Mel's aerobic and anaerobic respiration flashcards
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is respiration?
A catabolic process (breaks down large molecules into smaller ones) that releases energy (exergonic) in the form of ATP.
What type of bonds are broken during respiration?
High energy C-C, C-H, and C-OH bonds.
What happens to the energy released during respiration?
Most of the energy released during respiration is used to generate ATP.
Some is released as heat energy.
What is the role of enzymes in respiration? Give two examples.
Enzymes catalyze the reactions involved in breaking down respiratory substrates.
Dehydrogenase catalyses the removal of hydrogen atoms from substrates.
Decarboxylase catalyses the removal of carbon dioxide from substrates.
What does a cell use ATP for ?
1. active transport
2.DNA replication
3. Protein synthesis
4. endo/exocytosis
5. Muscle contraction (animal cells only)
What is glycolysis?
The breakdown of glucose into pyruvate.
Where does glycolysis take place?
In the cytoplasm of a cell.
Is glycolysis an aerobic or anaerobic process?
It is an anaerobic process.
It is the first part of both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Why is glucose phosporylated twice during glycolysis ?
Glucose is pretty unreactive.
It is phosphorylated to make it more reactive so it can be broken down.
Draw out glycolysis
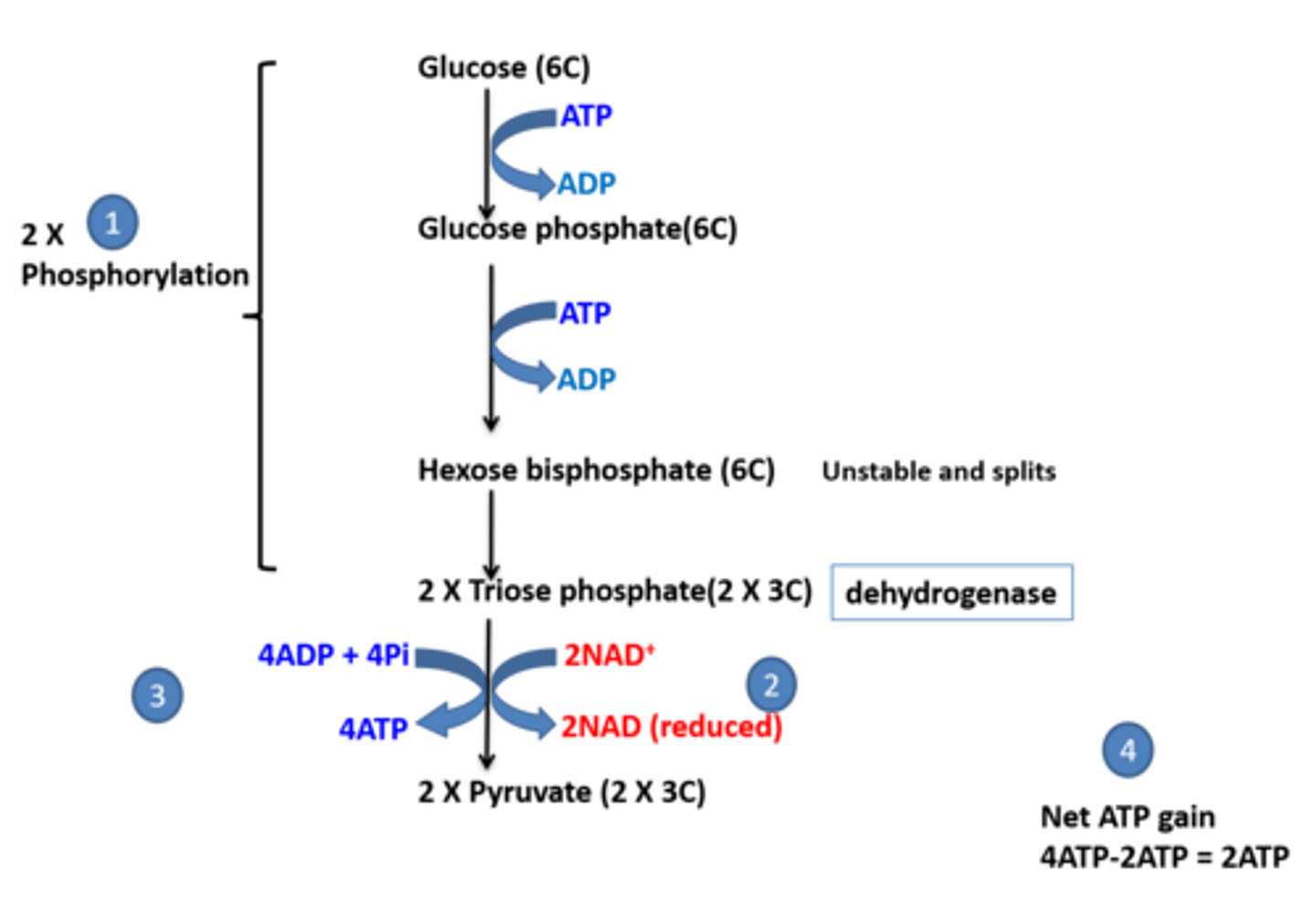
How is glucose phosphorylated during glycolysis ?
ATP is hydrolysed to ADP and Pi.
The Pi is added to glucose using the energy released from the hydroylsis (30.6 kj).
Glucose phosphate is produced
How is each triose phosphate molecule converted into a pyruvate molecule in glycolysis?
1. Dehydrogenase catalyses the removal of 2 hydrogen atoms from each triose phophate molecule.
2. This converts/oxidises the triose phosphate to pyruvate
What is the role of NAD in glycolysis ?
1. NAD is a co-enzyme
2. It has to be present for the enzyme dehydrogenase to work.
3. When dehdrogenase remove 2 hydrogen atoms from triose phosphate, NAD picks up these hydrogen atoms and becomes reduced NAD.
4. Reduced NAD carries the hydrogen atoms to oxidative phosphorylation and so is also a hyrogen carrier
How many ATP molecules are used and gained in glycolysis?
2 ATP are used and 4 ATP are gained.
This gives a net (overall) gain of 2 ATP molecules from glycolysis.
How is ATP produced during glycolysis ?
By substrate level phosphorylation
(Triose phosphate contains more energy in its bonds than pyruvate. When triose phosphate is converted/oxidised to pyruvate, the extra energy is released and used to instantly add a Pi to ADP to make ATP)
Draw out the link reaction
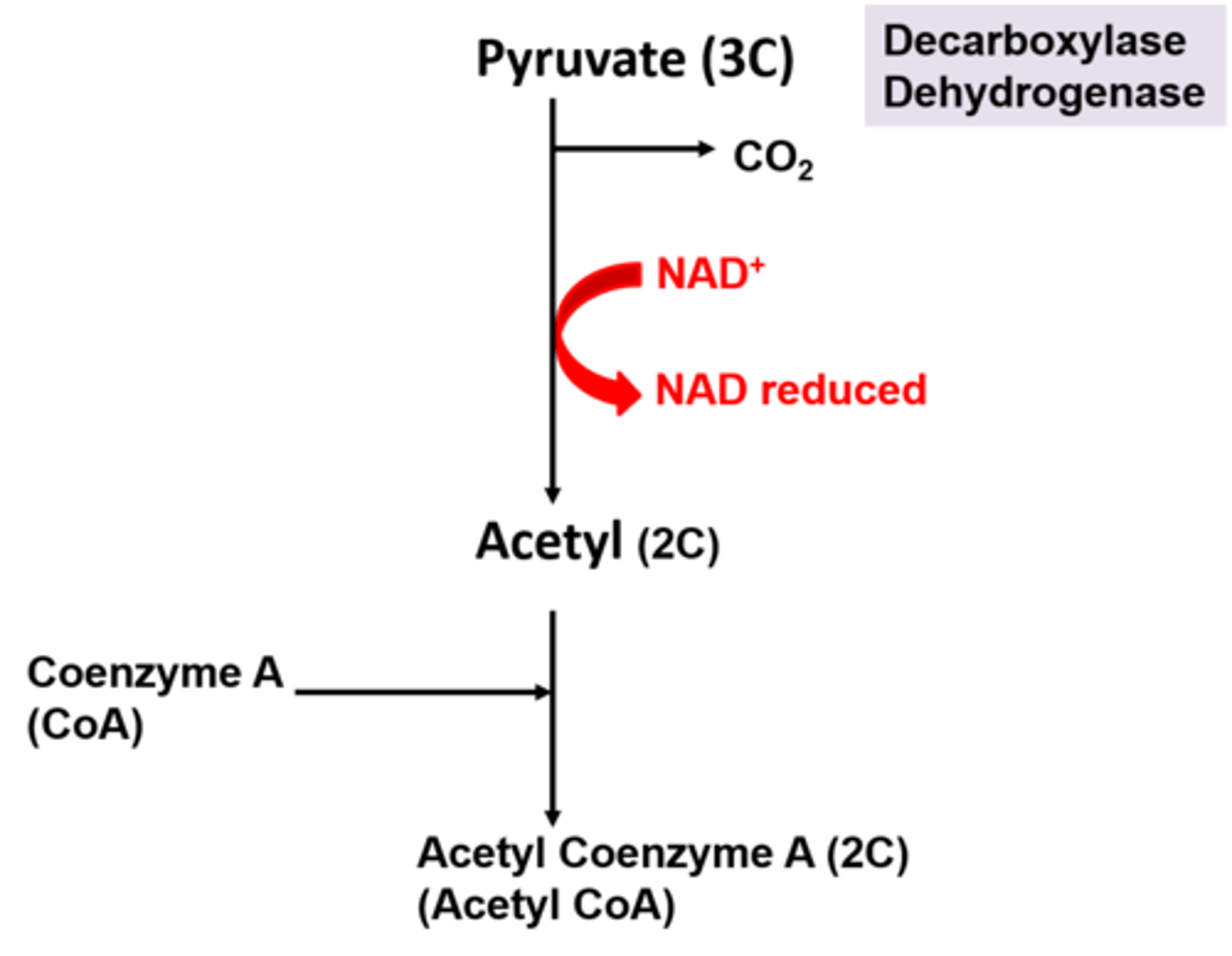
Where does the link reaction occur ?
