearrangement of the a chain gene and the expression of a functional TCR
What is the main difference between αβ and γδ T cells?
αβ T cells recognize peptide-MHC and undergo selection; γδ T cells do not depend on MHC and often develop early.
Early pro-B cell:
: D–J heavy chain rearrangement
Late pro-B cell:
V–DJ heavy chain rearrangement
Large pre-B cell:
Pre-B cell receptor (μ heavy + surrogate light chain) forms
Small pre-B cell:
Light chain V–J rearrangement
Immature B cell
Expresses surface IgM
Mature B cell
: Expresses IgM and IgD
productive rearrangement?
maintains the reading frame and produces a functional antibody chain
a nonproductive rearrangement?
creates a frameshift or stop codon, leading to a nonfunctional chain. If both alleles fail, the cell undergoes apoptosis.