chemistry unit 3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
1
New cards
what are organic molecules
a molecule containing carbon and hydrogen, can have others but must have those
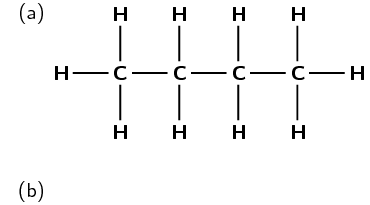
2
New cards
carbohydrates
sugar molecules your body breaks down into Glucose, which is your body's main source of energy (CHO)
3
New cards
lipids
compounds which are not soluble in water (fats, oils, waxes) (CHO)
4
New cards
proteins
organic compounds mainly composed of C,H, O,N
5
New cards
nucleic acids
macromolecules composed of nucleotides CHONP
6
New cards
anabolic
building molecules by dehydration synthesis (water is removed) aka condensation
7
New cards
catabolic
breakdown of molecules by hydrolysis (water is added)
8
New cards
monomer
simple molecule, one building block (ex: simple sugar)
9
New cards
polymer
made up of multiple monomers (Ex: starch)
10
New cards
main functions of carbohydrates
energy and digestion
11
New cards
what are the monomers for carbs
monosaccharides (simple sugars)
12
New cards
disaccharide
any substance that is composed of 2 molecules of simple sugars linked to each other (Ex: lactose)
13
New cards
polysaccharide
a carbohydrate whose molecules consist of a number of sugar molecules bonded together (Ex: cellu
14
New cards
what are the monomers for lipids
glycerol and fatty acids
15
New cards
monomers for carbohydrates
monosaccharides
16
New cards
four main polymer groups of lipids
Triglycerides (Fats and Oils) Waxes, Phosphiloids, and Steroids
17
New cards
Triglycerides
-composed of glycerol and fatty acids
-stores unused calories and provide your body with energy
-found in fats and oils
-stores unused calories and provide your body with energy
-found in fats and oils
18
New cards
waxes
-Hydrophobic
-repel water
-protects skin and leaves on plants
-Ex: earwax
-repel water
-protects skin and leaves on plants
-Ex: earwax
19
New cards
phospholipids
-produces effective and stable barrier for a cell
-MAIN COMPONENT OF PLASMA MEMBRANE
-Ex: eggs, meat, protein
-MAIN COMPONENT OF PLASMA MEMBRANE
-Ex: eggs, meat, protein
20
New cards
steroid hormones
-made of hydrocarbon rings
-can pass through cell membrane
-testosterone is steroid
-needed by body to function
-can pass through cell membrane
-testosterone is steroid
-needed by body to function
21
New cards
saturated fats
have no double bonds, solid
22
New cards
unsaturated fats
have a double bond in the H/C tail, liquid at room tempature
23
New cards
are lipids soluble in water
no, lipids are soluble in nonpolar organic solvents, and water is not organic
24
New cards
what are the monomers for proteins
amino acids, there are 20 of some, some are essential, some are not
25
New cards
what are the polymers of proteins called
polypeptides
26
New cards
what bonds form between amino acids
peptide bonds
27
New cards
what reaction causes peptide bonds
dehydration synthesis
28
New cards
essential amino acids
cannot be made by body, must come from food, 9
29
New cards
nonessential amino acids
produced by body, 11
30
New cards
6 functions of proteins
-storage
-transportation
-regulatory
-movement
-structural
-enzymes (almost always a protein)
-transportation
-regulatory
-movement
-structural
-enzymes (almost always a protein)
31
New cards
what are the monomers of a nucleic acid
Nucleotides (CHONP)
32
New cards
what are the 2 types
DNA and RNA
33
New cards
DNA and its function
double helix strand, serves as genetic info needed for an organism to grow and develop
34
New cards
RNA and its function
single strand, primary function of creating proteins via translation
35
New cards
ATP
the universal energy in molecules
36
New cards
large carbon molecules that are built from smaller simpler molecules
monomers
37
New cards
large carbon molecules made of monomers
polymers
38
New cards
large polymers
macromolecules
39
New cards
what type of reaction links monomers to make polymers
condensation reaction
40
New cards
condensation reactions involve the removal of a molecule of
water
41
New cards
all life processes require a constant supply of..
energy
42
New cards
ATP contains what 3 functional groups covalently bonded together?
3 phosphate groups
43
New cards
in what 3 forms do carbohydrates exist?
monosaccharides, polysaccharides, disaccharides
44
New cards
monomers of carbs
monosaccharides (simple sugars)
45
New cards
what are double sugars called
disaccharide
46
New cards
what forms a polysaccharide
combination of multiple monosaccharides, through glycosidic bond
47
New cards
what 4 elements make up proteins
CHON
48
New cards
monomers of proteins
amino acids
49
New cards
the main difference in amino acid is their ___ group
R
50
New cards
r group
An abbreviation for any group in which a carbon or hydrogen atom is attached to the rest of the molecule.
51
New cards