B7: Non-communicable diseases
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Health
A state of complete physical, social and mental well-being and not merely the absence of diseases or infirmity.
Lifestyles choices that can affect our health
The environment we live in, our physical activity levels and our food choices (among others).
Communicable vs Non-Communicable
Communicable = can be spread between people
Non-Communicable = cannot be spread
Correlation
Positive correlation means as one variable increases, so does the other variable. They have a positive connection. Negative correlation means as one variable increases, the other variable decreases. They have a negative connection.
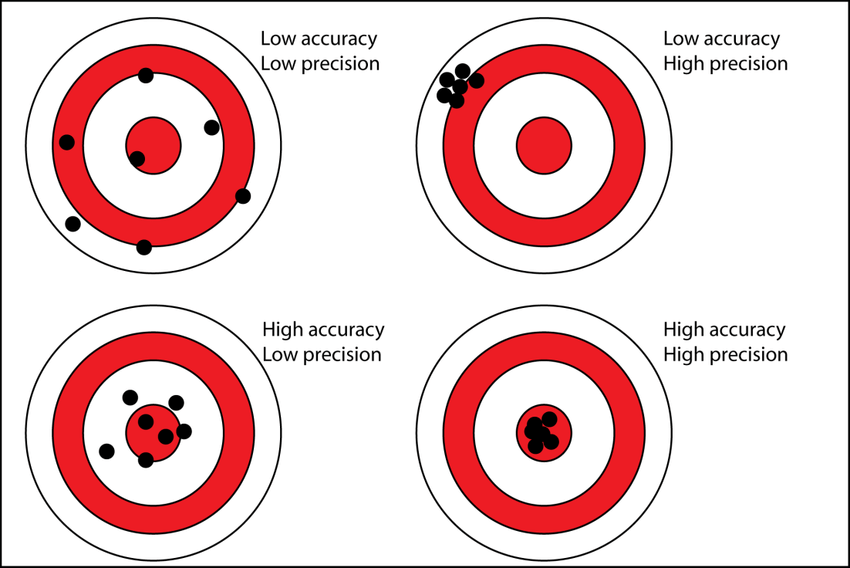
Precision and Accuracy
Accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the true or accepted value. Precision refers to how close measurements of the same item are to each other.
Risk factors for Cardiovascular disease (and how they cause disease)
Lack of exercise - heart and lungs are smaller. Body stores more fat.
Smoking - narrows blood vessels, increases heart rate and blood pressure. Damages lining of blood vessels.
High saturated fat - Obesity can lead to CVD.
Risk factors for Type 2 diabetes (and how they cause disease)
Obesity - can lead to type 2 diabetes, high blood sugar and blood pressure. Leads to heart disease.
Lack of exercise - body stores more fat.
Genetic Tendency - inherited by parents.
Insulin Resistance - caused by obesity.
Risk factors for Liver and brain damage (and how they cause disease)
Alcohol use - may develop cirrhosis (a disease that destroys liver tissue). Alcohol is a carcinogen, causes damage to the brain - causing it to become soft and pulpy, causing structures to be lost. Cirrhosis is where cells are replaced by scar tissue.
Risk factors for Lung diseases, including lung cancer (and how they cause disease)
Radioactive materials in soils and air/Ionising radiation - Breathing radioactive materials into the lungs enables the radiation to penetrate directly into the cells.
Smoking - Tar is a carcinogen and breaks down alveoli, reducing surface area. Cilia stop working.
Risk factors for Skin cancer (and how they cause disease)
UV Light from the sun/Ionising radiation/X-Rays - Ultraviolet Light increases the risk of melanoma.
Nuclear Power Accidents - Penetrates cells and mutates DNA.
Risk factors for Low birth weight in babies (and how they cause disease)
Alcohol use during pregnancy - Affects development of the baby’s body.
Smoking during pregnancy - Carbon monoxide prevents binding of oxygen to red blood cells. This means the fetus does not receive enough oxygen, so it cannot grow and respire.
Risk factors for Brain damage in babies (and how they cause disease)
Alcohol use during pregnancy - Drinking can cause miscarriage, stillbirths, premature births and low birthweight. Development of the brain and body of the baby can be affected. Risk of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS). Alcohol passes across placenta and causes disease.
