OTM 507: Neuro
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
Neurons
receive info, process info, generate output, basic structure for sending electrical signals throughout nervous systems
Cell body (soma)
synthesizes neurotransmitters, cell body of a neuron that produces neurotransmitters
Dendrites
main input sites for the cell, projections of a neuron (nerve cell) that receive signals (information) from other neurons
Axon
output unit of the cell
Presynaptic terminals
transmit elements of the neuron
Glia
glue, support cells for neurons
Macroglia
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells
Astrocytes
release/recycle neurotransmitters, clean up crew, CNS
Neuron function
action potential comes down, goes from presynaptic terminal to postsynaptic terminal (connects at synaptic cleft), tells the next part to pass the message on,
Basic functions: reception, integration, transmission, transfer of info
Oligodendrocytes
myelin in CNS
Schwann cells
myelin in PNS
Microglia
immune cells of central nervous system, dying cells attract microglia for clean up, CNS
Ependymal cells
line cavities of ventricles, help with transport, CNS
Satellite cells
support, protect, provide nutrients in PNS, PNS
Myelin
Sheath is formed by oligodendrocytes in CNS or Schwann cells in PNS, covers the axons of neurons, myelinates the neurons when the sheath wraps completely around the axon, sheath of proteins and fats surrounding an axon, insulates, prevents current flow across axonal membrane, increases speed of action potential and distance a current can passively spread, thicker myelin leads to faster conduction
