Chapter 7 Knowledge Management and Specialised Information Systems
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Knowledge Management Systems (KMS)
Data consists of raw facts
Information
Collection of facts organisation so that they have additional value beyond the value of the facts themselves
Knowledge
Awareness and understanding of set of information and the ways that information can be made useful to support a specific tasks or reach a decision
Knowledge Management Systems part 2
Organise collection of people, procedures, software, databases and devices
Used to create, store, share, and use the organisation’s knowledge and experience
Explicit Knowledge
Objective
Can be measured and documented in reports, papers and rules
Tacit Knowledge
Hard to measure and document
Typically not objective or formalised
Data and Knowledge Management Workers and Communities of Practice
Data workers
Secretaries, administrative assistants, book keepers and etc
Knowledge workers
Create use and disseminate knowledge
Professionals in science, engineers or business
Data and KM Workers and Communities of Practice part 2
Chief Knowledge Officer (CKO)
Top-level executive who helps the organisation use a KMS to create, store and use knowledge to achieve organisation goals
Communities of Practice (COP)
Group of people dedicated to a common discipline or practice
May be used to create, store and share knowledge
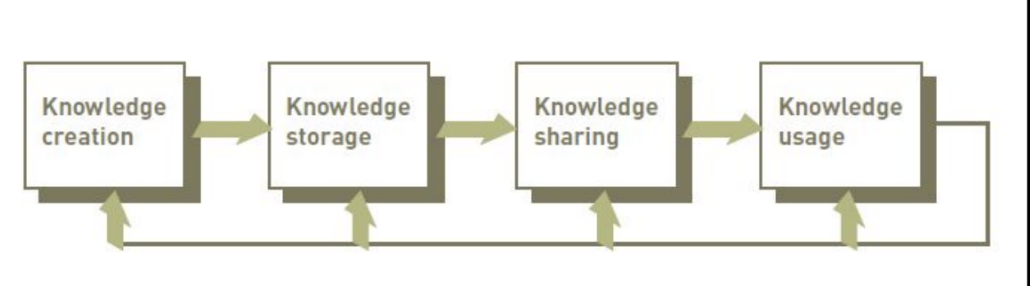
Obtaining, Storing, Sharing and Using Knowledge
Knowledge Workers
Often works in teams
Knowledge Repository
Includes documents, reports, files and databases
Knowledge Maps
Directory that points the knowledge worker to the needed knowledge
Technology to Support Knowledge Management
Effective KMS
Based on learning new knowledge and changing procedures and approaches as a result
Microsoft offers a number of knowledge management tools including Digital Dashboard
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Computers with the ability to mimic or duplicate the functions of the human brain
Many AI pioneers
Predicted that computers would be as ‘smart’ as people by the 1990s
Artificial Intelligence System (AIS)
Includes the people, procedures, hardware, software, data and knowledge needed to develop computer systems and machines that demonstrate characteristics of human intelligence
Turning Test:
Determines whether responses from a computer with intelligent behaviour are indistinguishable from those from human being
Characteristics of Intelligence behaviour include the ability to:
Learn from experiences and apply knowledge acquired from experience
Handle complex situations
Solve problems when important information is missing
Nature of Intelligence part 2
Characteristics of intelligent behaviour include the ability:
Determine what is important
React quickly and correctly to a new situation
Understand visual images
Process and manipulate symbols
Be creative and imaginative
Use Heuristics
Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI)
Idea is to directly connect human brain to computer and have human thought control computer activities
IF BCI is successful
The BCI experiment will allow people to control computers and artificial arms and legs though thought alone
AI is a broad field that includes:
Expert systems and robotics
Vision systems and natural language processing
Learning systems and neural networks
Expert systems:
Hardware and software that stores knowledges and makes interfaces, similar to a human expert
Robotics
Developing mechanical devices can:
Paint cars, make precise welds, and perform other tasks that require a high degree of precision
Manufacturers use robots to assemble and paint products
Contemporary robotics:
Combine both high-precision machines capabilities and sophisticated controlling software
Vision Systems
Hardware and Software that permit computers to capture, store and manipulate visual images and pictures
Effective at identifying people based on facial features
Natural Language Processing and Voice Recognition
Processing that allows that computer to understand and react to statements and commands made in a “natural” language, such as English
Voice recognition:
Converting sound waves into words
Learning Systems
Combination of software and hardware that:
Allow the computer to change how it functions or reacts to situations based on feedback it receives
Learning systems software
Requires feedback on results of actions or decisions
Neutral Networks
Computer system that stimulates functions of a human brain
Can process many pieces of data at the same time and learning to recognise patterns
Neural Network Program:
Helps engineers slow or a speed drilling operations to help increase drilling accuracy and reduce costs
Other Artificial Intelligence Application
Genetic algorithm:
