Antiarrhythmic Medicinal Chemistry Lecture
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Question-and-answer flashcards covering arrhythmia concepts, antiarrhythmic drug classes (I–IV), key pharmacophores, SAR, metabolism, pharmacokinetics, toxicity, and important drug–drug interactions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What is the medical term for an abnormal heart rhythm?
Arrhythmia or cardiac dysrhythmia.
Name four common forms of arrhythmias.
Bradycardia, tachycardia, flutter/fibrillation, and premature (early) heartbeat.
List at least three lifestyle or medical causes of arrhythmias.
Alcohol, tobacco, drugs, diet, hyperthyroidism, hypertension, and heart disease.
Which three cardiac‐related emergencies should you learn to distinguish?
Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke.
What are the four main classes of antiarrhythmic drugs?
Class I – Sodium channel blockers, Class II – β-blockers, Class III – Repolarization prolongers, Class IV – Calcium channel blockers.
Into which three subgroups is Class I subdivided?
Class Ia (intermediate), Class Ib (mild), and Class Ic (strong).
What are the three key features of the Class I pharmacophore?
(1) Aromatic ring that interacts with the Na⁺-channel pore, (2) flexible linker, and (3) basic nitrogen that ionically interacts with a negatively charged channel residue.
Give two example drugs from Class Ia.
Quinidine, procainamide, or disopyramide.
Which natural product is quinidine a diastereomer of?
Quinine.
What major CYP enzyme metabolizes quinidine?
CYP3A4.
Which important drug-metabolizing enzyme does quinidine inhibit, leading to many DDIs?
CYP2D6 (and also P-gp).
Why may slow acetylators have problems with procainamide?
They can accumulate N-acetylprocainamide (NAPA) and experience drug-induced lupus-like syndrome.
Name a common anticholinergic side effect of disopyramide.
Constipation or dry mouth.
What pKa range characterizes most Class Ia drugs?
Approximately 8–9.
Which opioid analgesic shares the antiarrhythmic Class I pharmacophore?
Methadone.
What pKa range is typical for Class Ib agents?
Approximately 6–7.
Why is lidocaine not given orally for arrhythmia treatment?
It undergoes extensive first-pass hepatic metabolism.
Name two orally active Class Ib drugs.
Mexiletine and tocainide.
Which Class Ic agent also acts as a β-blocker?
Propafenone.
What structural feature of flecainide enhances binding selectivity to the Na⁺ channel?
Two CF₃ groups on the aromatic ring (strong electron-withdrawing substituents).
State two key clinical cautions for Class I drugs in general.
They can provoke arrhythmias and cause anticholinergic effects.
Class III agents primarily block which ion channel?
Potassium channels (and some also block calcium channels).
Which two iodine atoms in amiodarone aid in channel binding?
They enhance lipophilicity and interaction with K⁺ and Ca²⁺ channels.
List two toxicity issues reduced in dronedarone versus amiodarone.
Lower neurotoxicity, lung toxicity, and thyroid toxicity.
What is the approximate elimination half-life of amiodarone?
8–107 days (very long).
Which clearance mechanism dominates for lidocaine?
Hepatic metabolism.
Which antiarrhythmic is cleared mainly by the kidneys and lacks significant hepatic metabolism?
Sotalol.
Name the four characteristic SAR points for 1,4-dihydropyridine (DHP) calcium channel blockers.
1) 1,4-DHP core required; 2) C-2 & C-6 methyl or larger; 3) C-3 & C-5 ester groups optimal; 4) C-4 aryl ring with ortho/meta substitution for activity.
Which DHP is formulated for IV use owing to its protonatable tertiary amine?
Nicardipine.
How do DHP calcium channel blockers typically affect blood pressure?
They decrease blood pressure by vasodilation.
What major CYP enzyme controls the metabolism of most DHPs?
CYP3A4.
Why can DHPs with nitro substituents have faster onset?
Nitro groups enhance lipophilicity and absorption.
Which non-DHP calcium channel blocker belongs to the phenylalkylamine class?
Verapamil.
Give two pharmacokinetic properties common to DHP calcium channel blockers.
Extensive first-pass metabolism and high protein binding.
How does food generally affect DHP absorption?
Food can increase or delay absorption depending on the agent; clinicians monitor for food effects.