Cancer
Cancer is the result of changes in cells that lead to uncontrolled growth and division.
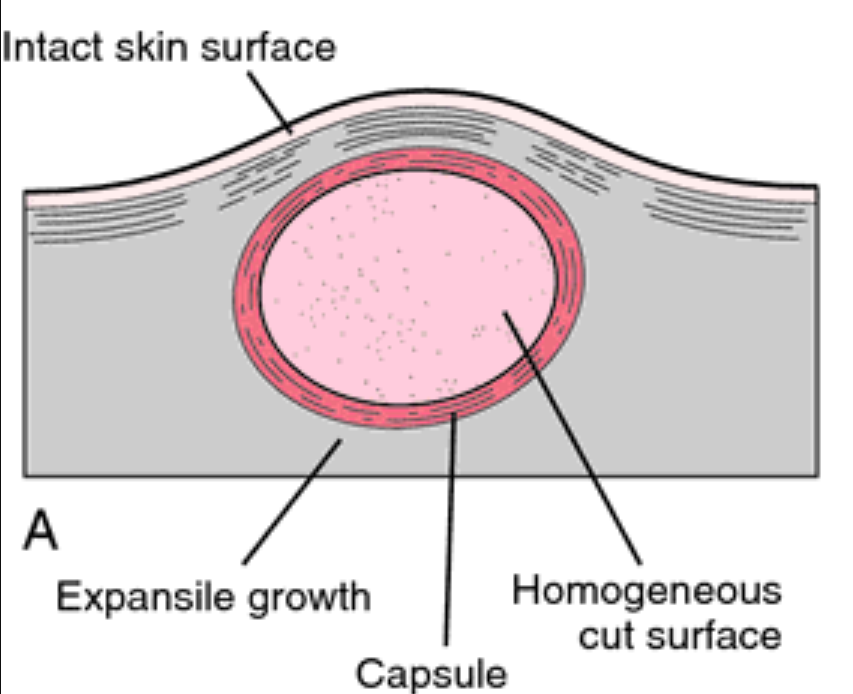
Benign tumour
Does not spread, and is enclosed in a capsule. Grows slowly. Can cause pressure or damage to surrounding tissues. Can be treated by chemotherapy, radiotherapy or surgery.
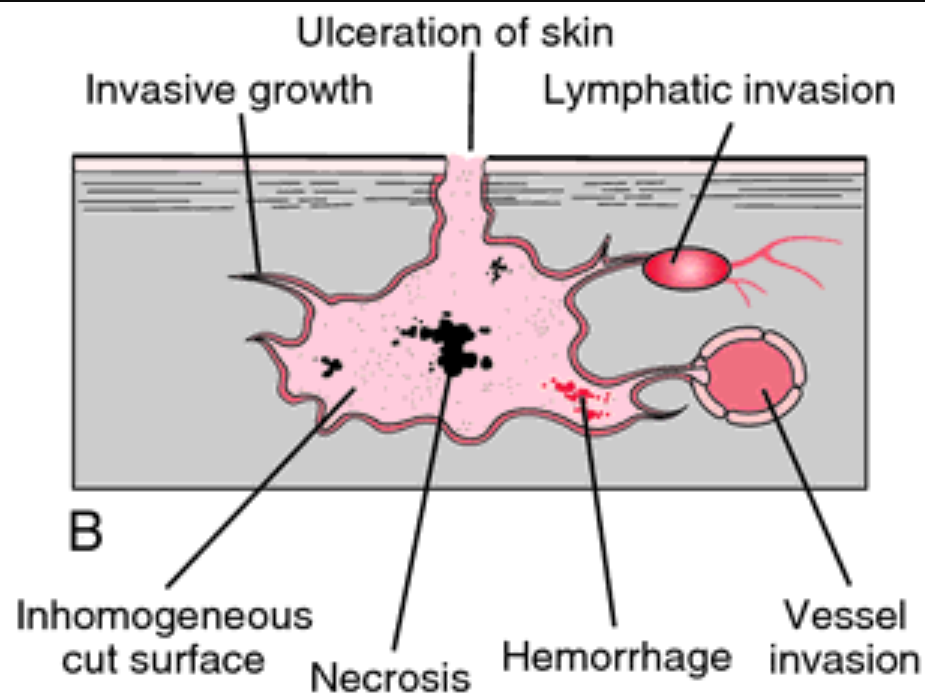
Malignant tumour
Spreads. Initial tumour may rupture and release clumps of cells. Faster growing. Disrupts normal tissue function. Can be treated by chemotherapy, radiotherapy or surgery.
