Central Nervous System
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, and cerebellum
What are the four primary regions of the brain?
cerebral hemisphere
what structure is labeled by #1?
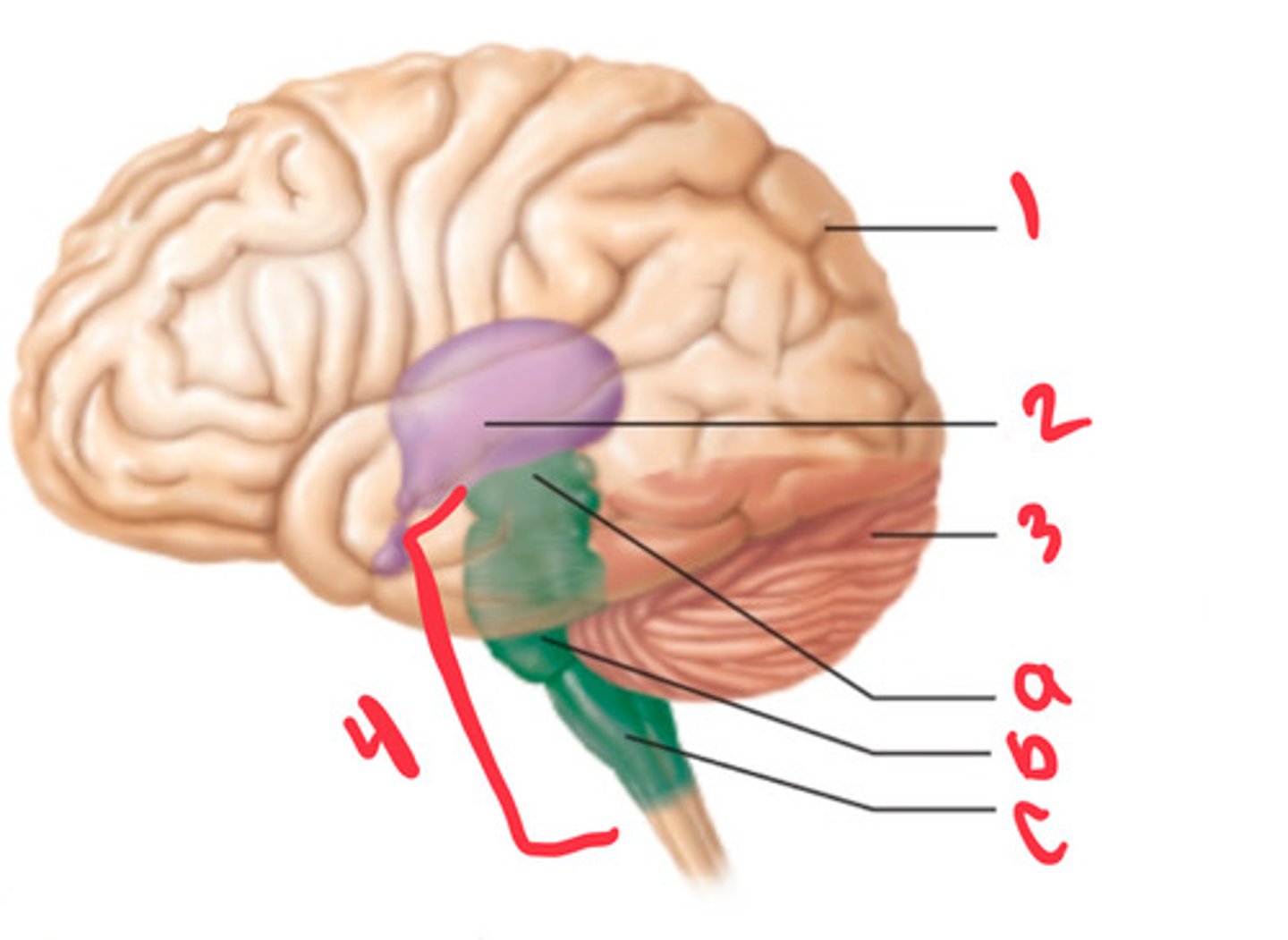
diencephalon
what structure is labeled by #2?
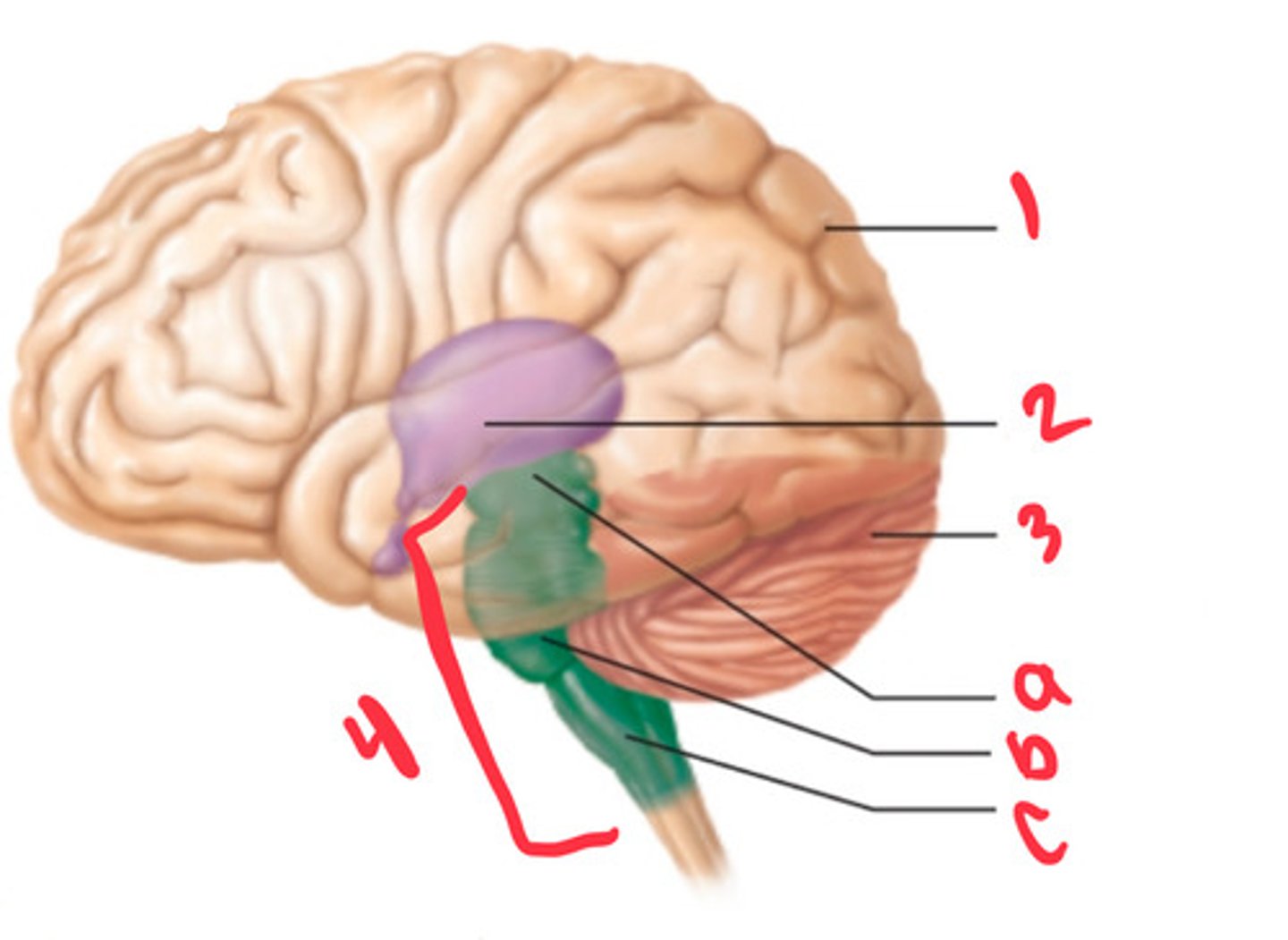
cerebellum
what structure is labeled by #3?
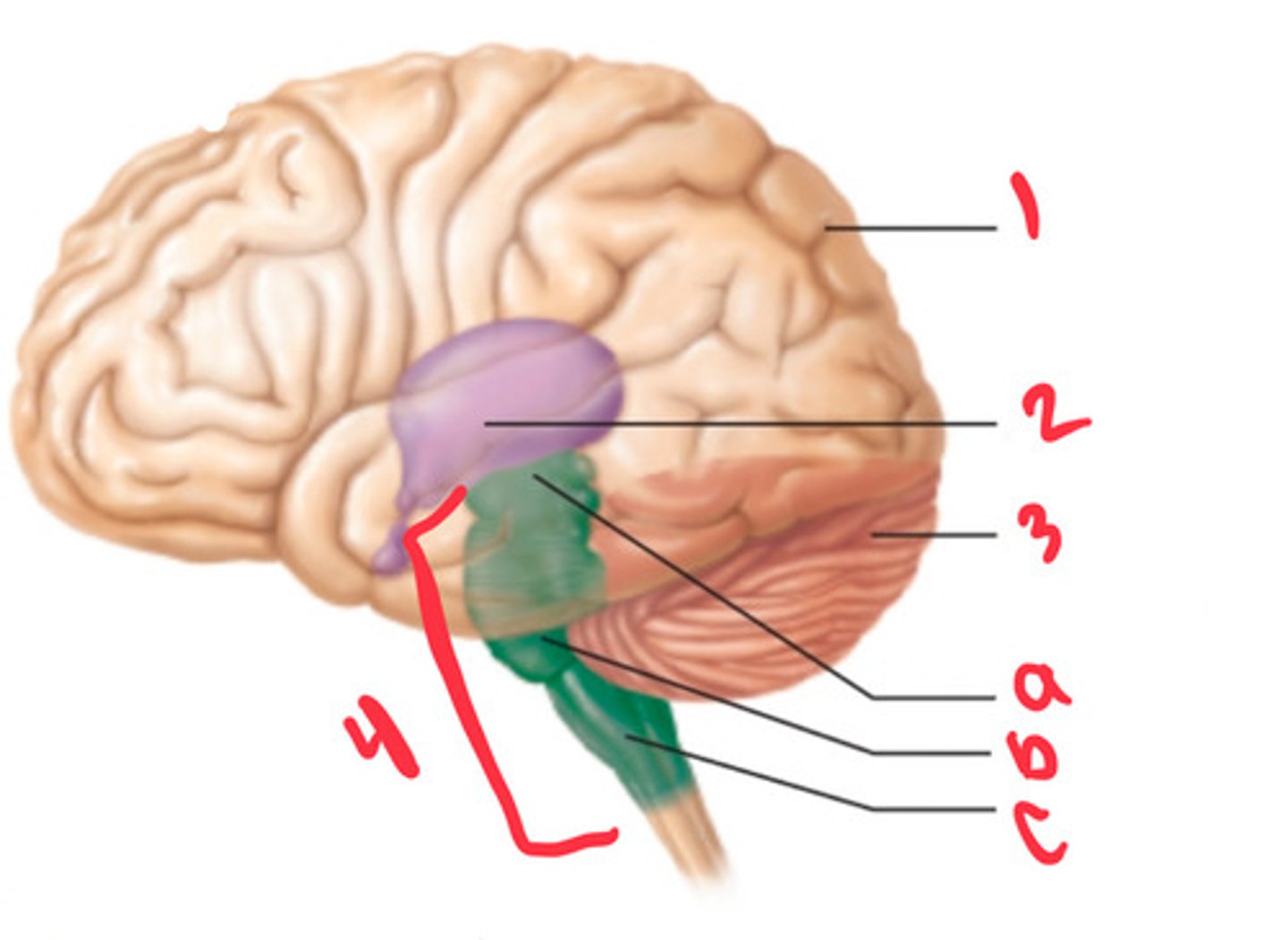
brain stem
what structure is labeled by #4?