Why can quinidine co-administration increase plasma levels of other drugs like codeine?
Because quinidine inhibits CYP2D6, reducing metabolism of CYP2D6 substrates.
Which metabolic reaction converts procainamide to NAPA?
Acetylation (Phase II).
What metabolite results from CYP3A4 oxidation of quinidine?
3-Hydroxyquinidine.
Which Class I drug is light sensitive and must be protected from light?
Quinidine.
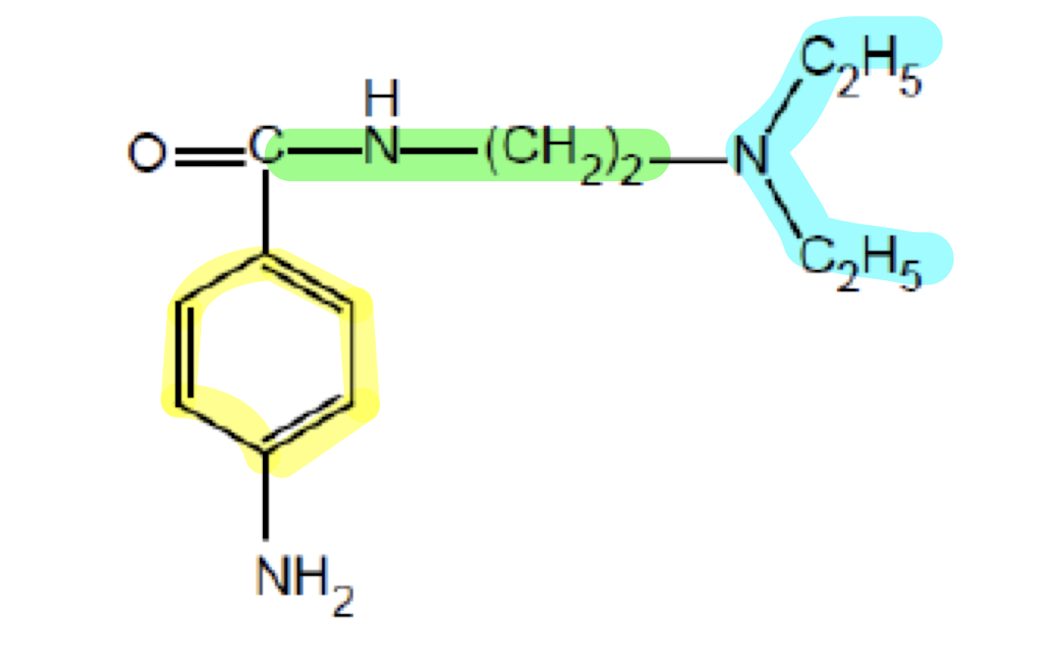
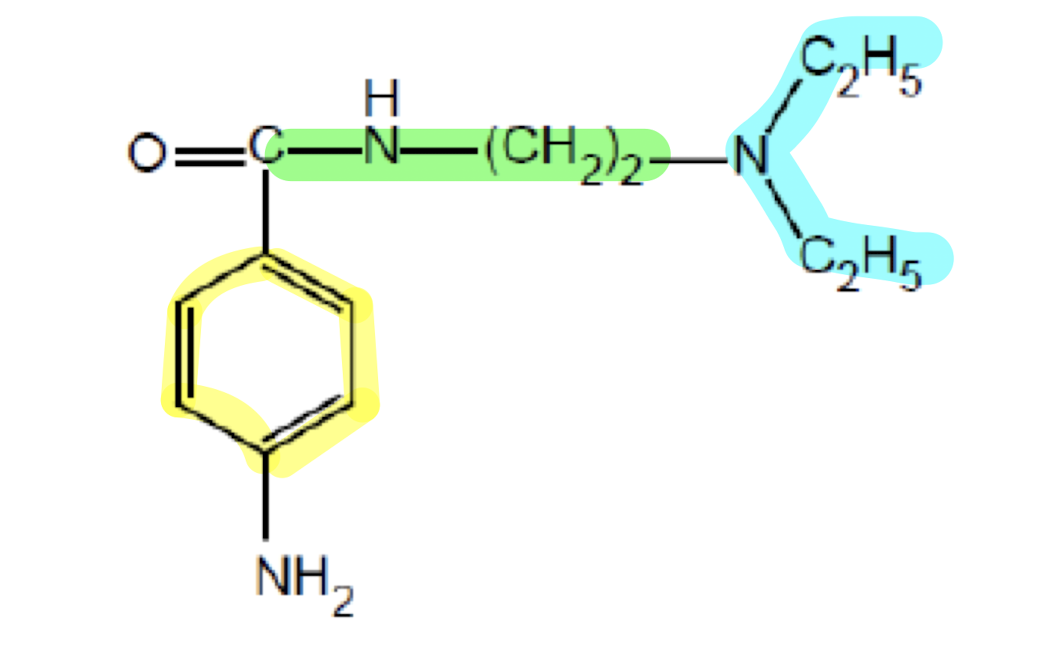
What does the functional group highlighted in yellow do?