Resting membrane potential
no information is being transmitted
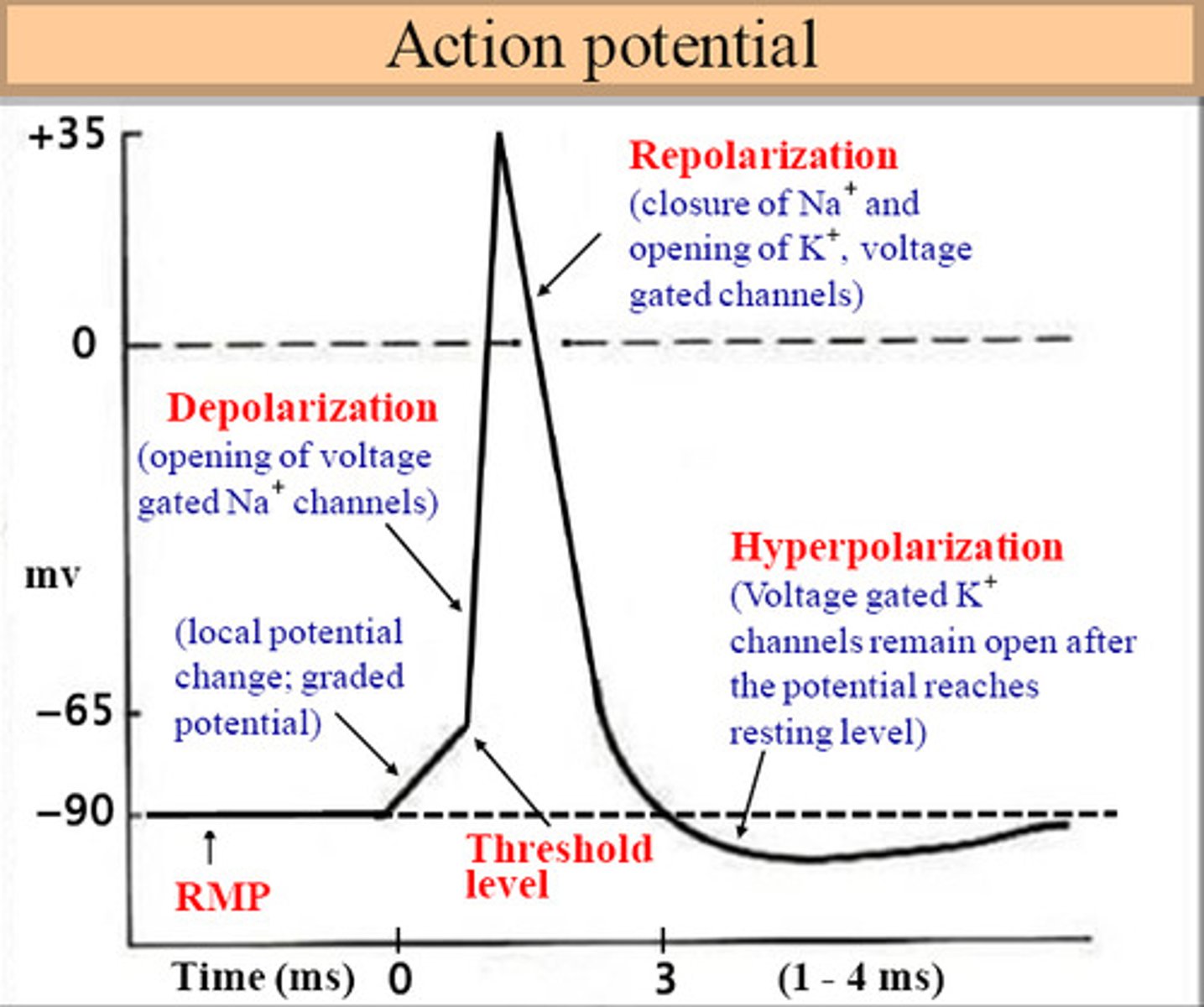
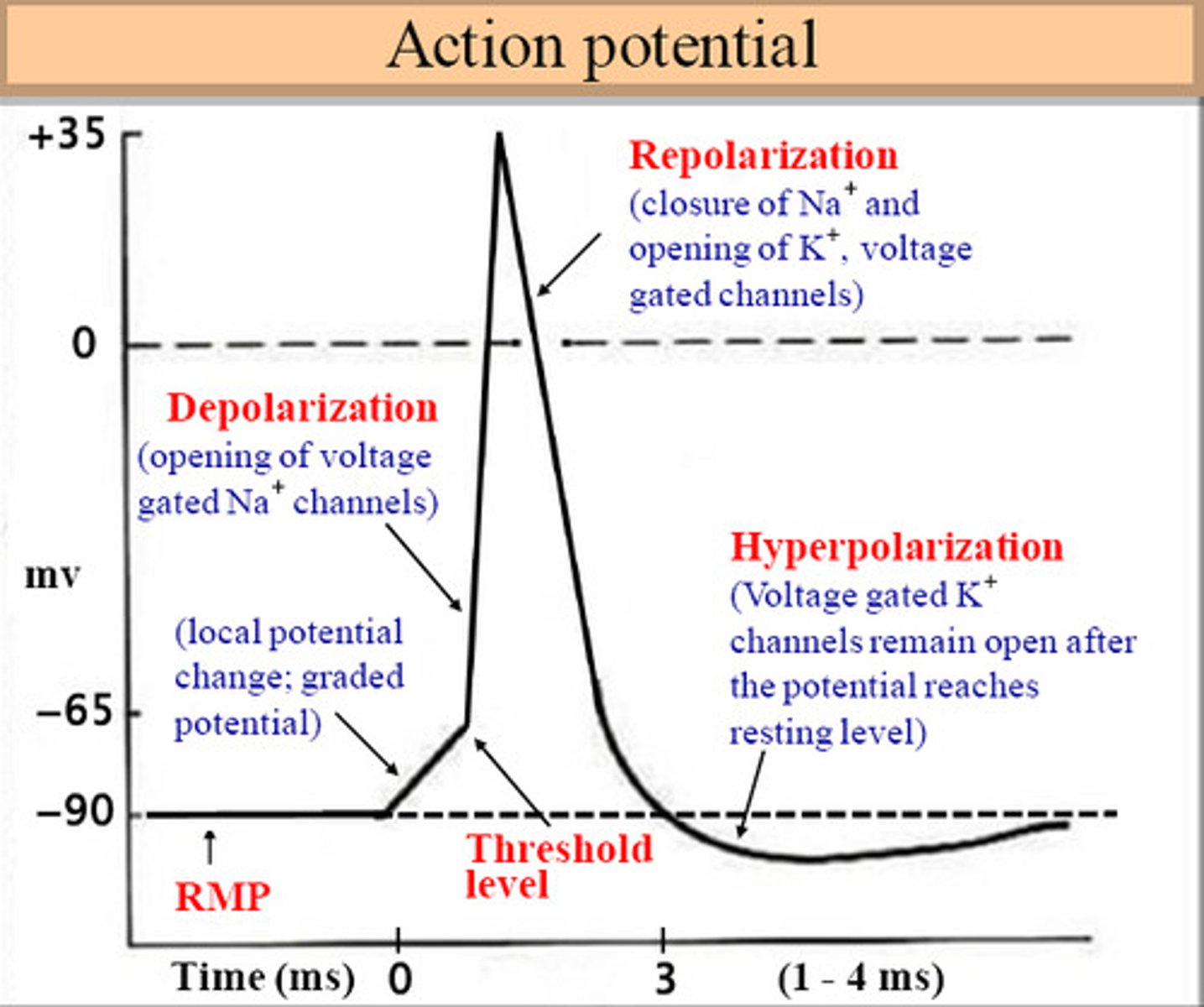
Depolarization
potential becomes less negative inside the cell, neuron is excitatory, electrical signal can be transmitted, due to influx of sodium ions into cell
Electrical potential
difference in electrical charge, carried by ions
Action potential
repeated generation of a depolarizing signal, signal is all or none, The change in electrical potential, associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle cell or nerve cell.
Nodes of ranvier
small area of myelinated axons that lack myelin, area for action potential allowing ion flow across the membrane, point of depolarization, action potential slows when crossing, a space between two consecutive myelin sheaths where an axon comes in contact with the extracellular fluid
Afferent neurons
carry sensory info from outer body to CNS, sensory, Afferent = ARRIVE, The type of nerve that carries sensory nerve impulses from the periphery towards the central nervous system (CNS)
Efferent neurons
relay commands from CNS to smooth and striated muscles and to glands, motor, Efferent = EXIT, A nerve that conveys impulses toward or to muscles or glands.