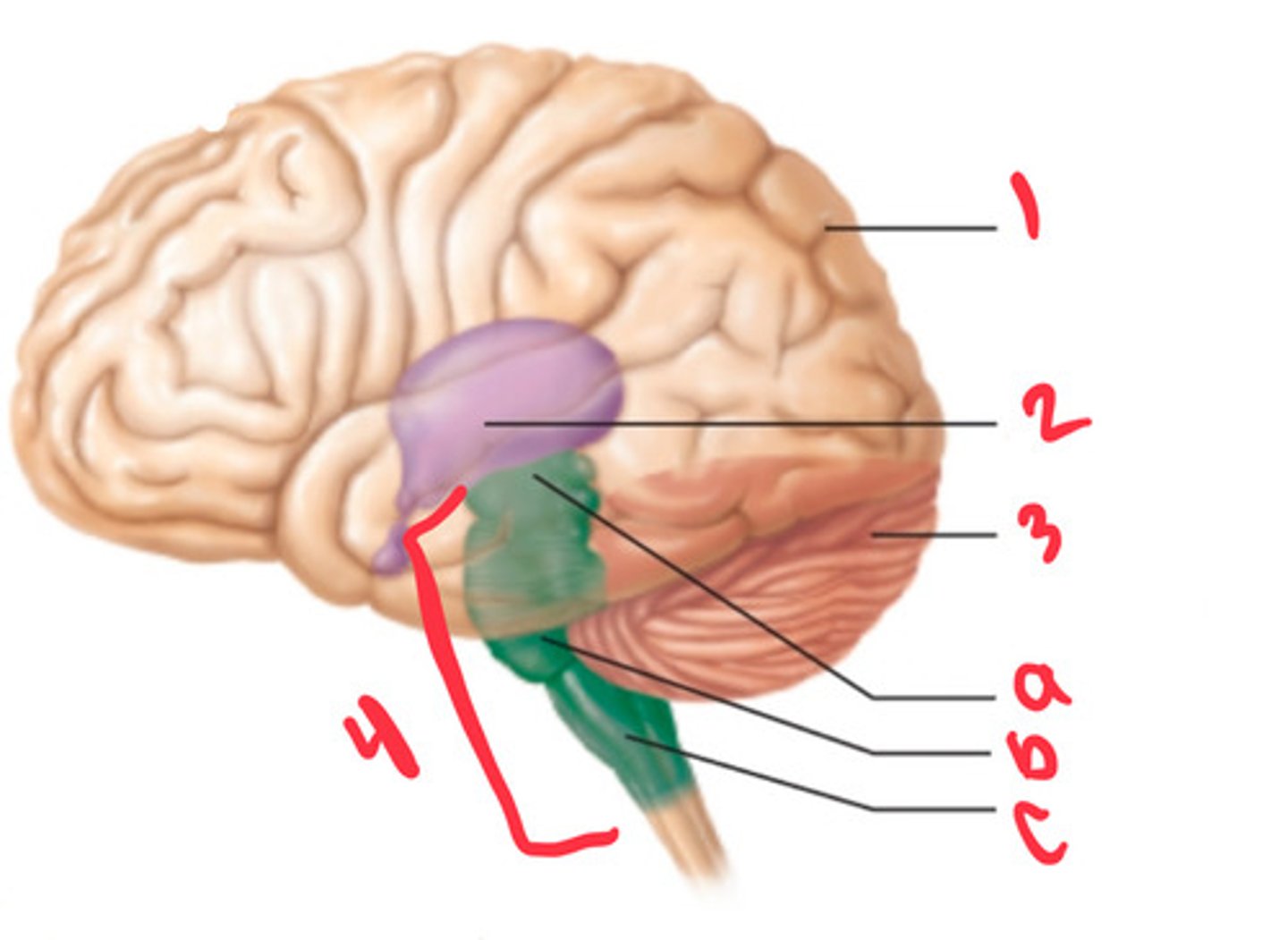
midbrain
what structure is labeled by A?
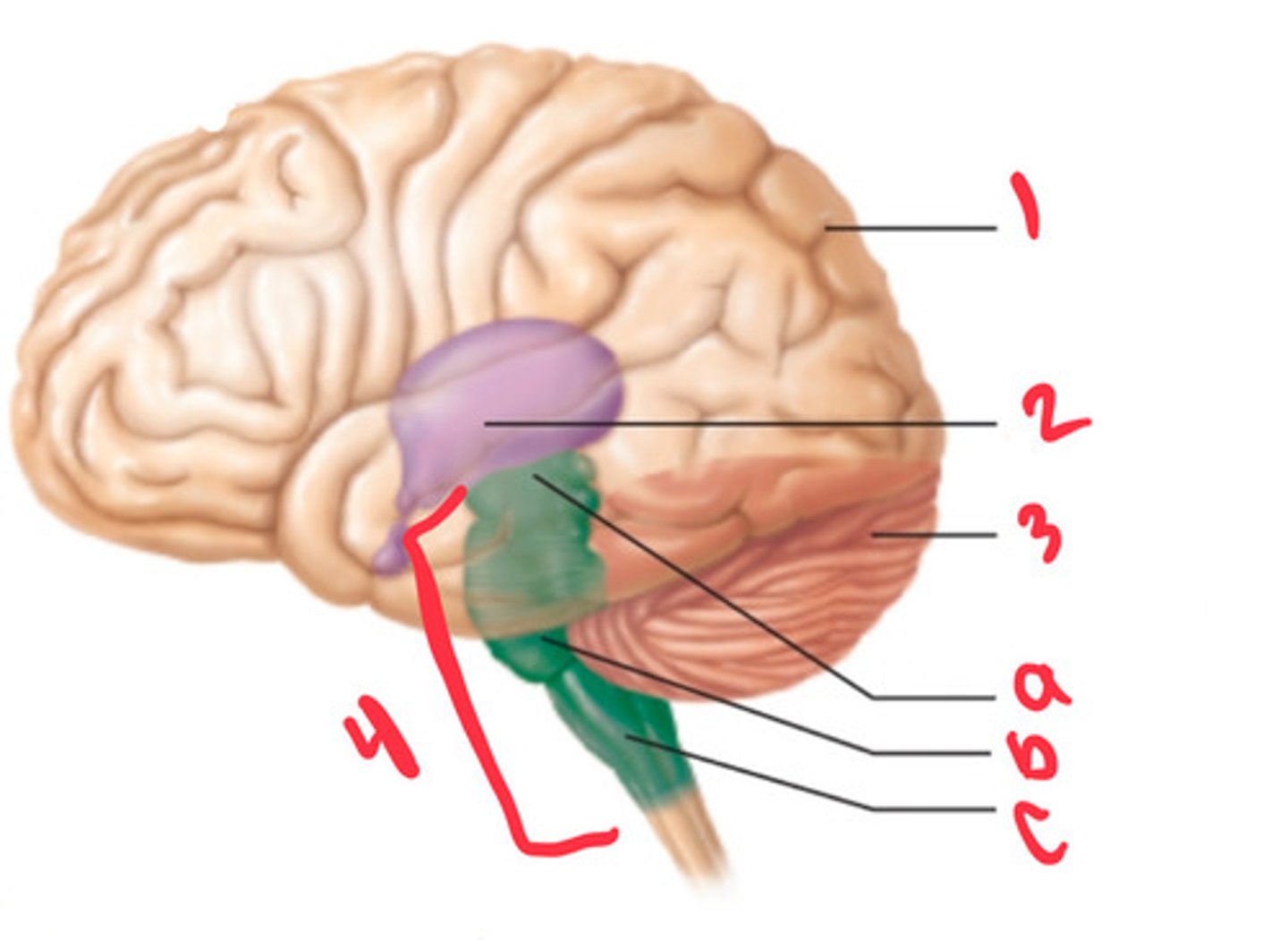
pons
what structure is labeled by B?
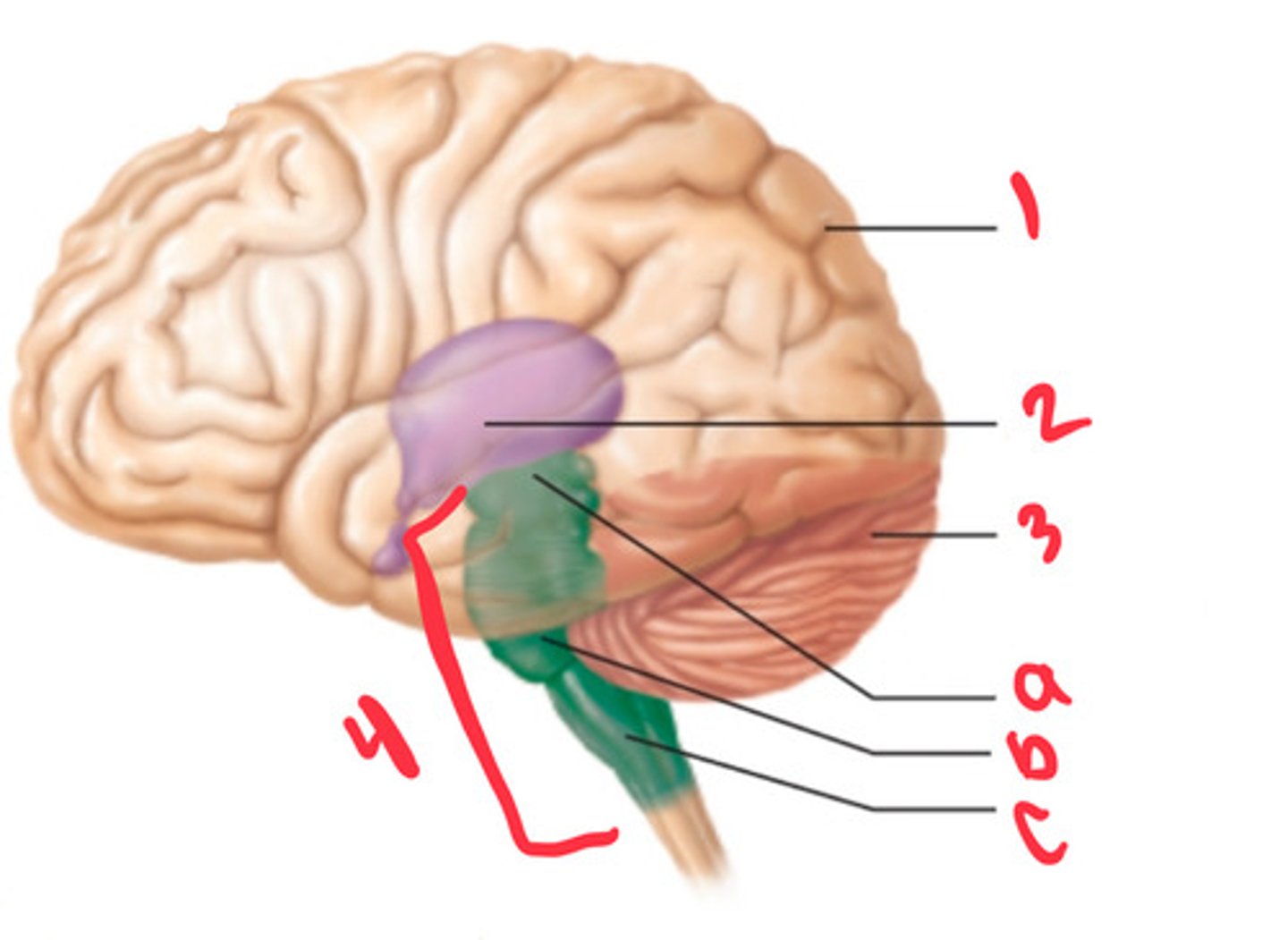
medulla
what structure is labeled by C?
core brain component
What is the diencephalon?
diencephalon to spinal cord
What does the brain stem connect?
gray matter
what is highlighted in red?
