Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What is a genome?
A) the complete complement of an organism's genes
B) a specific sequence of polypeptides within each cell
C) a specialized polymer of four different kinds of monomers
D) a specific segment of DNA that is found within a prokaryotic chromosome
E) an ordered display of chromosomes arranged from largest to smallest
A
Which of the following statements about genes is incorrect?
A) Genes correspond to segments of DNA.
B) Many genes contain the information needed for cells to synthesize enzymes and other proteins.
C) During fertilization, both the sperm and the ovum contribute genes to the resulting fertilized egg.
D) Under normal circumstances, each chromosome contains precisely one gene.
E) Genetic differences can result from changes in the DNA called mutations.
D
Asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction are different in that
A) individuals reproducing asexually transmit 100% of their genes to their progeny, whereas individuals
reproducing sexually only transmit 50%.
B) asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parents, whereas sexual reproduction gives rise to genetically distinct offspring.
C) asexual reproduction involves a single parent, whereas sexual reproduction involves two.
D) asexual reproduction only requires mitosis, whereas sexual reproduction always involves meiosis.
E) all of the above
E
How do the two members of a pair of homologous chromosomes differ from each other?
A) their length
B) the identity and relative position of the genes present on each of the chromosomes
C) their staining patterns
D) the position of the centromere within each of the chromosomes
E) the precise sequence of the DNA within each of the chromosomes
E
What is a karyotype?
A) the set of unique physical characteristics that define an individual
B) the collection of all the mutations present within a genome
C) a unique combination of chromosomes found in a gamete
D) a system of classifying cell nuclei
E) a display of every pair of homologous chromosomes within a cell, organized according to size and shape
E
By examining a karyotype, it is possible to determine
A) which of two related plant forms is a gametophyte, and which is a sporophyte.
B) the sex of an animal.
C) the age of a fungus.
D) A and B only
E) A, B, and C
D
At which stage of mitosis are chromosomes photographed in the preparation of a karyotype?
A) prophase
B) metaphase
C) anaphase
D) telophase
E) interphase
B
The human X and Y chromosomes are
A) both present in every somatic cell of males and females alike.
B) of approximately equal size.
C) almost entirely homologous, despite their different names.
D) called "sex chromosomes" because they determine an individual's sex.
E) all of the above
D
If the liver cells of an animal have 24 chromosomes, how many chromosomes do its sperm cells have?
A) 6
B) 12
C) 24
D) 48
E) 64
B
Which of the following is true of a species that has a chromosome number of 2n = 16?
A) The species is diploid with 32 chromosomes.
B) The species has 16 sets of chromosomes.
C) There are 8 homologous pairs.
D) During the S phase of the cell cycle there will be 32 separate chromosomes.
E) A gamete from this species has 4 chromosomes.
C
Which of the following is a term for a human cell that contains 22 pairs of autosomes and two X chromosomes?
A) an unfertilized egg cell
B) a sperm cell
C) a male somatic cell
D) a female somatic cell
E) both A and D
D
Eukaryotic sexual life cycles show tremendous variation. Of the following elements, which do all sexual life cycles have in common?
I. alternation of generations
II. meiosis
III. fertilization
IV. gametes
V. sporse
A) I, IV, and V
B) II, II, and IV
C) II, III, and IV
D) II, IV, and V
E) all of the above
C
Which of these statements is false?
A) In humans, each of the 22 maternal autosomes has a homologous paternal chromosome
B) In humans, the 23rd pair, the sex chromosomes, determines whether the person is female (XX) or male (XY)
C) Single, haploid (n) sets of chromosomes in ovum and sperm unite during fertilization, forming a diploid (2n), single-celled zygote
D) At sexual maturity, ovariies and testes produce diploid gametes by meiosis
E) Sexual life cycles differ with respect to the relative timing of meiosis and fertilization
D
In animals, meiosis results in gamates, and fertilization results in
A) spores
B) gametophytes
C) zygotes
D) sporophytes
E) clones
C
Referring to a plant sexual life cylce, which of the following tems describes the process that leads directly to the formation of gametes?