Aromatic Ring; interacts with the Na+ channel pore to bind to it
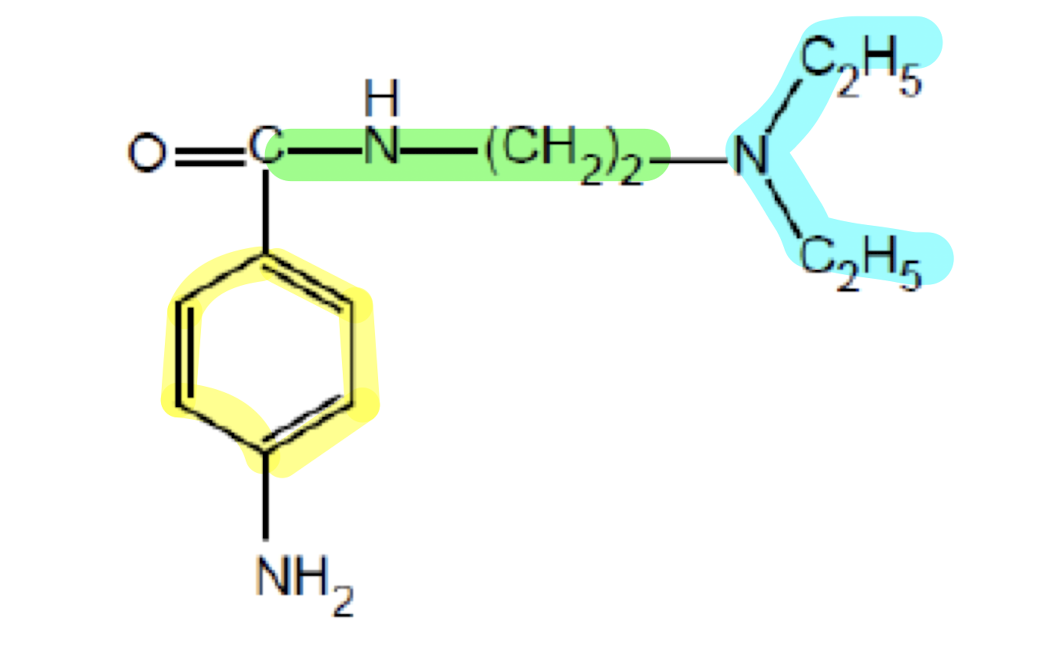
What does the functional group highlighted in green do?
Linker region; adds flexibility for molecular mobitility and enhancing binding affinity of the drug.
