SBI3U1 Evolution Unit Test//FINAL
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
What is evolution?
How populations & species change over time
What are the 4 major mechanics that promote evolution?
Natural selection, mutation, Gene flow, Genetic Drift
What is variation?
Differences between traits in individuals of the same specie
What are the two kinds of variation?
Continuous and discontinuous (discrete)
What is continuous variation?
Continuous variation is where a characteristic can have any value over a range, from minimum to maximum
What is discontinuous variation?
When there are two or more distinct categories, each individual falls into only one of these categories
What causes variation?
Due to a relationship between an organism's genotype and their phenotype
What does phenotypic display (variations) depend on?
Phenotypic display depends on genetic makeup or their environments when the phenotype is "plastic"
What is the source of genetic variation?
Mutations which cause changes in the DNA of an organism's germ cells creating new alleles that can be passed to offspring
When do these mutations occur?
These mutations occur spontaneously or through mutagens
How are more variants made?
Because of sexual reproduction which "mixes and matches" gene variants to make more variation
What can variations be?
Variations can be neutral, detrimental, or beneficial
What does adaptation require?
All adaptation requires genetic variation, but not all variation becomes adaptation
What may beneficial mutations confer?
Selective advantage
What is selective advantage?
The traits that are "selected for" which become the adaptations (species do not "choose" to adapt)
What is natural selection?
The process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring
What is fitness?
Describes an organism's reproductive successfulness and how well it is adapted to its environment for survival & reproduction
What is adaptation?
A characteristic or feature of a species that makes it well suited for survival and reproductive success in its environment
What can adaptations be?
Can be structural, behavioral, or physiological
What is structural adaptation?
Physical characteristics or traits of an organism that enhance its ability to survive in its environment
What are examples of structural adaptation?
Mimicry, camouflauge, quills, long snots, posion
What is behavioural adaptation?
Is the response an animal gives to environmental stimulus and a change in that behaviour for protection
What are examples of behavioural adaptation?
Migration, school of fish, playing dead
What is physiological adaptation?
Chemical changes within the body, and hormones for protection
What are examples of physiological adaptations?
Hibernation and venom production
What does natural selection depend on?
The environment, which creates selective pressures based on abiotic factors or biotic factors
What are abiotic factors?
Non-living factors of the environment that affect organisms
What are biotic factors?
Living factors of the environment that affect organisms
What does natural selection favour?
Favors traits that are beneficial and help an organism survive and reproduce more effectively in a specific environment
Is one trait favourable in all environments?
No. Traits that are helpful in one environment might actually be harmful in another environment
What does natural selection act on?
Existing heritable variation
For natural selection to act on a feature, what does there need to be?
There must already be differences among individuals for that feature and the differences have to be heritable (have the ability to be passed on)
Why is variation important?
As variation is essential to the long-term survival of a population—variation that is not advantageous now might become important in the future due to environmental changes
What is normal distribution?
A function that represents the distribution of many random variables as a symmetrical bell-shaped graph
What is stabilizing selection?