A) sporophyte meiosis
B) gametophyte mitosis
C) gametophyte meiosis
D) sporophyte mitosis
E) alternation of generations
B
Which of the following is an example of alternation of generations?
A) A grandparent and grandchild each have dark hair, but the parent has blond hair.
B) A diploid plant (sporophyte) produces, by meiosis, a spore that gives rise to a multicellular, haploid pollen grain (gametophyte).
C) A diploid animal produces gametes by meiosis, and the gametes undergo fertilization to produce a diploid zygote.
D) A haploid mushroom produces gametes by mitosis, and the gametes undergo fertilization, which is immediately followed by meiosis.
E) A diploid cell divides by mitosis to produce two diploid daughter cells, which then fuse to produce a tetraploid cell.
B
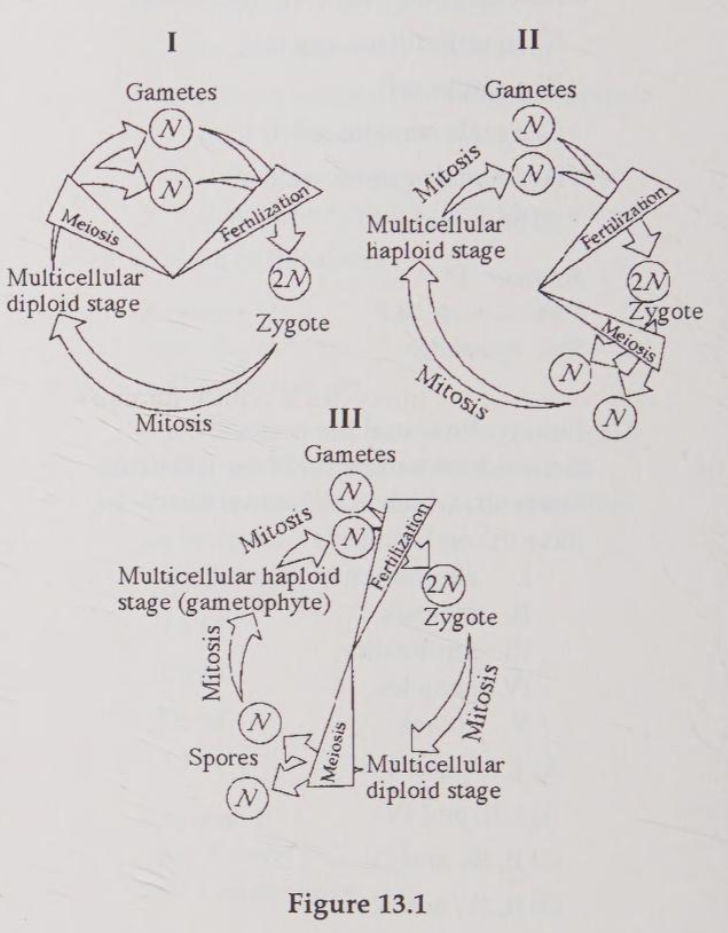
Which of the life cycles is typical for animals?
A) L only
B) I only
C) Ill only
D) I and II
E) I and III
A
Which of the life cycles typical for plants and some algae?
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and II
E) I and III
C
Which of the life cycles is typical for most fungi and some protists?