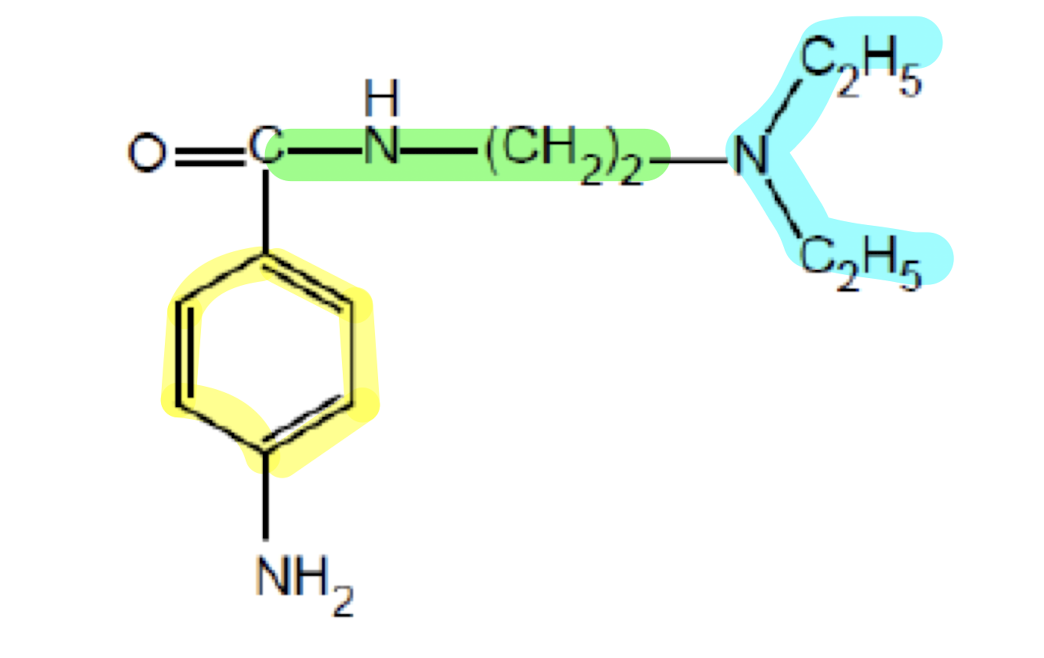
What does the functional group highlighted in blue do?
Amine group; interacts with negatively-charged Na+ channel pore
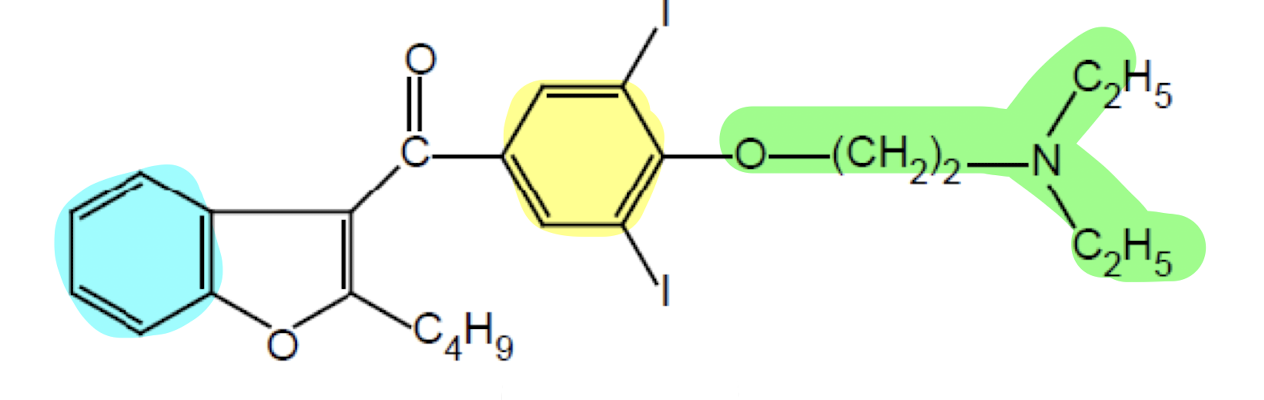
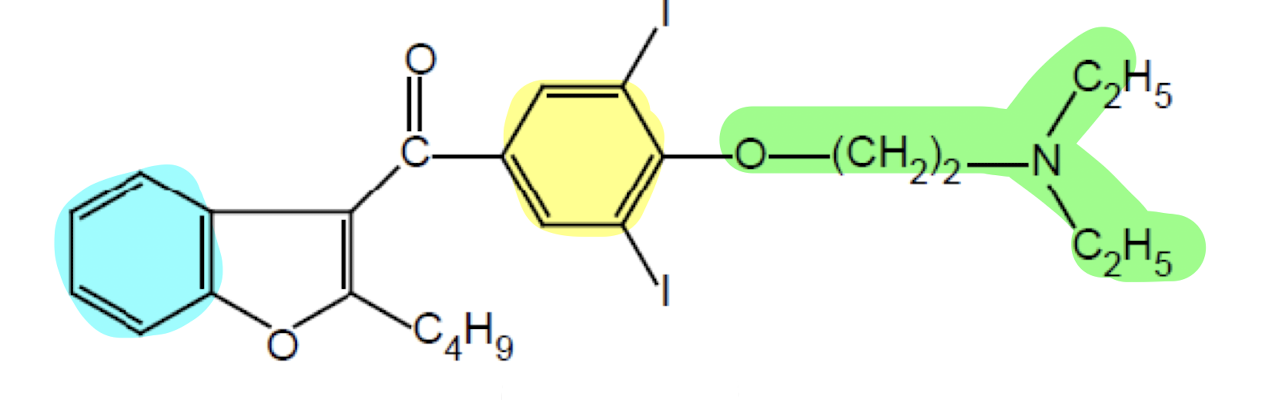
What does the functional group highlighted in yellow do?