Communicable Diseases
Flu, Cold, amongst others
Non-Communicable diseases
Lung cancer, skin cancer, diabetes, scurvy, atheroma, cirrhosis, amongst others
How can different diseases interact?
Defects in the immune system → Increased chance of suffering from infectious diseases
Viruses in cells e.g HPV → Certain cancers
Immune reactions caused by pathogens → Allergic reactions such as asthma
Severe physical ill health → Depression and other mental illness
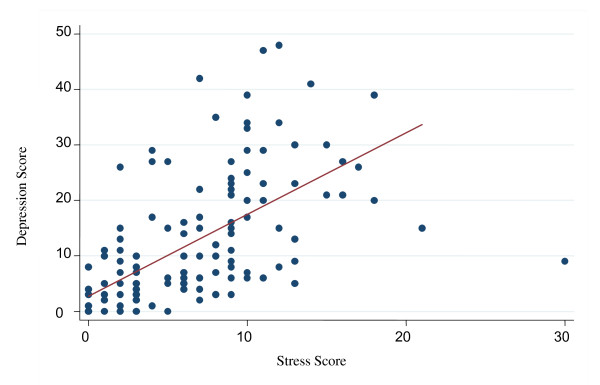
A journalist concluded that stress causes depression. Evaluate this conclusion.
As stress score increases, so does depression score. Weak positive correlation.
HOWEVER:
Correlation doesn’t always equal causation. Another factor may be causing this. There is overlap in scatter points, which suggests results are not significantly different.
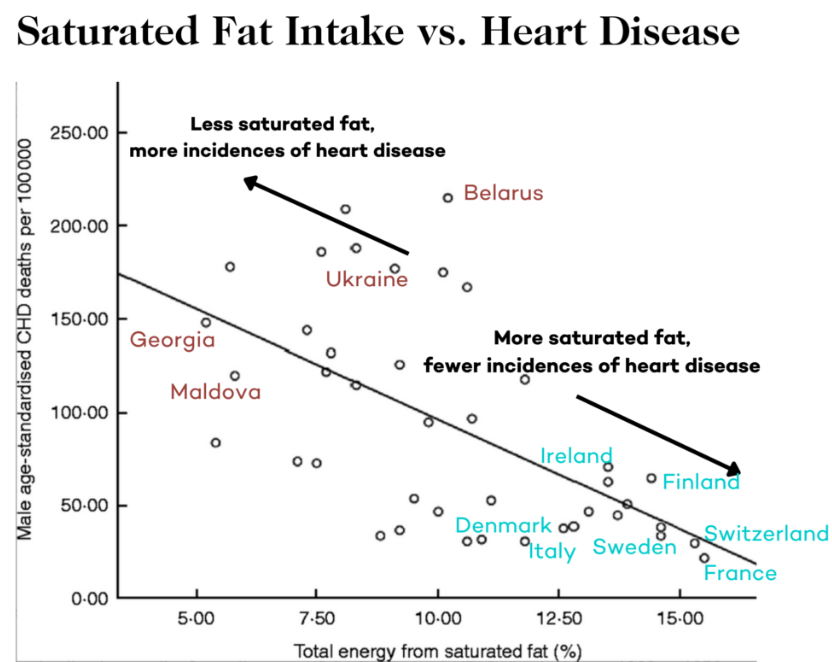
1) Describe the results
2) Current dietary advice is to reduce the intake of saturated fats to reduce the risk of coronary heart disease. One journalist concluded from these results that current dietary advice was incorrect. Why might this journalist’s conclusion have been wrong?
1) Negative correlation. The more saturated fats you intake, the less likely you are to die of CHD.
2) They may not be directly linked. Countries with a higher intake of saturated fats may have better healthcare. The graph only documents deaths due to CHD, not overall cases.