AP Biology Unit 2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
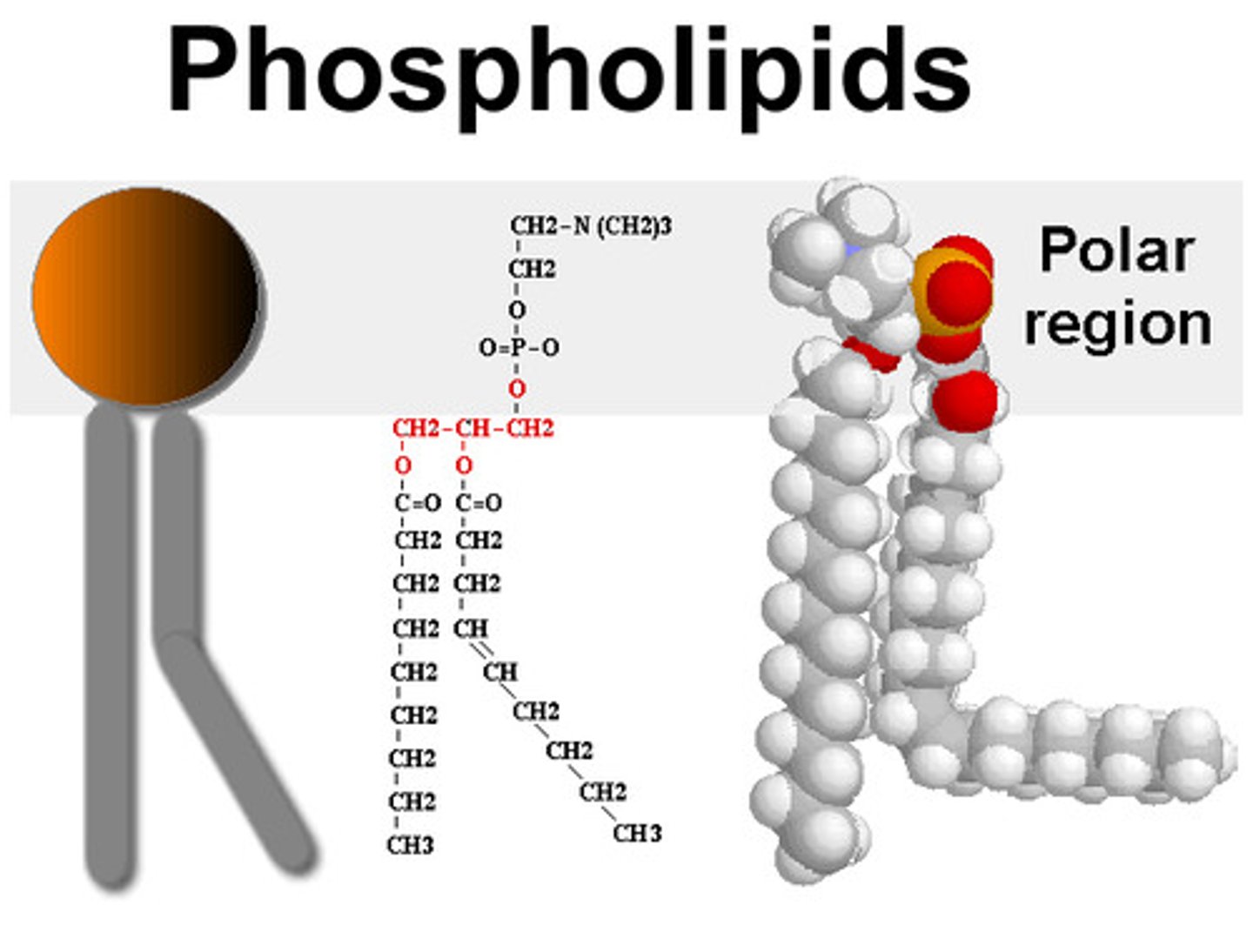
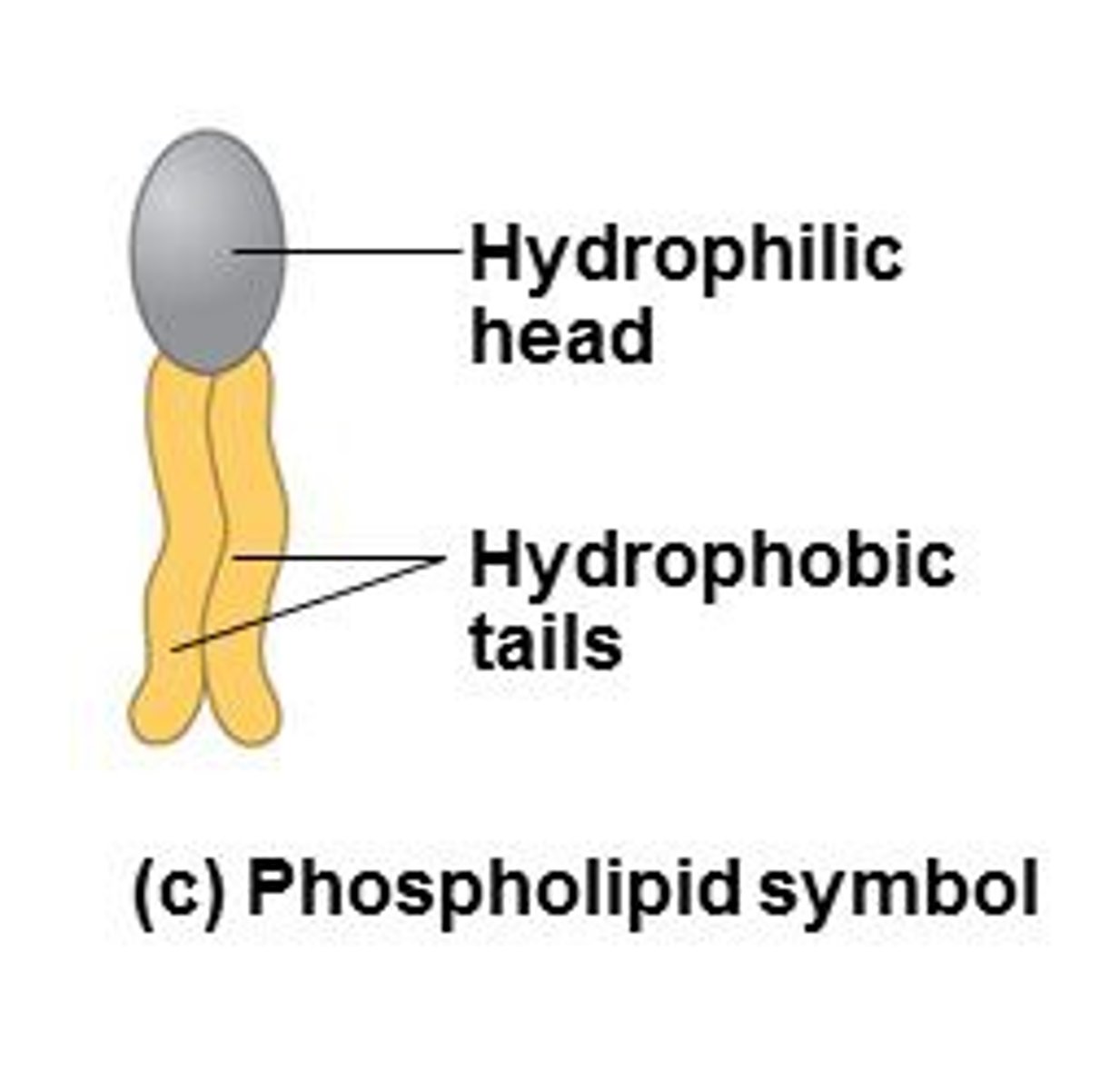
Phospholipid
a lipid that contains phosphorus and that is a structural component in cell membranes
Ribosome
Made of rRNA, synthesizes proteins
Plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
Smooth ER
Functions in detoxification and lipid synthesis
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
Rough ER
Associated with ribosomes, compartmentalizes the cell
Hydrophilic
water loving
Golgi complex
Corrects the folding and chemical modification of newly synthesized proteins, packaging for protein trafficking
Fluid mosaic model
model that describes that cell membranes consist of a structural framework of phospholipid molecules that is embedded with steroids and proteins
Lysosome
Membrane-enclosed sac that contain hydrolytic enzymes
Vacuole
Storage and release of macromolecules and cellular waste products.
