exam 5: autonomic nervous system
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
afferent (visceral sensory) pathways
feedback
regulate effectors
efferent (viscera motor) pathways
sympathetic division
parasympathetic division
dual innervation (most structures)
enteric nervous system
visceral reflexes ( bypass spinal cord)!
regional “command center”
regulated by ANS
sympathetic division overview
origin: preganglionic neurons originate in lateral horns of T1-L2 segments of spinal cord (thoracolumbar)
Functions:
maintains body during conditions of “flight-or-fight”
increases alertness and metabolic activities
sympathetic preganglionic fibers
arise from cell bodies in thoracolumbar lateral gray horns
exit cord via ventral nerve root → ventral rami T1- L2
exit ventral rami via white rami communications
sympathetic postganglionic fibers- spinal nerve pathway
preganglionic fibers synapse in sympathetic chain ganglia @ same level, level above or level below
postganglionic fibers return to ventral ramus via gray rami comminicans
continues through spinal nerves
innervates neck, torso & limb skin effectors
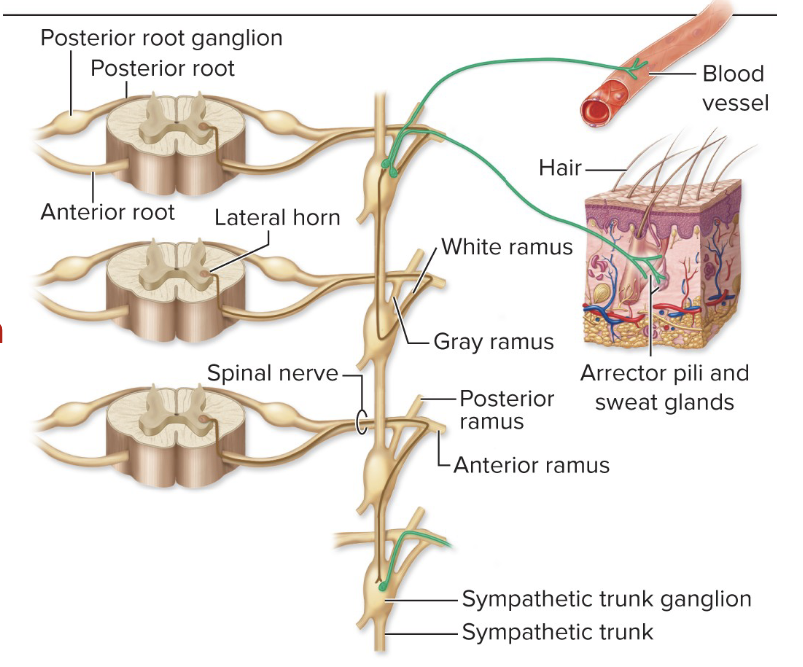
sympathetic postganglionic fibers- sympathetic nerve pathway
reganglionic fibers synapse in sympathetic chain ganglia @ same level, level above or level below
postganglionic fibers pass through sympathetic chain
sympathetic nerves join upper cervical spinal nerves & cranial nerves
innervate head & face skin effectors, organs of cervical region & thoracic cavity
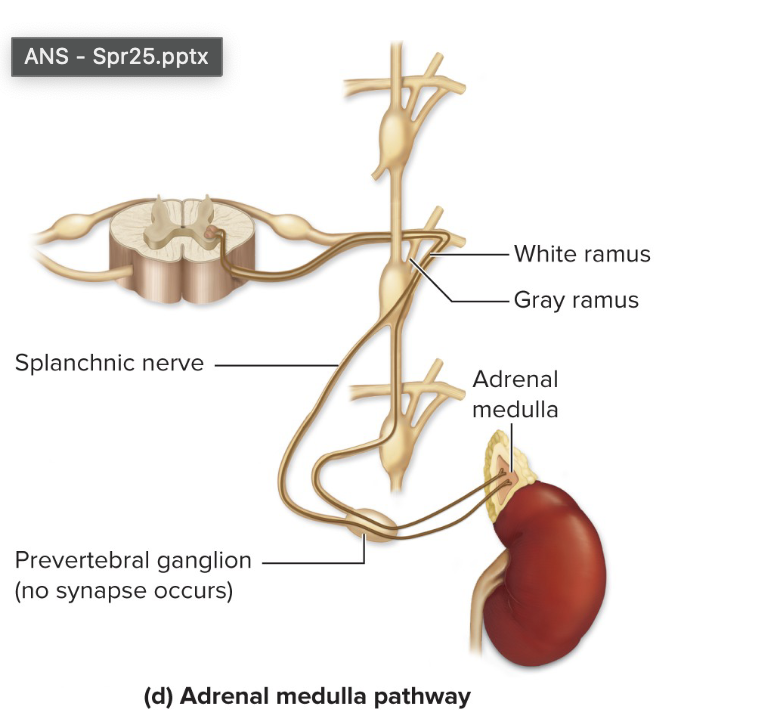
sympathetic postganglionic fibers- splanchnic nerve pathway
preganglionic fibers pass through sympathetic chain ganglia @ same level, level above or level below
form splanchnic nerves
synapse @ prevertebral ganglia
postganglionic fibers innervate abdominal & pelvic organs
parasympathetic divison
preganglionic neurons
arise from brain stem nuclei
exit brain stem via CN III, VII, IX & X
arise from sacral lateral gray horns
exit cord via ventral nerve roots S2- 4 & travel through ventral rami
postganglionic neurons
terminal ganglia: near or imbedded within effectors
parasympathetic divison overview:
origin: preganglionic neurons originate in brainstem nuclei and S2-4 segments of spinal cord (craniosacral)
functions: maintain body during conditions of “rest-and-digest”
converses energy and replenishes nutrient stores
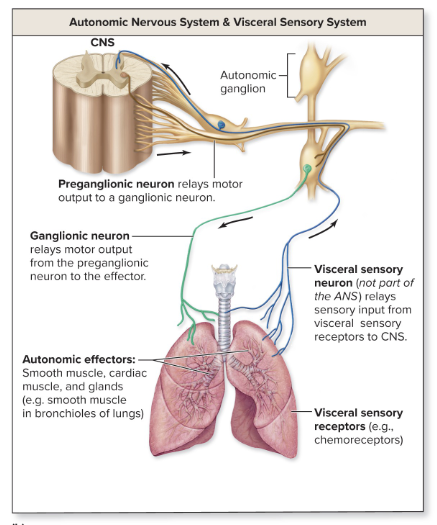
visceral reflex arc
visceral sensory neurons ( not somatic sensory)
2 motor neurons ( not just one)
effectors (not skeletal muscle)
smooth
cardiac
glands
Acetylcholine (AcH): ANS neurotransmitters