Aromatic Ring; lipophilic anchor for the membrane with the two iodines to enhance channel binding
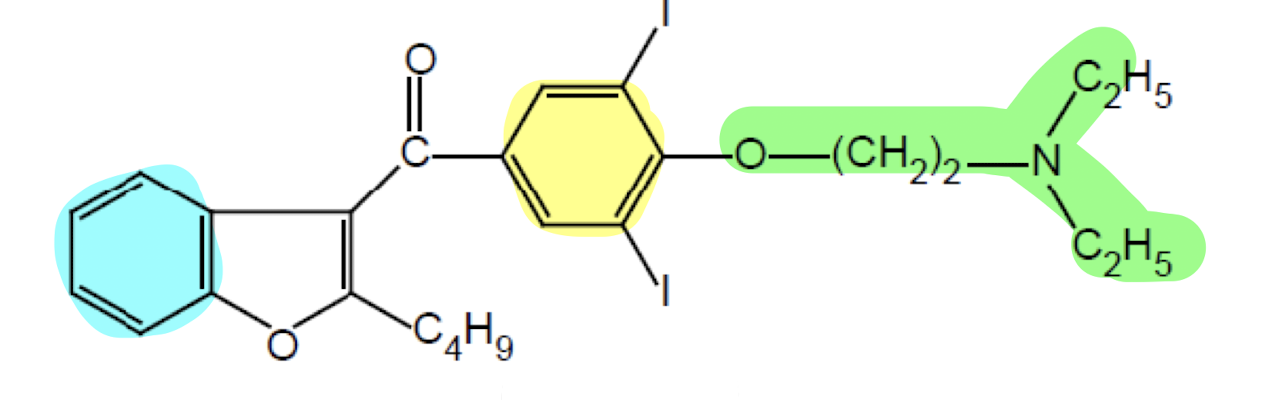
What does the functional group highlighted in green do?
Linker region; enhance flexibility for channel blocky protonate the "N" to enhance the ionic interactin with channel
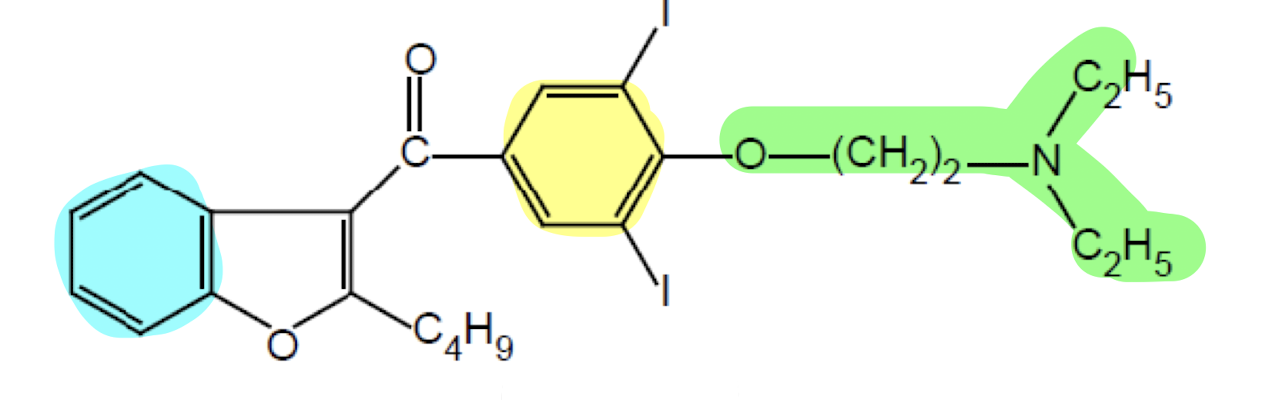
What does the functional group highlighted in blue do?