Correct arrangement of phospholipids in bilayer
hydrophobic tails pointing toward inside the membrane, hydrophilic heads pointing out to the extracellular or intracellular space
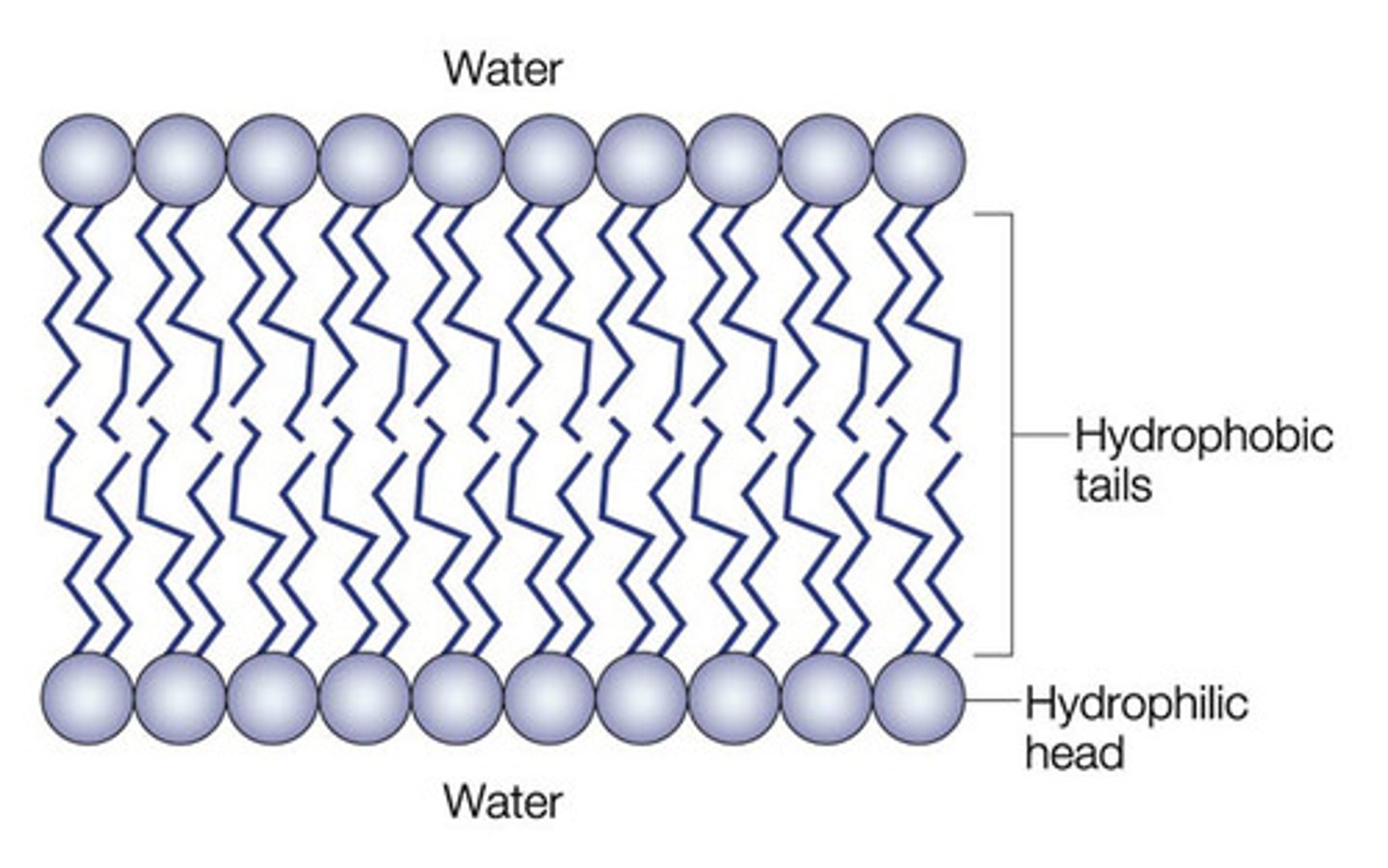
Bilayer
a layer that is two molecules thick
Mitochondria
Provides compartments for different metabolic reactions.
Phosphate group
A functional group consisting of a phosphorus atom covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms

Chloroplast
Specialized organelles that are found in photosynthetic algae and plants.
