X-ray Interactions with Matter
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Attenuation
The reduction in the number of x-ray photons (intensity) of the primary beam and the resulting loss of energy, as the beam passes through matter
Attenuation includes both ______ and scattering
Absorption
Attenuation is influenced by:
Tissue type (atomic #)
Subject thickness/volume of tissue-subject density
Photon quality-energy/quality (kV)
mA does not affect the probability of attenuation; however, it can impact the amount or number of photons attenuated
False
When x-ray photons interact with human tissue atoms, the initial x-ray photon may:
Scatter or change direction (deflected)
Be completely absorbed
May pass through matter and not interact
These are x-rays that pass through the patient and interact with the image receptor
Transmitted or remnant beam
As kVp increases, the total number of photons which are transmitted without interaction ______
Increases
With an increase in kVp, the percentage of _______ interactions decreases while the percentage of Compton interactions ________
Photoelectric, increases
At low energies, most x-ray interactions with tissue are?
Photoelectric
As photons energy increases, the chance of photoelectric interactions ______ drastically
Decreases
At approximately 50 kVp, the number of Compton verses Photoelectric interactions are?
Equal
As the atomic number of an atom increases, the probability of a Compton interaction increases
False
Binding Energy
The energy required to remove orbital electron from its shell
For any given atom, the ____ shell electrons possess the highest binding energy
K
Elements with a higher atomic number will have a _____ k-shell binding energy
Higher
Electrons further from the nucleus require less energy to remove them from their orbits and therefore possess a ______ total “net” energy
Greater
Regarding the Compton Effect: a relatively high-energy x-ray photon ejects or removes a loosely bound, outer-shell electron
True
Regarding the Compton Effect: The ejected electron is referred to as a Compton or “recoil” electron
True
Regarding the Compton Effect: The incident (original) photon is completely absorbed in the process
False
Regarding the Compton Effect: Can be mathematically expressed as Ei= Es + Eb + Eke
True
Regarding the Compton Effect: is the least common interaction in the human body
False
The ______ is the single most important scattering object in both radiography and fluoroscopy
Patient
Scatter radiation emitted from the patient is the primary source of ________ exposure
Occupational
Relatively low-energy x-ray photon interacts with and ejects an inner-shell electron
Photoelectric
Incident x-ray photon interacts with loosely bound, outer-shell electron
Compton
Ejected electron is known as a Compton or “recoil” electron
Compton
These interactions are more likely to occur in bone than in soft tissue
Photoelectric
Responsible for the majority of scatter reaching the IR
Compton
Contributes mostly to patient dose
Photoelectric
Is a partial energy transfer
Compton
An electron vacancy or hole causes a characteristic cascade
Photoelectric
This interaction between x-ray photons and tissue is responsible for subject contrast and also contributes significantly to patient dose
Photoelectric
This interaction is more likely to occur with absorbers having a high atomic number, such as positive contrast media
Photoelectric
What happens to the incident x-ray photon during the Photoelectric Effect?
X-ray photon is absorbed and no longer exists
How is the Photoelectric Effect mathematically expressed?
Ei = Eb + Eke
A photoelectric interaction is more likely to occur when the x-ray photon energy and the electron binding energy are nearer to one another
True
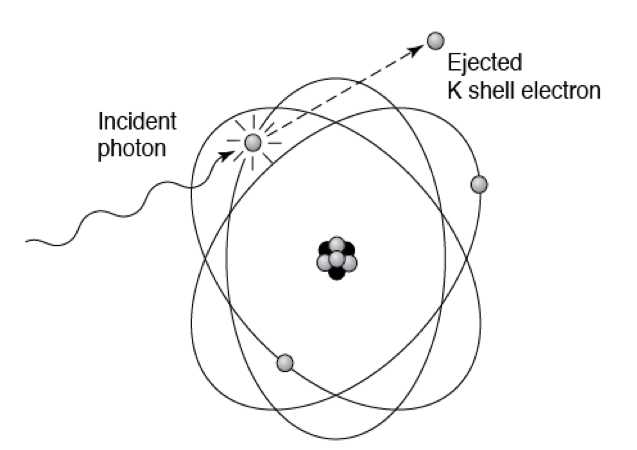
What is true about this image?