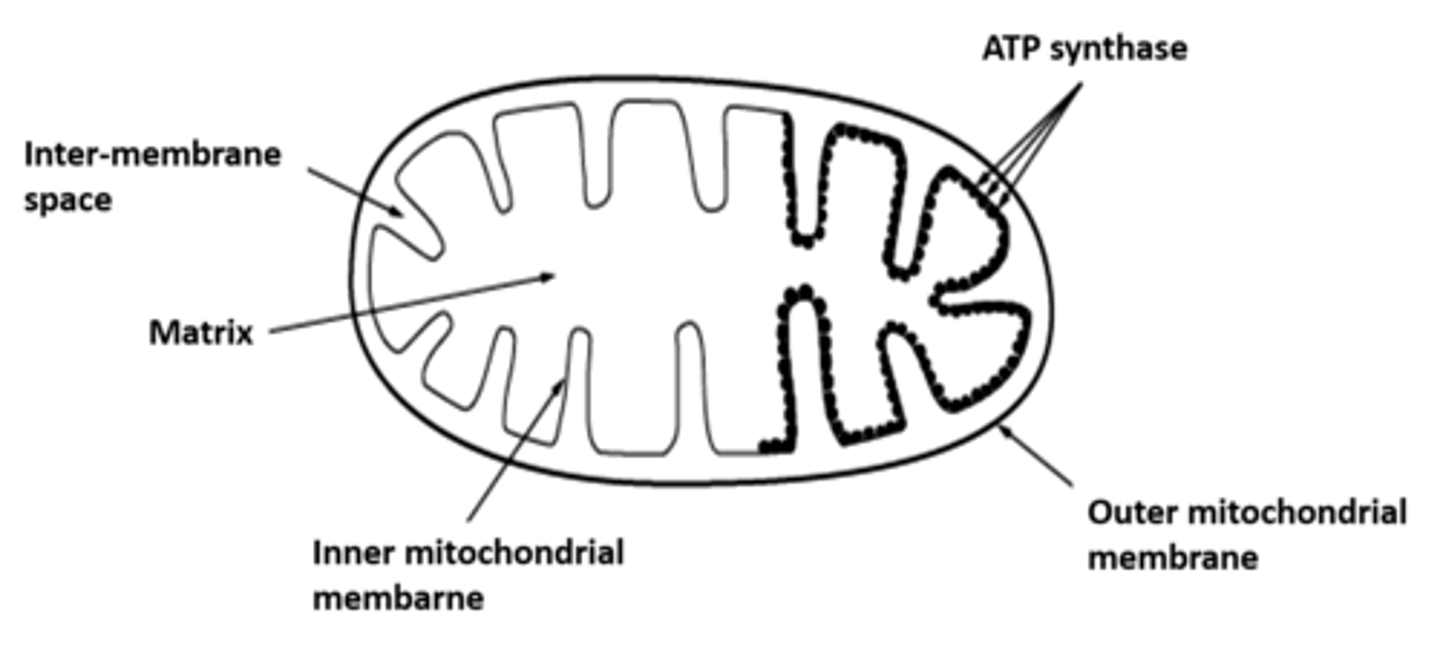
In the matrix of a mitochondrion.
(in the same cell where glycolysis has happened in its cytoplasm first !!)
What is the respiratory substrate of a mitochondrion ?
Pyruvate
The pyruvate has to first enter the mitochondrion from the cytoplasm where glycolysis took place.
Glucose cannot enter a mitochondrion (it's too large)
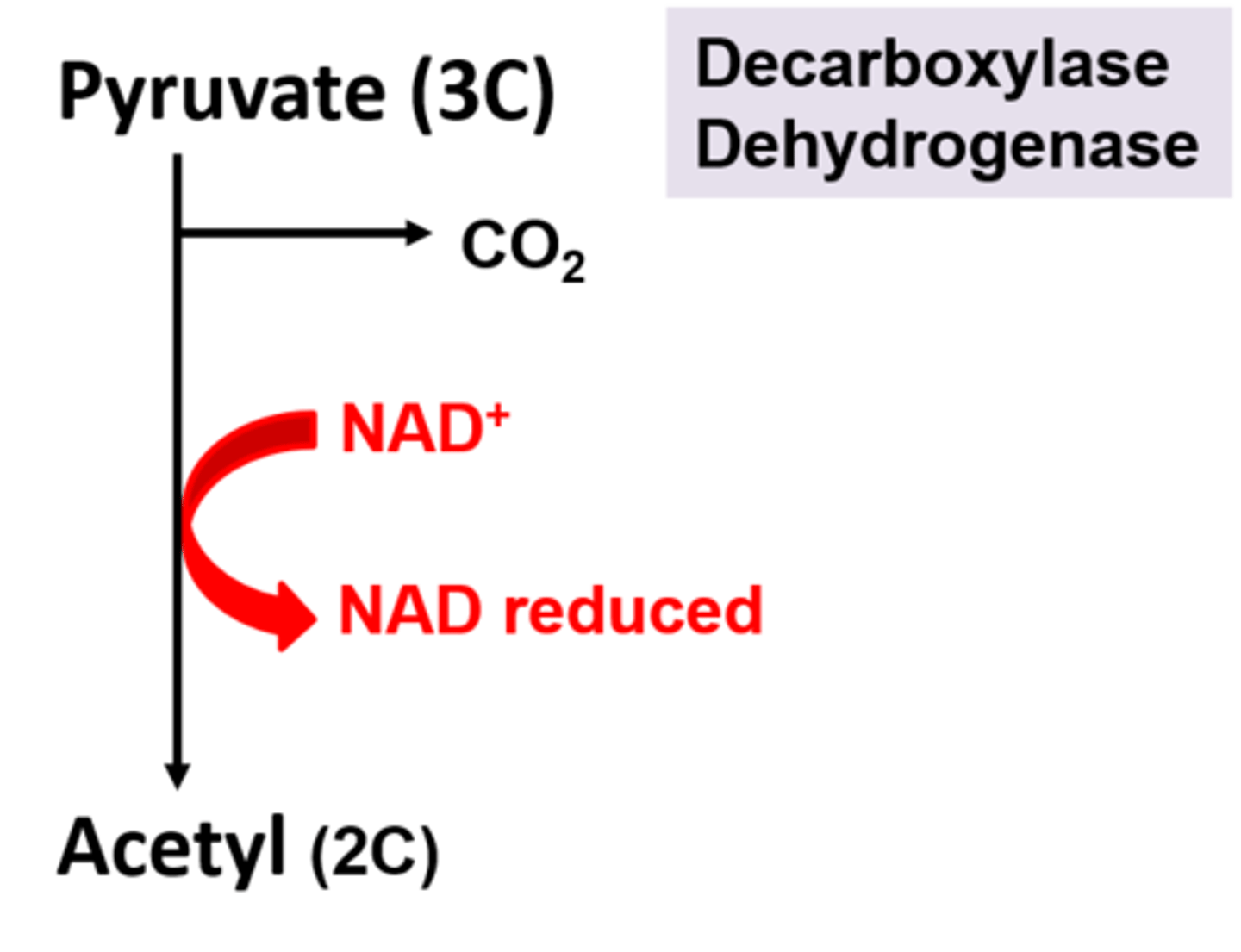
How is pyruvate (3C) converted into acetyl (2C) during the link reaction ?
Pyruvate (3C)
1. is decarboxylated (carbon dioxide removed) by decarboxylase.
2. Is dehydrogenated (hydrogen is removed) by dehydrogenase. The hydrogen is then taken up by NAD to form reduced NAD :
Both these events convert pyruvate into acetyl (2C)
What is the role of coenzyme A in the link reaction ?