A selection against individuals exhibiting traits that deviate from the current population average
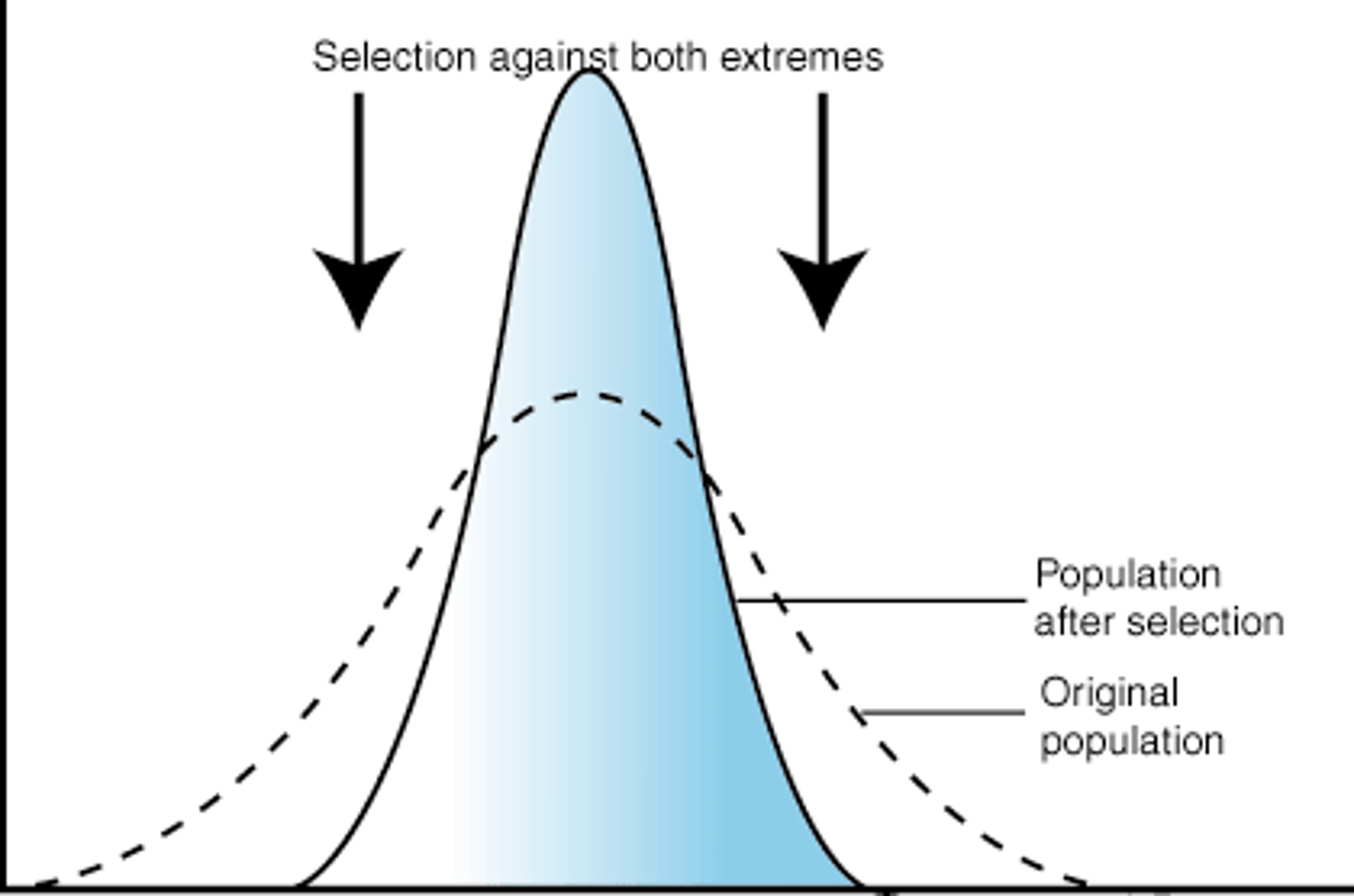
When does stabilizing selection occur?
Occurs when the average phenotype within a population is favoured by the environment
What is directional selection?
A selection that favours individuals with a more extreme variation of a trait
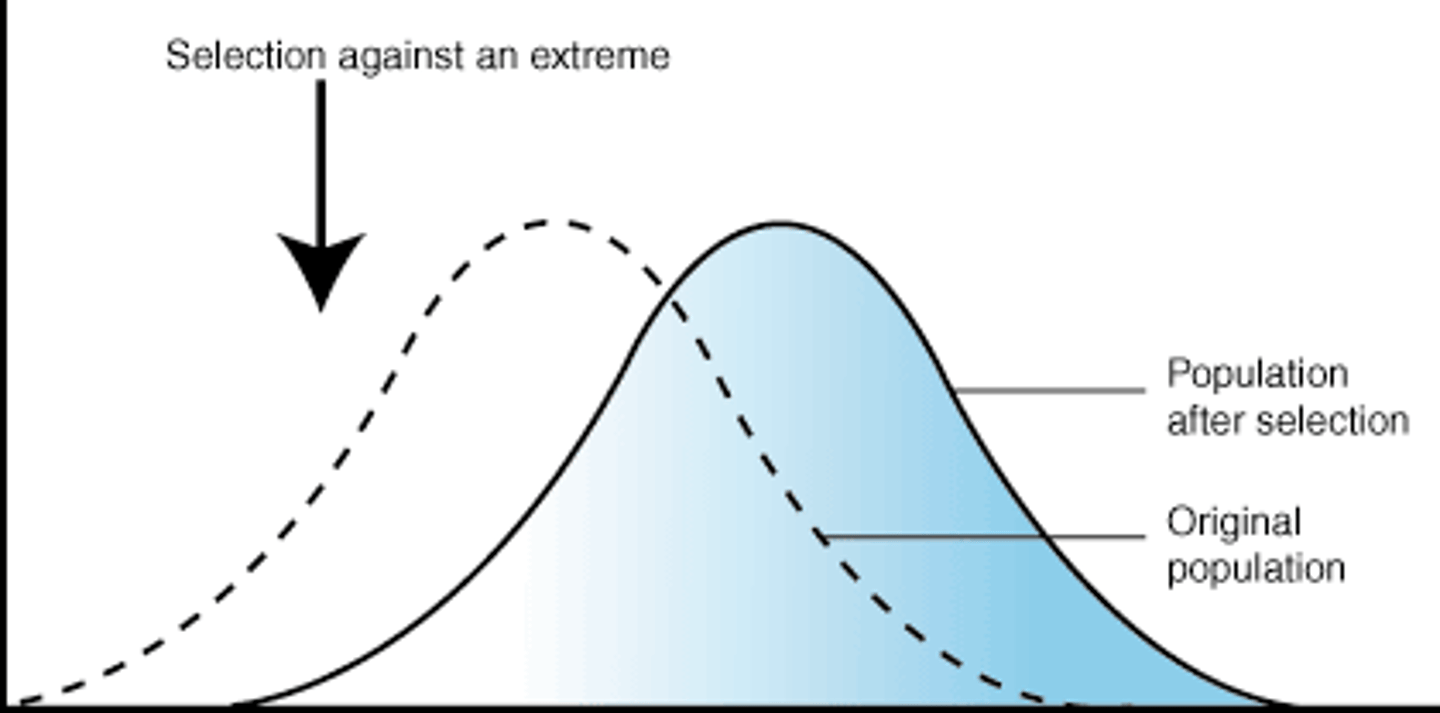
What does directional selection result in?
This selection results in a shift away from the average phenotype
When does direction selection occur?
Usually during artificial breeding/selection
What is disruptive selection?
A selection that favours two or more variations of a trait
that differ from the current population average
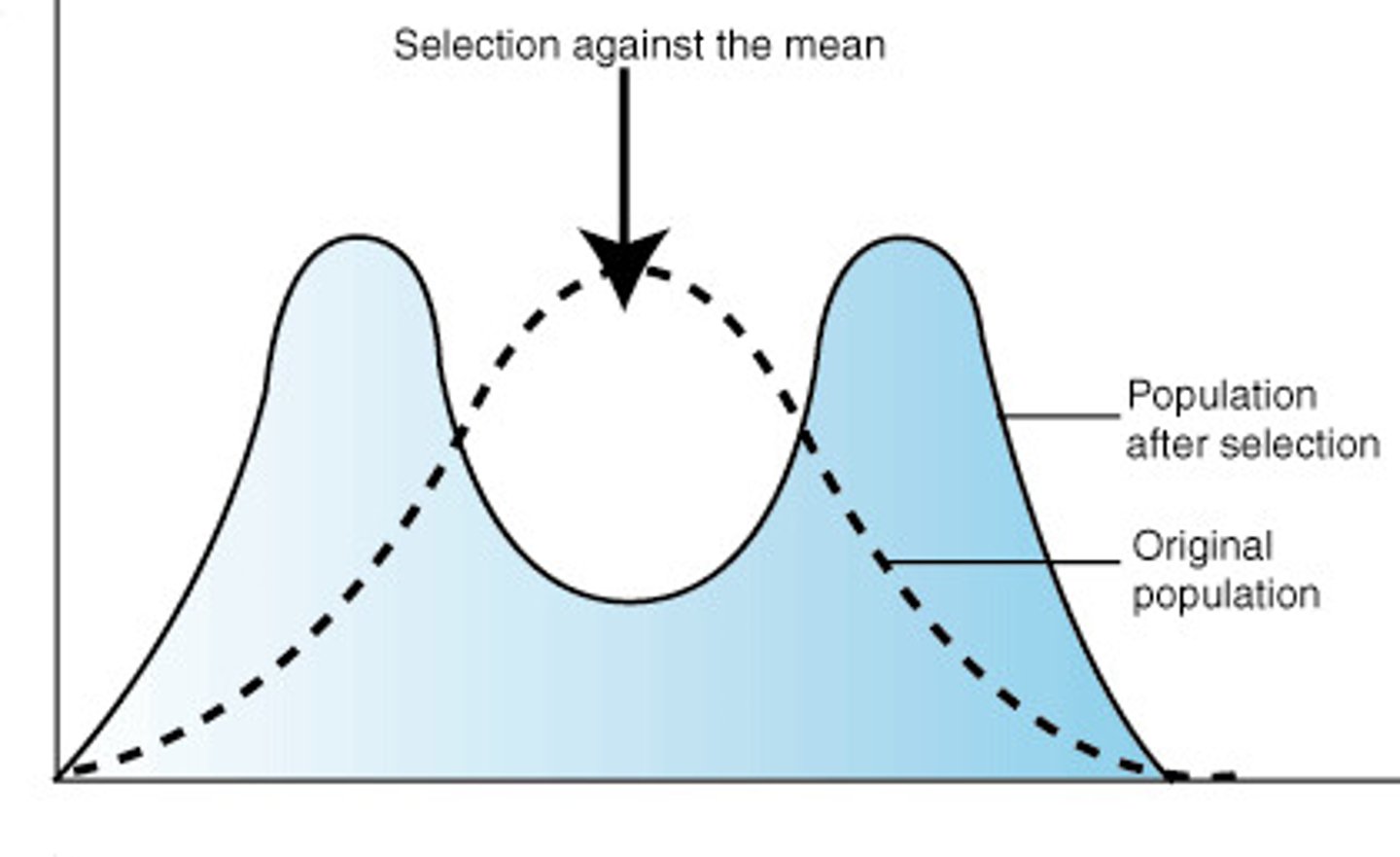
What does disruptive selection result in?
Favouring individuals with variations at opposite extremes of a trait over the intermediate phenotypes
What is sexual selection?
Differential reproductive success caused by variation in the ability to obtain mates
What is sexual selection the favouring of?