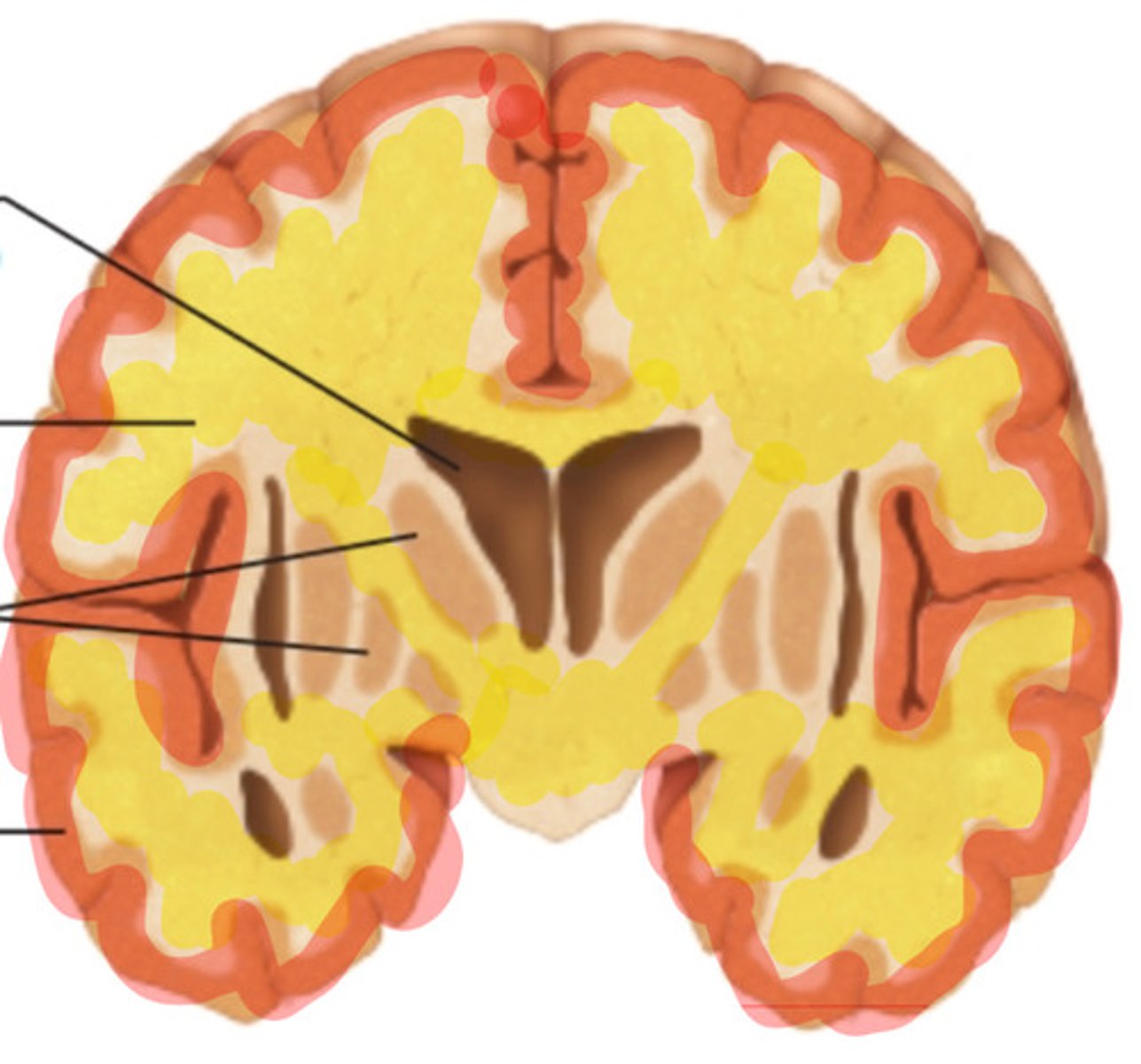
white matter
what is highlighted in yellow?
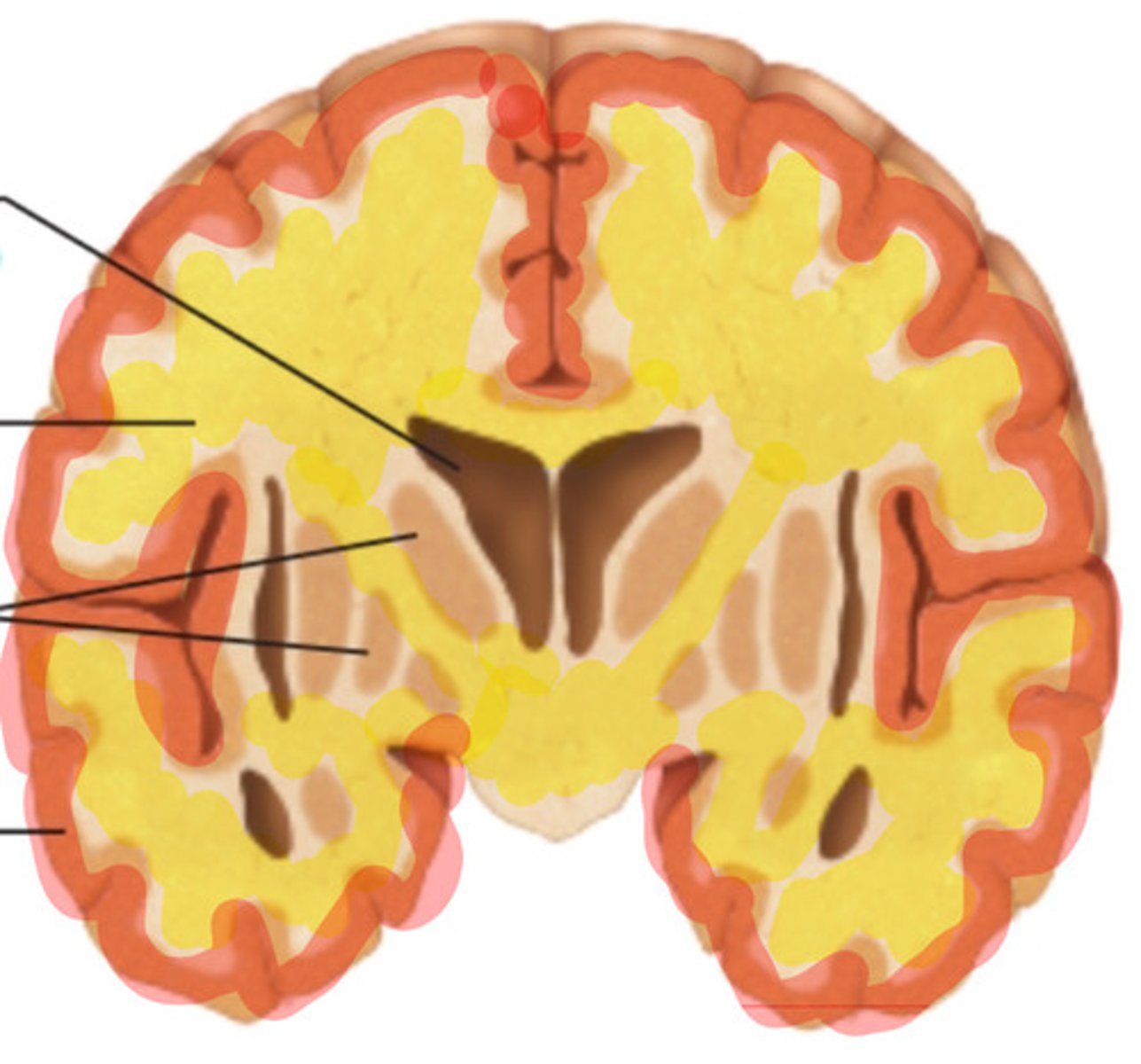
myelinated neurons
What is white matter?
short, nonmyelinated neurons
What is gray matter?
two hemispheres divided into 5 lobes
What is the cerebral cortex?