Interneurons
act throughout the nervous system, process info locally or conveying info short distances, largest class of neurons, between sensory and motor
Neuroinflammation
inflammation of neurons, CNS's response to infections, disease, and injury, causes death of neurons and oligodendrocytes, causes inhibition of neural regeneration
Peripheral nerves system demyelination
result of trauma, autoimmune, viruses (COVID?), pathologic change involving peripheral nerves, destruction of myelin, disrupt proprioception, tingling/numbness, pain, weakness
Guillain Barre syndrome
acute inflammation of Schwann cells resulting in demyelination, causes ascending weakness, rapid onset with complete recovery possible, difficulty chewing, swallowing, speaking, fascial expressions, treatment with plasmapheresis and intravenous immunoglobulin therapy
Multiple sclerosis
immune system produces antibodies that attack oligodendrocytes, causes weakness, lack of coordination, impaired vision, double vision, impaired sensation, slurred speech, disruption of memory, emotions, and attention, onset between 20 and 40, primarily affects women
Types of MS
Relapsing/remitting
Secondary progressive
Primary progressive
Progressive relapsing
Clinically isolated syndrome
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that convey info among neurons, released by presynaptic neuron
Neuromodulators
released into extracellular fluid, adjust activity of many neurons
Myasthenia Gravis
Acetylcholine receptors destroyed in motor cells, autoimmune, normal amounts released but unable to bind, causes constant excitatory of muscles
Peptides
act as hormones, neurotransmitters, neuromodulators
Amines
dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, histamine
Dopamine
associated with reward and pleasure, leads to addictive behaviors, affects motor activity and behavior
Norepinephrine
excess can lead to panic/anxiety disorders, ptsd, alertness, fight or flight
Serotonin
low levels associated with depression, affects mood and pain perception
Agonists
drugs that bind to the receptor and mimic the effects of naturally occurring neurotransmitters
Antagonists
drugs that prevent the release of neurotransmitters or bind to the receptor and impede the effects of a naturally occurring transmitter
Reuptake inhibitor
slows breakdown in synaptic cleft toallow more time for neurotransmitter to bind