Coenzyme A attaches to the acetyl (2C) and carries the acetyl to the Krebs cycle.
Where does the Krebs cycle occur ?
In the matrix of a mitochondrion
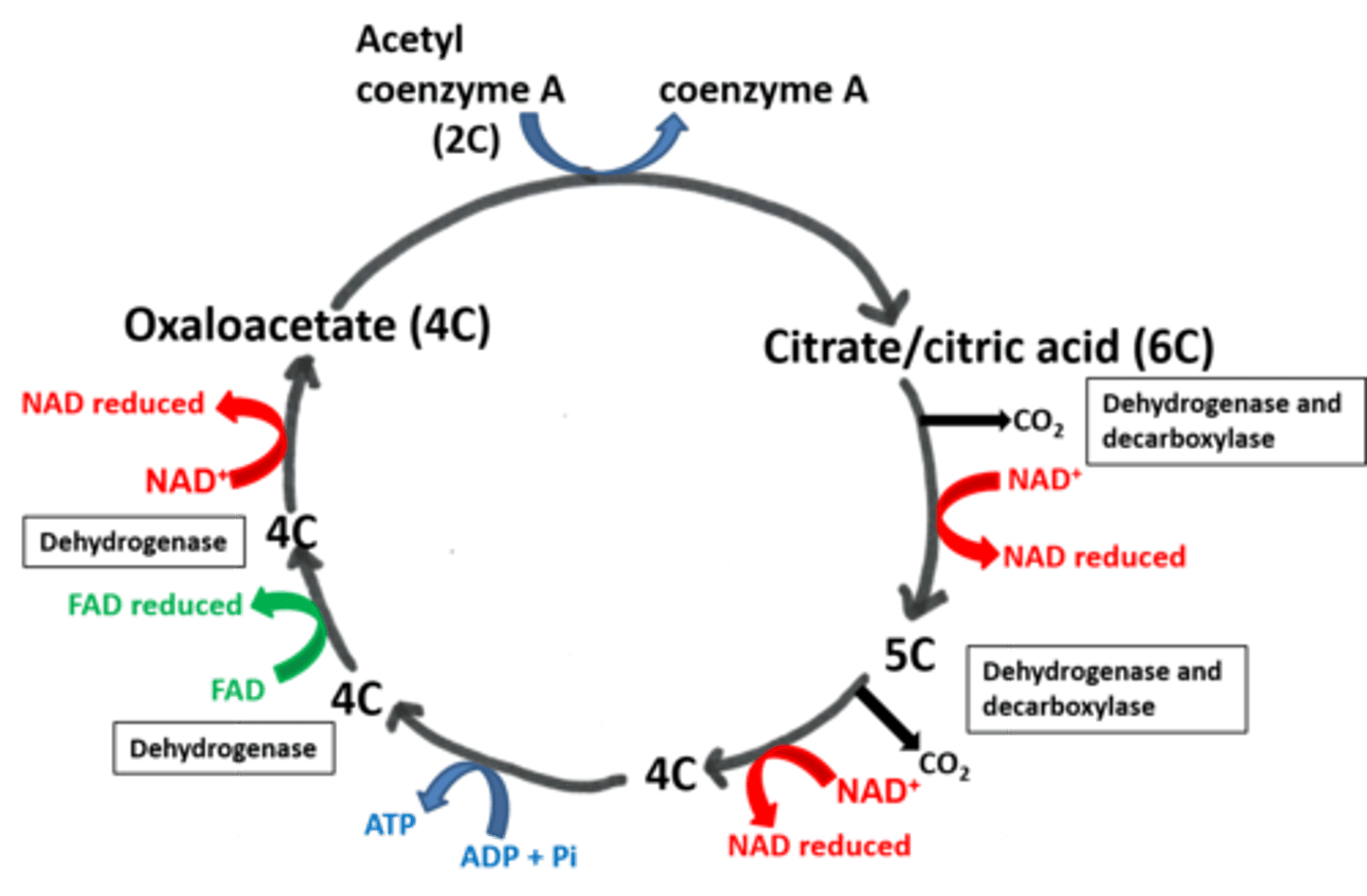
Draw out the Krebs cycle
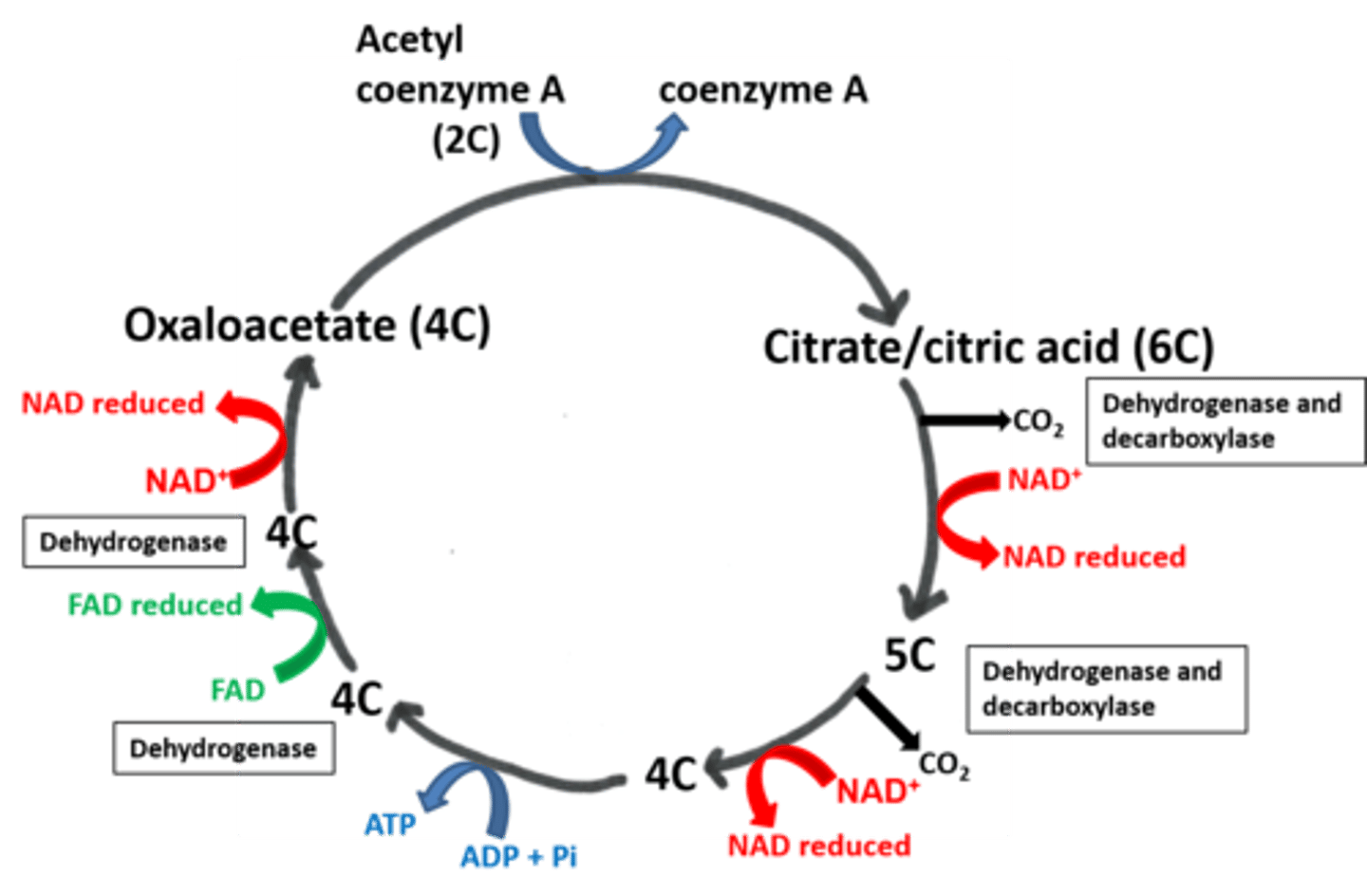
What happens when acetyl co-enzyme A enters the Krebs cycle?
Acetyl combines with a 4C compound (oxaloacetate) to produce a 6C compound (citric acid).
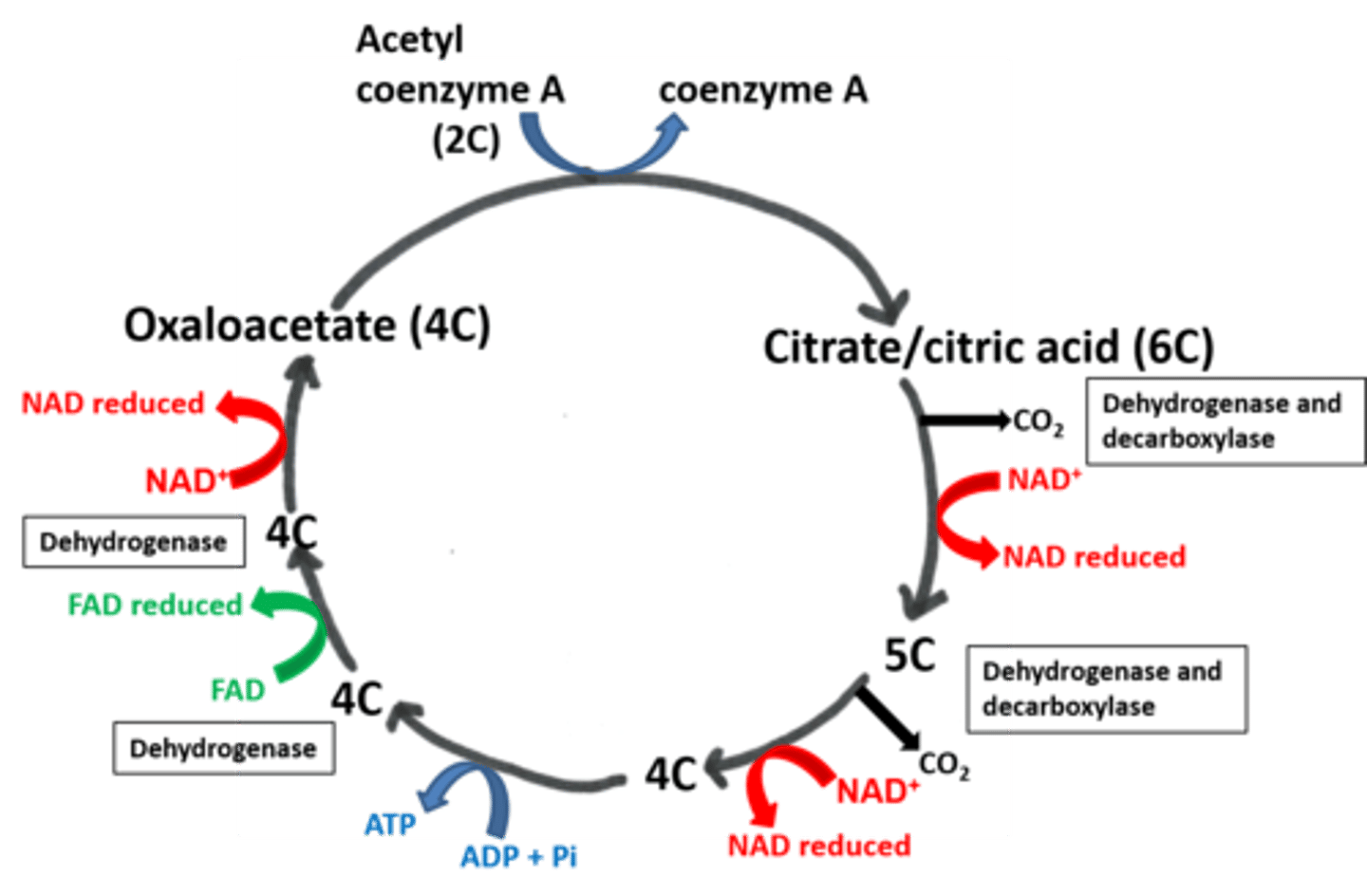
What is the main function of the Krebs cycle?
To release hydrogen atoms for ATP production via a series of dehyrogenations (using dehydrogenase).
The Hyrogen atoms are picked up by NAD/FAD and taken to oxidative phosphorylation
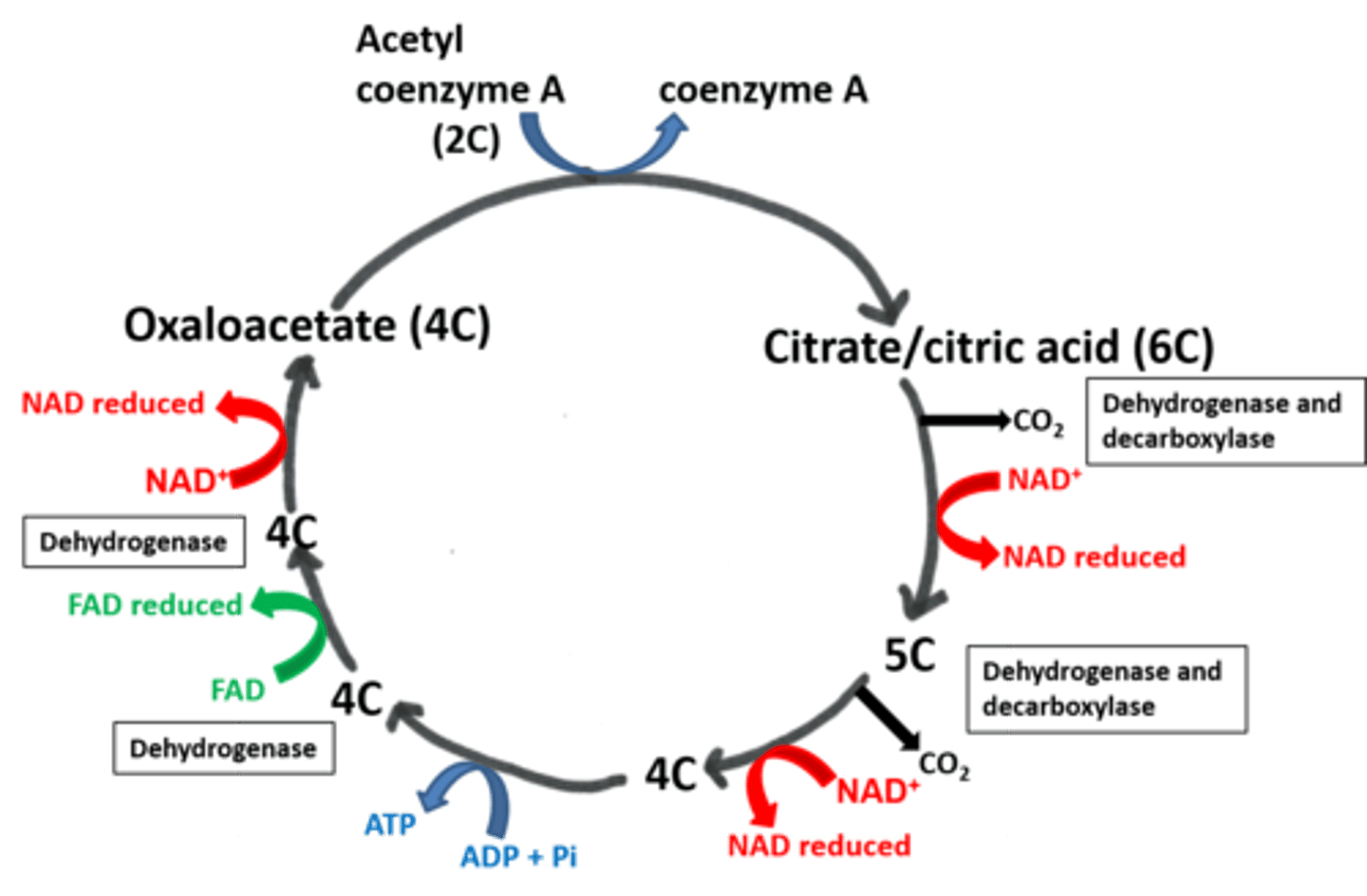
Where do the reduced NAD and reduced FAD deliver their hydrogen atoms?
