Kin 3304 Final Exam: Key Terms & Definitions in Physics
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
List the joints in movement allowed order
synarthrodial (immovable)
amphiarthrodial (subtly movable)
diarthrodial (movable)
list the subsets of synovial joints
- hinge
- ball & socket
- plane
- pivot
- condyloid
- saddle
- found between bones
what are the structural features of diarthrodial joints?
- freely moving
- encased with articular cartilage + tissues
- synovial fluid
sagital plane
- left + right regions
- frontal axis
- flexion & extention
frontal plane
- front & back regions
- sagital axis
- abduction & adduction
transverse plane
- upper & lower regions
- vertical axis
- internal & external rotation
hinge joint
- uniaxial
- sagital plane: flexion and extension
ball & socket joint
- multiaxial
- movement in all 3 planes
plane joint
- multiaxial
- movement in all 3 planes
pivot joint
- uniaxial
- movement in transverse plane: IR & ER
condyloid joint
- biaxial
- movement in saggittal and frontal plane
saddle joint
- multiaxial
- movement in all 3 planes
a saddle joint has ____ DOF, and a pivot joint has ___ DOF
3; 1
What is the relationship between joint stability and joint mobility?
Joints with more stability are less mobile
Joints with more mobility are less stable
What structures provide stability to a diarthrodial joint?
ligaments, cartilage, muscle, tendons (connective tissue)
Wolf's Law
states that bones grow or remodel in response to demands placed on them
Davis's Law
Soft tissue will align along the lines of stress that are placed upon it
Words to describe a bony process
- condyle
- head
- trochanter
- tubercle
- epicondyle
terms associated with bony cavities or depressions
- facet
- foramen
- fossa
- sulcus (groove)
- notch
abduction
lateral movement away from the midline in frontal plane
adduction
movement towards the midline in the frontal plane
extension
straightening movement in saggittal plane
flexion
bending movement in saggittal plane
external rotation
rotary movement away from the midline in transverse plane
internal rotation