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II
E) I and III
B
Which of the following is misisng from the life cycle progression shown below?
sporophyte - meiosis - spore - _____ - gametophyte - mitosis - gametes - fertilization - zygote
A) meiosis
B) mitosis
C) synapsis
D) karyotype
E) fertilization
B
In animals, somatic cells are produced by mitosis and _____ are produced by meiosis
A) gametes
B) clones
C) zygotes
D) spores
E) diploid cells
A
All of the following are functions of meiosis in plants except
A) production of spores
B) reduction of chromosome number by half
C) independent assortment of chromosomes
D) crossing over and recombination of homologous chromosomes
E) production of identical daughter cells
E
After telophase I of meiosis, the chromosomal makeup of each daughter cell is
A) diploid, and the chromsomes are composed of a single chromatid
B) diploid, and the chromomes are composed of two chromatids
C) haploid, and the chromomes are composed of a single chromatid
D) haploid, and the chromosmes are composed of two chromatids
E) tetraploid, and the chromeoms are composed of two chromatids
D
How do cells at the completion of meiosis compare with cells that have replicated their DNA and are just about to begin meiosis?
A) They have twice the amount of cytoplasm and half the amount of DNA.
B) They have half the number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
C) They have the same number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
D) They have half the number of chromosomes and one-fourth the amount of DNA.
E) They have half the amount of cytoplasm and twice the amount of DNA.
D
When does the synaptonemal complex disappear?
A) late prophase of meiosis I
B) during fertilization or fusion of gametes
C) early anaphase of meiosis I
D) mid-prophase of meiosis II
E) late metaphase of meiosis II
