Neurogenesis
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
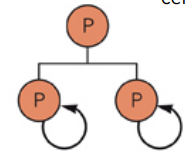
Symmetric cell division
Daughter cells are same as parent/progeitor
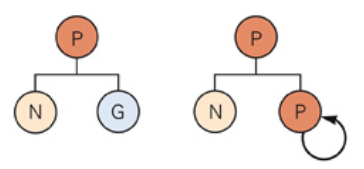
Asymmetric cell division
at least one daughter cell is different from the parent/progenitor cell
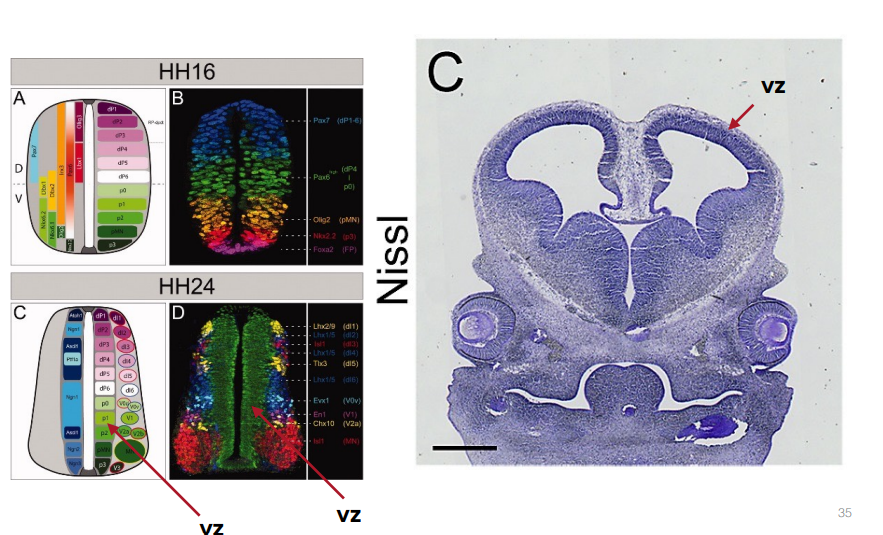
Ventricular Zone (VZ)
Cells that are lining the ventricles
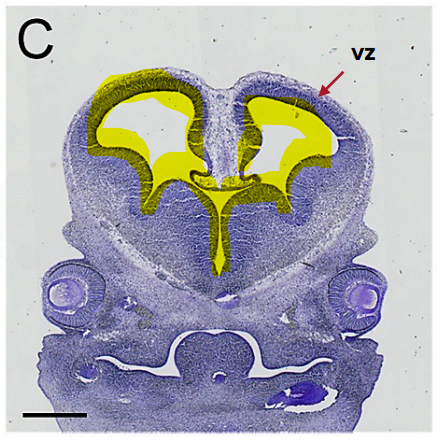
Nueral progenitor cells (reside)
Ventricular zone (VZ)
- p1 domain specifies interneurons
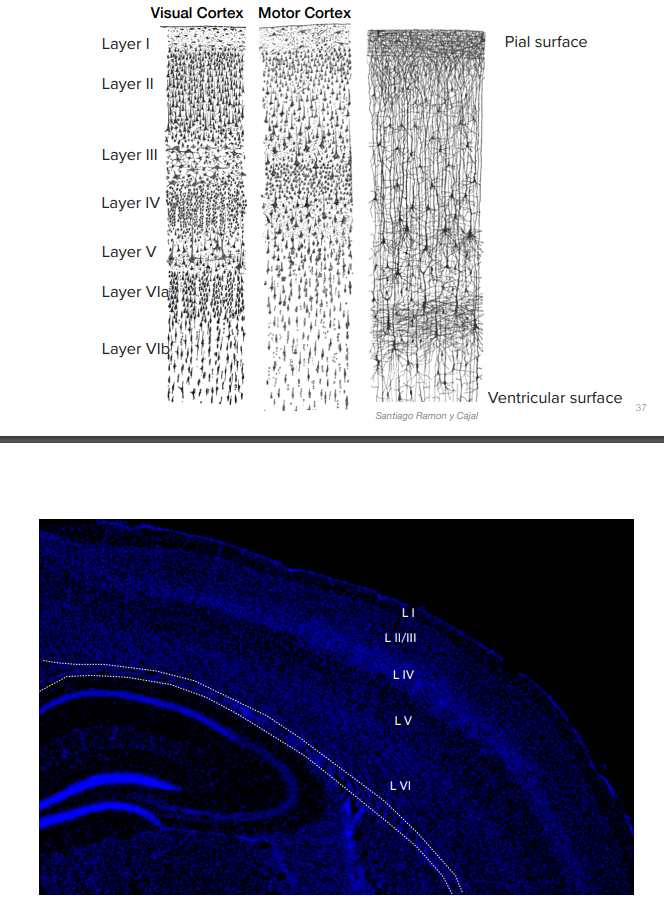
Layered Mammalian Neocortex
Comprised of 7 layers, each with different types of cells that reside there, making each layer have a distinct role in processing and transmitting info
- younger is at the top
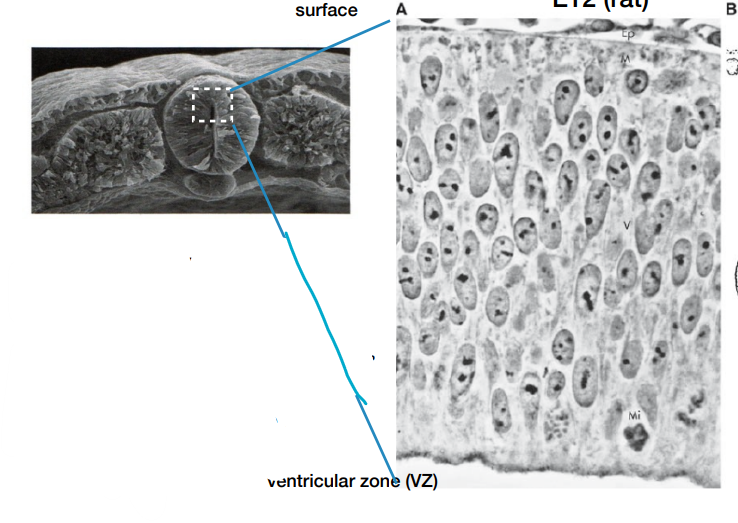
Pseudostratified epithelium
Epithelial tissues that looks like it is mutliplayered despite being one layered
- the neural tube is this
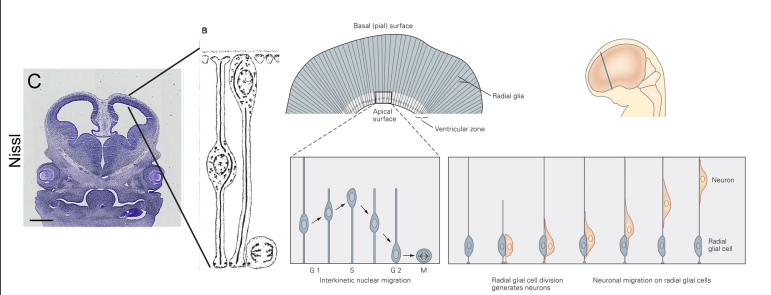
Interkinetic Nuclear Migration (IKNM)
