Ob chapter 2
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Dispositional Approach
Individuals possess stable traits or characteristics that influence their attitudes and behaviours
ex. A person who is naturally outgoing may perform well in team-based roles regardless of the situation
Situational Approach
Characteristics of the organizational setting influence people’s attitudes and behaviour.
ex. Employees may be more satisfied and perform better when tasks are clearly defined and rewarding, regardless of personality.
Interactionist Approach
Behaviour = Personality + Situation.
Weak situation: Few rules → personality shows more (e.g. extrovert shines at a networking event).
Strong situation: Clear rules/structure → everyone acts similarly (e.g. formal corporate job limits personal expression).
Trait Activation Theory
Personality traits are expressed only when the situation makes the trait relevant.
ex. person high in assertiveness will show it when asked to lead a team, but not during data entry
Five-Factor Model (Big Five)
framework describing personality using five broad dimensions that capture most personality traits.
ex. Used to predict how personality affects job performance and interpersonal behaviour
Extraversion
Degree to which a person is outgoing, sociable, energetic, and assertive versus shy and reserved.
ex. High extraverts excel in sales and management roles requiring interaction; introverts may avoid social situations
Emotional Stability (Neuroticism)
extent of emotional control; high emotional stability means calm and confident, low means anxious and insecure.
ex. employees with high emotional stability handle stress well and have better interactions at work.
Agreeableness
How friendly, cooperative, and warm a person is versus cold, argumentative, or uncooperative
ex. High agreeableness benefits teamwork and jobs requiring nurturing or helping others.
Conscientiousness (Strongeest)
Degree of responsibility, dependability, and motivation toward achievement
ex. Highly conscientious people are organized, hard-working, and tend to perform well on most jobs.
Openness to Experience
tendency to be creative, curious, and open to new ideas versus favoring routine
ex. High openness suits jobs involving creativity, learning, and innovation
Locus of Control
Personality trait about whether people believe they control their outcomes (internal) or if outside forces do (external).
Internal: You shape your future through effort (e.g. Laurie believes hard work earns promotions).
External: Outcomes depend on luck, fate, or others (e.g. Stan thinks success comes from connections).
Self-Monitoring
the degree to which a person adjusts their behavior to fit social situations.
High self-monitor: Reads the room and adapts (e.g. salesperson changes tone for each client).
Low self-monitor: Acts true to self, regardless of setting (e.g. vents frustration openly, doesn’t care who’s watching).
Self-Esteem
degree to which a person has a positive self-evaluation.
ex. Someone with high self-esteem sees themselves positively and feels confident in their actions and opinions.
Behavioural Plasticity Theory
idea that people with low self-esteem are more susceptible to external and social influence
ex. low self-esteem employee might change their opinion after hearing a manager or peer express a different view
Positive Affectivity
tendency to experience positive emotions and moods like joy, excitement, and enthusiasm
ex. person high in PA walks into work with a smile, stays optimistic during challenges, and brings good energy to meeting
Negative Affectivity
personality trait reflecting the tendency to experience negative emotions such as fear, sadness, or anxiety, and to view the world pessimistically.
Proactive Behaviour + Personality
taking initiative to improve current circumstances or creating new ones
ex. proactive employee might suggest a new scheduling system that improves team efficiency instead of just complaining about current issues.
General Self-Efficacy (GSE)
general belief in one’s ability to succeed in a wide range of situations. It’s a motivational trait developed through life experiences
ex. student with high GSE might feel confident tackling an unfamiliar group project, believing they can figure it out.
Core Self-Evaluations (CSEs)
how you see yourself overall
Self-esteem – How much you value yourself.
Generalized self-efficacy – How confident you are in your ability to handle tasks and challenges.
Locus of control – Whether you believe you have control over what happens to you (vs. believing it's all luck/fate).
Emotional stability (low neuroticism)
Operant Learning theory
type of learning where behaviour is controlled by its consequences—people learn to act in certain ways to get rewards or avoid punishments.