To the electron transport chain.
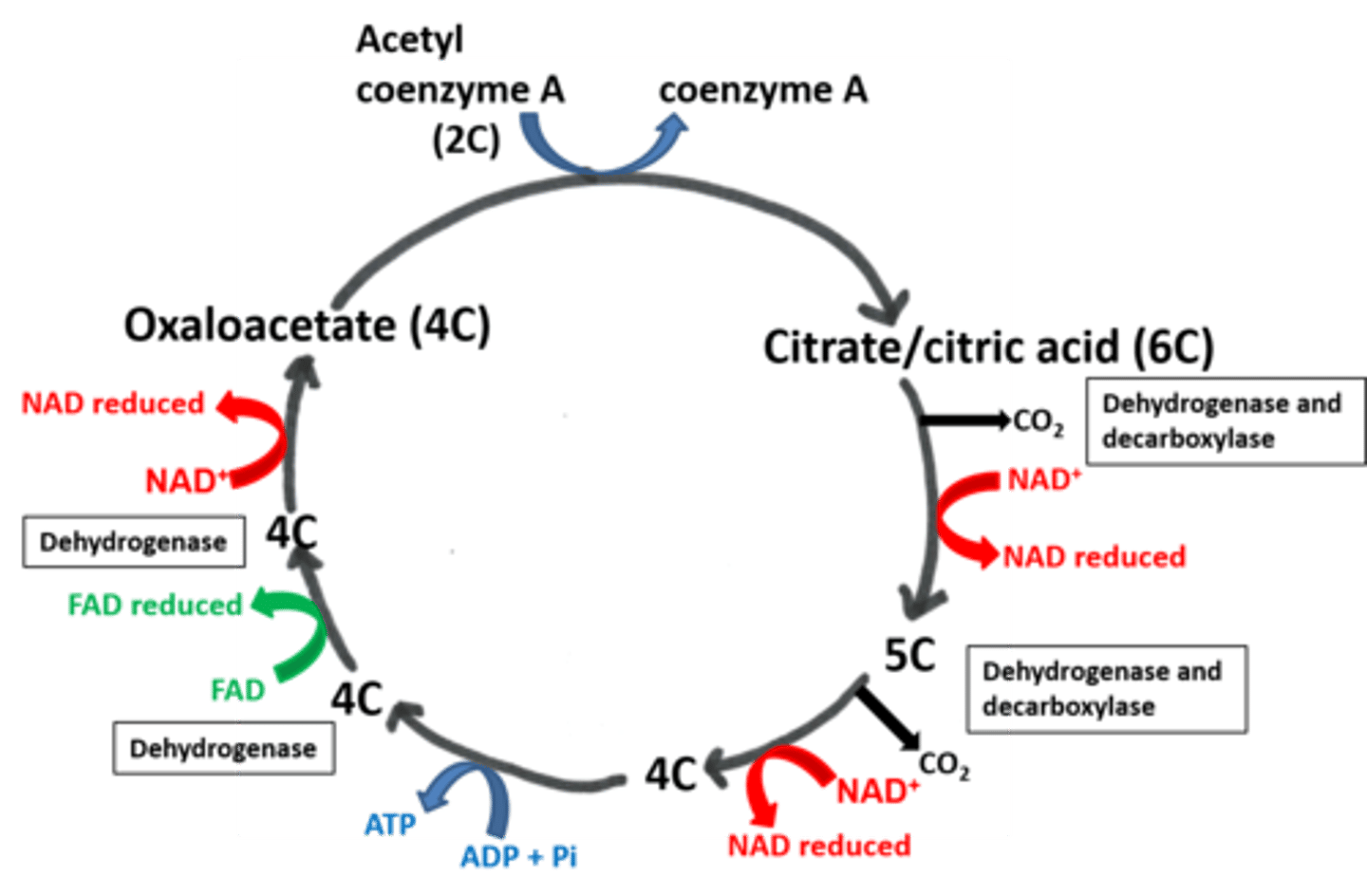
What are the two main processes involved in oxidative phosphorylation?
Electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
Where does oxidative phosphorylation occur?
On the inner membrane of the mitochondrion
Draw out oxidative phosphorylation !!!
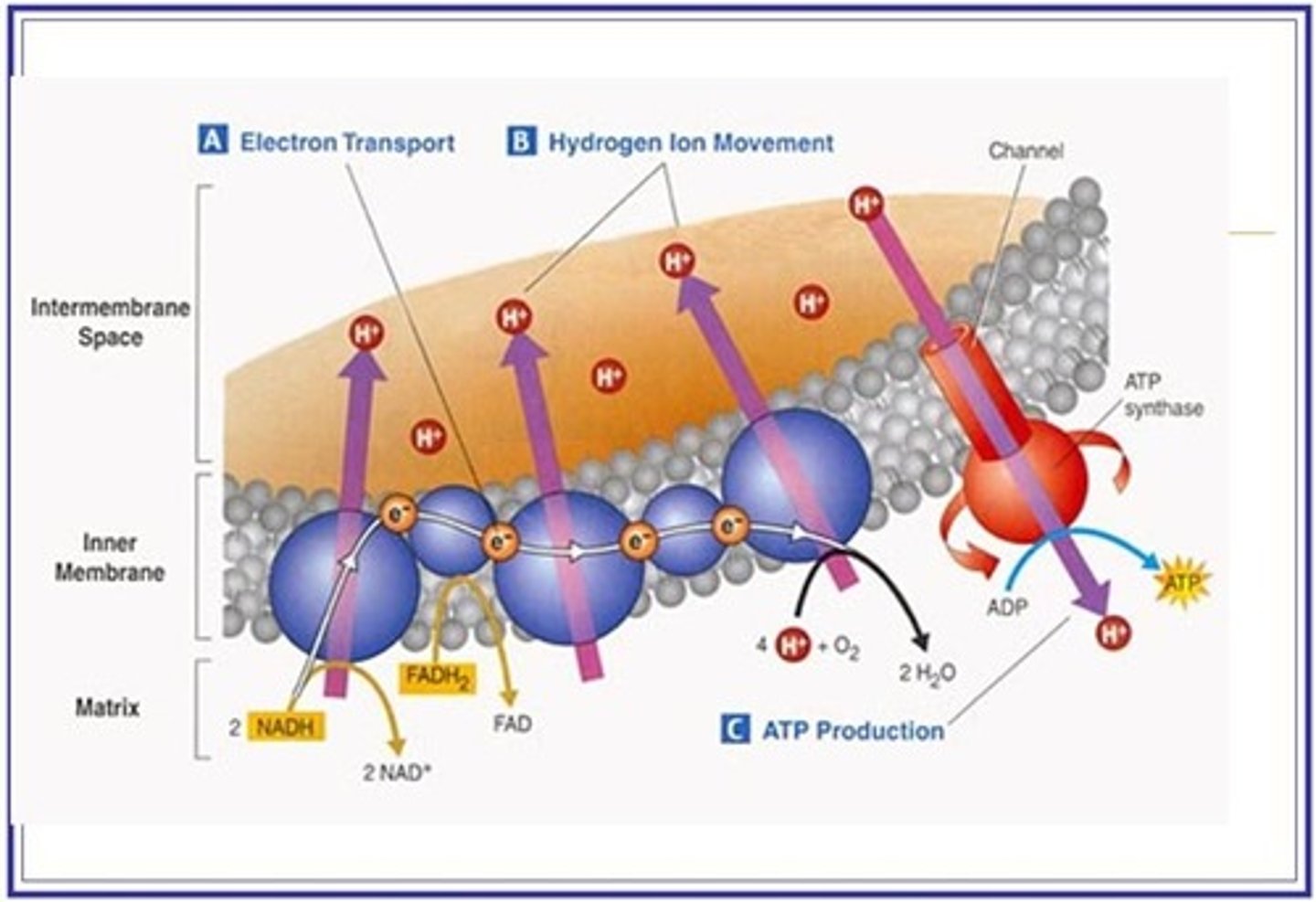
In oxidative phosphorylation - What happens to the hydrogen atoms delivered to the electron transport chain by reduced NAD and reduced FAD
1. Each hydrogen atom splits into an electron and a proton (hydrogen ion)
2. The protons wait in the matrix to be pumped.
3. The electrons go along the electron transport chain and release their energy.
4. the electron energy is used to fuel the proton pumps which actively transport the protons from the matrix to the intermembrane space.