Is the favouring of any trait that specifically enhances the mating success of an individual
What might sexual selection confer?
May confer a selective disadvantage to other selective pressures
What is direct competition?
Large body size or features that provide males with tools to compete and establish control over a territory where they can mate
What is female mating choice?
When females select mates based on physical traits such as bright colours or specific behavior
What is artificial selection?
Selective pressure exerted by humans on populations in order to improve or modify particular desirable traits (in animals/agriculture)
What is the difference between natural and artificial selection?
Artificial selection is a controlled process caused by humans, whereas natural selection occurs due to natural cause
Why is artificial selection used?
Because artificial selection is a comparatively faster process where the effects are seen over a few generations
What are monocultures?
Are extensive plantings of the same varieties of a species over large expanses of land for the purpose of easing the maintenance of a crop
What does the lack of variation in monocultures lead to?
The inability to adapt in the event of an environmental change
What are gene banks?
Banks that contain populations of early ancestors of modern plants -provide a means to reintroduce genetic diversity
What is an example of a gene bank?
The Svalbard Global Seed Vault which was developed to maintain current seed varieties in the event of a global crisis
What did Carl Linnaeus create?
Created classification systems for plants and animals based on anatomy and physiology
What did Carl Linnaeus hypothesize?
Hypothesized that species came from hybridization and interbreeding of a handful of original species
What did George-Louis Leclerc suggest?
Suggested species change over time to make new organisms
What similarities did George-Louis Leclerc notice?
Noticed similarities between humans and apes and proposed a common ancestor
What did Mary Anning contribute to?
Contributed to the field of paleontology (study of fossils)
What did Mary Anning discover?
Discovered the first plesiosaur (aquatic reptile fossil)
What are the steps of fossil formation?