Neuroplasticity
ability of neurons to change function, chemical profile, structure
New learning, relearning, Memory
Habituation
decrease in response to a repeated, benign stimulus,
PT/OT uses to decrease neural response to a stimulus for autism, complex regional pain syndrome, visual/vestibular disorders
Experience dependent plasticity
long lasting changes in strength of synapses between neurons and in neural networks, learning curve, brain initially works harder and when skill is learned less brain activity is required
Collateral sprouting
neighboring axons branch to reinnervate, exercise stimulates regeneration, PNS injuries
Regenerative sprouting
axon and target cell damaged, axon sends branches to new target, exercise stimulates regeneration, PNS injuries
Axon injury in CNS
damage on cellular level, axon swells, breaks, cell body dies, no regeneration in CNS
Recovery: edema/ischemic reduction, other receptor sites become more sensitive, increased neurotransmitter released through intact axons, silent synapses used, neurogenesis through stem cells
Silent synapses
unused synapses in brain waiting for a job, develop new functions
Reorganization of cerebral cortex
brain activity shifts to surrounding areas, explains stroke recovery, explains why other senses are more sensitive when others are defected
Metabolic effects of brain injury
Neurons die due to deprivation of oxygen, no known cures for stroke, TBI, or neurodegenerative disease, drugs minimize effects
Rehab after brain injury
recovery influences by intensity and timing of rehab, early rehab is necessary, avoid bed rest (could cause other brain areas to suffer), task specific training
Constraint induced movement therapy
treatment used in stroke, unaffected limb is constrained, forces affected limb to function, allows for functional reorganization, Avoid intense CIMT (could increase damage)
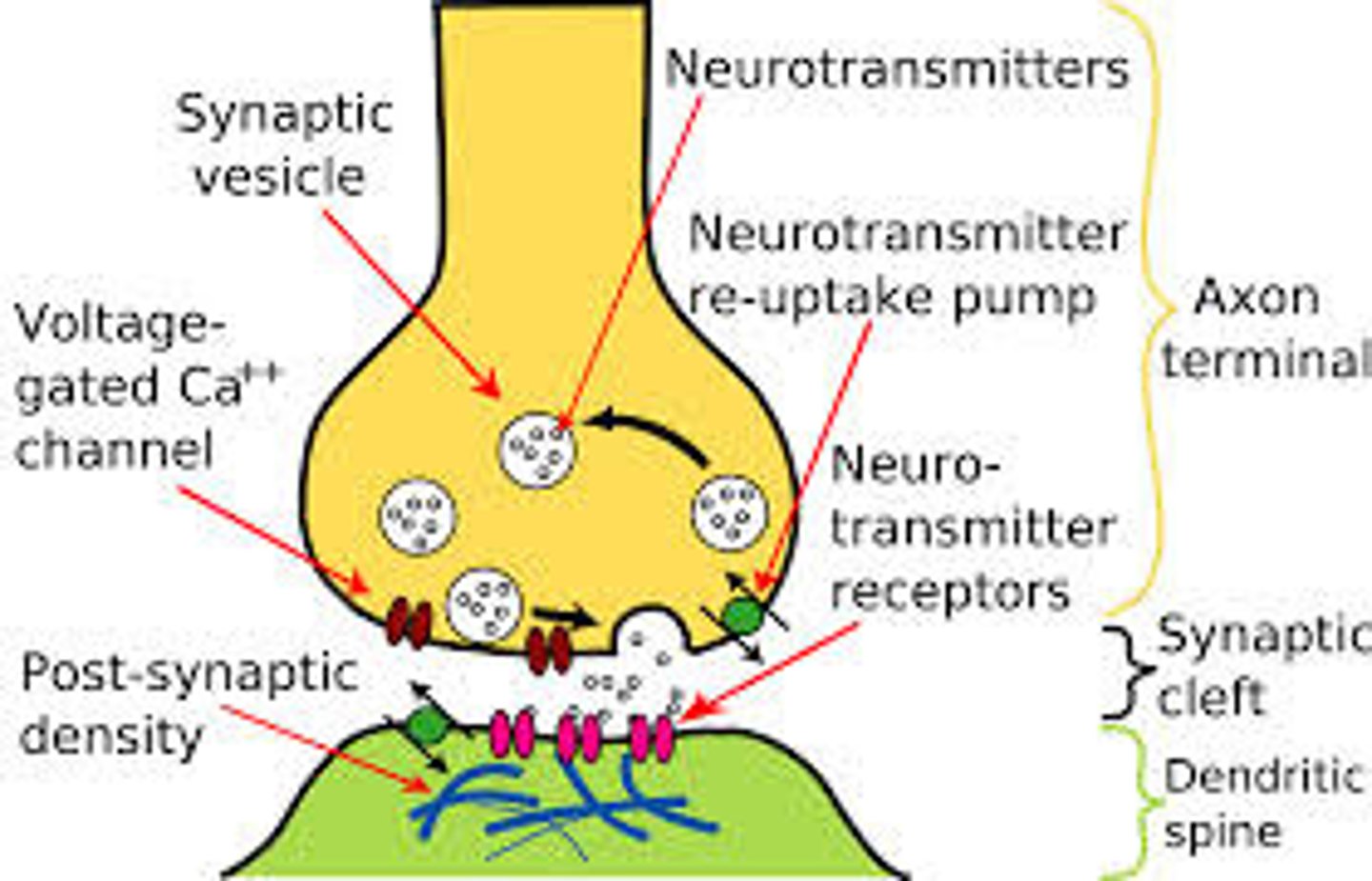
Neurotransmitter
A chemical that is released by the pre-synaptic element of the neuron upon stimulation and activates post-synaptic receptors
Membrane potential
the electric potential that exists on the two sides of a membrane or across the wall of a cell
depolarization
when the membrane potential become more positive then when it is at resting potential
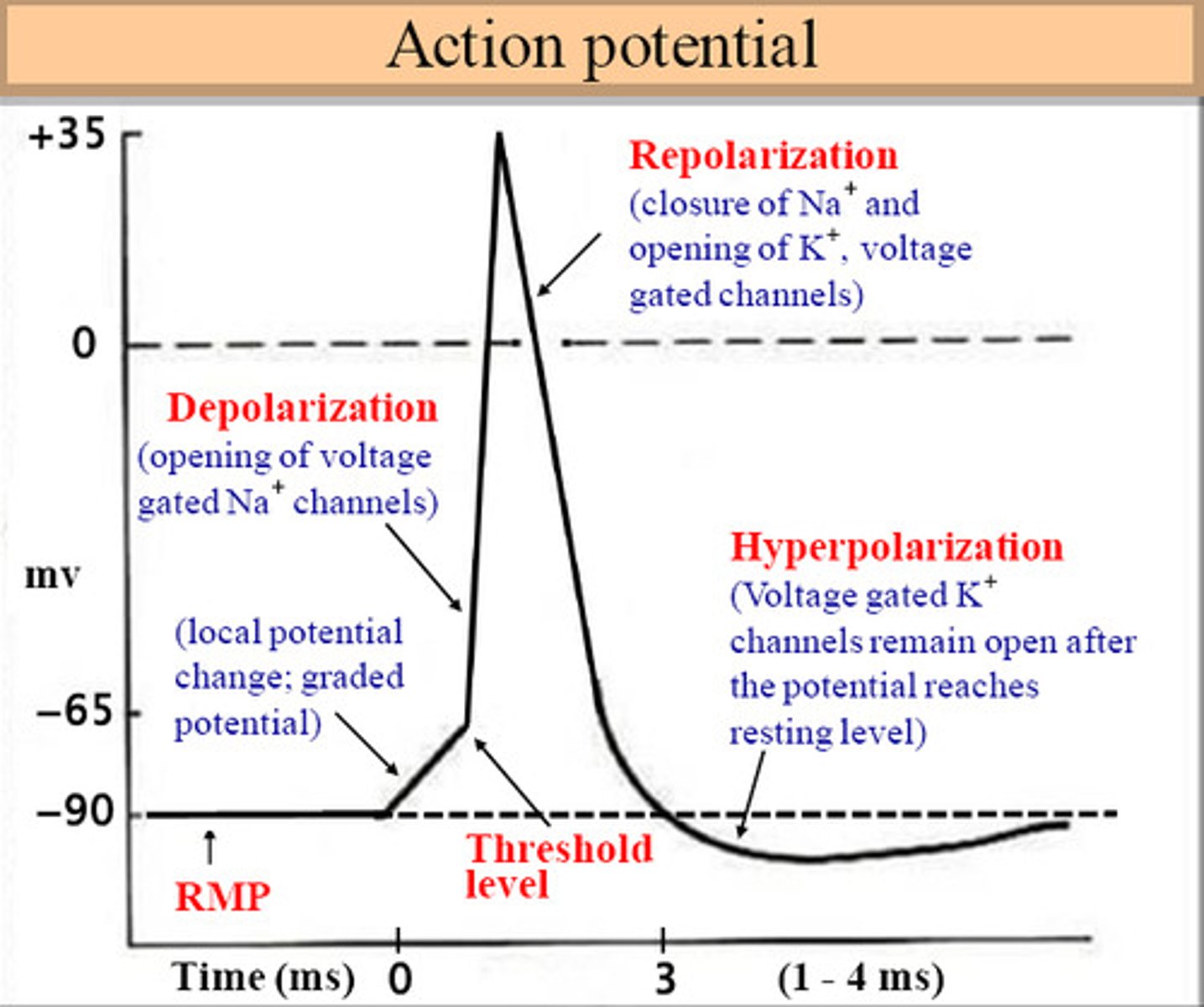
repolarization
when the membrane potential returns back to resting state by decreasing the voltage