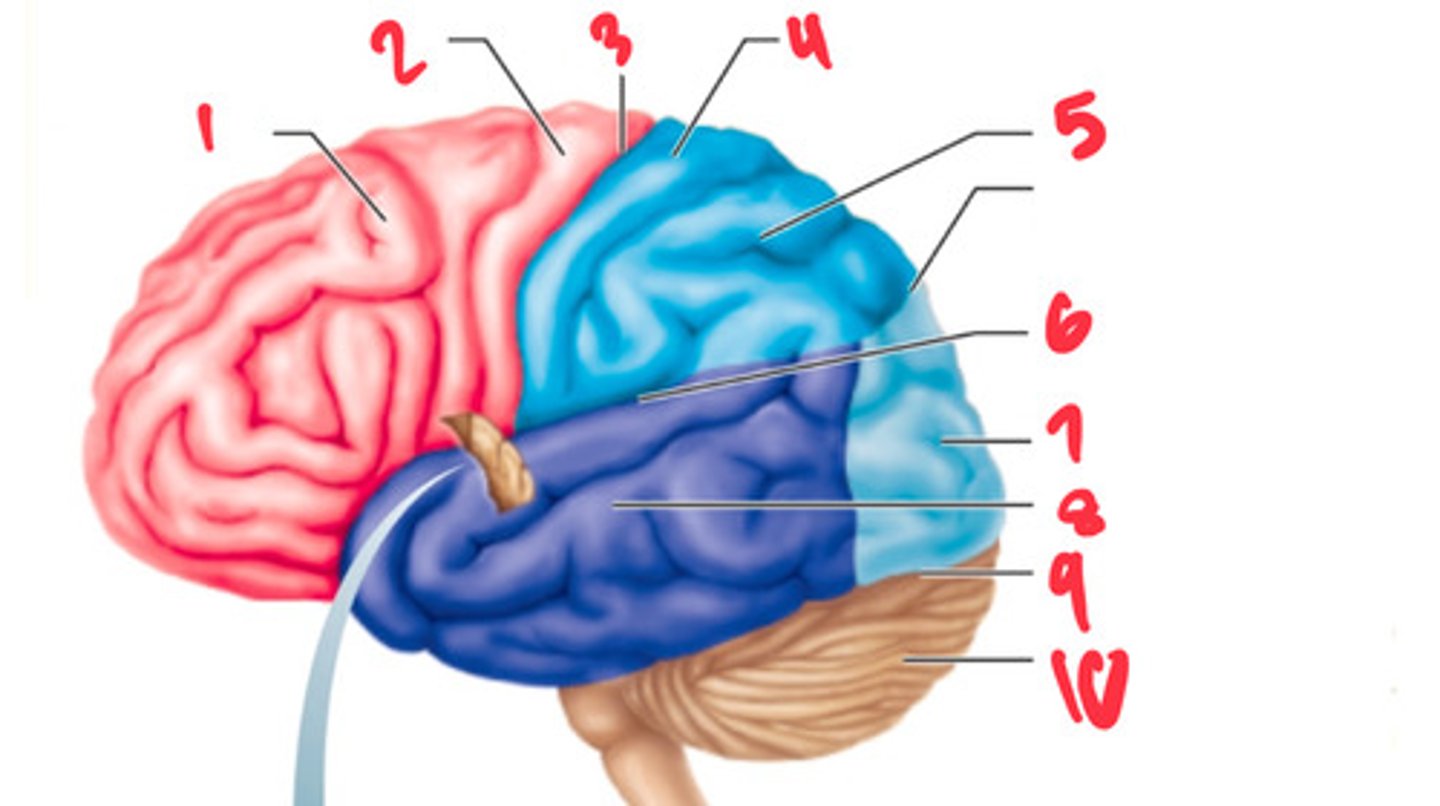
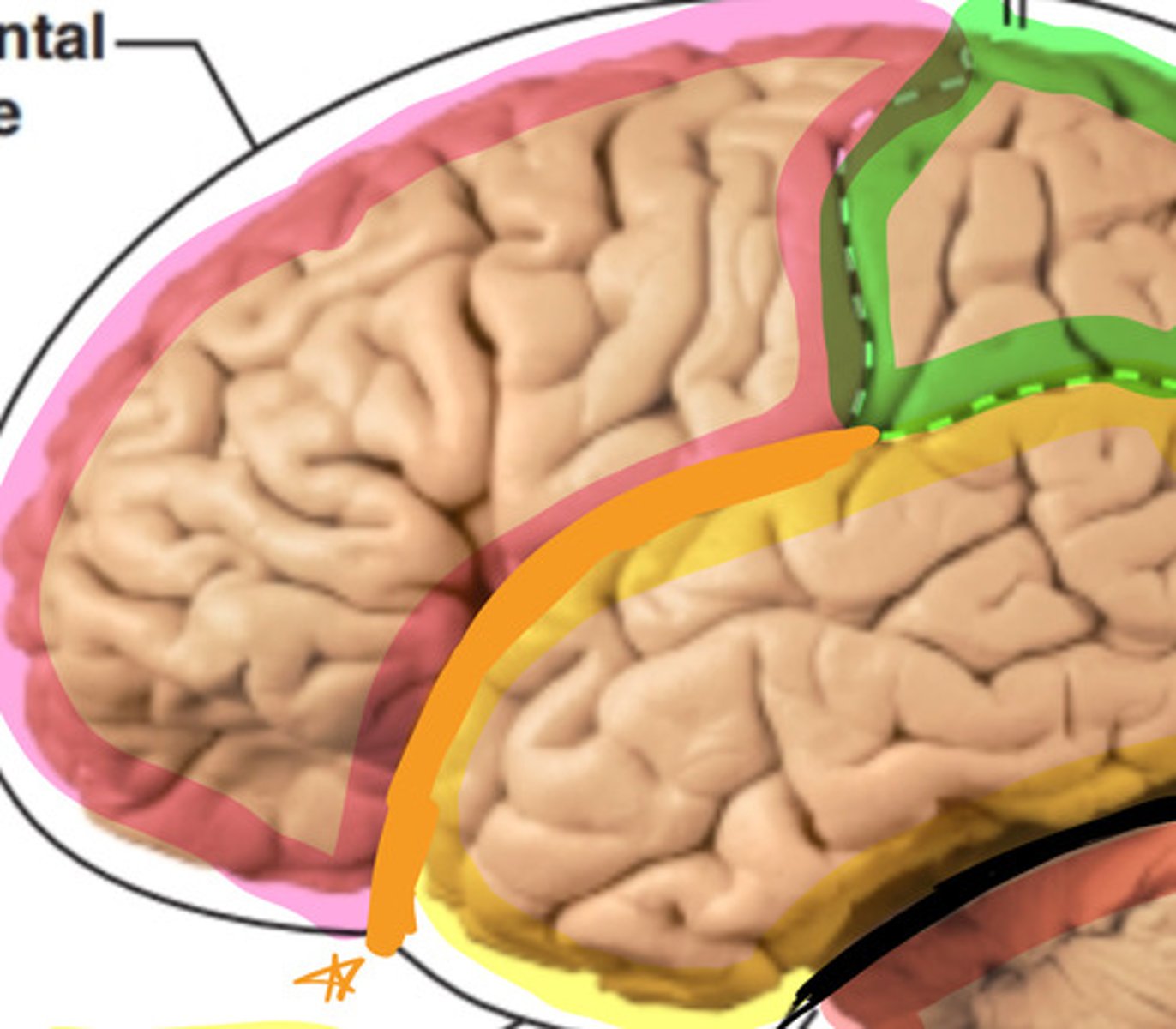
frontal lobe
what structure is labeled by #1?
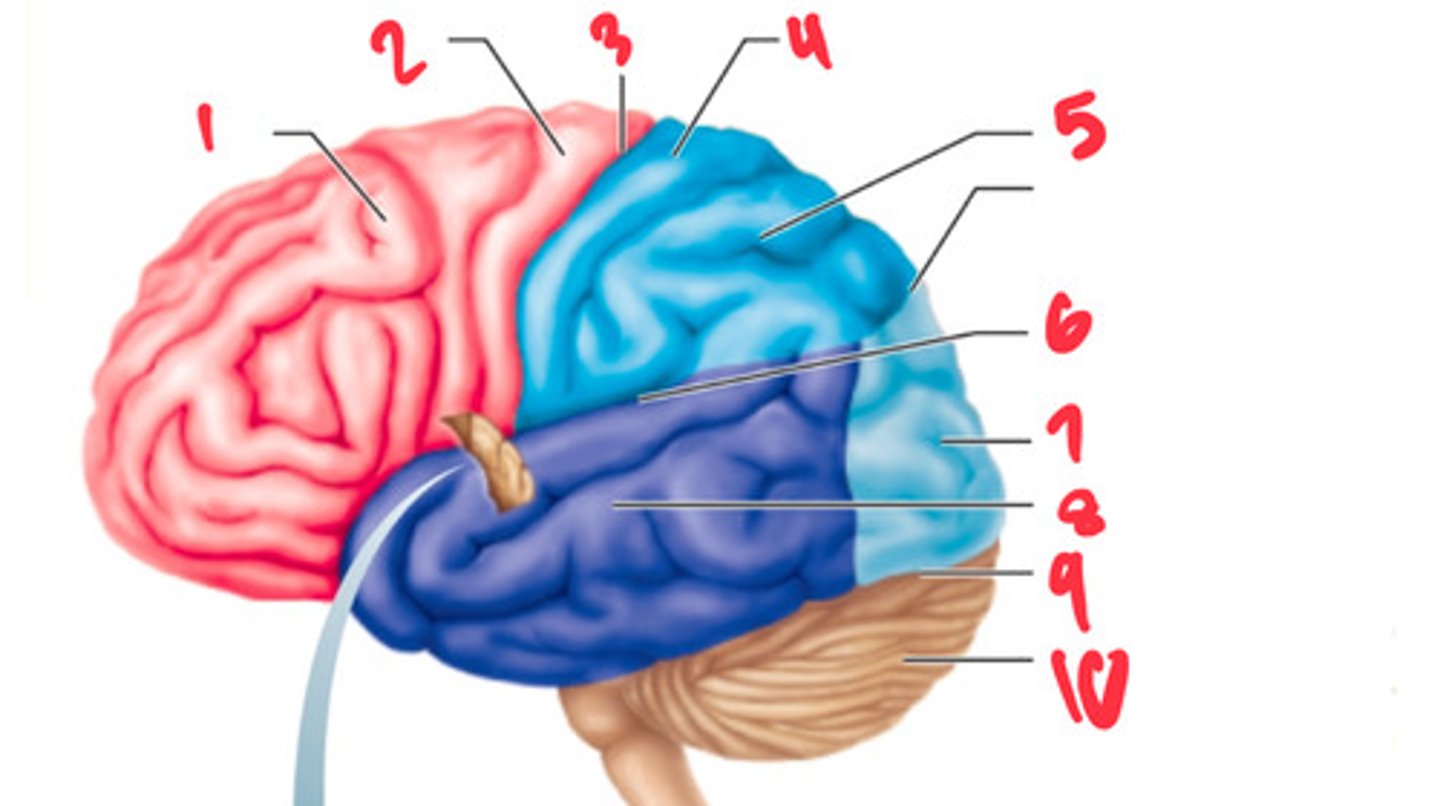
precentral gyrus
what structure is labeled by #2?