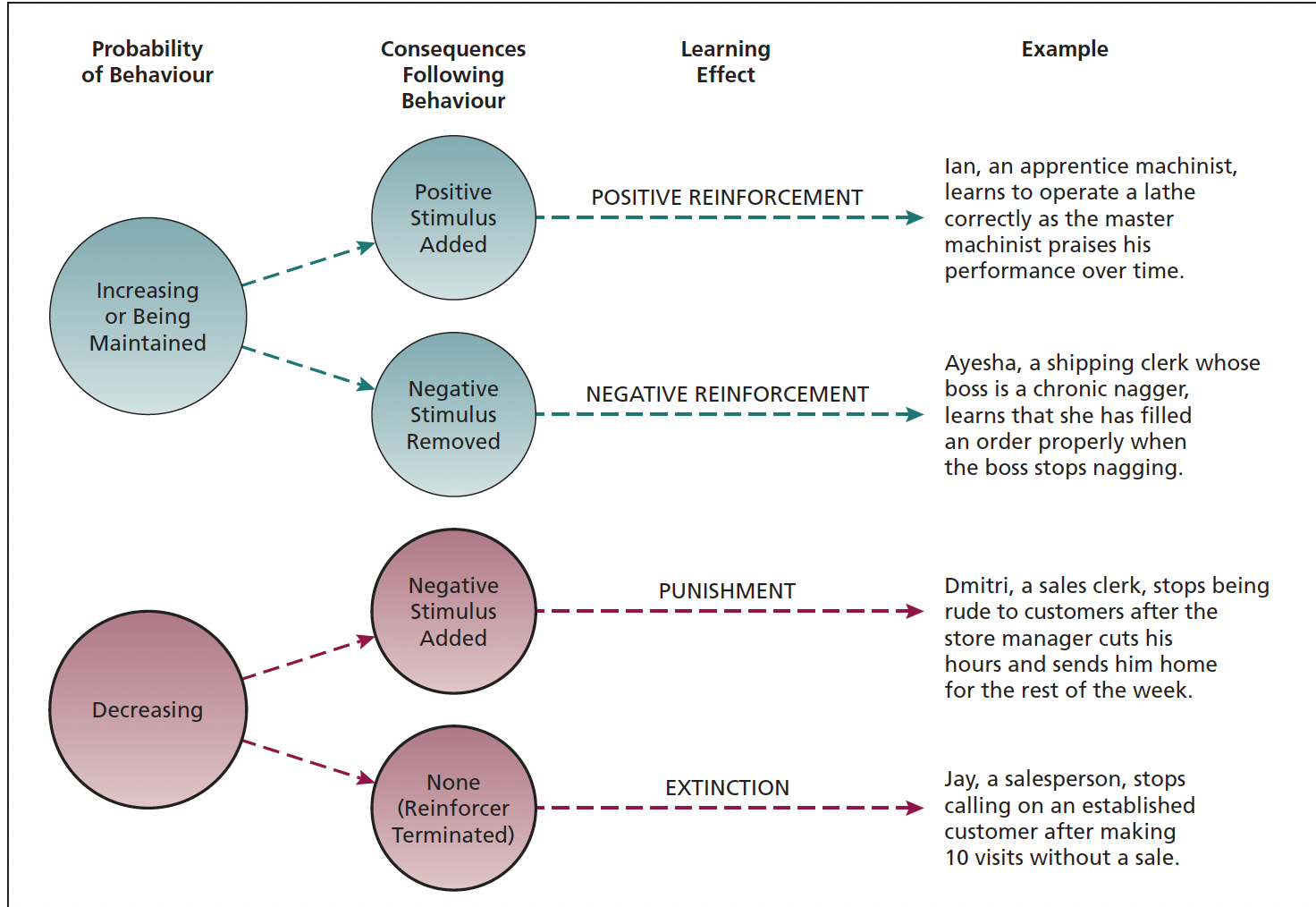
reinforcement
process that strengthens behaviour by either adding something pleasant or removing something unpleasant after the behaviour occurs
Positive Reinforcement
pleasant stimulus is added after a behaviour to increase the chances of that behaviour happening again
ex. money for good work
Negative Reinforcement
unpleasant stimulus is removed or avoided after a behaviour, making that behaviour more likely to happen again
ex. work harder to avoid manger naggging
Confusing Rewards with Reinforcers
Rewards don’t work if not clearly tied to the desired behavior.