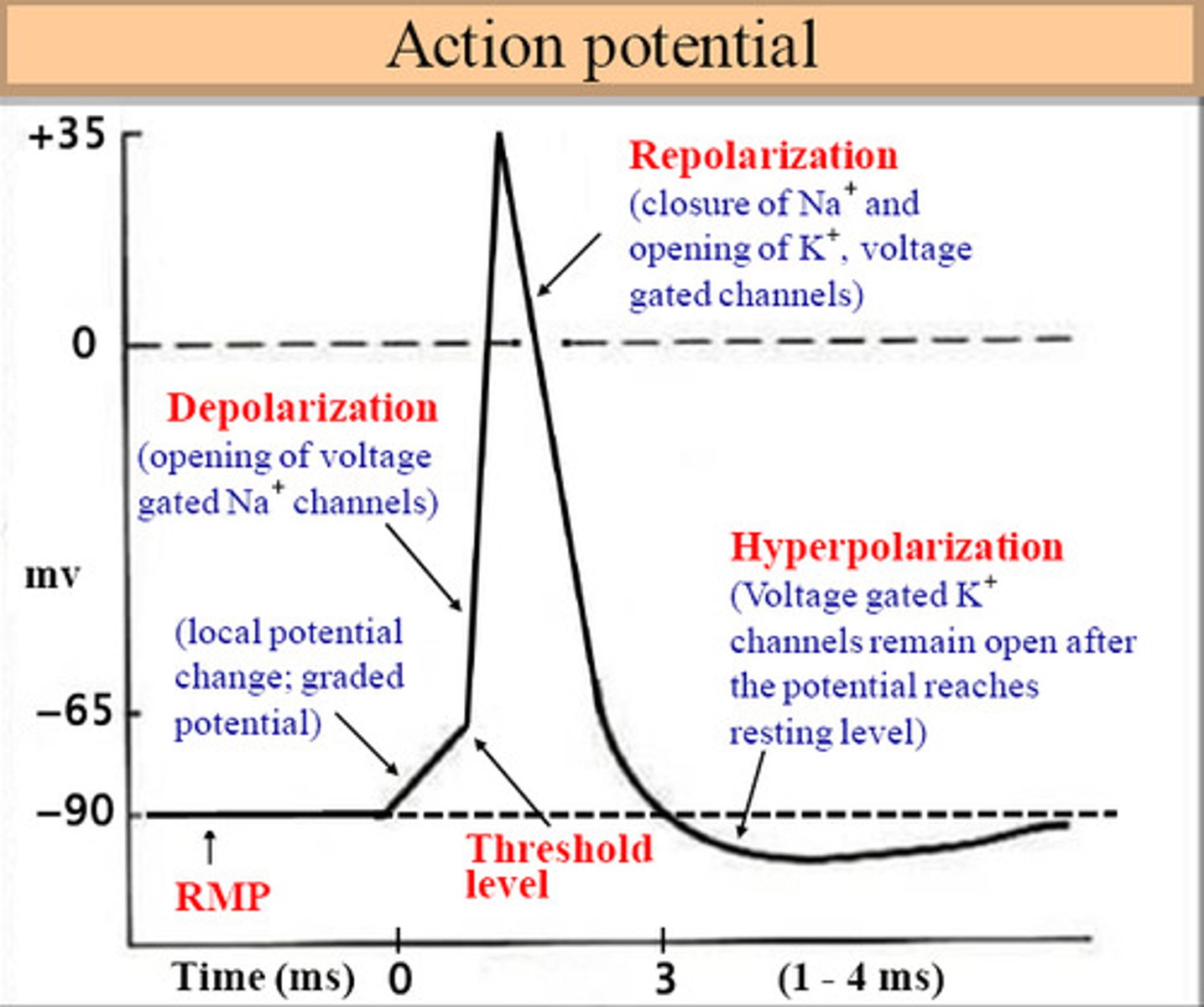
Saltatory conduction
Characterized by an action potential "jumping" between Nodes of Ranvier as it is propagated down the axon
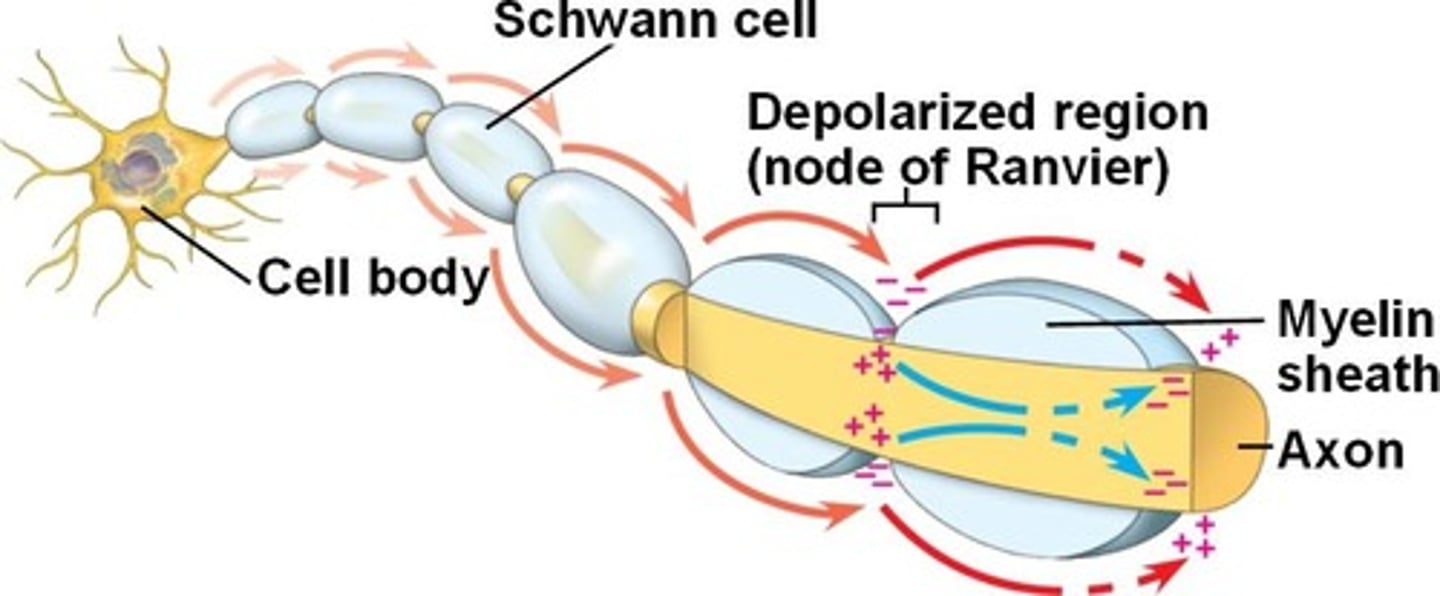
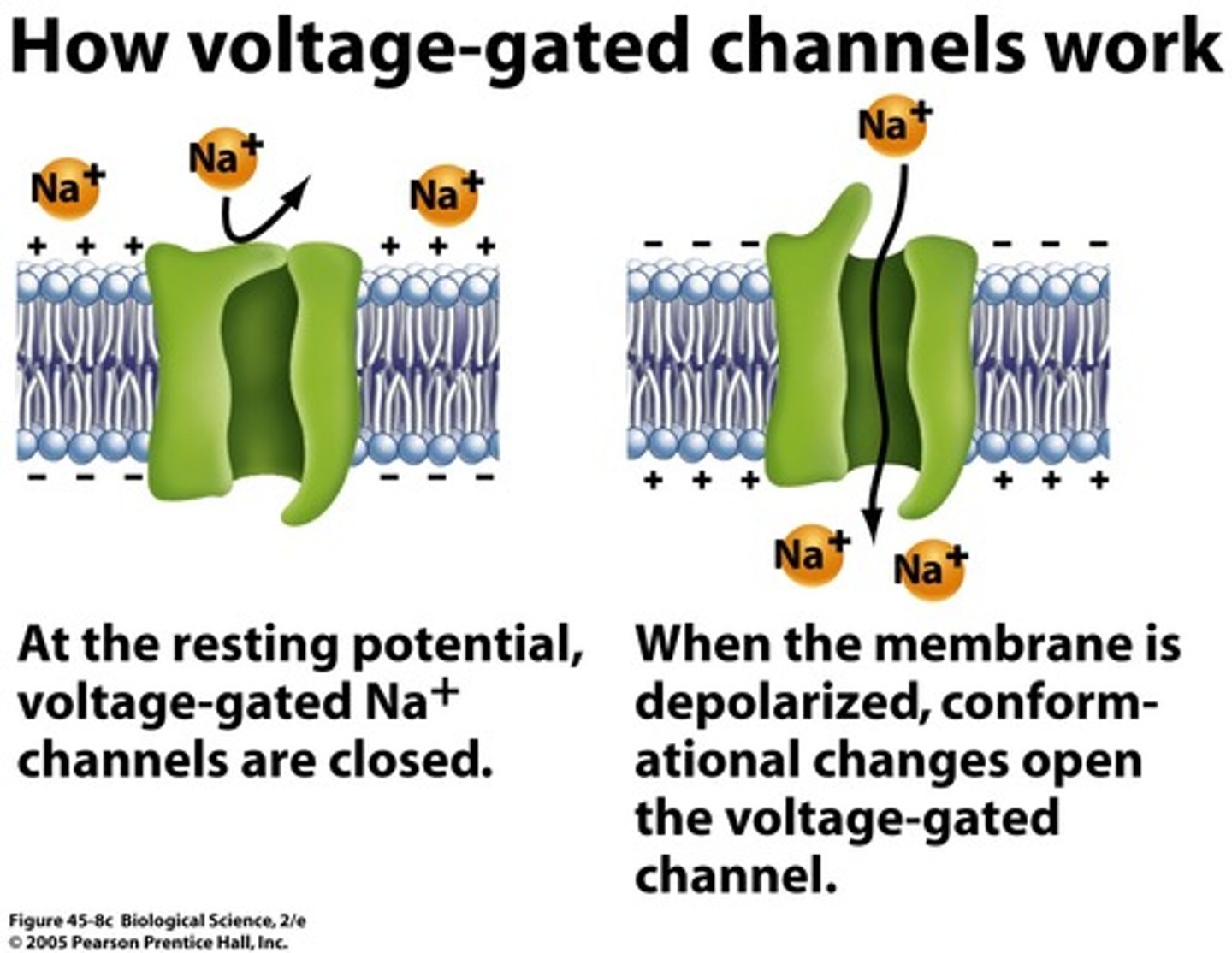
voltage gated channel
transmembrane proteins that open when the neuron gets depolarized or when the voltage of the membrane changes sufficiently
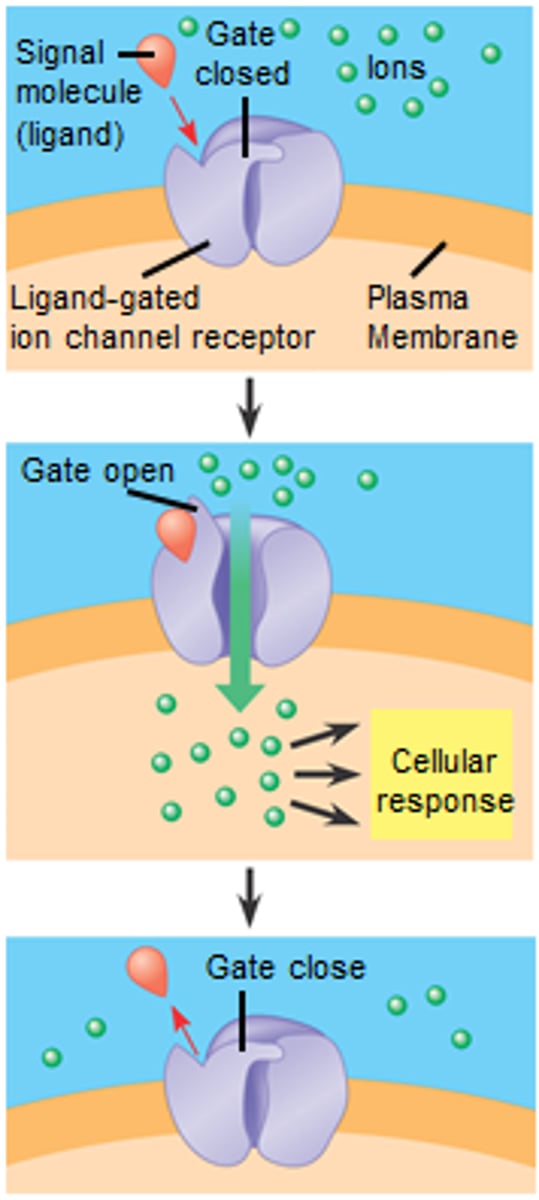
Ligand gated channel
group of transmembrane ion-channel proteins which open to allow ions to pass through the membrane in response to the binding of a neurotransmitter
Hyperpolarization
when the membrane potential becomes more negative than when it is at resting potential
Synapse
site where an arriving action potential, through excitation-secretion coupling involving Ca2+ influx, triggers the release of one or more neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft
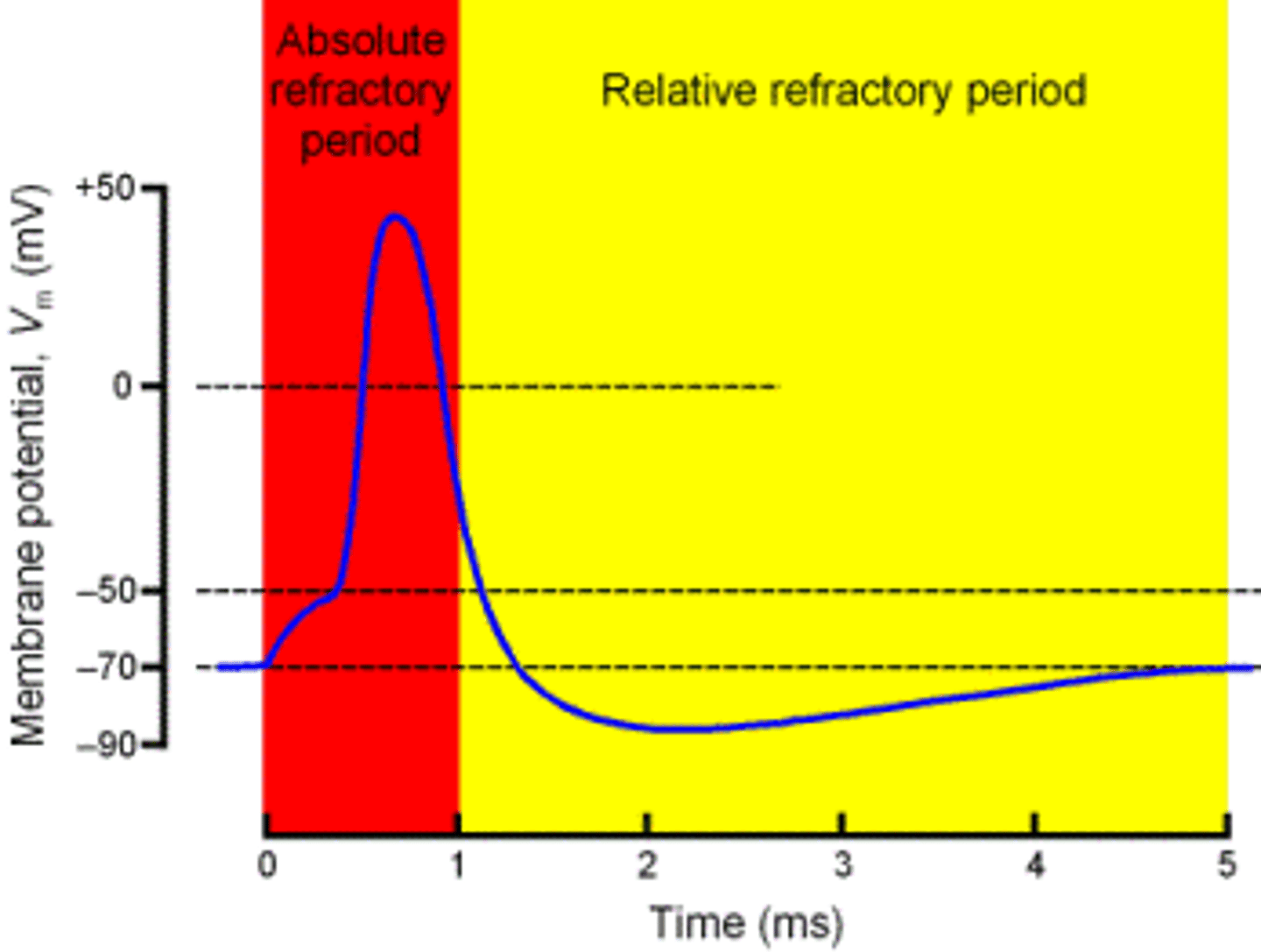
absolute refractory period
The time period from the beginning of the action potential to the return of the resting state during which the membrane will not respond normally to an additional stimuli.