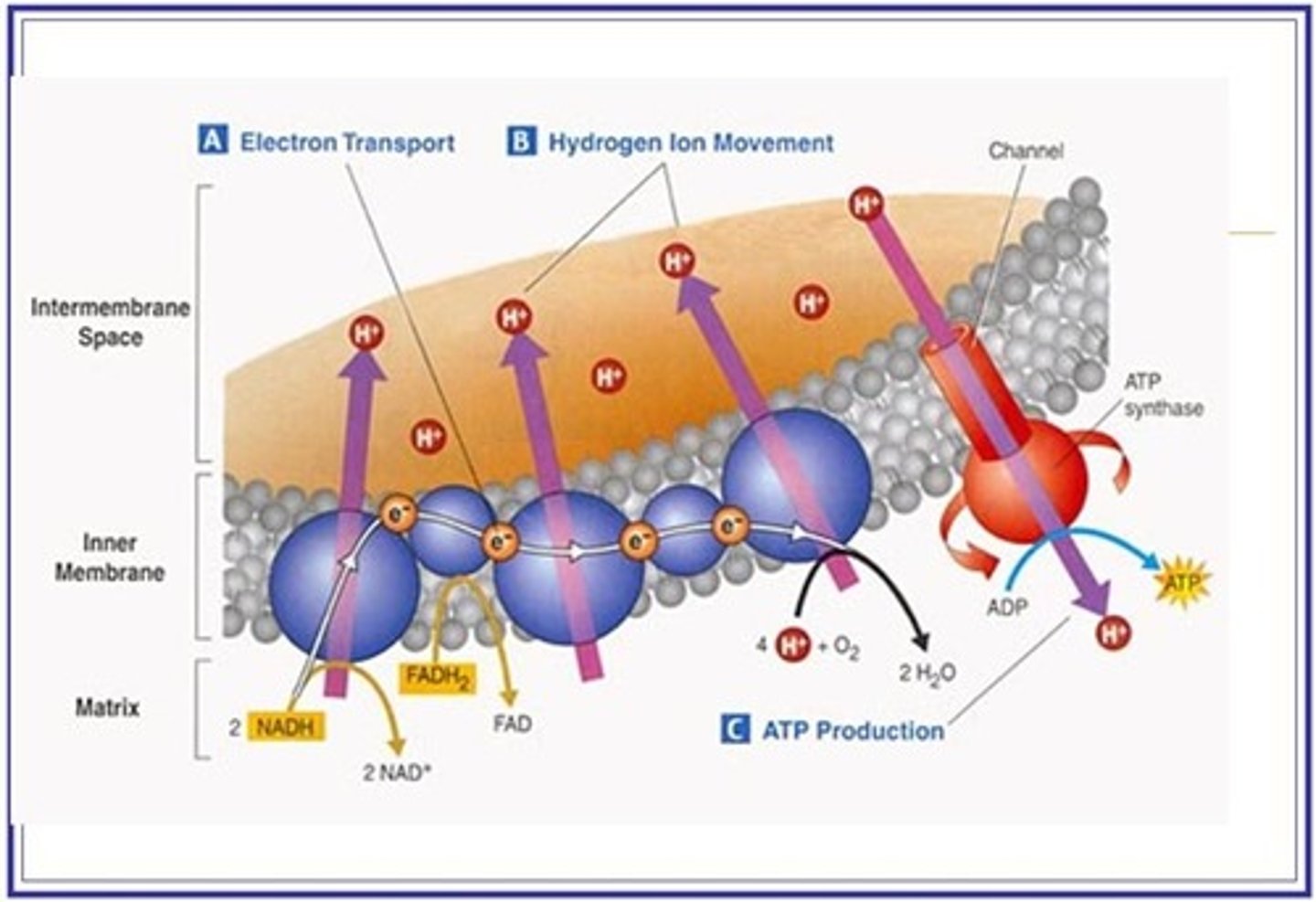
In oxidative phosphorylation - How is the high concentration of protons in the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion achieved ?
By the proton pumps actively transporting the protons into the intermembrane space from the matrix of the mitochondrion.
The energy to fuel the proton pumps comes from the electrons.
Describe chemiosmosis during oxidative phosphorylation
1. The protons diffuse down their electrochemical gradient through a stalked particle containing ATP synthase
2. from the intermembrane space
3. to the matrix
4. As the protons pass through ATP synthase, ATP is generated from ADP and Pi.
What is the final electron acceptor in oxidative phosphorylation?
Oxygen
Oxygen picks up the electrons at the end of the electron transport chain and 2 protons entering the matrix.
Water is formed
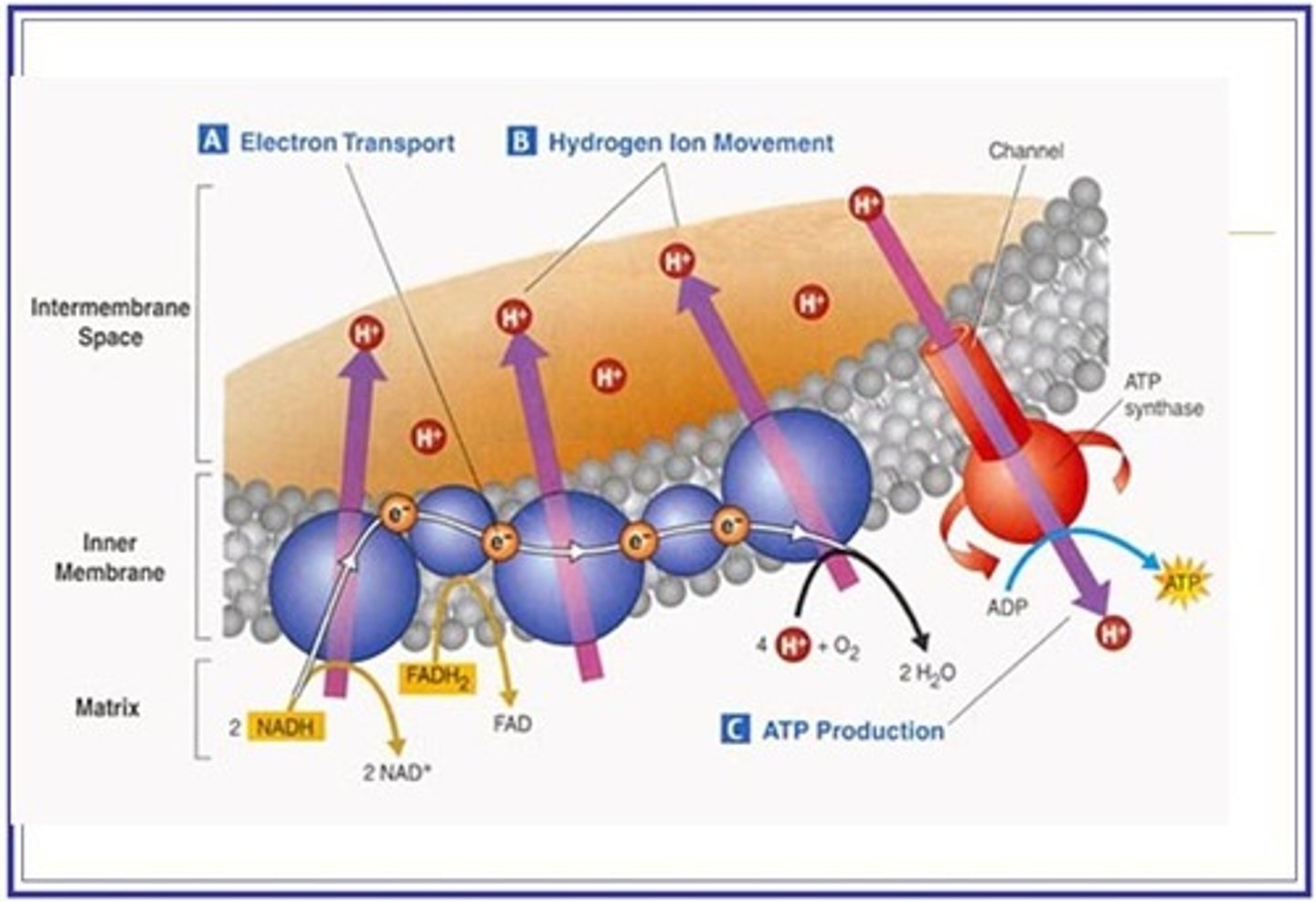
Why does every reduced NAD arriving at the electron transport chain produce 3 ATPs but each reduced FAD only produces 2 ATPs ?
The electrons from each reduced NAD pass and operate 3 proton pumps while electrons from reduced FAD only use two proton pumps
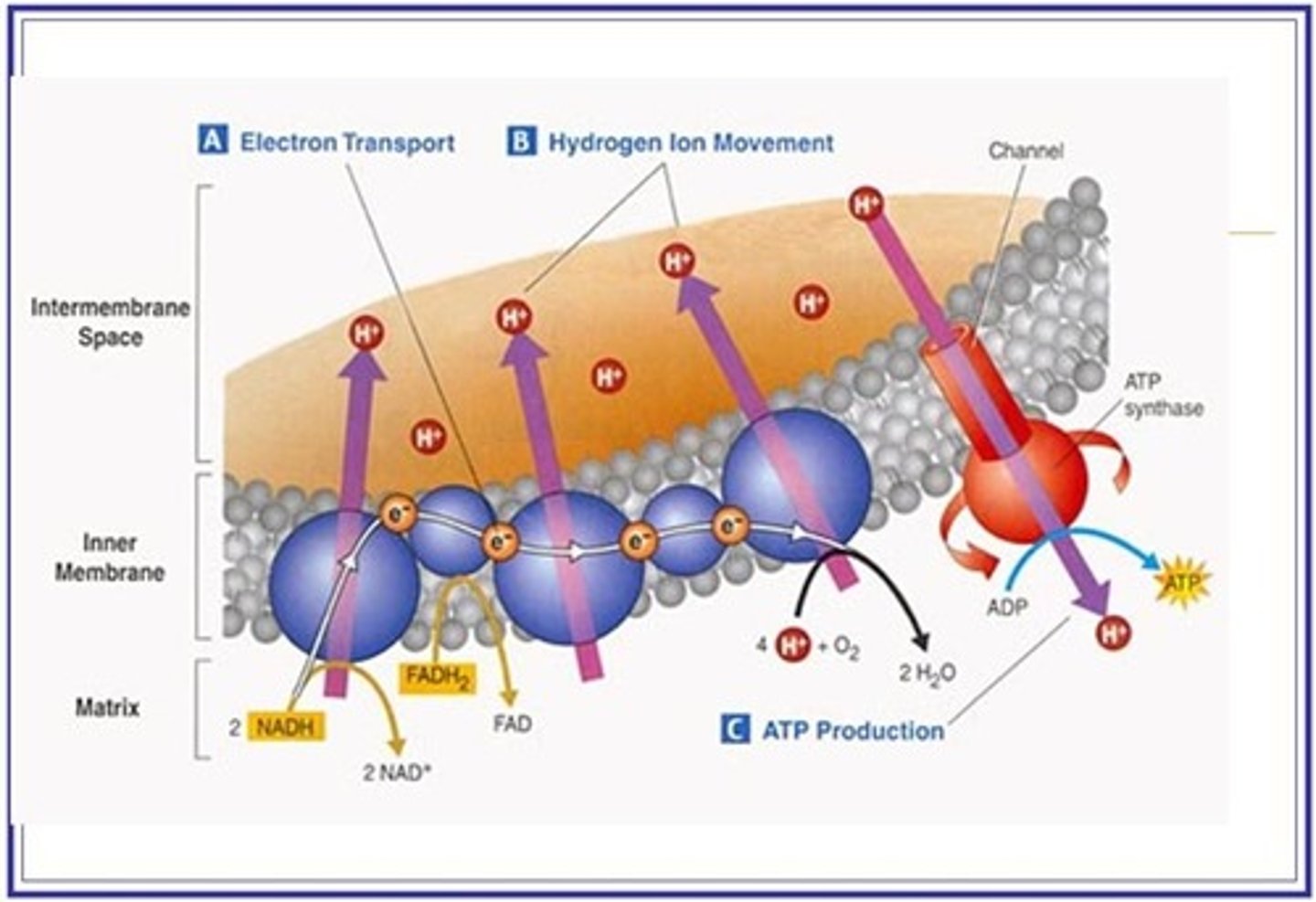
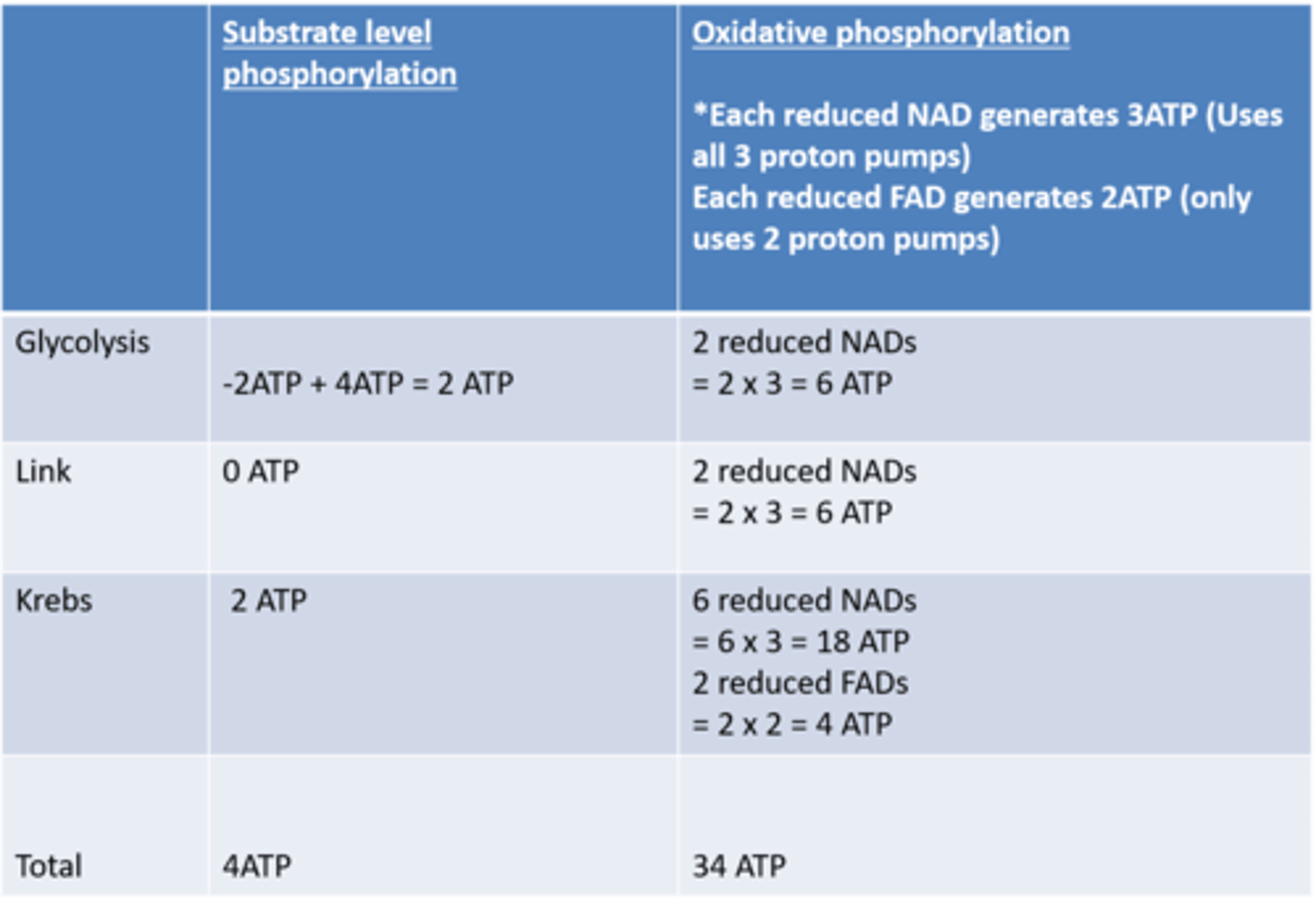
How and where are the 38 ATP molecules generated in aerobic respiration ?
What happens if oxygen is not available to a cell?
The cell may be able to do anaerobic respiration