rotary movement towards the midline in transverse plane
name the categories of a parallel muscle fiber arrangement
- flat
- fusiform
- strap
- sphincter
Synergist
assist with agonists and assist in refined movement
Neutralizers
contract and prevent undesirable movements
The muscle's origin is typically located ____ and displays less movement
proximally
Decelerates movement, lessens in tension, force < resistance, joint angle changes in direction of resistance
eccentric
causes body to move against gravity, joint angle changes in direction of applies muscle, accelerates movement, develops force, force > resistance
concentric
prevents movement by external forces, muscle tension acts to maintain joint angle
isometric
stretch reflex
contraction in response to stretching a muscle, uses muscle spindle & golgi tendon organ
Reciprocal inhibition
automatic antagonist alpha motor neuron inhibition evoked by contraction of an agonist muscle
muscles are usually named based on what factors?
- shape
- size
- # of divisions
- fiber direction
- location
- action
3 ways the body increases the # of muscle fibers
- activating motor units containing a greater # of fibers
- activating more motor units
- increasing frequency of motor unit activation
what is the relationship between muscle tension and muscle length
length of muscle during contraction is a factor of tension
what is the advantage of countercurrent movements?
allows biarticular muscles to maintain a relatively consistent length because of the extension at the joints
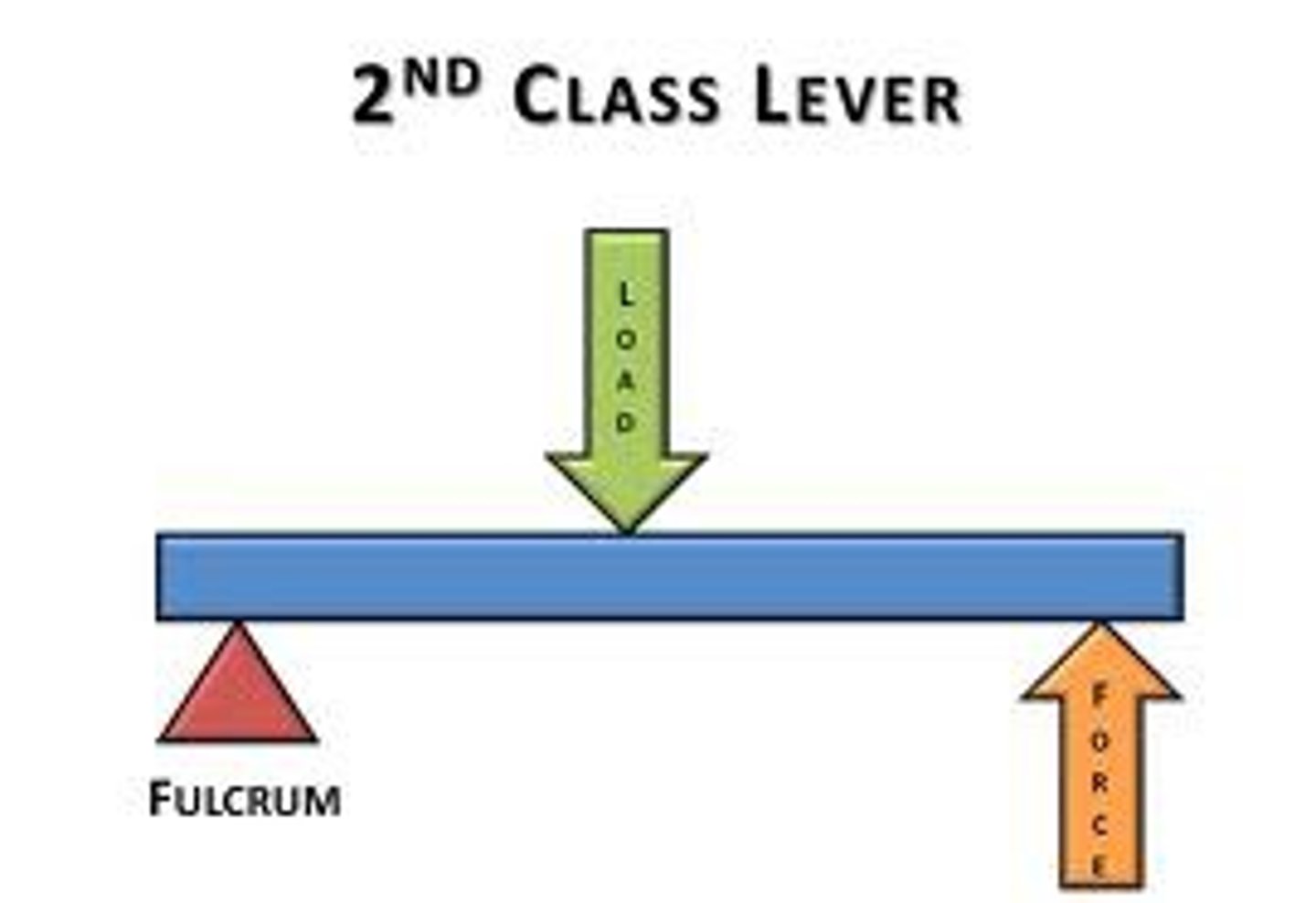
2nd class lever
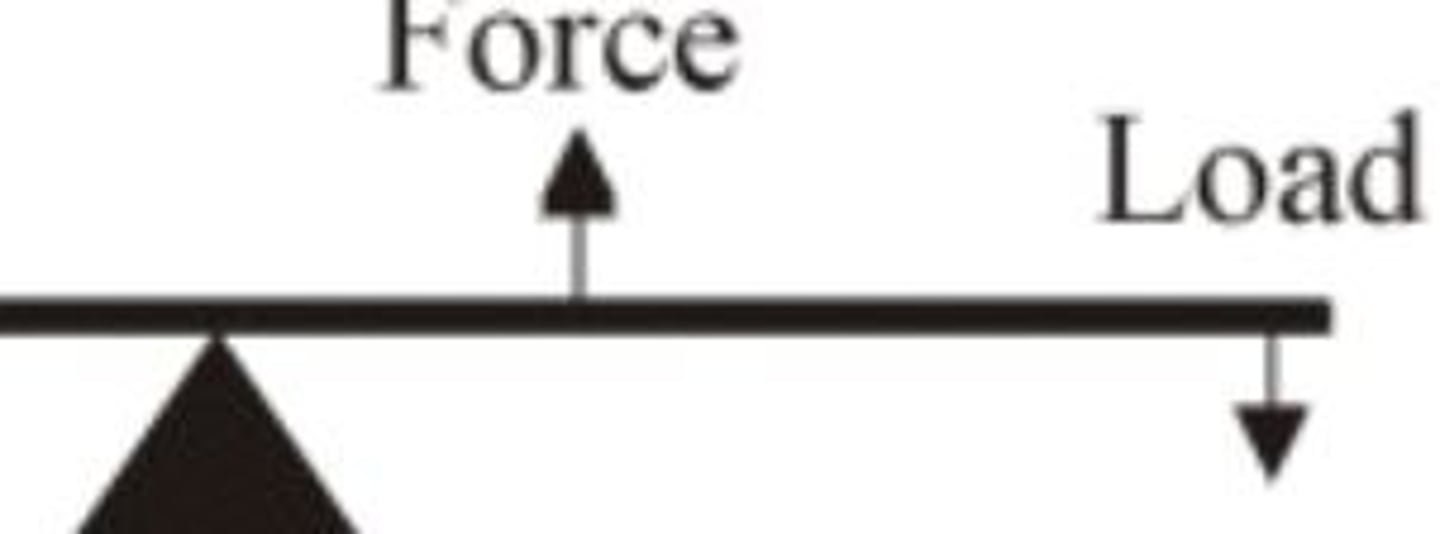
3rd class lever
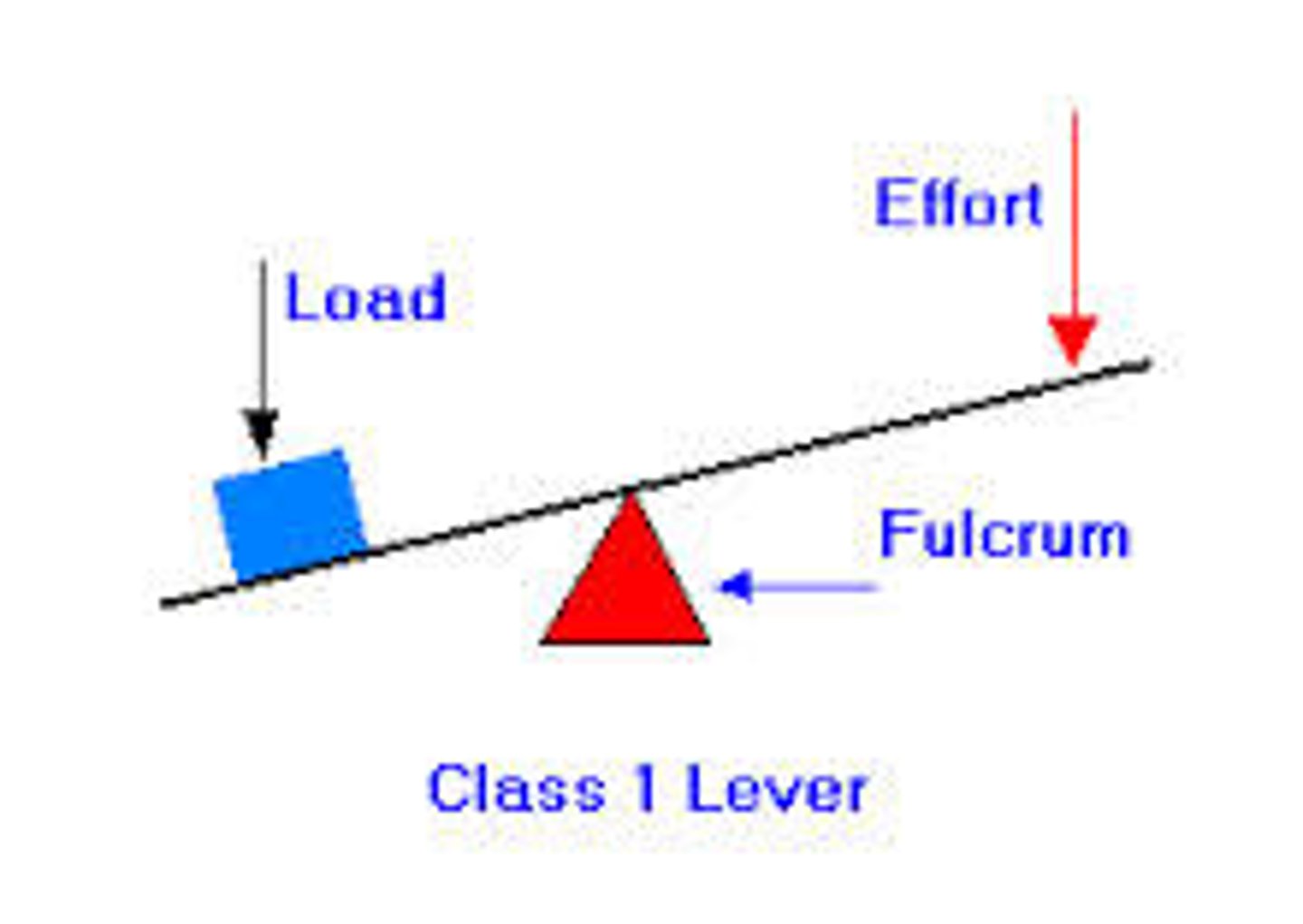
1st class lever
fulcrum in the middle
benefit of 3rd class lever
speed and range of motion
benefit of 2nd class lever
force
lever equation
F X FA = R X RA
MA equation
FA/RA
advantage of wheels & axels
better ROM + speed
advantage of pulleys
force
sternoclavicular joint
arthrodial (plane) or saddle
acromioclavicular joint
arthrodial (plane)
scapulothoracic
false joint
glenohumeral joint
ball & socket joint
humeroulnar joint
hinge joint
radioulnar joint