A
Which of the following terms belongs with the words synapsis, tetrads, and chiasmata?
A) haploid
B) crossing over
C) autosomes
D) prophase II
E) fertilization
B
Tetrads of chromosomes are aligned at the center of the cell; independent assortment soon follows during
I. prophase I
II. metaphase I
III. anaphase I
IV. telophase I
V. prophase II
VI. metaphase II
VII. anaphase II
VIII. telophase II
A) I
B) I
C) IV
D) VII
E) VIII
B
Synapsis of homologous pairs occurs; crossing Over may occur during
I. prophase I
II. metaphase I
III. anaphase I
IV. telophase I
V. prophase II
VI. metaphase II
VII. anaphase II
VIII. telophase II
A) I
B) Il
C) IV
D) VI
E) VI
A
Centromeres of sister chromatids uncouple and chromatids separate during
I. prophase I
II. metaphase I
III. anaphase I
IV. telophase I
V. prophase II
VI. metaphase II
VII. anaphase II
VIII. telophase II
A) Ill
B) Ul
C) IV
D) V
E) VII
E
Which of the following happens at the conclusion of meiosis I?
A) Homologous chromosomes are separated.
B) The chromosome number is conserved.
C) Sister chromatids are separated.
D) Four daughter cells are formed.
E) The sperm cells elongate to form a head and a tail end.
A
Which of the following is true of the process of meiosis?
A) Two diploid cells result.
B) Four diploid cells result.
C) Four haploid cells result.
D) Four autosomes result.
E) Four chiasmata result.
C
Crossing over occurs during which phase of meiosis?
A) prophase I
B) anaphase |
C) telophase I
D) prophase II
E) metaphase II
A
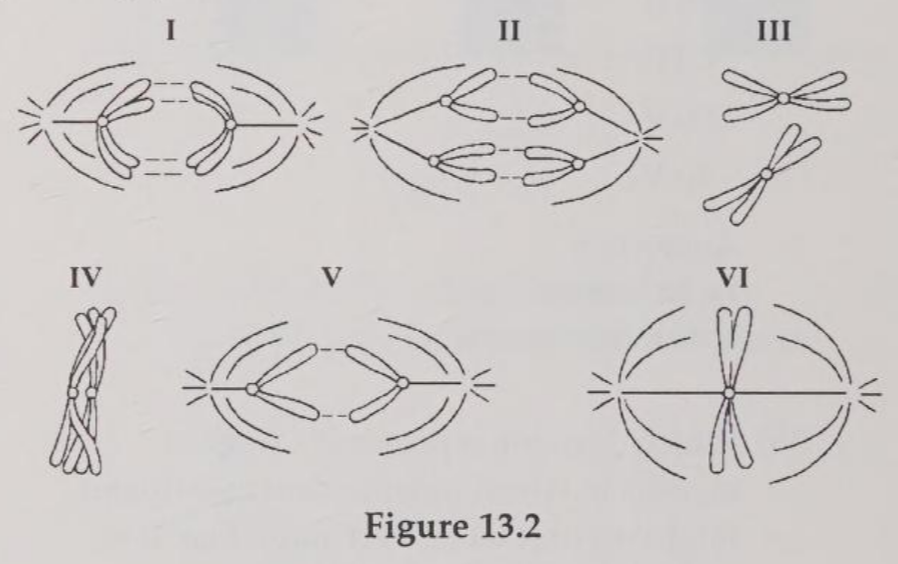
Which diagram represents prophase I of meiosis?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
D
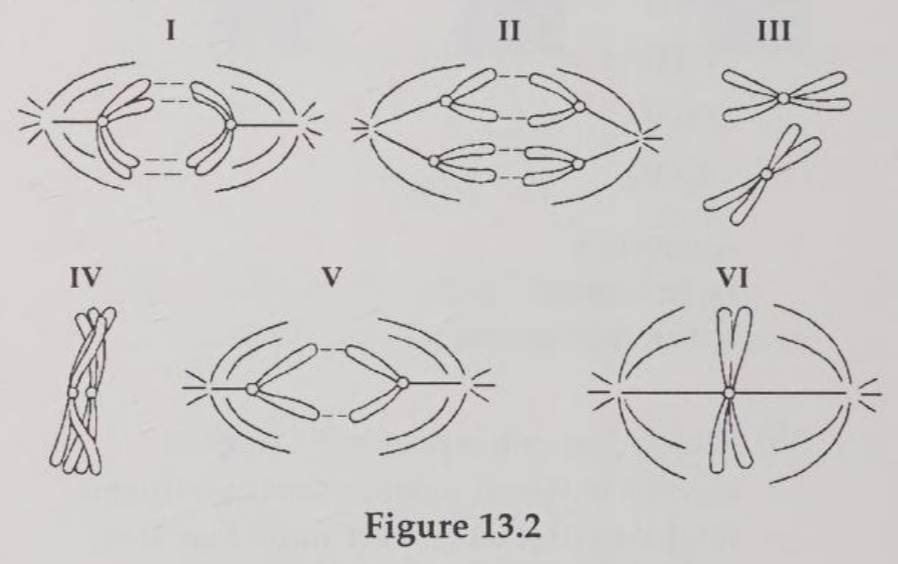
Which drawing represents anaphase of mitosis?
A) Il
B) Il
C)IV
D) V
E) VI
A
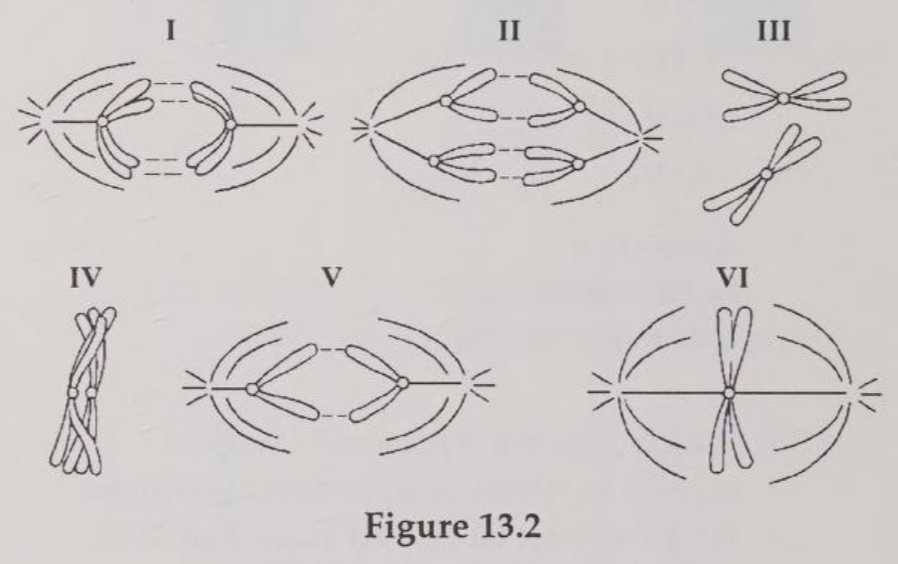
Which drawing represents metaphase II of meiosis?