Coordinated movement of nucleus within neuroepithelial cells (cells that differentiate into neurons and glia)
Radial Migration
Neural progenitor cells (NPCs) in the ventricular zone (VZ) migrate along radial glial fibers into cortical plate (CP)
- Radial Glia cells provide scaffolding for the neurons to migrate up on
- cortical or excitatory/projection neurons go through this process
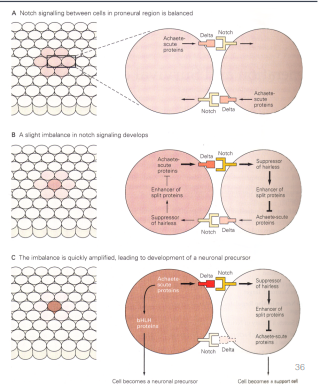
Notch Signaling
Delta ligand bings to a Notch receptor on a neighboring cells, this signaling in the souroudning cells represses proneural genes
- this random event imbalances the Detla expression, and since Delta signaling promotes neural cell fate this affect stops it
- promote ragial glia production & activation of Hes transcription repressions which maintains glial identity by repressing neuronal fate
Cortical Neuron formation
Excitatory cortical neurons are born inside first-outside last
- younger born at the bottom and climb to the top via radial glia scaffolding
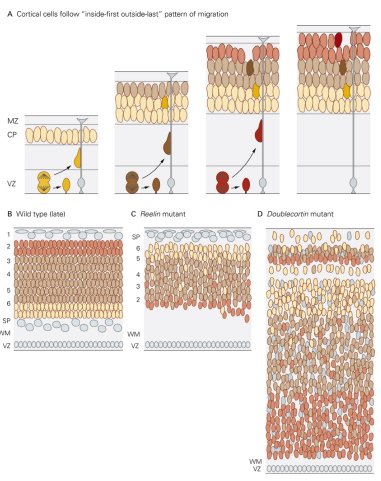
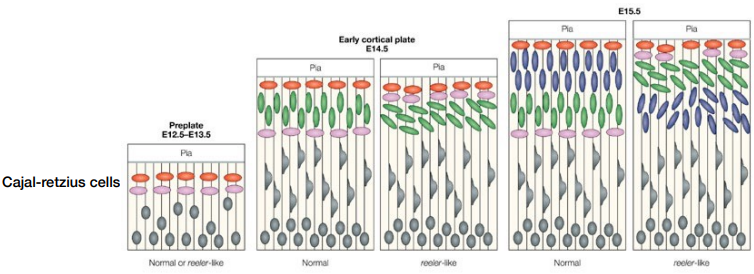
Reelin Mutation