pivot joint
what makes up the shoulder girdle
- sternoclavicular
- acromioclavicular
- scapulothoracic
what is the relationship between movements at the shoulder girdle and the shoulder girdle
- shoulder girdle = scapular movements
- work together for stabilizing
- proper positiong for greater ROM
Shoulder joint actions to shoulder girdle actions
- abduction: UR/Elevation
- adduction: DR
- flexion: Elevation/UR
- extention: downward/DR
- IR : Protraction
- ER: Retraction
- Horizontal abduction: retraction
- horizontal adduction: protraction
- diagonal abduction: Retraction/UR/elevation
- diagonal adduction: protraction/depression/DR
muscles of the shoulder girdle
- levator scapulae
- trapezius
- rhomboids
- SA
- Pectoralis minor
- subclavius
muscles of the shoulder joint
- pectoralis major
- coracobrachialis
- deltoid
- latissimus dorsi
- teres major
- subscapularis
- infraspinatus
- teres minor
- supraspinatus
elbow & radioulnar muscles
- biceps brachii
- brachialis
- brachioradialis
- triceps brachii
- anconeus
- pronator teres
- pronator quadratus
- supinator
which muscles cause elbow flexion in the sagittal plane
biceps brachii, brachialis, brachioradialis
what muscles cause extention in the sagittal plane
triceps + anconeus
what muscles cause pronation in the transverse plane
pronator teres & pronator quadratus
what muscles cause supination in the transverse plane
supinator, brachioradialis
what muscle causes retraction?
trapezius
what muscle causes elevation
trapezius, levator scapulae, rhomboids
what muscle causes shoulder flexion
deltoid, pectoralis major
shoulder abduction
pectoralis major, deltoid, supraspinatus
elbow flexion
biceps muscles
elbow extention
triceps bachii
the elbow joint is between which bones?
humerus, radius, ulna
which muscles work to tighten a screw with your right hand?
supinator, biceps brachii, brachioradialis
which muscles work to loosen a screw with your right hand?
pronator teres, pronator quadratus, brachioradialis
which muscles produce shoulder girdle movements?
rotator cuff: infraspinatus, supraspinatus, subscapularis, teres minor