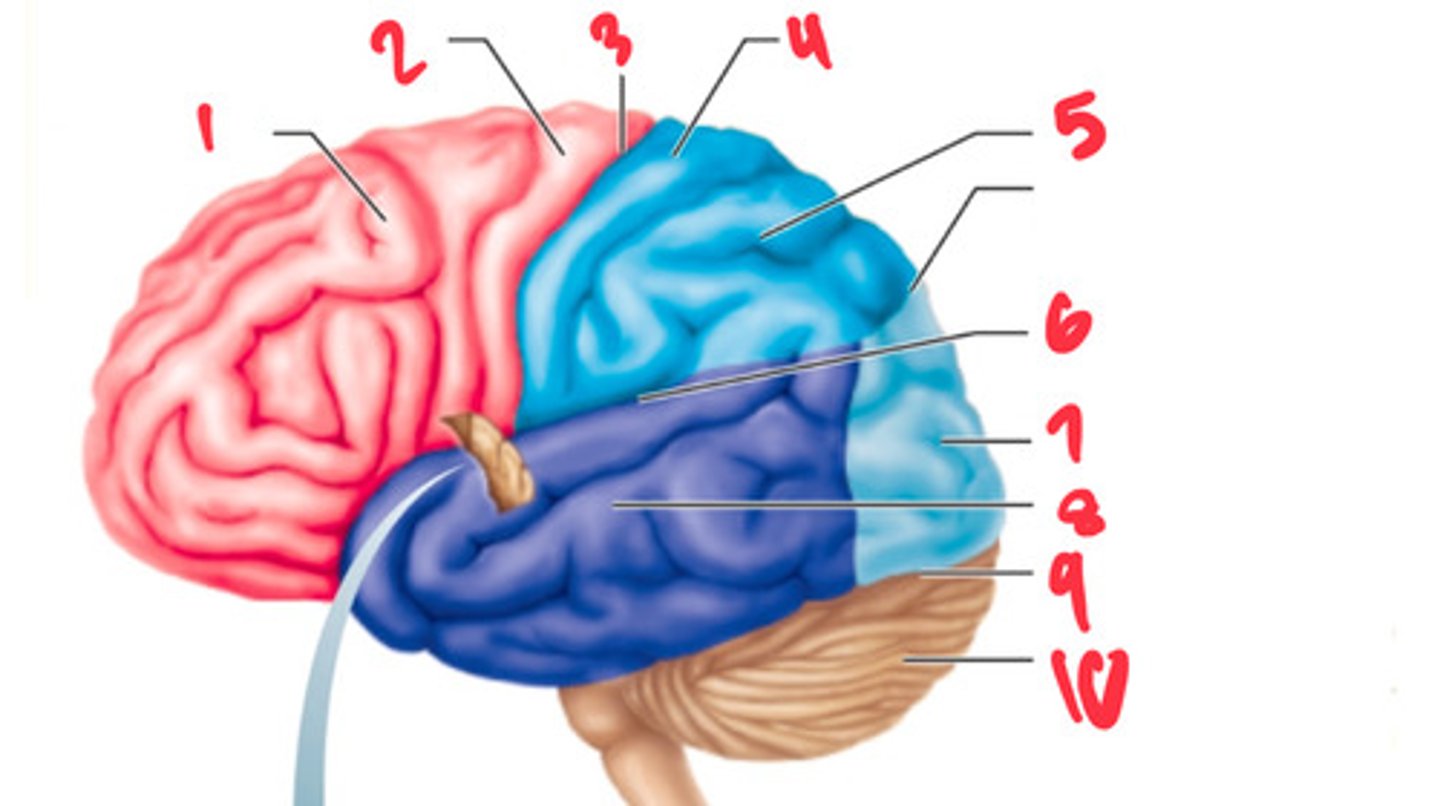
central sulcus
what structure is labeled by #3?
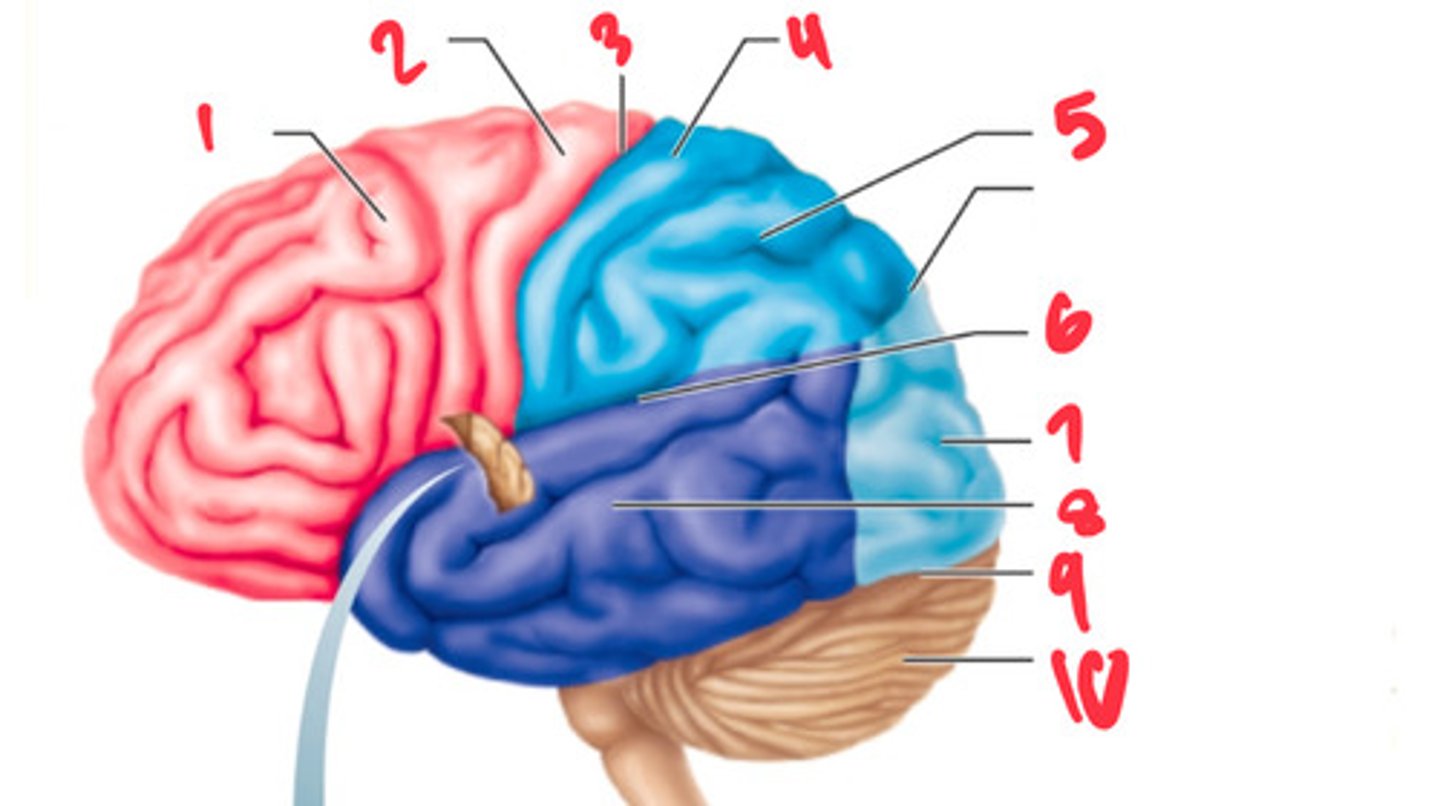
postcentral gyrus
what structure is labeled by #4?
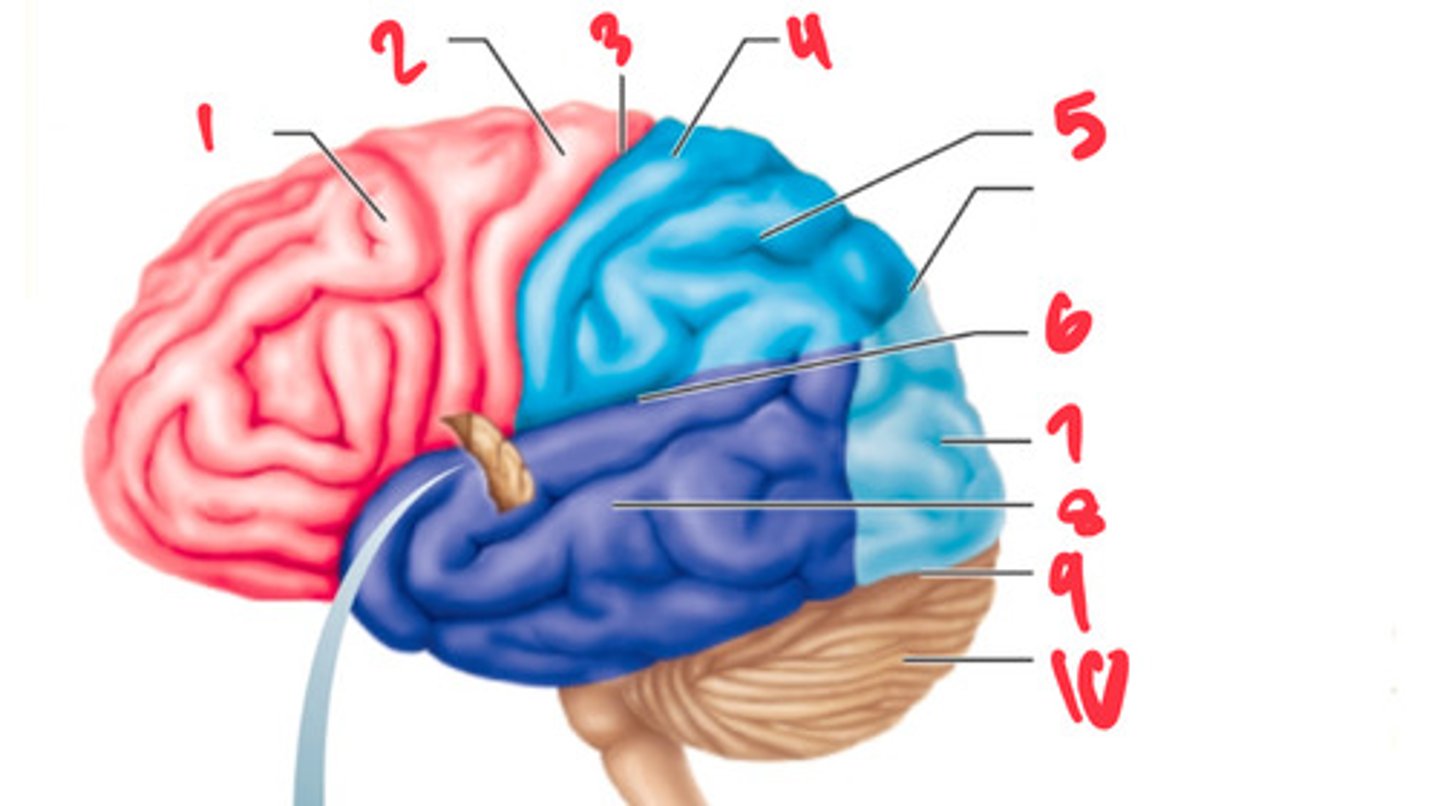
parietal lobe
what structure is labeled by #5?