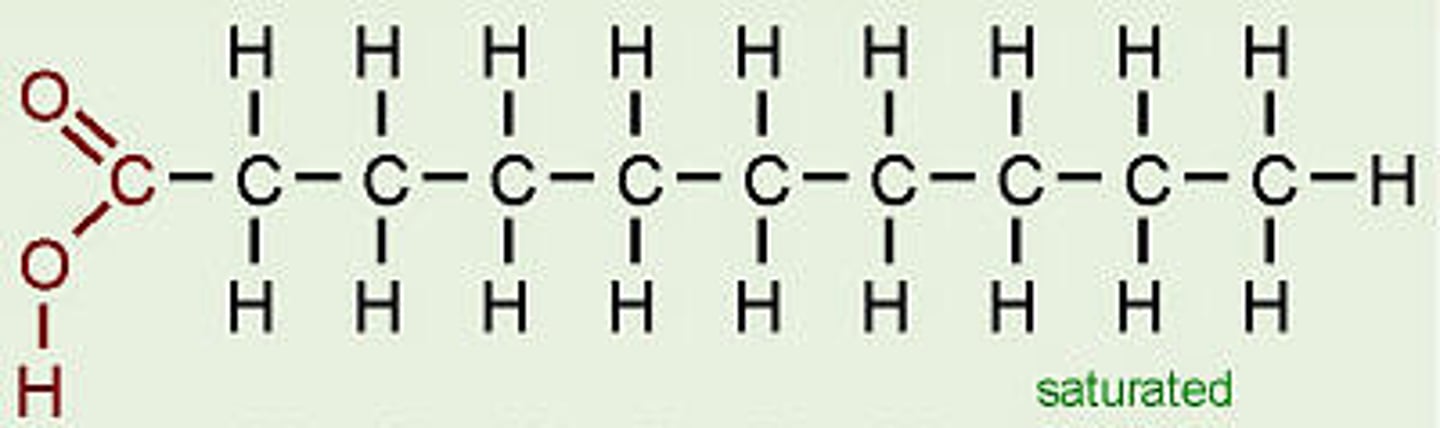
Fatty acid
hydrocarbon chain often bonded to glycerol in a lipid
Matrix
Inside mitochondria, the Krebs cycle (aka citric
acid cycle) occurs here
Phospholipid structure
Phosphate group, glycerol, 2 fatty acids
Inner mitochondrial membrane
Electron transport and ATP synthesis occurs
Thylakoid
Inside the chloroplast, organized in stacks called grana. Responsible for the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis
Stroma
The fluid within the inner chloroplast membrane and outside of the thylakoid, involved in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis (Calvin cycle)
Surface area-to-volume ratio
Ratio of a cell's outside area to its internal volume.
hydrophilic region of phospholipid
phosphate "head" pointed away from the interior of the cell membrane
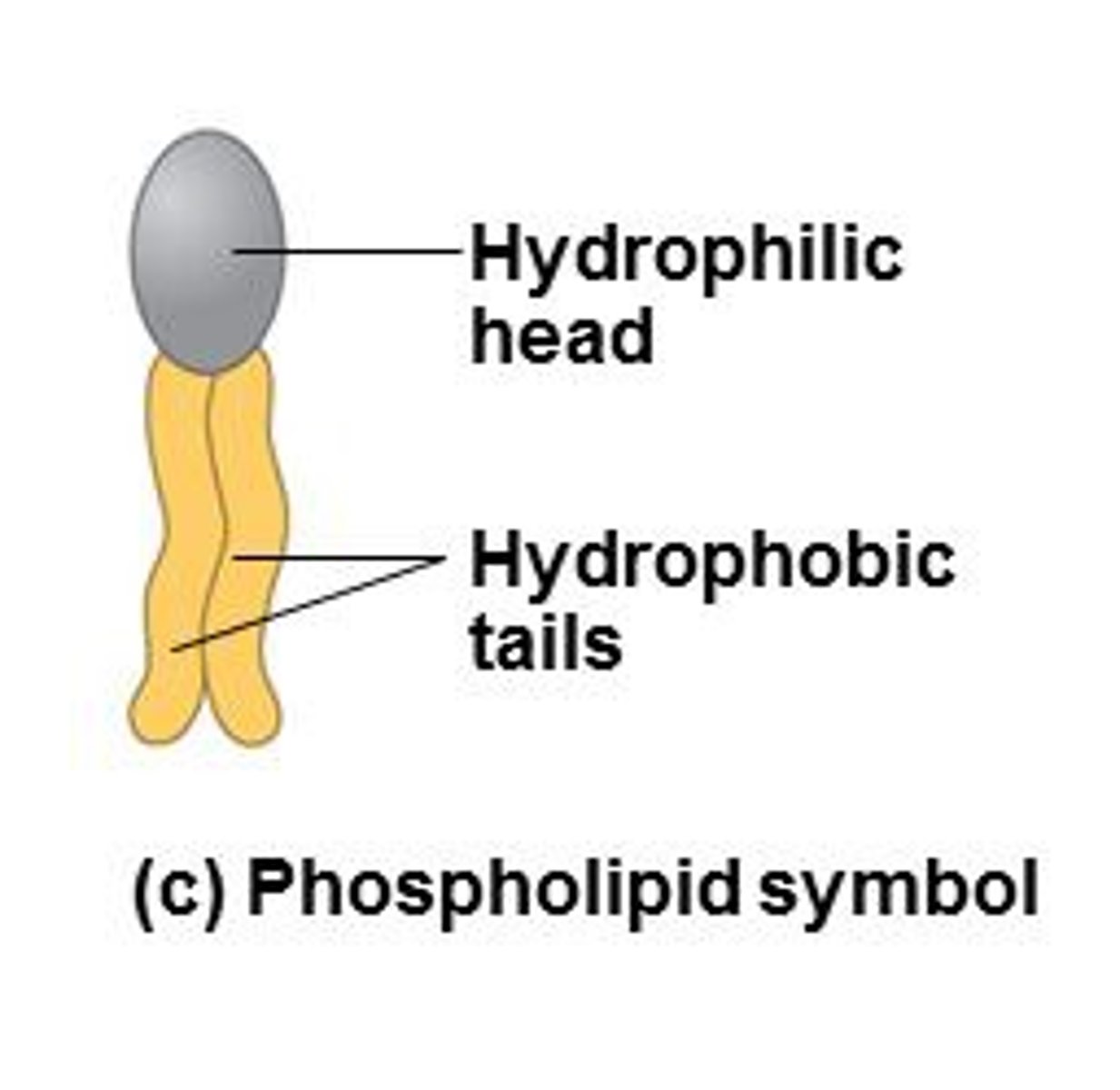
hydrophobic region of phospholipid
fatty acid "tails" pointed towards the interior of the cell membrane
embedded protein
proteins embedded into the phospholipid bilayer
selective permeability
A property of a plasma membrane that allows some substances to cross more easily than others.
substances that can freely pass through the plasma membrane
small nonpolar molecules, such as N2, O2, and CO2
substances that pass through embedded channels and transport proteins
hydrophilic substances such as large polar molecules and ions
cell wall
provides structural boundary for plants, fungi, and prokaryotes, composed of complex carbohydrates
passive transport
the net movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration without the use of energy
active transport
requires the direct input of energy to move molecules from low concentration to high concentration
exocytosis
process of moving substances out of the cell, internal vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane and secrete large macromolecules out of the cell, requires energy input
endocytosis
the cell takes in macromolecules and particulate matter by forming new vesicles derived from the plasma membrane, requires energy input
facilitated diffusion
movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
aquaporins
water channel proteins
membrane potential
The voltage across a cell's plasma membrane, generated by a difference in ion concentrations on either side
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
water potential
the physical property that predicts the direction in which water will flow
hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
isotonic
the concentration of two solutions is the same
solute potential
This measurement has a maximum value of 0; it decreases as the concentration of a solute increases.
pressure potential
This measurement has a minimum value of 0 (when the solution is open to the environment); it increases as pressure increases.
water potential equation
Ψ = Ψp+Ψs
solute potential equation
Ψs = -iCRT
symbol for pressure potential
Ψp
symbol for solute potential
Ψs
symbol for water potential
Ψ
endosymbiosis
A theorized process in which early eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes.
prokaryote
type of cell that generally lack internal membrane-bound organelles, but have internal regions with specialized structures and functions
eukaryote
type of cell that maintain internal membranes, partitioning the cell into specialized regions