A) I
B) II
C) IV
D) V
E) VI
E
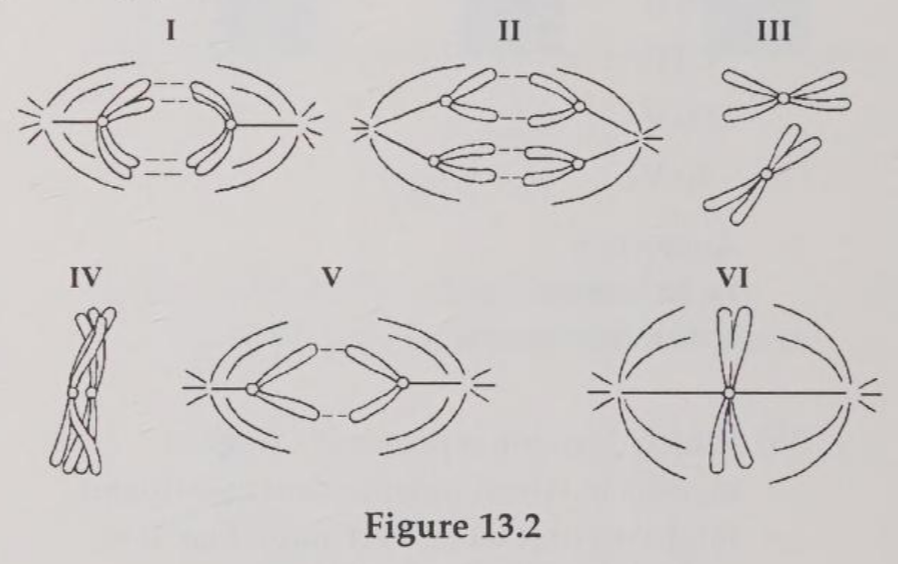
Which drawing represents a stage of meiosis in which independent assortment might occur if there were more than one pair of chromosomes represented?
A) I
B) II
C) IV
D) V
E) VI
A
A cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identica.
A) The statement is true for mitosis only.
B) The statement is true for meiosis I only.
C) The statement is true for meiosis II only.
D) The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis I.
E) The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II.
A
Homologous chromosomes synapse and crossing over occurs.
A) The statement is true for mitosis only.
B) The statement is true for meiosis I only.
C) The statement is true for meiosis II only.
D) The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis I.
E) The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II.
B
Centromeres uncouple and chromatids are separated from each other.
A) The statement is true for mitosis only.
B) The statement is true for meiosis I only.
C) The statement is true for meiosis II only.
D) The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis I.
E) The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II.
E
Independent assortment of chromosmes occurs.
A) The statement is true for mitosis only.
B) The statement is true for meiosis I only.
C) The statement is true for meiosis II only.
D) The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis I.
E) The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II.
B
The process is preceeded by replication fo the DNA.
A) The statement is true for mitosis only.
B) The statement is true for meiosis I only.
C) The statement is true for meiosis II only.
D) The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis I.
E) The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II.
D
You have in your possession a microscope slide with meiotic cells on it and a light microscope. What would you look for if you wanted to identify metaphase I cells on the slide?