What happens to the electron transport chain if oxygen is not available?
The electron transport chain will stop.
(Oxygen will not be able to pick up the electrons at the end of the electron transport chain which therefore ceases to operate).
What happens to the reduced NAD made in link and Krebs if oxygen is not available?
The reduced NAD cannot unload their hydrogen atoms at the electron transport chain.
NAD will run out.
Krebs and Link reaction stop due to the lack of NAD
What happens to glycolysis if oxygen is not available?
Glycolysis would also stop due to no NAD, but the cell may be able to do anaerobic respiration instead
What does anaerobic respiration consist of ?
Glycolysis then fermentation
(fermentation is a way of making some NAD available so glycolysis can continue and generate 2 ATPs)
Draw out anaerobic respration in a human muscle cell
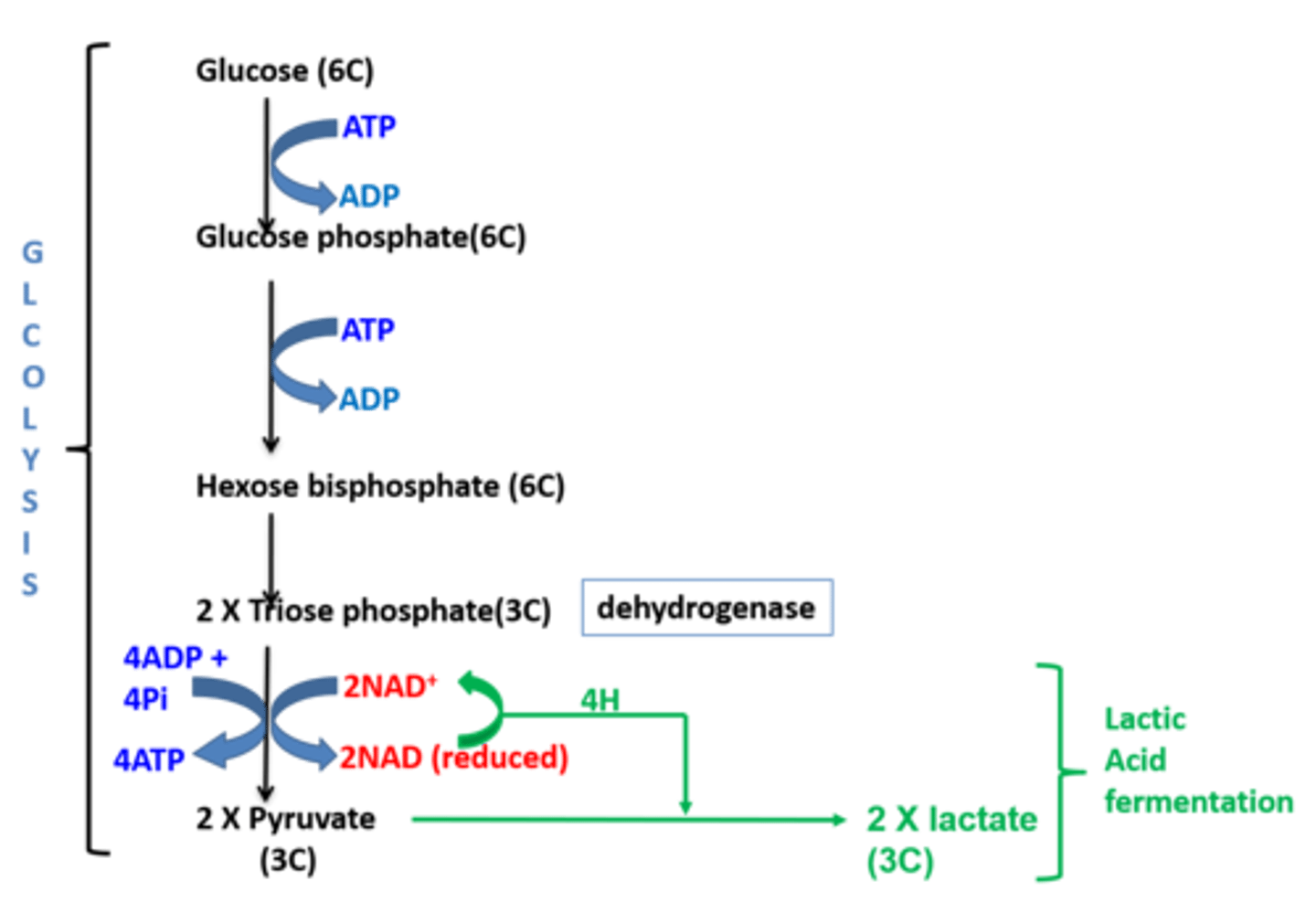
How is glycolsis able to continue (without oxygen available) as a result of lactic acid fermentation ?
1. The reduced NAD gives its hyrogen to Pyruvate.
2. This coverts the pyruvate to lactic acid.
3. The NAD has been oxidised and can accept more hydrogen from triose phosphate to keep glycolysis going.
4. That means 2 ATP can continue to be produced by glycolysis.
(This happens repeatedly.)
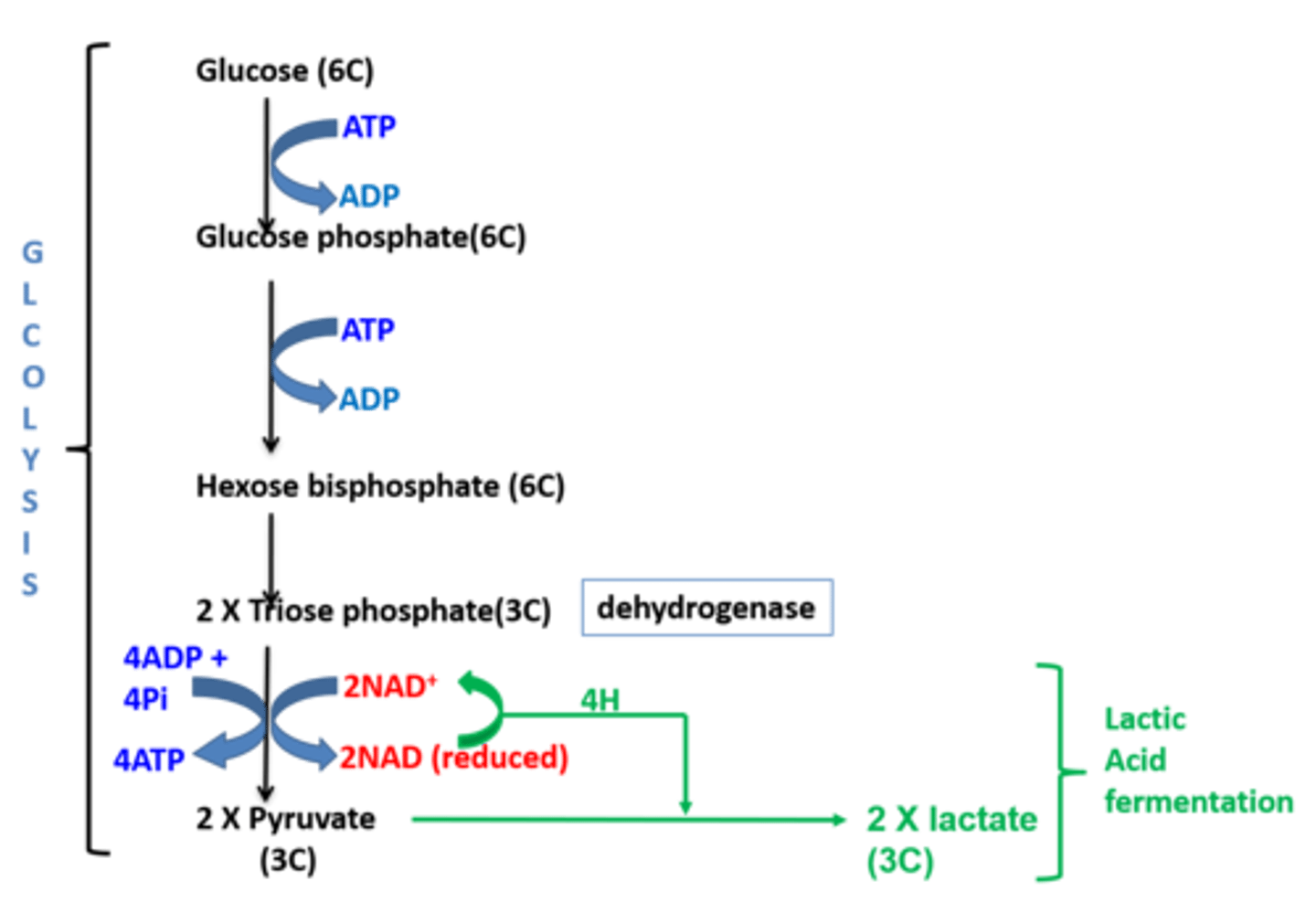
Why is important to a cell that anaerobic respiration can occur ?