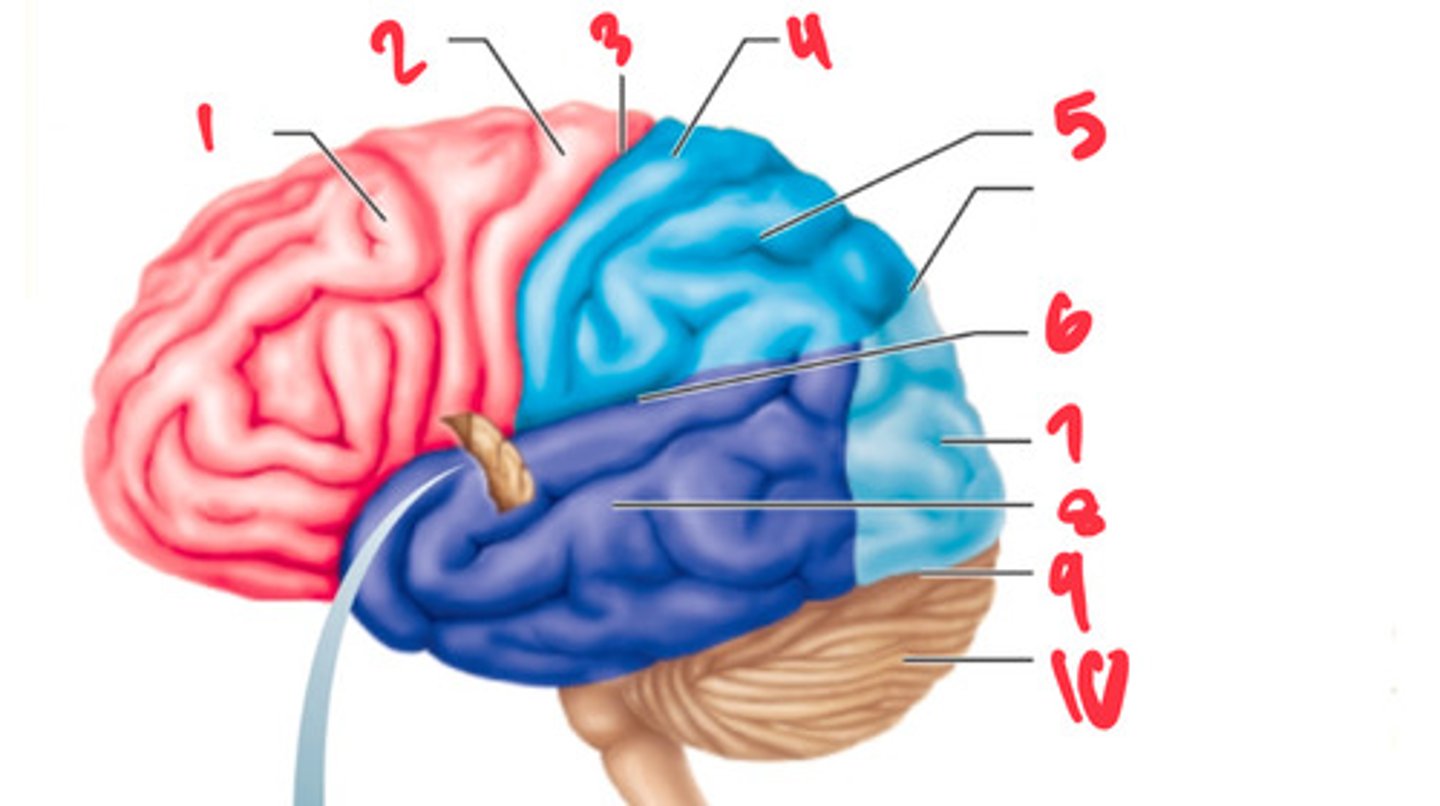
lateral sulcus
what structure is labeled by #6?
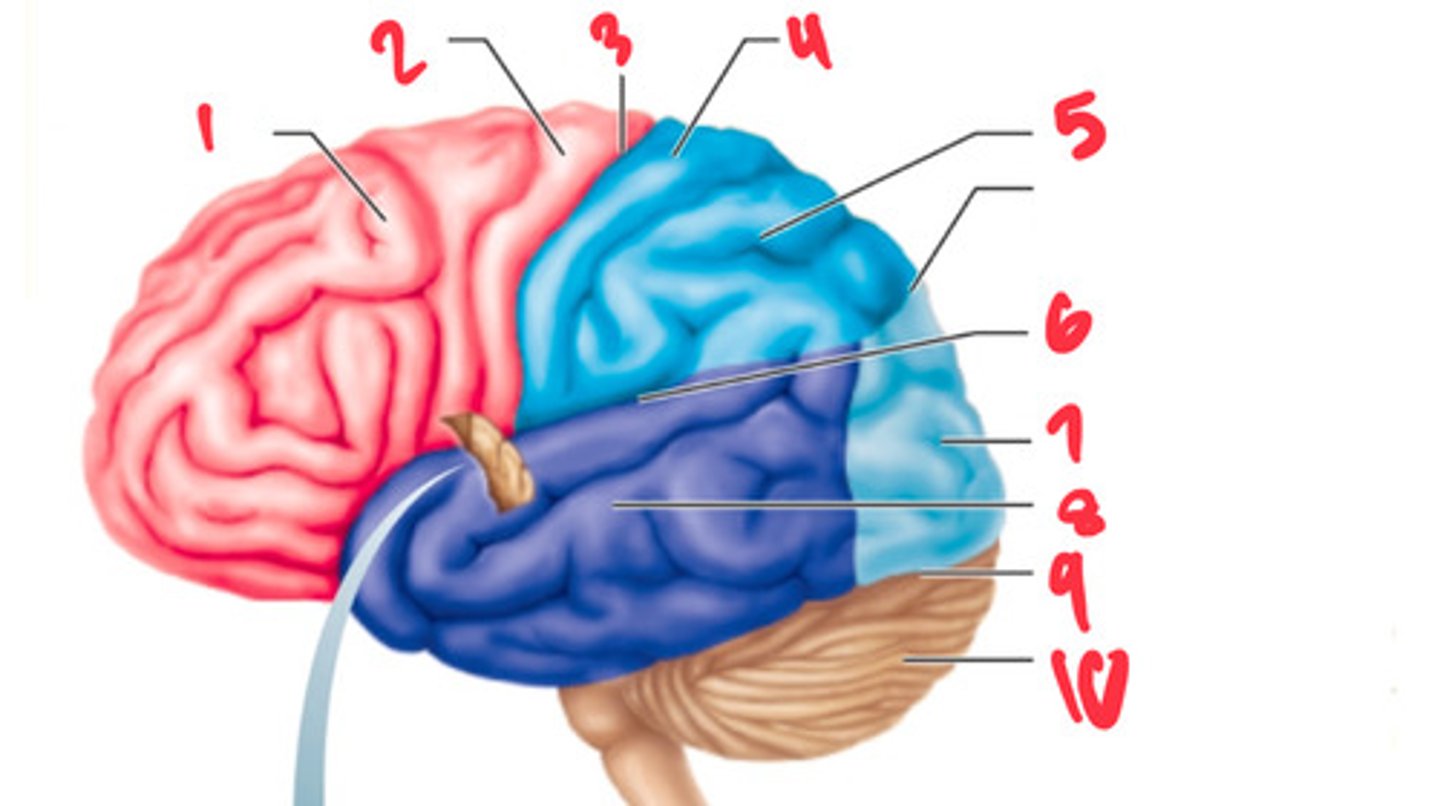
occipital lobe
what structure is labeled by #7?
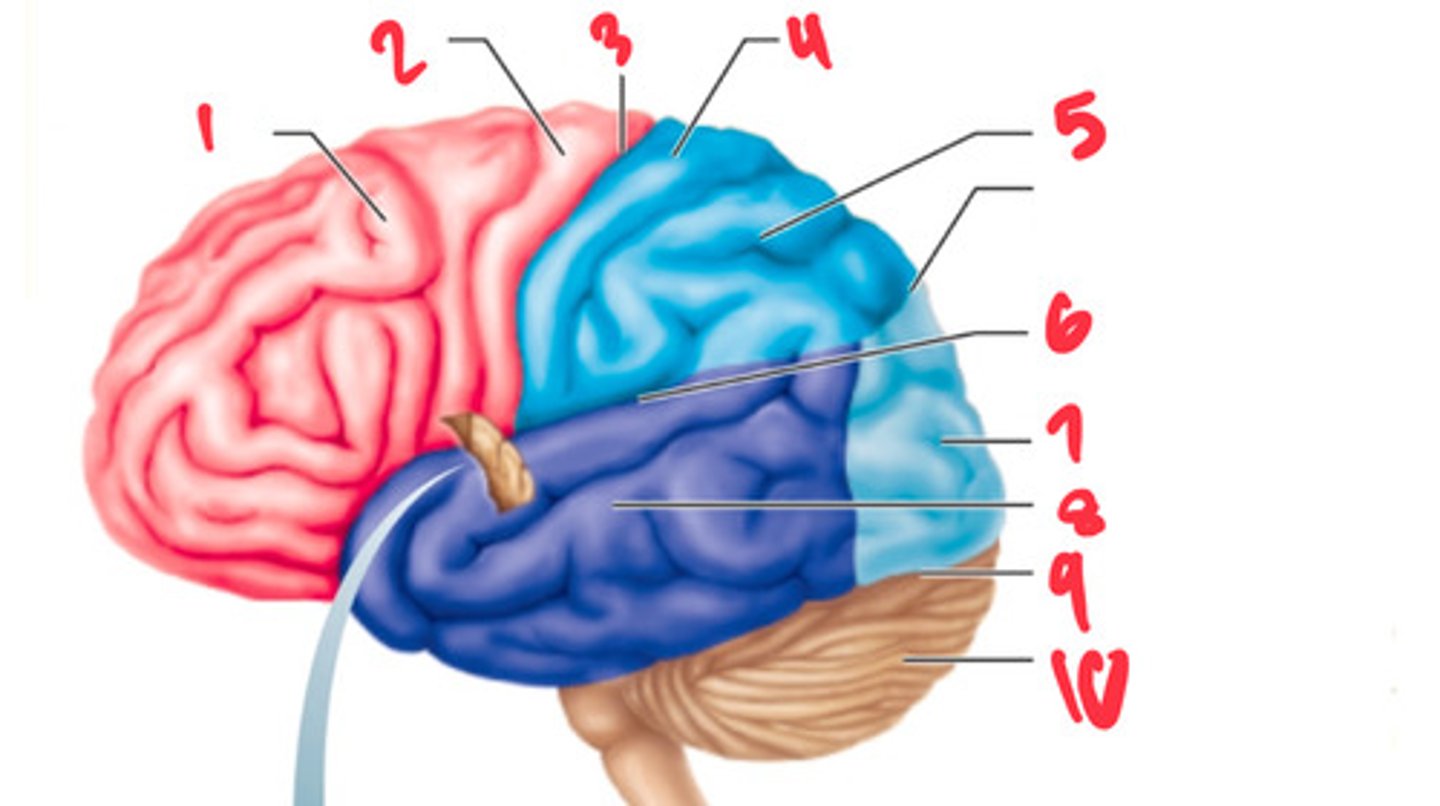
temporal lobe
what structure is labeled by #8?