A) a visible nuclear envelope
B) separated sister chromatids at each pole of teh cell
C) tetrads lined up at the center of the cell
D) a synaptonemal compelx
E) a cleavage furrow
C
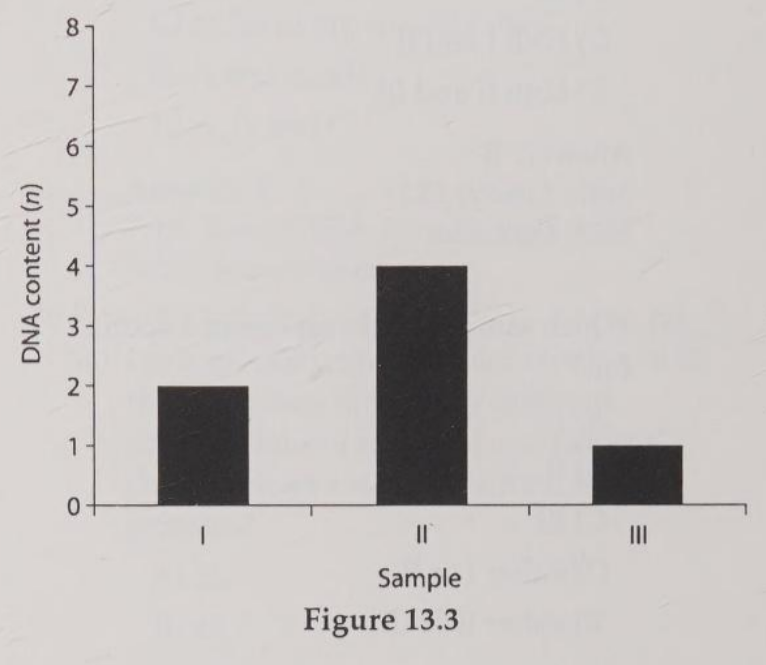
You siolate DNA from three different cell types of an organism, determine the relative DNA content for each types, and plot the reslts on the graph. If the cell were from a plant, which sample might represent a gametophyte cell?
A) I
B) II
D) either I or I
E) either II or III
C
Which sample of DNA might be from a nerve cell arrested in G0 of the cell cycle?
A) I
B) Il
C) Ill
D) either I or II
E) either II or II
A
Which sample might represent an animal cell in G2 phase of the cell cycle?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) both I and II
E) both II and III
B
Which sample might represent a sperm cell?
A) I
B) II
C) Ill
D) either I or II
E) either II or III
C
During meiosis, cells go from what number to what number?
A) I to Il to l to IlI
B) I to II to II
C) II to I
D) Ill to l
E) always remain at I
A
During mitosis, diploid cells go from what number to what numbers?
A) I to III
B) I to II
C) II to III
D) II to I
E) always remain at II
D
From the descriptions above, which of the following is the order that most logically illustrates a sequence of meiosis?
1. formation of four new nuclei, each with half the chromosomes present in the parental nucleus
2. alignment of tetrads at the metaphase plate
3. separation of sister chromatids
4. separation of the homologues; no uncoupling of the centromere
5. synapsis; chromosomes moving to the middle of the cell in pair
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 5, 4, 2, 1, 3
C) 5, 3, 2, 4, 1
D) 4, 5, 2, 1, 3
E) 5, 2, 4, 3, 1
E
Which of the steps take place in both mitosis and meiosis?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 5
D) 2 and 3 only
E) 2, 3, and 5
B
When comparing prophase I of meiosis with prophase of mitosis, which of the following occurs only in meiosis?
A) the chromosomes condense
B) tetrads form
C) the nuclear envelope diassembles
D) a spindle forms
E) each chromosom is composed of two chromatids
B
Which of the following occurs in meiosis but not in mitosis?
A) chromosome replication
B) synapsis
C) production of daughter cells
D) alignment of tetrads at metaphase plate
E) both B and D
E
How does the sexual life cycle increase the genetic variation in a species?
A) by allowing independent assortmentof chromosomes
B) by allowing random fertilization
C) by allowing crosisng over
D) A and B only
E) A, B, and C
E
For a species with a haploid number of 23 chromsomes, how many different combinations of maternal and paternal chromsomes are posisble for the gametes?
A) 23
B) 46
C) 460
D) 920
E) about 8 million
E
For a species with a diploid number of 10 chromsomes, how many different combinations of maternal and paternal chromsomes are posisble for the gametes?