The cell at least gets the 2 ATP from glycolysis (repeatedly).
(In human muscle cells this may allow us to keep running and get out of danger !)
Draw out anaerobic respiration in yeast cells/ plant cells
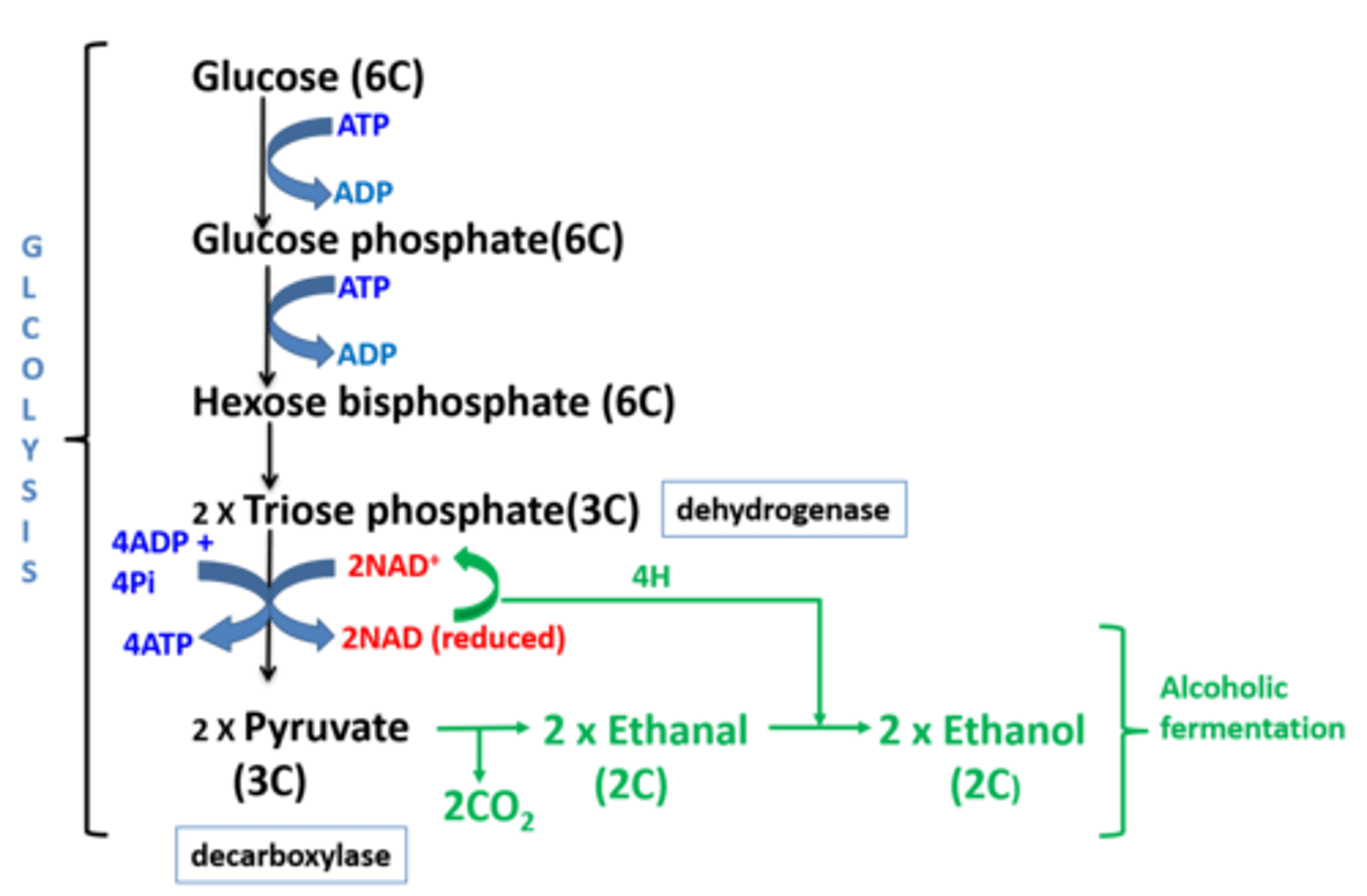
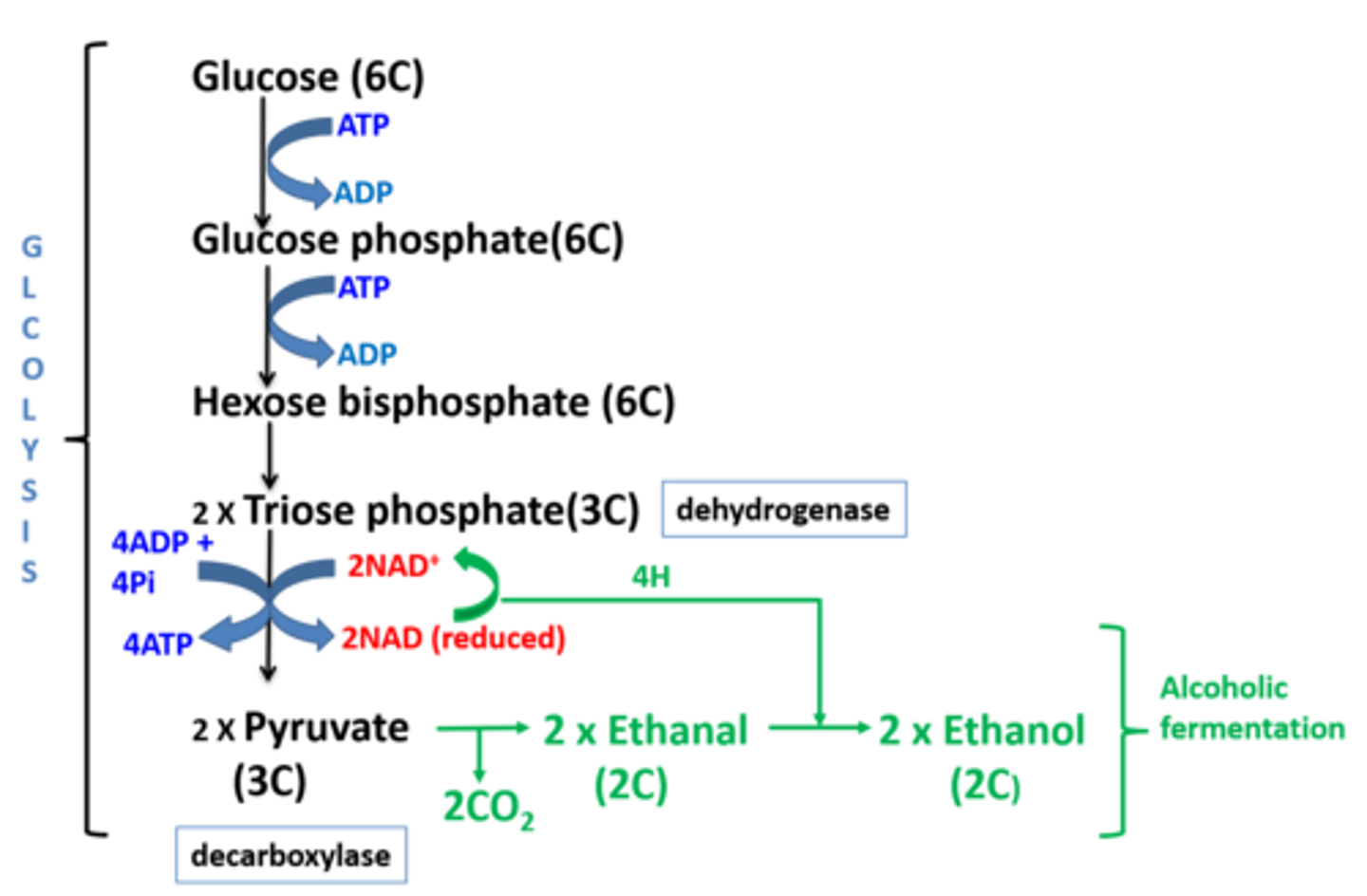
How is glycolysis able to continue (without oxygen available) as a result of alcohol fermentation ?
