TRIPLE Astrophysics part 3: Cosmology
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Astrophysics 3
The evolution of the Universe
What is the Big Bang theory?
It states that at some time in the past, all the matter in the Universe was in one place and then it suddenly exploded and the Universe has been expanding ever since.
Estimate que nuestro universe is abut 14 billion years old
Describe how the size and temperature of the universe have changed since the Big Bang
Universe is expaning
Universe is cooling
What are the main arguments in favour of the Big Bang theory?
The red shift of galaxies
The Cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR)
NOTE: Always refer to the redshift of GALAXIES not just redshift.
Also they condone stars as galaxies (aunque preferiblemente no hagas eso) but they don’t if you say planets
State what is meant by redshift (2)
Textboook definition: emitted waves have their wavelength increased, that is moved to the end of the spectrum
The fractional increase in wavelength
Due to the source and observer moving away/receding from eachother
Describe how the ‘red shift of galaxies’ supports the Big Bang theory (4)
MP0: If question was ‘discuss two pieces of evidence that support the Big Bang theory’ a mark would just come from idetifying the existence of the red shift of galaxies meaning that the wavelengths of the light they emit have become longer
MP2: The further the galaxy is from Earth the greater the red shift
MP3: Larger redshift means faster movement of galaxies
MP4: Therefore the further away, the faster the galaxy is moving away from the Earth
accept speed of galaxy increases (is directly proportional to) with increased distance.
MP5: Galaxies moving apart from each other implies expansion from a single point or since the Big Bang
accept ‘relationship between speed and distance’ for ‘galaxies moving apart from each other’
NOT IN MS: almost all the galaxies emit light with red shift
If we observe the light spectra for other galaxies we can see that the wavelenghts of the light they emit have become longer

Describe the red-shift in light received from galaxies at diff distances away from the Earth and expklain why they move at diff velocitites
The further away a galaxy is the greater the red-shift so therefore the faster it is moving away from us = the matter that makes up this galaxy is lighter as it has moved a greater distance (faster)
What is the Doppler effect in this case?
When something that emits a wave (a wave source e.g a galaxy) is moving relative to an observer there will be a change in the observed frequency and wavelength.
If the source is moving away from the observer, then the wavelength of the sound will become longer and the frequency lower. However the opposite happens when it is moving towards the observer
NOTE: The Doppler effect is a property of all waves. It happens not only with sound waves but also with light waves
Light from galaxy B has twice the redshift as light from galaxy A. Galaxy B is twice as far away from Earth as galaxy A.
Explain how these observations support the Big Bang theory of the origin of the Universe (3)
Explain why the red-shift of galaxies provides evidence for the expansion of the universe (same question)
MP1: link between twice the redshift and twice the speed
condone larger redshift means larger speed (redshift and speed are directly proportional)
MP2: link between larger speed and larger distance;
MP3: (which in turn means that) galaxies are moving apart /moving away/receding from each other;
More distant galaxies have greater red-shift and therefore are receding faster because the space between all galaxies is stretching as the universe expands.

While redshift indicates that the source of light waves is moving away from the observer, blue-shift would indicate that the source is moving towards the observer
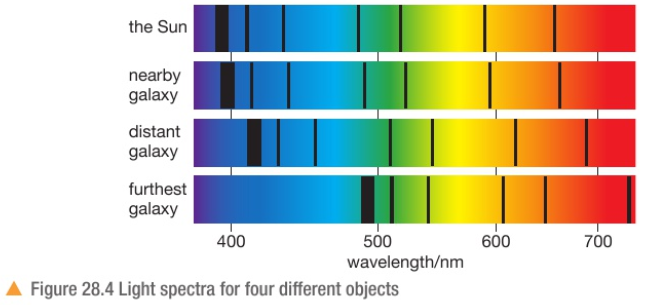
This shows the spectra from 4 diff objects. The dark lines are called absorption lines and are the frequencies of light that have been absorbed by hydrogen (basicamente es como si esa parte del light haya desaparecido) y asi podemos ver el wavelength del light emitted
What is the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation?
These were high frequency radiation waves that were stretched over time as the universe expanded and became much longer wavelengths than before, and are now in the microwave region of the spectrum
Describe how the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation supports the Big Bang theory
MP0: If question was ‘discuss two pieces of evidence that support the Big Bang theory’ a mark would just come from idetifying the existence of cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR)
MP1: CMBR appears to be the same in all directions/everywhwere
MP2: which implies all the parts of the Universe were in contact a long time ago
allow idea of coming from a single point
MP3: wavelength has increased as the universe has expanded
allow ‘frequency has decreased as the universe has expanded’
MP4: universe was (significantly) hotter long ago
Explain further the CMBR
Scientists looked for something else that might connect with an explosion: the release of energy (in this case in the form of waves)
But as the universe expands these radiation waves stretched from having very short wavelengths to long ones that they would be in the microwave part of the EM spectrum.
In the 1960s scientists detected this afterglow of energy and as predicted, these were microwaves that could be detected in all directions of the universe/everywhere in the universe
Why were the scientists unable to test for their theory of the CMB radiation sooner?
Microwaves are absorbed by the atnosphere.
Around this time, space flight was developed which enabked astronomers to send telescopes into orbit above the atmosphere
Equation to calculate the speed at which a star or galaxy is moving relative to us (the Doppler equation)