Approach to solving complex problems in which a number of related operations or models change and evolve until the best one emerges
Intelligent agent:
Programs and a knowledge base used to perform a specific task for a person, a process, or another program
Expert System
Computerised expert systems
Use heuristics, or rules of thumb to arrive at conclusions or make suggestions
The U.S Army:
Uses the Knowledge and Information Fusion Exchange (KnIFE) expert system to help soldiers in the field maker better military decisions
When to use Expert Systems
People and organisations should develop an expert system if it can:
Provide a high potential payoff or significantly reduce downside risk
Capture and preserve irreplaceable human expertise
Solve a problem that is not easily solved using traditional programming techniques
When to use Expert System part 2
Provide expertise needed at a number of locations at the same time or in a hostile environment that is dangerous to human health
Provide expertise that is expensive and rare
Develop a solution that is faster than human expert can
Provide expertise needed for training and development
Components of Expert System
Expert System:
Consists of a collection if integrated and related components
Knowledge Base:
Stores all relevant information, data, rules, cases and relationship used by expert system
Creates knowledge base by using rules and cases
The Interface Engine
Purpose
To seek information and relationships from the knowledge base
To provide answers, predictions, and suggestions, like a human expert
The Explanation Facility
Allows a user or decision maker to understand how the expert system arrive at a certain conclusions or results
The Knowledge Acquisition Facility
Provides convenient and efficient means of
capturing and storing all components of knowledge base
Knowledge acquisition software:
Can present users and decision makers with easy-to-use menus
The User Interface
Permits decision makers to develop and use their own expert systems
Main purpose:
To make development and use of an expert system easier for users and decision makers
Participants in Developing and Using Expert Systems
Domain expert:
Person or group with the expertise or knowledge the expert system is trying to capture
Knowledge engineer:
Person who has training or experience in the design, development, implementation, and maintenance of an expert system
Knowledge user:
Person or group who uses and benefits from the expert system
Expert Systems Development Tools and Techniques
Theoretically, expert systems can be developed from any programming language
Expert system shells and products:
Collections of software packages and tools used to design, develop, implement, and maintain expert systems
Multimedia and Virtual Reality
Use of multimedia and virtual reality:
Has helped many companies achieve a competitive advantage and increase profits
The approach and technology used in multimedia:
Is often the foundation of virtual reality systems
Multimedia
Text and graphics
Audio
Video and animation
File conversion and compression
Designing a multimedia application:
Requires careful thought and a systematic approach
Requires that the end use of the document or file be carefully considered
Virtual reality system:
Enables one or more users to move and react in a computer-simulated environment
Immersive virtual reality:
User becomes fully immersed in an artificial, 3D world that is completely generated by a computer
Interface Devices
To see in a virtual world:
Often the user wears a head-mounted display (HMD) with screens directed at each eye
Haptic interface:
Relays sense of touch and other sensations in a virtual world
Most challenging to create
Forms of Virtual Reality
Immersive virtual reality
Applications that are not fully immersive:
Mouse-controlled navigation through a 3D environment on a graphics monitor
Stereo projection systems
Stereo viewing from the monitor via stereo glasses
Virtual Reality Applications
Medicine:
VR program called SnowWorld helps treat burn patients
Education and training:
Virtual technology has also been applied by the military
Business and Commerce:
Boeing used virtual reality to help it design and manufacture airplane parts and new planes
Entertainment:
Movies use CGI to bring realism to the silver screen
Specialised Systems
Segway:
Uses sophisticated software, sensors, and gyro motors to transport people
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags:
Contain small chips with information about products or packages
Can be quickly scanned to perform inventory control
Specialised Systems part 2
Game theory:
Involves the use of information systems to develop competitive strategies for people, organisations, or even countries
Informatics:
Combines traditional disciplines, such as science and medicine, with computer systems and technology