Benzene Ring; blocks the K+ and Ca2+ with the two iodine.
What drug class has this pharmacophore?
Drug Class III (Repolarization Blockers)
What drug class has this pharmacophore?
Drug Class I (Sodium Channel Blockers)
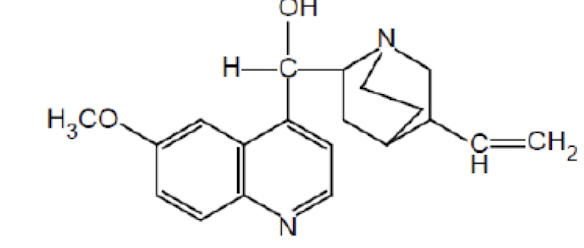
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Quinidine; Class 1a
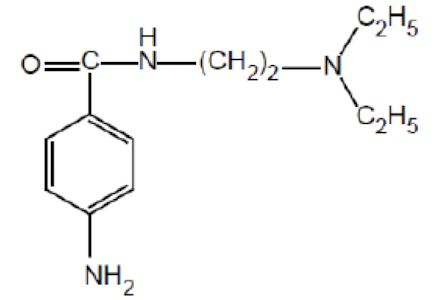
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Procainamide; Class 1a
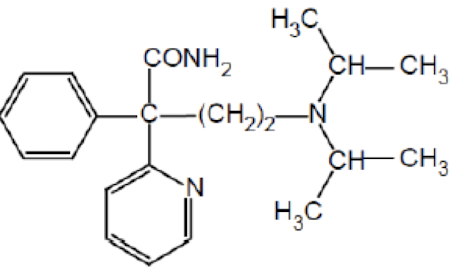
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Disopyramide; Class 1a
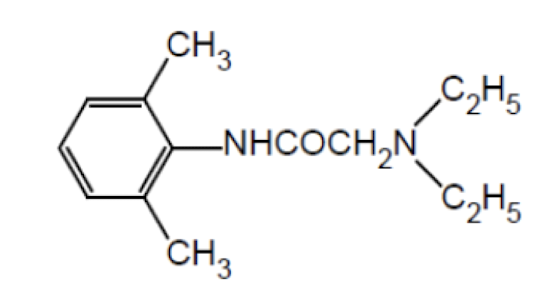
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Lidocaine; Class 1b
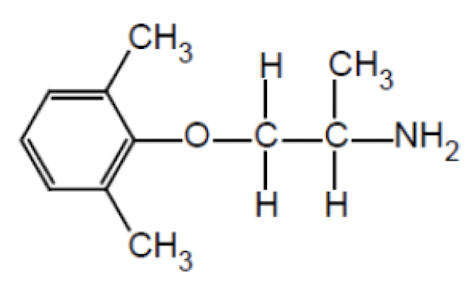
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Mexiletine; Class 1b
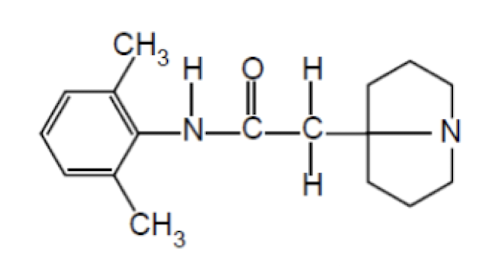