Dorsal root
One of two nerve roots that emerge from the spinal cord carries sensory information towards the spinal cord and connects with the ventral root to combine and form the spinal nerve
Ventral root
one of the two nerve roots of a spinal nerve that passes anteriorly from the spinal cord to send motor signals to muscle and organs
Dorsal horn
grey longitudinal columns found within the spinal cord; primarily acts as the termination of primary afferent sensory fibers via the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves.
Ventral horn
one of the grey longitudinal columns found within the spinal cord; contains the cell bodies of the lower motor neurons which have axons leaving through the anterior spinal roots on their way to innervate muscle fibers
Tracts
bundles of axons that travel to and from the body and cortex and carry specific sensory or motorinformation
Dorsal root ganglion
cluster of neuron that contain the cell bodies of sensory neurons
Gray commissure
A cross bar of gray matter in the spinal cord that connects the dorsal horns and ventral horns and surrounds the central canal in the spinal cord. Contains mostly interneurons
Vertebral bodies
bony segments of the spinal column; functions as a protective layer for the spinal cord
Frontal lobe
part of the cerebral cortex in either hemisphere of the brain, lying directly behind the forehead; involved in a wide range of "higher" cognitive functions
Temporal lobe
Portion of the cerebral cortex that is above the ears, and involves in hearing, language processing and memory
Parietal lobe
located after the frontal lobe after the central sulcus and is responsible for processing information from the body's senses and awareness
Occipital lobe
located in the posterior part of the brain, which is responsible for visual information
Brainstem
an area of the central nervous system that connects the brain and spinal cord responsible for breathing, swallowing, heart rate, blood pressure, consciousness, and sleep wake cycle; consists of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata
Midbrain
Connects the pons and diencephalon and is the upper part of the brainstem, important in motor control such as eye movements and processing vision and hearing, contains cranial nerves 3, 4
Pons
The the middle structure of the brainstem that coordinates face and eye movements, facial sensations, hearing, balance, and acts as a bridge between the cerebellum and the rest of the brain, contains cranial nerves 5, 6, 7, 8
Medulla oblongata
The lower part of the brainstem that coordinates cardiovascular control (blood pressure/heartbeat), breathing, head and eye movement, swallowing, reflexes, contains cranial nerves 9, 10, 12
Ventricles
hollow cavities of the brain, that contain the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which circulates within the brain and spinal cord.
Hypothalamus
Part of the diencephalon that regulates neuroendocrine function. It assists helps with eating, drinking, emotion, sexual behavior, regulating body temperature and other motivated behaviors.
Amygdala
art of the limbic system that is linked to emotion, smell, and motivation. Also know as the Amygdaloid nucleus. Responsible for the "fight or flight" response
Thalamus
small structure within the brain located just above the brain stem between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain and functions to relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral cortex
Cerebellum
receives information from the sensory systems, the spinal cord, and other parts of the brain and then regulates motor movements coordinating voluntary movements like posture, balance, and speech
Glial cells
Their supportive functions help define synaptic contacts and maintain the signaling abilities and health of neurons; not involved in direct synaptic connections, a support cell in the nervous system classified into astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and Schwann cells
Axon terminal
The end region of an axon and a site of synaptic contact with another cell (AKA presynaptic terminal)
World test/ digit span test
spell "world" backwards and forwards and list the letters in alphabetical order, recite a series of 5 numbers forwards and backwards
Declarative memory
problems due to damaged hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and parietotemporal association cortex
working - give patient 3 words to remember, discuss other topics, then ask for 3 words again
recent - ask about activities from past couple days
long term - ask about past events in their life or in history
Goal directed behavior
deciding on a goal, planning, following through with plan, and monitoring progress
One minute naming test
generate as many words as possible that begin with a single letter in one minute
Consciousness level
the level of consciousness at which mental activities accessible to awareness occur
Alert
Lethargic
Obtunded
Stupor
Coma
Lethargic
lose track of conversations and tasks, falls asleep if little stimulation is provided
Obtunded
alert briefly to strong stimuli, no meaningful answers
Stupor
alert only during vigorous stimulation
Language and speech
Comprehension: relationships, instructions
Naming: objects, body parts
Reading
Writing
One minute category naming test
name as many objects as possible from one category in one minute
Aphasias
Language disorders, which are associated with Broca's and Wernicke's areas in the brain.
Wernicke's aphasia
receptive, impaired language comprehension, normal rate, rhythm, and grammar of speech but jumbled and nonsensical, word salad, often due to ischemic stroke, they are more likely confused
Broca's aphasia
expressive, speech is poorly articulated and difficult to get out, use primarily nouns and verbs and no linking words, disconnected speech w/ long pauses, easily frustrated, comprehends very well
Dysarthria
speech impairment causing difficulty articulating words
Orientation
Person: ask about the individual such as name, place of birth
Place: where you are now, what city/state
Time: what time is it, day of week, month, year
Situation: why are you here, what happened, why evaluating
A & O x3, A & O x4
Stereognosis
use light touch, proprioceptive, and movement information to identify an object placed in the hand
have patient close eyes, place common object (key, paperclip, pen) in their hand, have them tell what it is
Bilateral simultaneous stimulation
assess patient's awareness of stimuli presented at same time to both sides of body, touch and visual
Touch: close eyes, lightly touch one limb or both simultaneously and ask if left, right, or both were touched
Visual: show patient objects w/ one in right visual and one in left visual and ask for names of each