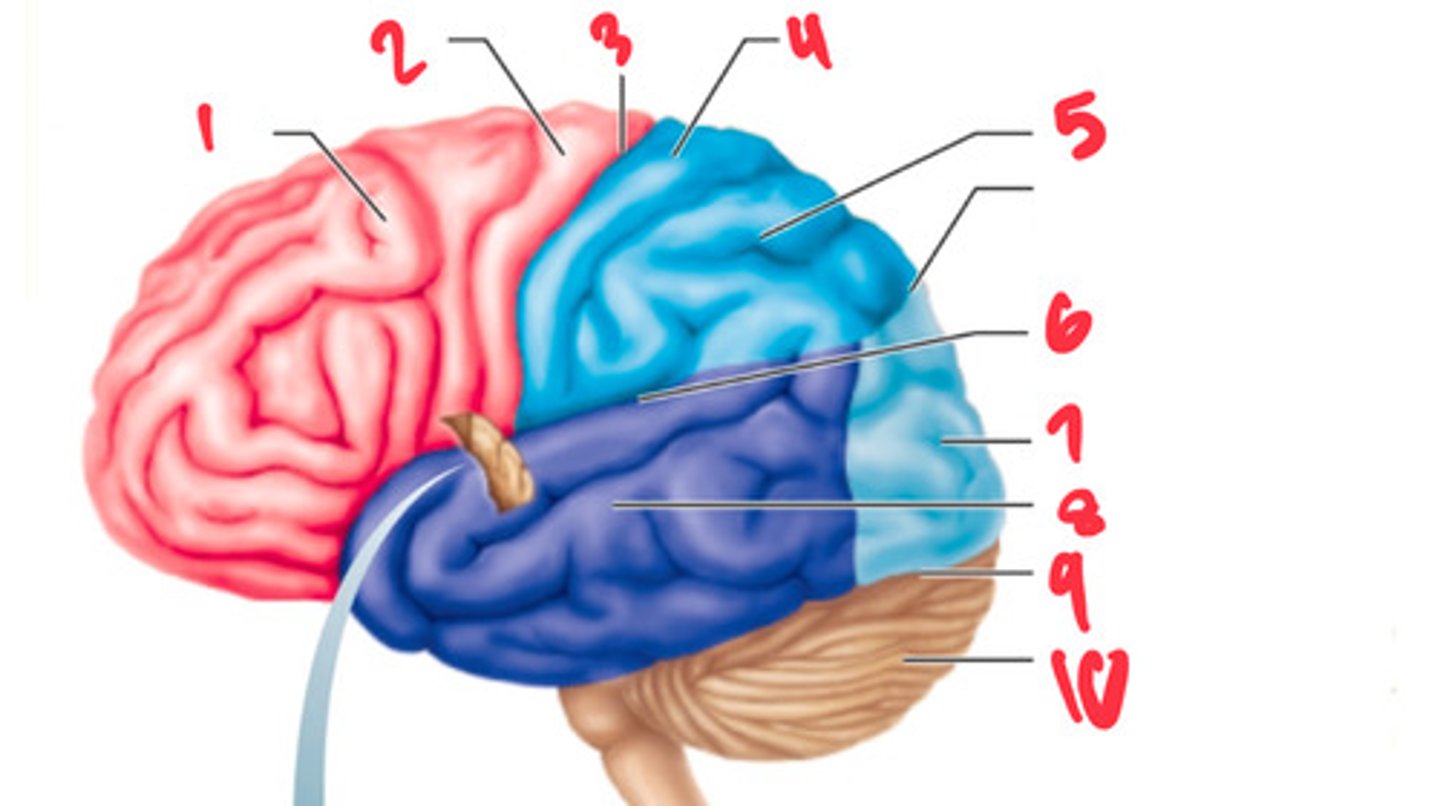
transverse cerebral fissure
what structure is labeled by #9?
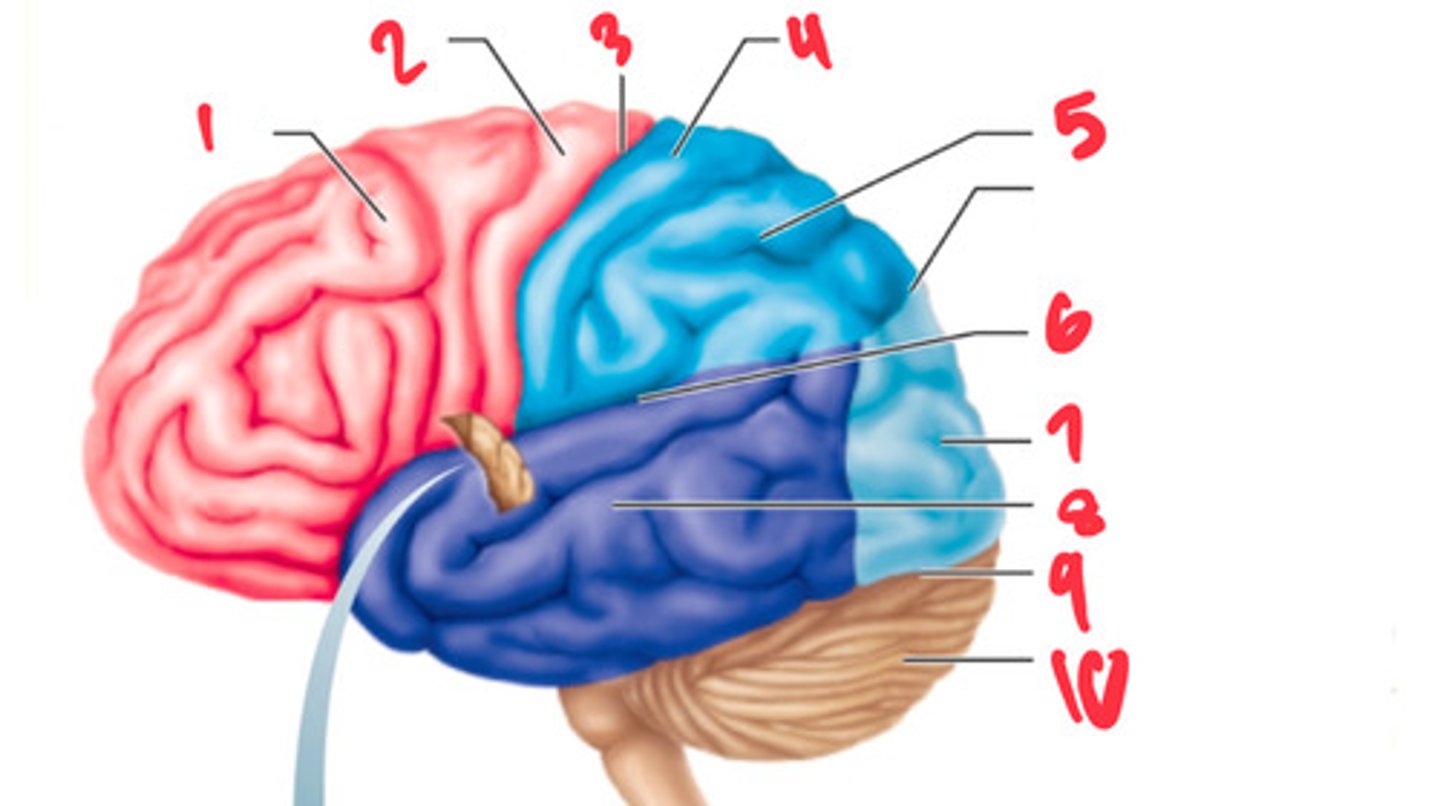
cerebellum
what structure is labeled by #10?
elevated ridges
What are gyri?
shallow grooves
What are sulci?
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, insula
What are the five lobes of the brain?
insula
what structure is highlighted in yellow?
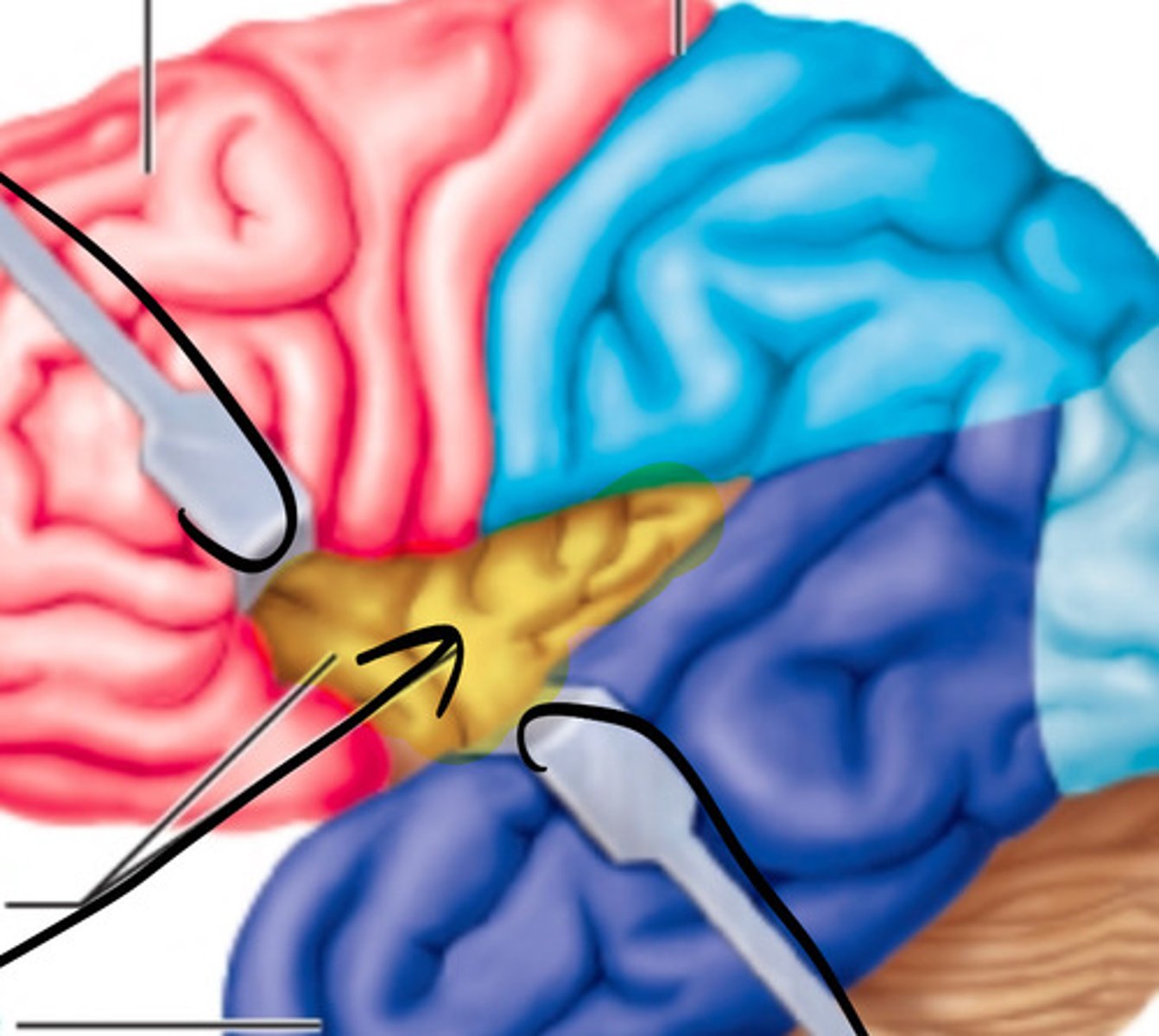
longitudinal fissure
what structure is highlighted in blue?
transverse cerebral, longitudinal
What are the two main fissures?
lateral & central
What are the two main sulci?
lateral sulcus
what structure is highlighted in orange?
motor area, association area, sensory areas
What are the three functional regions of the brain?