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Tocainide; Class 1b
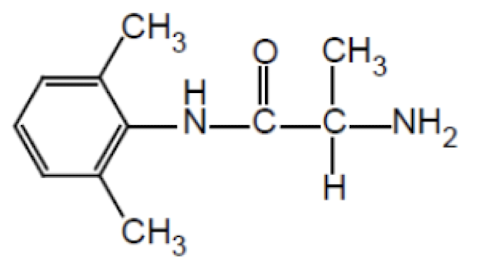
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Pilsicainide; Class 1c
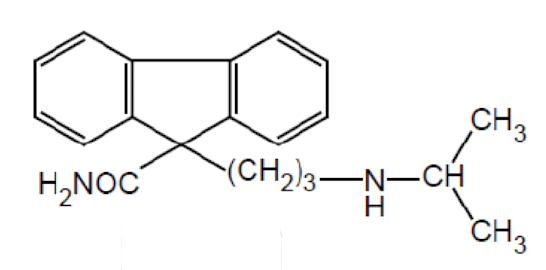
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Indecainide; Class 1c
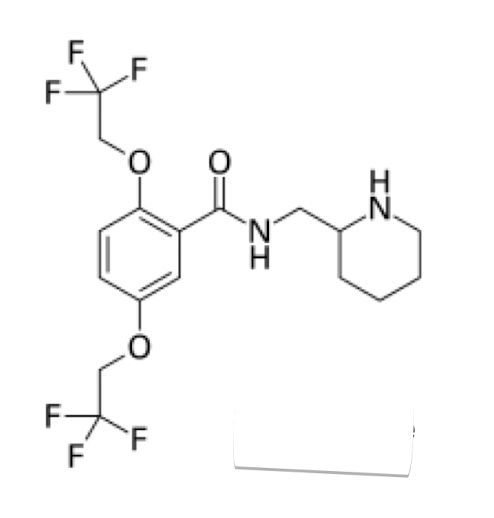
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Flecainide; Class 1c
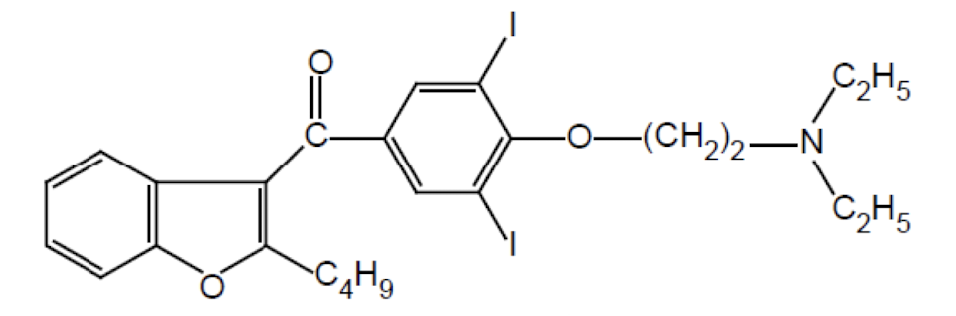
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Amiodarone; Class 3
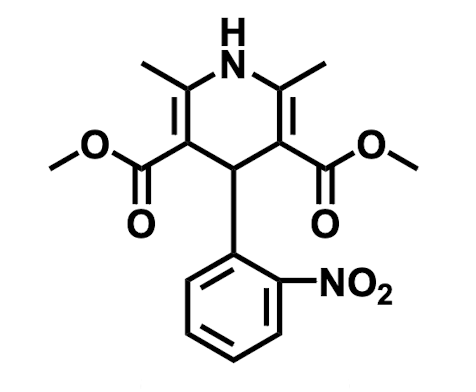
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Nifedipine; Class 4 (Calcium Channel Blockers)
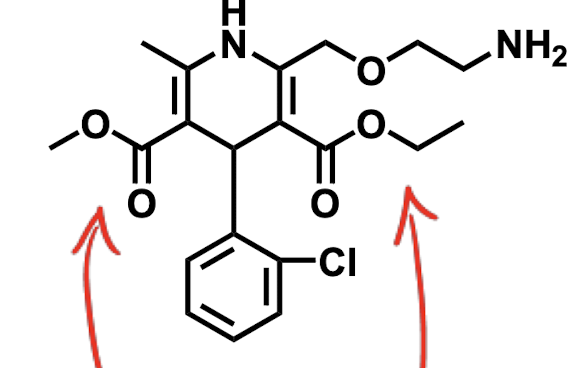
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Amlodipine; Class 4 (Calcium Channel Blockers)