Reelin helps guide new/younger neurons to the top layer of the neocortex, so a mutation would not allow new neurons to get to the top
- Cajal Retzuis cells (red & pink) are made first and expression reelin & make the cortical plate and allow neurons to get to the correct place
- create inverted neocortex layers
- produce unusual cortical structures
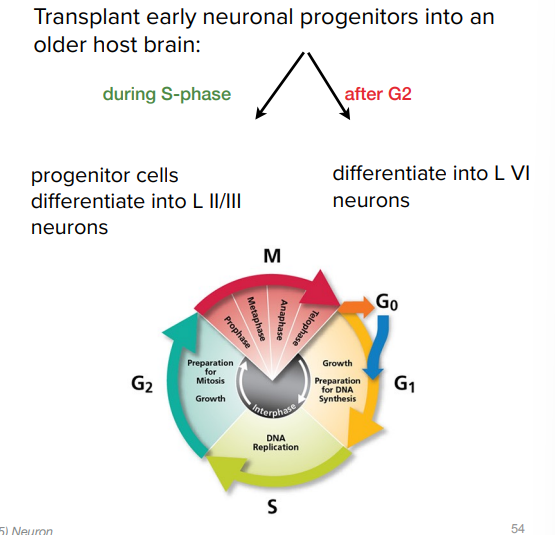
Laminar Fate
Final identity or position can be programmed by local environmental signals
- some plasticity because limited to where the cell is in the cell cycle
- can be during S-phase
- after G2 phase its too late
Projection Neurons
Have long axons that can extend from one region to the brain to another, or spinal cord, or even peripheral tissues
- highly specialized to communicate with target cell over long distances
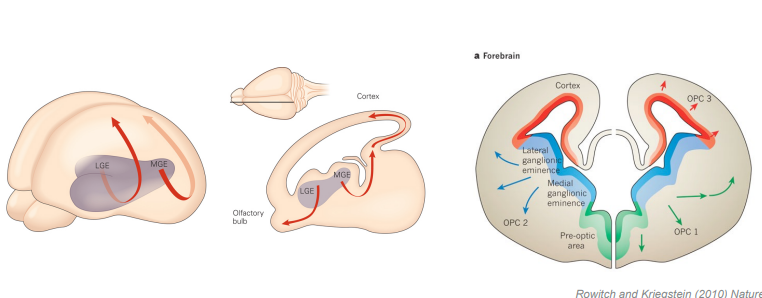
Interneurons (derived from)
ganglionic emenece
- MGE = medial ganglonic emenece
- LGE = lateral ganglonic emence
- both are anatomically and molecularly different
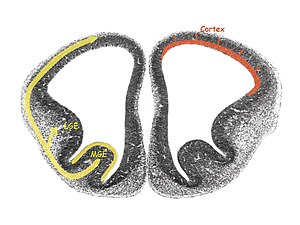
Tangential Migration
Interneurions migrate baesed on ganglionic eminece