cholinergic fiber
all pre & postganglionic parasympathetic neurons
all preganglionic sympathetic neurons
some postganglionic sympathetic neurons
Norepinephrine (NE) : ANS neurotransmitters
Adrenergic fibers
most postganglionic sympathetic neurons
ANS receptors
an effectors (target organ) response to neurotransmitter is dependent on what kind of receptors are on that effector cell
most effector cells have > 1 receptor type
pharm treatment:
medications to block receptors & minimize neurotransmitters effect
medications to inhibit reuptake of neurotransmitters to maximize its effect
Nicotinic cholingeric receptors
all post-ganglionic autonmic dendrite & cell bodies: excitatory
adrenal medial- excitatory
motor endplate skeletal muscle- excitatory
muscarinic cholinergic 1
all parasympathetic target organs
smooth muscle walls of hallow organs- excitatory
glandular tissue- excitatory
visceral sphincters- inhibitory
is the visceral sphincters inhibitory or excitatory of the muscarinic cholinergic?
inhibitory
muscarinic cholinergic 2
all parasympathetic target organs
cardiac muscle- inhibitory
decrease heart rate
pupillary sphincter- excitatory
sweat glands: muscarinic cholinergic
excitatory
SYMPATHETIC innervation only
alpha adrenergic reporters
smooth muscle in blood vessel walls- excitatory
smooth muscle in visceral sphincters- excitatory
smooth muscle of dilator pupillae muscle- excitatory
smooth muscle of arrestor pili muscles- excitatory
beta adrenergic receptors
smooth muscle walls of hallow viscera- inhibitory
digestive organs
urinary organs
reproductive organs
respiratory organs
cardiac muscle: beta adrenergic receptors
excitatory
increase heart rate
increase strength of contraction
beta blockers- decrease heart strain
sympathetic functions
“flight or fight”
faster, stronger heartbeat
vasoconstriction: sympathetic tone or vasomotor tone
bronchodilation:
increase glycogenolysis
increase lipolysis
increase sweat
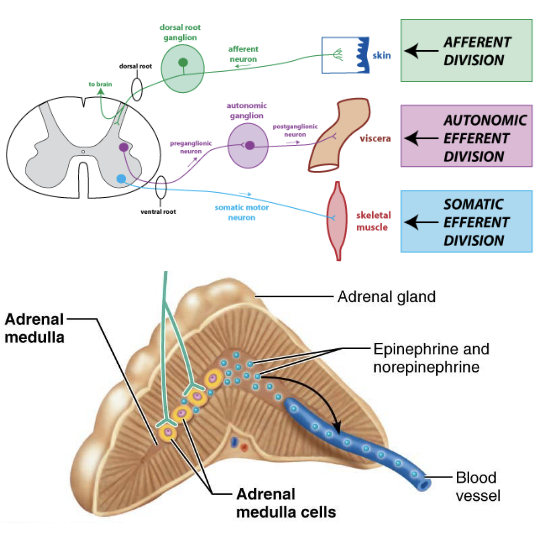
stimulates adrenal medulla
epinephrine
prolonged & widespread effects
adrenal glans
pre-ganglionic sympathetic connection
acts like post-ganglionic neuron
secretes epinephrine & norepinephrine
ANS- endocrine link!
parasympathetic functions
“rest & digest”
smooth muscle contraction
lining of viscera
digestion
elimination
increase gland secretions
vasodilation (genitalia)
pupillary constriction
effects are shorter duration & more localized
parasympathetic tone (heart, digestive & urinary tracts)
important point
sympathetic innervation only
smooth muscle walls of most blood vessels
sweat glands
arrector pili muscles
adrenal medulla