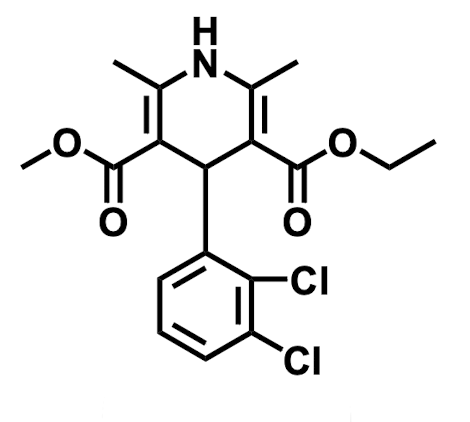
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Felodipine; Class 4 (Calcium Channel Blockers)
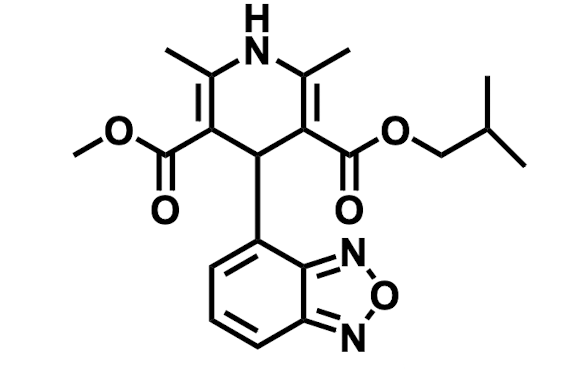
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Isradipine; Class 4 (Calcium Channel Blockers)
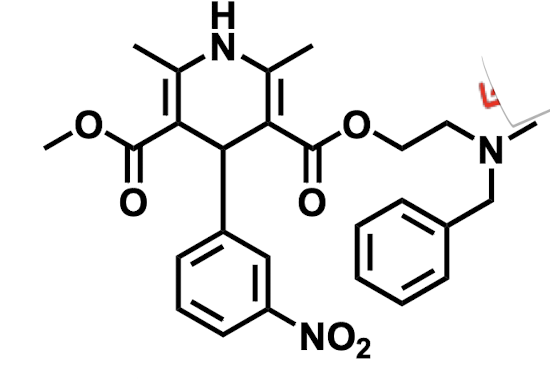
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Nicardipine; Class 4 (Calcium Channel Blockers)
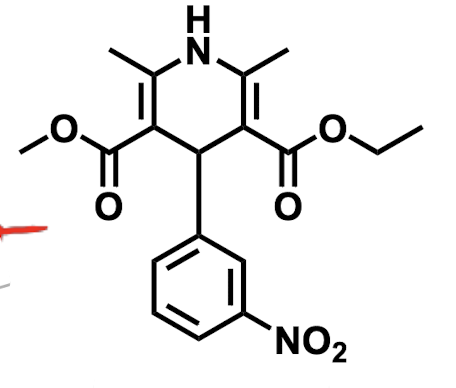
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Nitrendipine; Class 4 (Calcium Channel Blockers)
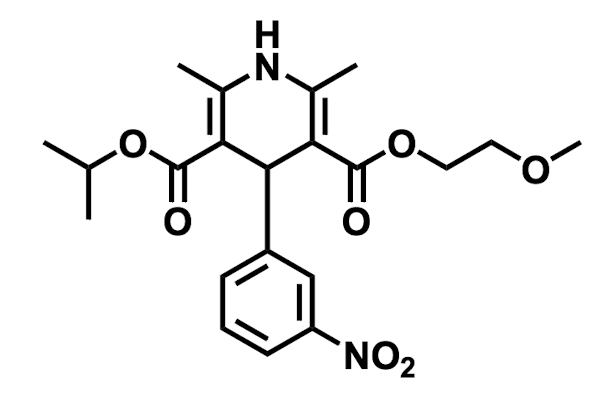
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Nimodipine; Class 4 (Calcium Channel Blockers)
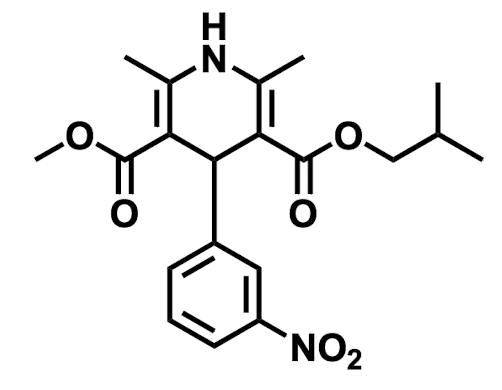
Name the drug’s name and its class.
Nisoldipine; Class 4 (Calcium Channel Blockers)