- Loss of NKx2.1 expression imparis intenruron production
- M(edial)GE are dispersed widely throughout the brain
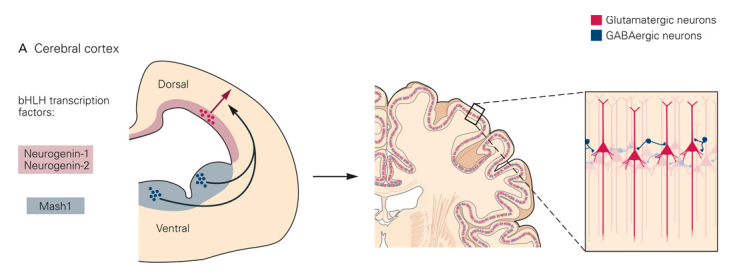
Mature cortrex (composed of)
composed of neurons derived from different progenitor regions
- ventricular zone (VZ), subventriular zone (SVZ), outer subventricuarl zone (OSVZ), cortical plate (CP), & Intermedicate zone (IZ)
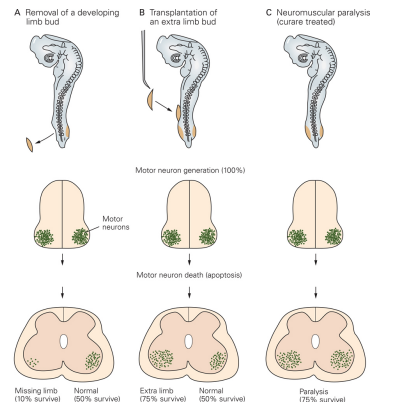
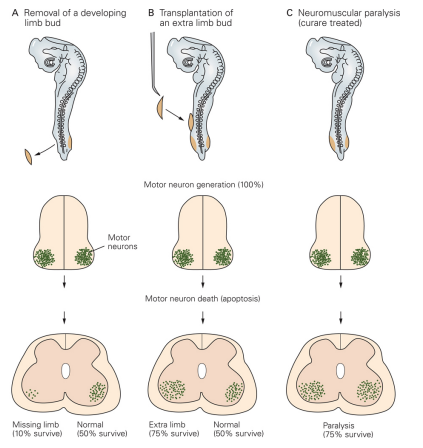
Neural Surival & Target Regions
Signals from target regions’ cells are essential to neural survial
- target structure is destroyed = ↑ neural death
- extra limb graft = ↑ neural survival
- blocking neural activity with curare (ACh antagonist) = ↓ neural death
Neureulin 1 (NRG)
Family of singaling protiens that regular glial-neuron signaling which is vital for neural ciruit formation and sypatic development
Neuregulin 1 (NRG1) Knock out
Where NRG1 is deletion or mutated to not express
- leads to an lack of signaling promoting Radial Glial identity
- no binding to ErB receptor
Neurotrophic factors