Is the total energy transfer from photon to electron
Interaction is more likely to occur in bone than in soft tissue
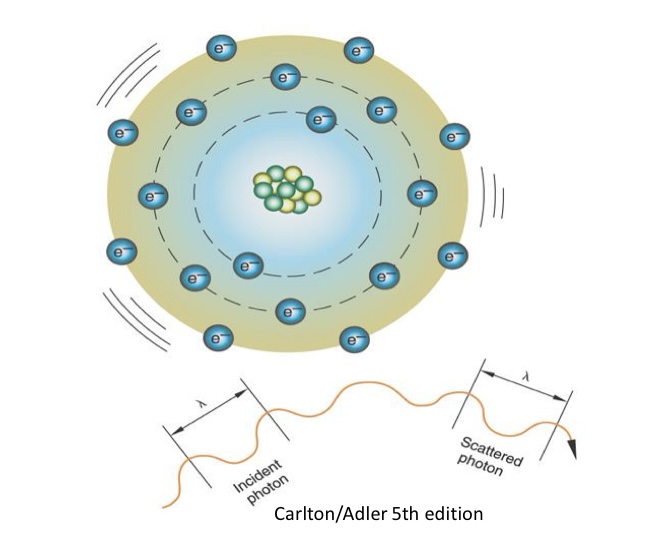
What is true about this image?
Interaction of very low-energy x-ray photons (below 10keV)
Is called coherent, classical, or unmodified scattering
Has little effect on image quality; insignificant in diagnostic radiology
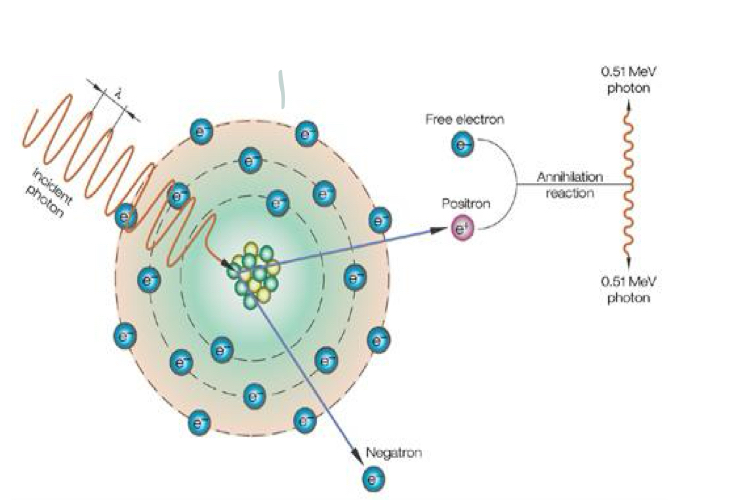
What is this image demonstrating?
Pair production
For pair production: Interaction between high-energy photons, at least _____ MeV, and matter
1.02
For pair production: A high-energy incident photon comes close to a strong _____ field and loses all of its ____ in the interaction
Nuclear, energy
For pair production: Energy is used to create ____ of electrons, a negation and a positron
Pair
For pair production: After the annihilation reaction, each photon possesses ____ MeV
0.51
Pair production _____ occur in diagnostic x-ray
Does not
Subject Density
How tightly packed at atomic level, not the thickness of the part
The probability of Compton scattering does not depend on the atomic number of an atom
True
How many more times is it likely that an x-ray photon will undergo a photoelectric interaction in bone verses soft tissue?
7 times greater
3 things that influence x-ray photon beam attenuation:
Tissue type
Subject thickness
Photon quality
Rank (water, bone, air, fat, muscle) from greatest amount of attenuation to least amount of attenuation
Bone, muscle, water, fat, air
At 50 kVp, what percentage of photons are attenuated in 10 cm of tissue?
>99%
At 130 kVp, what percentage of photons are transmitted in 10 cm of tissue?
6%