1. Organism dies and sinks to the bottom of a body of water
2. Organism rots, leaving only bones that get covered by mud
3. Millions of years pass and the mud turns to rock
4. The organism's bone matter completely changes into mineral matter and is now a fossil
What two principles contribute to rock layer formation?
Principle of original horizontality and the law of superposition
What does the principle of original horizontality state?
States that layers of sediment are generally deposited in a horizontal position
What does the law of superposition state?
States that in an undeformed sequence of rocks, the rock layers (strata) are progressively younger upward
What did Cuvier propose the idea of?
Catastrophism
What is the idea of catastrophism?
The idea that suggests that drastic environmental events caused large population extinction events
What did Cuvier suggest would happen to affected areas?
That the affected areas would be repopulated by species from nearby unaffected areas
What did Sir Charles Lyell propose the idea of?
Proposed the idea of uniformitarianism
What does the idea of uniformitarianism suggest?
Suggests that geological events in the past are no different than in the present
What did this idea imply?
That geological events are slow and continuous, meaning the Earth is very old
What did Jean-Baptiste Lamarck propose?
Propose the idea of inheritance of acquired characteristics
How did Lamarck depict the inheritance of acquired characteristics?
Lamarck chronologically ordered fossils to interpret a "line of descent"
What were Lamarck's hypotheses?
1. Species became more complex over time to achieve "perfection"
2. Organisms become progressively better adapted to their environment during their lifetime
What are the errors within Lamarck's first hypothesis?
-There is no "end goal" to evolution
-Species don't "choose" to adapt
-"Complex" is not necessarily better
What is the error within Lamarck's second hypothesis?
That "Acquired" characteristics cannot be inherited through genes
What was Darwin's first observation?
Different regions had structurally similar but distinctly different organisms (Why are these organisms clustered geographically)
What was Darwin's second observation?
That fossils in a region shared characteristics ofliving organisms in that region
What was Darwin's third observation?
Organisms in proximal regions share greater organism characteristics
What was Darwin's fourth observation?
Galapagos species demonstrated variation between islands
What was Darwin's fifth observation?
Artificial selection (breeding) selected for heritable traits (Was it possible for this idea to occur in nature)
What did Thomas Malthus propose?
That populations produced far more offspring than their environments could support (populations were eventually reduced by starvation or disease)
What did Wallace propose?
Proposed idea of evolution through natural selection
What was Wallace's first observation?
He noticed a sharp boundary between nearby islands that
separates distinct ecosystems of Asia and Australia
What was Wallace's second observation?
That to the west of the line, placental mammals are prevalent
What is the Wallace Line?
A line that separates species with Asian and Australian affinities
What was Wallace's third observation?
That to the east of the line, marsupials are prevalent
What are plate tectonics?
A theory explaining how the pieces of Earth's surface move
What are the differences between Wallace's and Darwin's theories?
Wallace's theory of evolution by natural selection emphasized environmental pressures, while Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection emphasized competition between organisms
What are the big ideas of evolution?
-All living organisms descended from a universal common ancestor
-Evolution of living things is powered by natural processes/ natural selection
What is the fossil record?
The remains and traces of past life that are found in sedimentary rock and reveal the history of life on Earth
What are 3 key points fossil records provide for the evidence of evolution?
-Fossils found in young layers of rock are more
similar to species alive today
-Fossils can be used to trace the evolution of
modern species through time
-Not all organisms appear in the fossil record at the same time
What is biogeography?
The study of geographic distribution of organisms based on both living species & fossil
Where are animals most similar found?
Animals that are the most similar are typically found in the same region
How can similar species in different regions be explained?
Similar species in very different regions can be explained by shifting landmasses
Where are closely related species never found?
Closely related species are almost never found inexactly the same location or habitat
What is a homologous feature?
A structure with a common evolutionary origin that may serve difference functions in modern species
What is divergent evolution?
Species that were once similar to an ancestral species become
increasingly distinct
What are analogous features?
Structures of different species having similar functions but not from the same ancestor
What is convergent evolution?
Similar traits that arise because different species have independently adapted to similar environmental conditions
What are vestigial structures?
Anatomical remnants that were important in the organism's ancestors, but are no longer used in the same way
What are examples of vestigial structures in humans?
Wisdom teeth, appendix, muscles for moving the ear, body hair, little toe, tailbone