Family of proteins that are essential for growth, surival, and maintenance of neurons
- Nerve growth factor (NCF) is produced by target cells, promote neuron surival
- Also helps with singling diversity
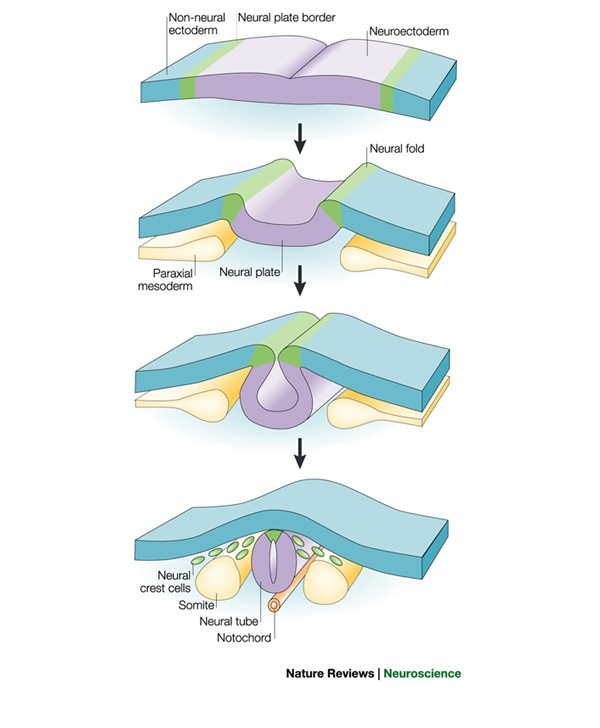
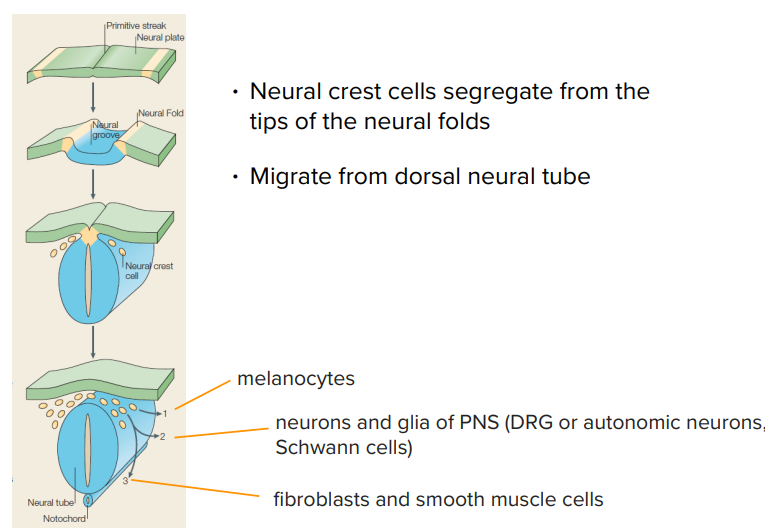
Peripheral Nervous System (resides from)
Neural crest
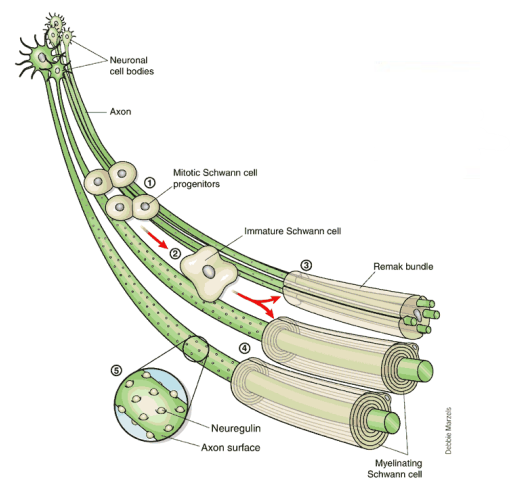
Schwann cells
Type of Glial cell that sourunds nuerons (myelination)
- are dervied from neural crest
- reside in the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Motorneuronal surival & glial cells
Schwaan cells provide strucal support to help nourish and protext motorneurons
- Myelin sheath from schwann cells allows fast signaling between neurons and/or motorneurons
Neuroal surival (requires ALL)
Overproduction of neurons followed by neuronal cell death
- Removal of the target structure increases neuron cell death
- Graft extra limb bud increases motor neuron survival
- Suggests that neuronal survival is dependent on cells in target region
- Blocking neuronal activity with curare (ACh antagonist) attenuates neuronal cell deat