A) 5
B) 25
C) 32
D) 100
E) about 10,000
C
Independent assortment of chromosomes is a result of
A) the random and independent way in which each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up at the metaphase plate during meiosis I.
B) the random nature of the fertilization of ova by sperm.
C) the random distribution of the sister chromatids to the two daughter cells during anaphase II.
D) the relatively small degree of homology shared by the X and Y
chromosomes.
E) all of the above
A
When pairs of homologous chromosomes separate during anaphase I,
A) the maternal chromosomes all move to one daughter cell, and the paternal chromosomes all move to the other daughter cell.
B) the sister chromatids remain linked to one another.
C) most of the recombination has already occurred, with the remainder taking place during prophase II.
D) the synaptonemal complex is visible under the light microscope.
B
Which of the following statements about crossing over is incorrect?
A) Crossing over combines sections of the maternal and paternal chromosomes.
B) Crossing over plays a role in both sexual and asexual reproduction.
C) There are on average one to three crossover events per chromosome.
D) Crossing over increases the extent of genetic variation beyond what is possible through independent assortment alone.
E) Crossing over results in recombinant chromosomes.
B
What name is given to the process that restores the diploid number of chromosomes?
A) fertilization
B) asexual reproduction
C) meiosis
D) mitosis
E) the cell cycle
A
At the end of ______ and cytokinesis, haploid cells contain chromosomes that each consist of two sister chromatids.
A) metaphase Il
B) telophase I
C) telophase
D) telophase II
E) interphase
B
Synapsis occurs during
A) prophase I.
B) telophase I and cytokinesis.
C) prophase II.
D) metaphase II.
E) anaphase II.
A
Homologous chromosomes migrate to opposite poles during
A) telophase II and cytokinesis.
B) prophase II.
C) anaphase I.
D) metaphase I.
E) metaphase II.
C
In a cell in which 2n = 6, the independent assortment of chromosomes during meiosis can by itself give rise to _____ genetically different gametes.
A) two
B) four
C) five
D) six
E) eight
E
A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is
A) a somatic cell of a male.
B) a zygote.
C) asomatic cell of a female.
D) a sperm cell.
E) an ovum.
D
Homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles of a dividing cell during
A) mitosis.
B) meiosis I.
C) meiosis II.
D) fertilization.
E) binary fission.
B
Meiosis II is similar to mitosis in that
A) homologous chromosomes synapse.
B) DNA replicates before the division.
C) the daughter cells are diploid.
D) sister chromatids separate during anaphase.
E) the chromosome number is reduced.
D
If the DNA content of a diploid cell in the G0 phase of the cell cycle is x, then the DNA content of the same cell at metaphase of meiosis I would be
A) 0.25x
B) 0.5x
C) x.
D) 2x.
E) 4x.
D
If we continued to follow the cell lineage from question 4, then the DNA content at metaphase of meiosis II would be
A) 0.25x.
B) 0.5x.
C) x
D) 2x
E) 4x
C
How many different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes can be packaged in gametes made by an organism with a diploid number of 8 (2n = 8)?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
E) 32
D
The immediate product of meiosis in a plant is a
A) spore.
B) gamete.
C) sporophyte.
D) gametophyte.
E) zygote.
A
Multicellular haploid organisms
A) are typically called sporophytes.
B) produce new cells for growth by meiosis.
C) produce gametes by mitosis.
D) are found only in aquatic environments.
E) are the direct result of fertilization
C
Crossing over usually contributes to genetic variation by exchanging chromosomal segments between
A) sister chromatids of a chromosome.
B) chromatids of nonhomologues.
C) nonsister chromatids of homologues.
D) nonhomologous loci of the genome.
E) autosomes and sex chromosomes.
C
In comparing the typical life cycles of plants and animals, a stage found in plants but not in animals is a
A) gamete.
B) zygote.
C) multicellular diploid.
D) multicellular haploid.
C