1. Pyruvate (3C) is first decarboxylated (by decarboxylase) to produce ethanal (2C).
2. The reduced NAD gives its hydrogen to ethanal which then forms ethanol
3. The NAD is now oxidised/free to accept more hydrogen from triose phosphate and keep glycolysis going .
4. 2ATP can keep being produced from glycolysis this way
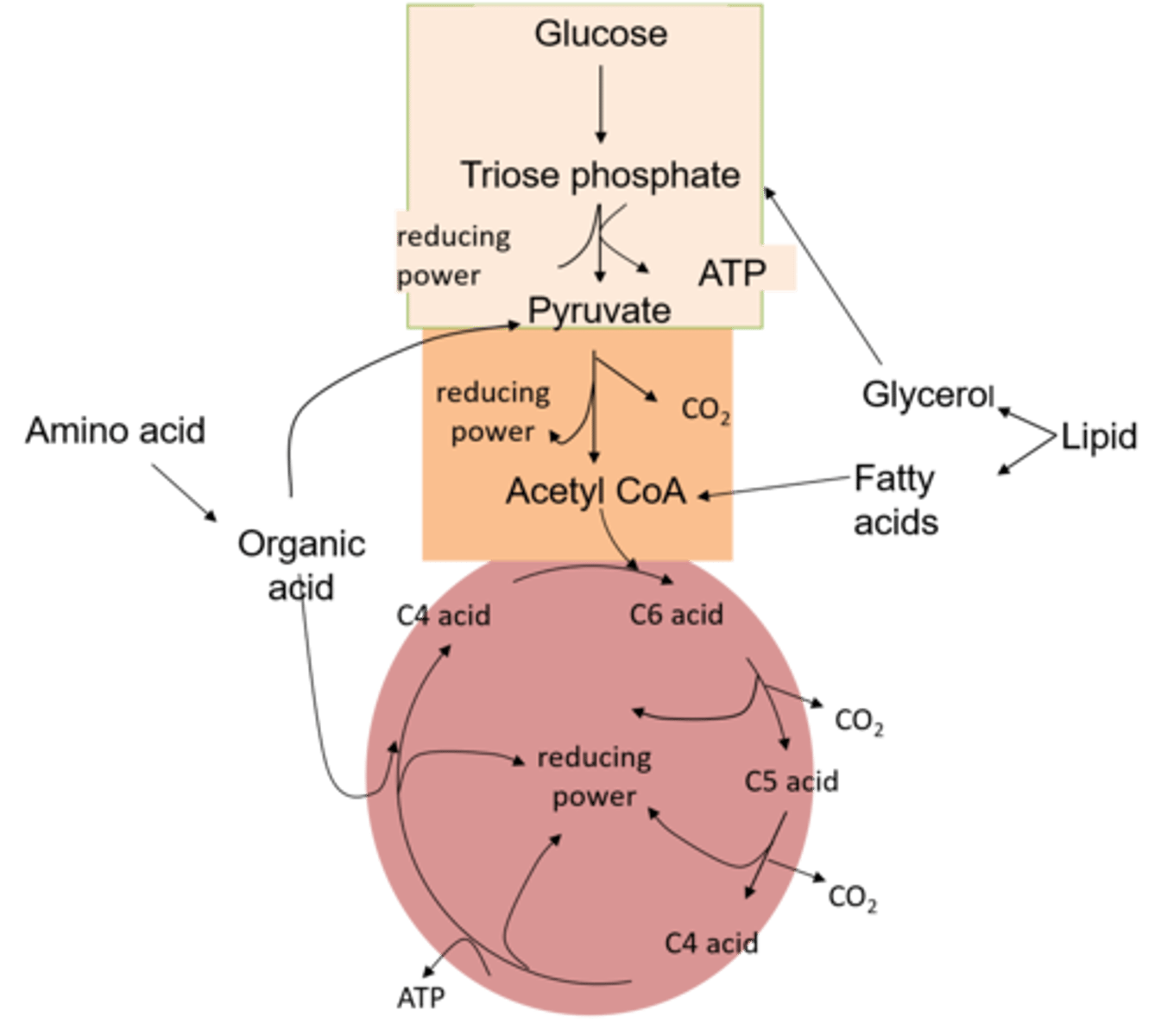
What is a respiratory substrate?
An organic molecule that can be respired to produce ATP.
eg glucose !!!
What happens to protein before they can be respired ?
1. Proteins are first hyrolysed (by proteases) into amino acids.
How are amino acids repired ?
1. They are deaminated to produce keto acid (and urea).
2. The keto acid is fed in as pyruvate or as one of the acids in the krebs cycle.
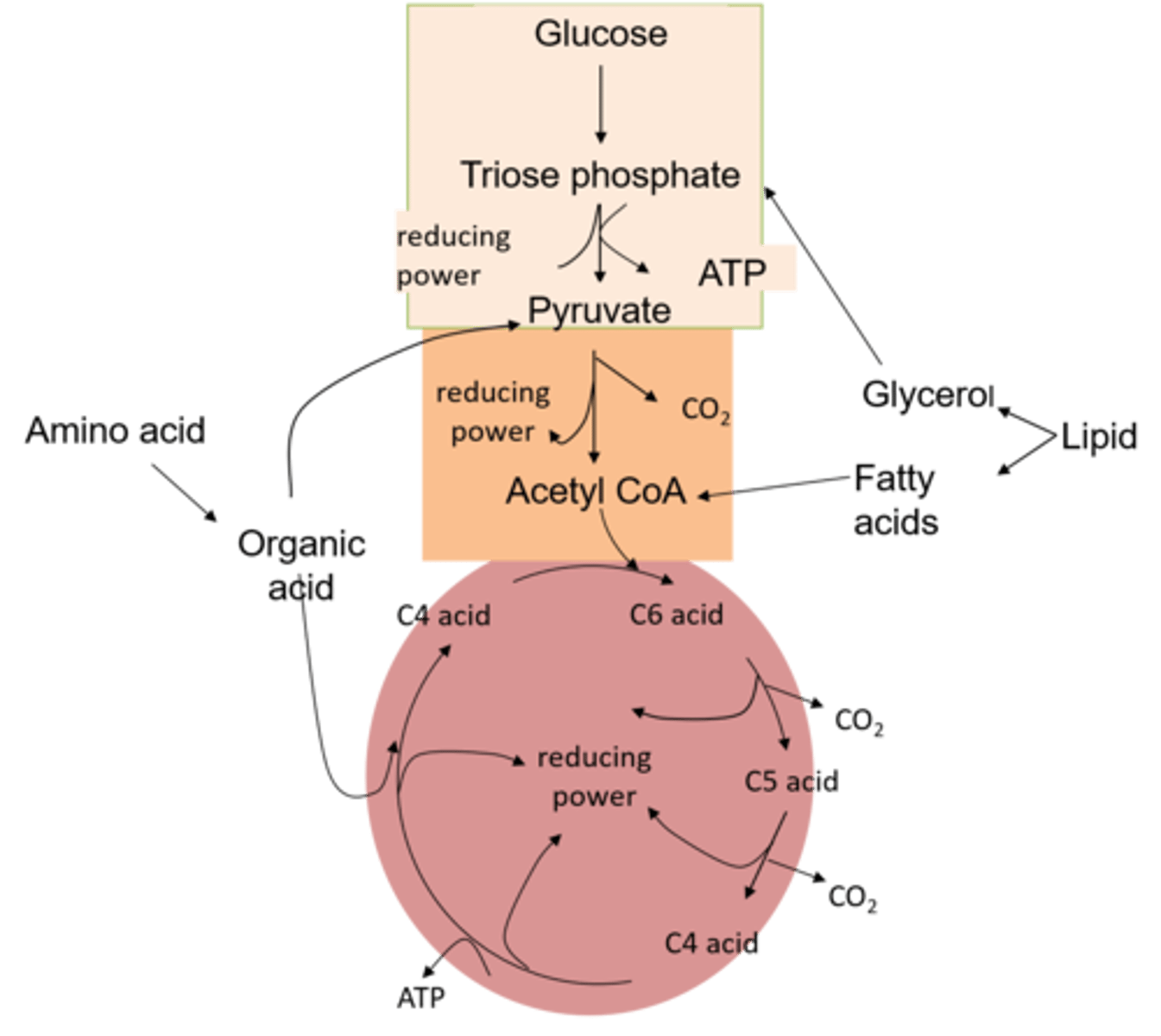
What must happen to lipids before they can be respired ?
1. Lipids must first be hydrolsed (by lipase) to produce glycerol and fatty acids.
How is glycerol respired ?
The glycerol is converted to triose phosphate and fed into glycolysis.
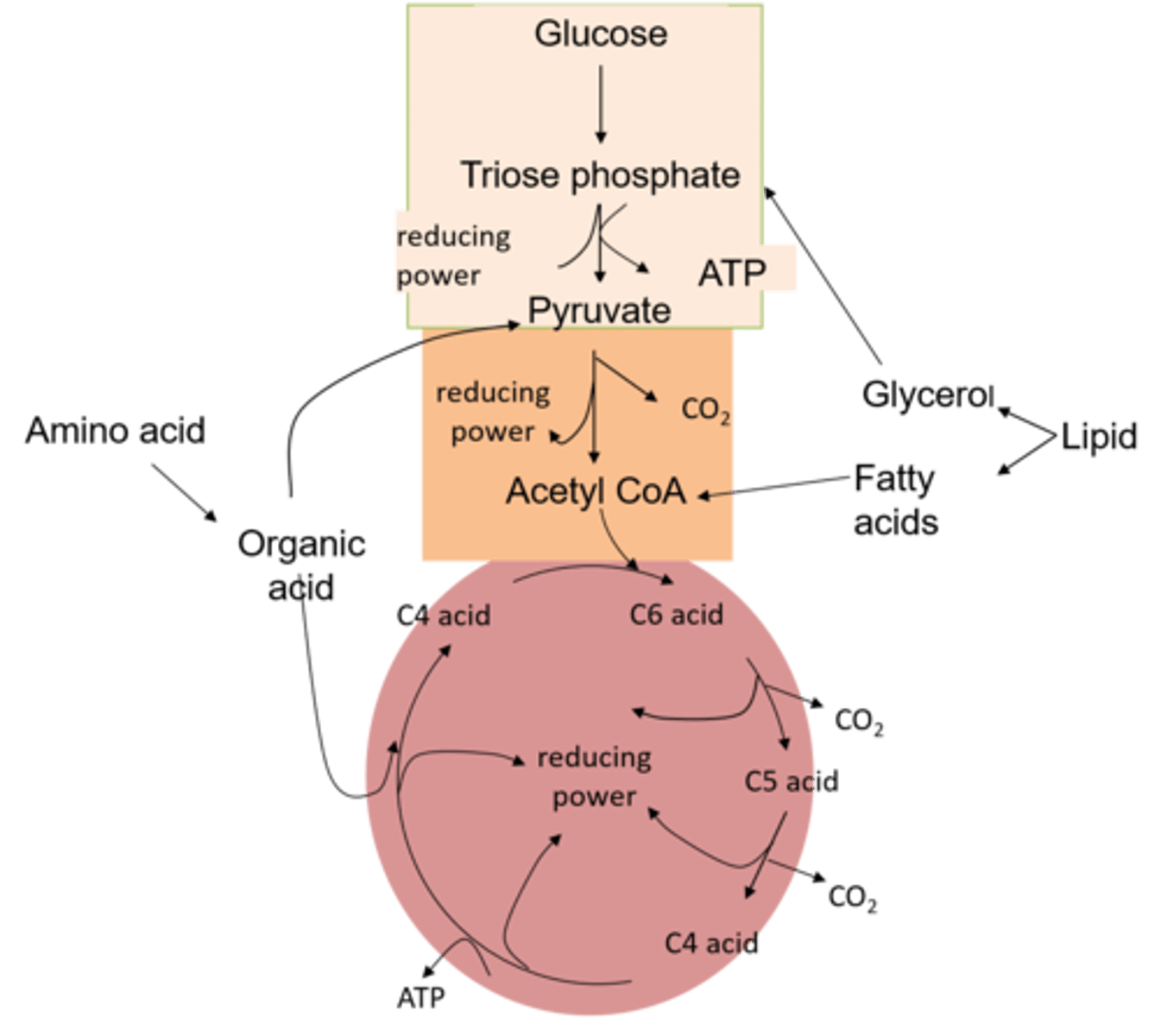
How are fatty acids respired ?
The fatty acids are split into 2C acetyl fragments and fed into the Krebs cycle as acetyl CoA.
Draw and label a mitochondrion