what is an agonist of the pectoralis minor?
SA & rhomboids
Atlantoocipital joint
condyloid
hip joint
ball and socket joint
intervertebral joint
hinge joint
metatarso-phalangeal
condyloid joint
patellofemoral
plane joint
talocural joint
hinge
tibiofibular joint
amphiarthrodial joint
tibiofemoral
modified hinge joint
three segments of the pelvic girdle
- ilium: superior
- ischium: posterior + inferior
- pubis: anterior + inferior
the lateral & medial malleoli are landmarks on which bones?
tibia (medial) & fibula (lateral)
- serves as a pulley
where are the menisci located?
proximal end of tibia on condylar surfaces
- function to cushion + enhance stability
the patella glies between what structures?
M+L condyles
where is the nucleous pulpous?
inside of a intervetebral disc
anterior pelvic rotation
- iliac crest tilts towards sagital plane
- pubis symphosis moves inferiorly
posterior pelvic rotation
- iliac crest tilts backwards
- pubis symphosis moves superiorly
left lateral pelvic rotation
left pelvis moves inferiorly relative to right pelvis
left transverse pelvic rotation
- twisting to left
- rotation of body to the left
- right iliac crest moves anteriorly to left iliac crest, left moves posteriorly, right moves anteriorly
iliopsoas muscles
iliacus and psoas major/minor
muscles that cross the posterior aspect of the knee are usually involved in
flexion
muscles at the hip joint for flexion
iliopsoas, pectineus, rectus femoris, sartorious
muscles at the hip joint for extention
gluteus maximus, biceps femoris, semitendenous, semimembraneous
muscles at the hip joint for adduction
adductor brevis, longus, magnus, and gracilis
muscles at the hip joint for abduction
gluteus medius, minimus, EK, TFL
quadriceps and action
- rectus femoris, vastus intermedius, vastus lateralis, vastus mediallis
- knee extention, hip flexion
hamstrings and action
- biceps femoris, semimembranosus, semitendinosis
- knee flexion & hip extention
anterior compartment of lower leg & action
- tibialis anterior
- peroneus terius
- extensor digitorium longus
- extensor hallucis longus
- inversion, dorsiflexion, eversion, extention