Companies overlook that people prefer different types of rewards.
Managers often ignore key reinforcers like performance feedback and social recognition.
They also miss reinforcers from co-workers or the job itself (intrinsic motivation).
Performance Feedback
Info about past work to improve or keep good performance.
Ex. Manager reviews sales numbers with employee.
Social Recognition
Informal praise or thanks for good work.
ex. Boss publicly praises employee in team meeting.
Reinforcement strat
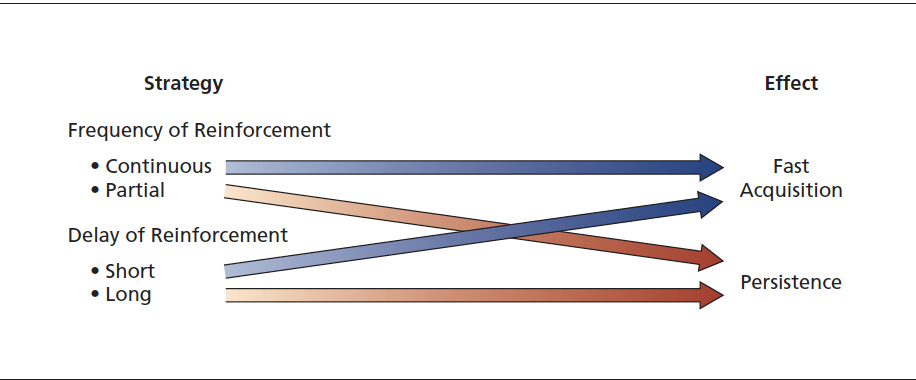
Continuous & Immediate Reinforcement:
Reward every correct behavior right away.
Effect: Fast learning but stops quickly if rewards stop.
Use: Training new hires, fixing issues, emergencies.
Partial & Delayed Reinforcement:
Reward some behaviors, sometimes later.
Effect: Behavior lasts longer, more persistent without constant rewards.
Use: Keeping behavior steady when constant supervision isn’t possible
Extinction
Stopping the reinforcement that maintains an unwanted behaviour so the behaviour gradually disappears
ex. A marketing expert’s joking in meetings stopped after co-workers ignored him, removing the laughs that reinforced the jokes
Punishment
application of an unpleasant stimulus following a behavior, designed to decrease the probability of that behavior occurring again
Social Cognitive Theory (SCT)
Learning involves cognitive processes like attention, memory, and motivation that help people observe, imitate, and regulate their behavior.
Example: A student watches a teacher solve a math problem, then tries it themselves while monitoring their own work.
Observational Learning
Learning by watching and copying the behavior of others, rather than by doing it yourself. People watch others (models), notice the results they get, and decide whether to imitate based on expected outcomes
ex. new vice president, acts like an experienced leader because he watched how others behave in meetings and copied their style..
Self-Efficacy Beliefs
Belief in one’s ability to successfully perform a specific task, shaped by experience, observation, encouragement, and emotions.
Example: Vincent feels confident running meetings because he’s watched others, received positive feedback, feels calm, and has succeeded before.
Self-Regulation
Using learning principles—like reinforcement or observation—to guide and control your own behaviour.
ex. A student rewards themselves with a break after finishing a study goal to stay motivated and focused.
Organizational Behaviour Modification (O.B. Mod)
using learning techniques to change how people act at work
ex.company showed workers how to be safe, gave feedback, and praised them. Safe behaviour went from 74% to 97%.
Employee Recognition Programs:
formal programs at work that publicly praise and reward employees for doing specific good things
ex. employee of the month award for great customer service.
Peer Recognition Programs:
Formal programs where employees can publicly praise and reward their coworkers for doing great wor
ex. shout-out board where team members post notes recognizing each other's help or achievements.
Behaviour Modelling Training (BMT)
training method where employees watch someone perform a task, then practise doing it themselves
Intra vs inter personal
Intrapersonal skills = Skills within yourself
→ e.g. self-awareness, managing emotions, motivation, reflectionInterpersonal skills = Skills with others
→ e.g. communication, teamwork, conflict resolution, empathy