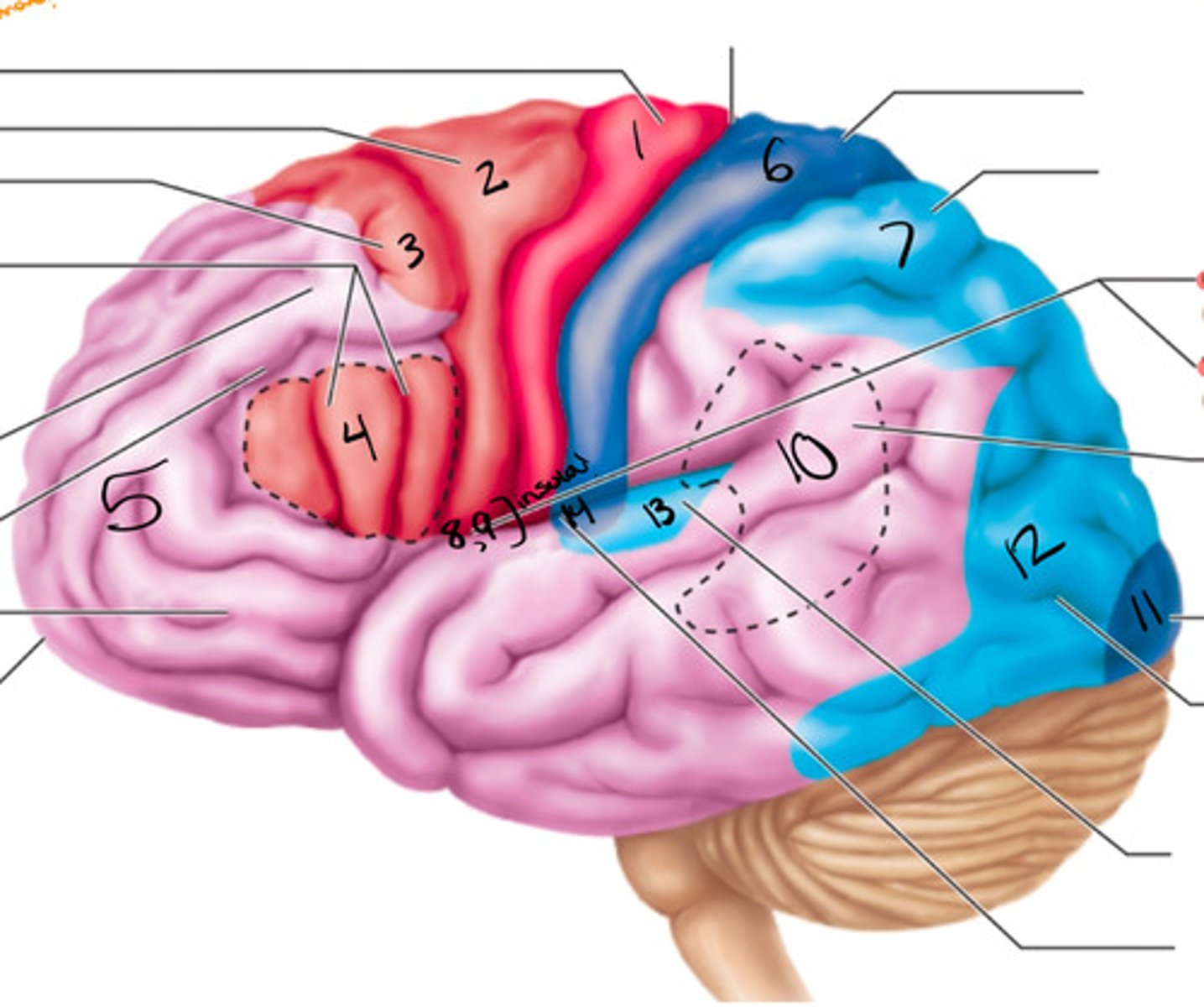
primary motor cortex
what structure is labeled by #1?
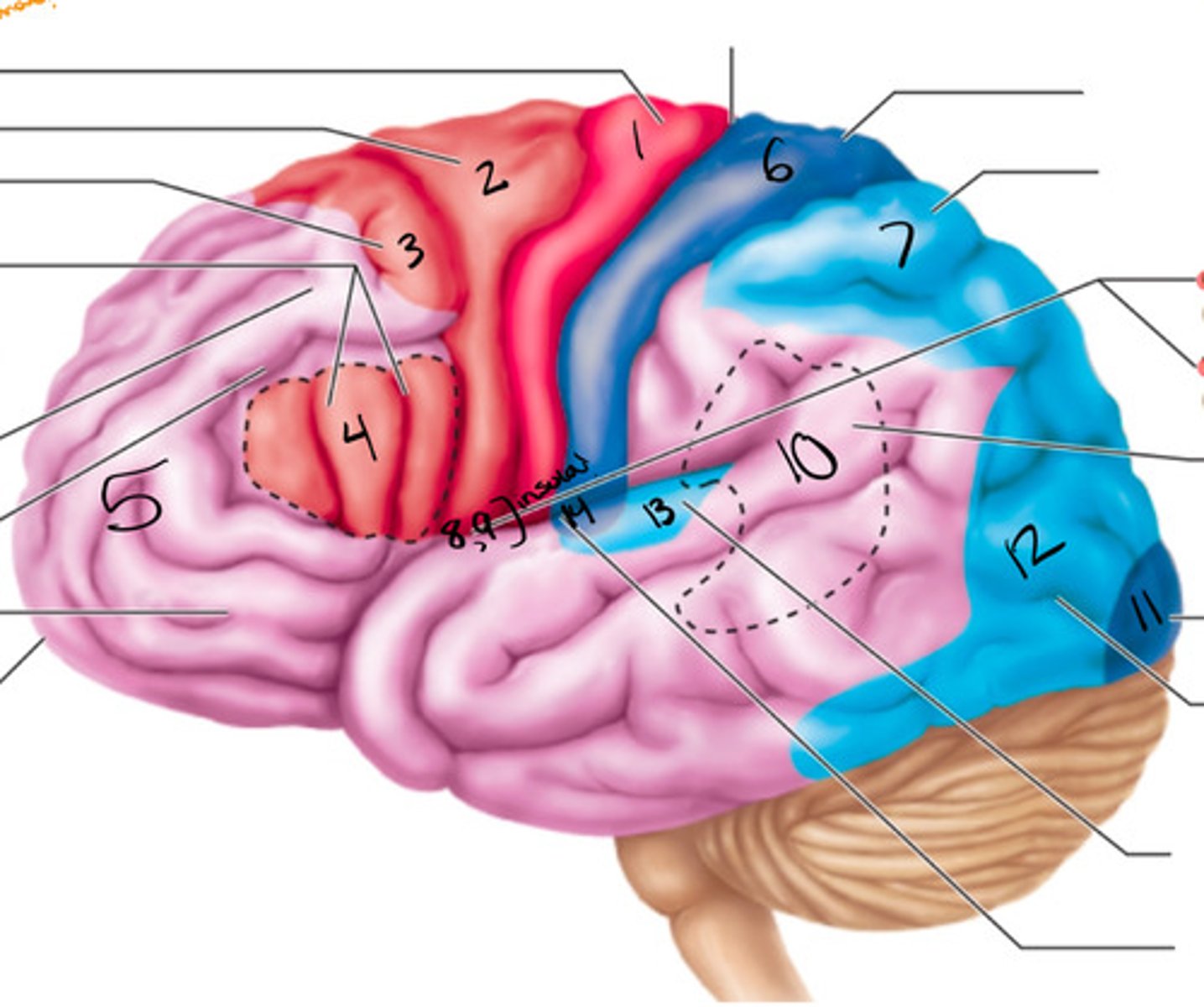
premotor cortex
what structure is labeled by #2?
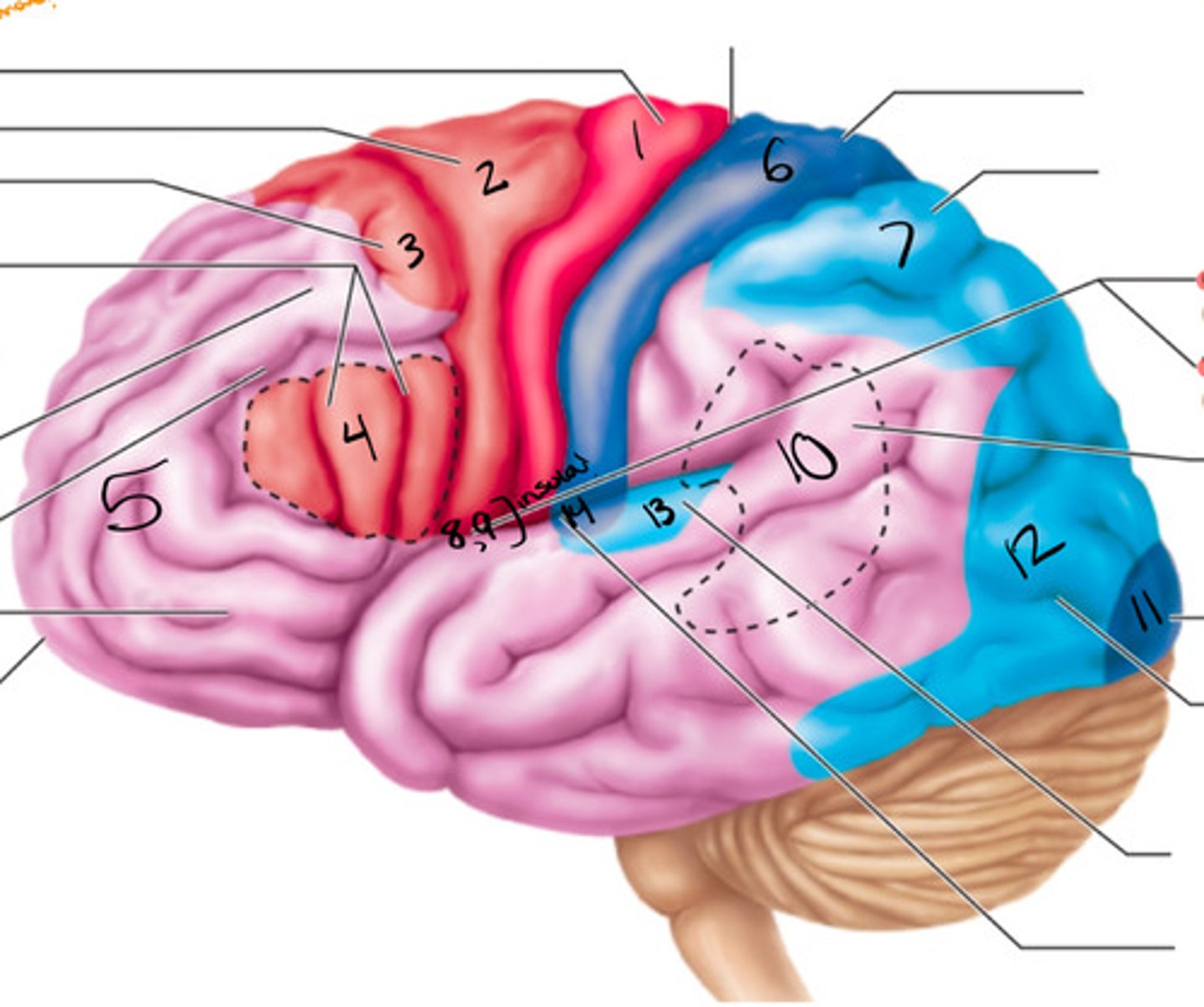
frontal eye field
what structure is labeled by #3?
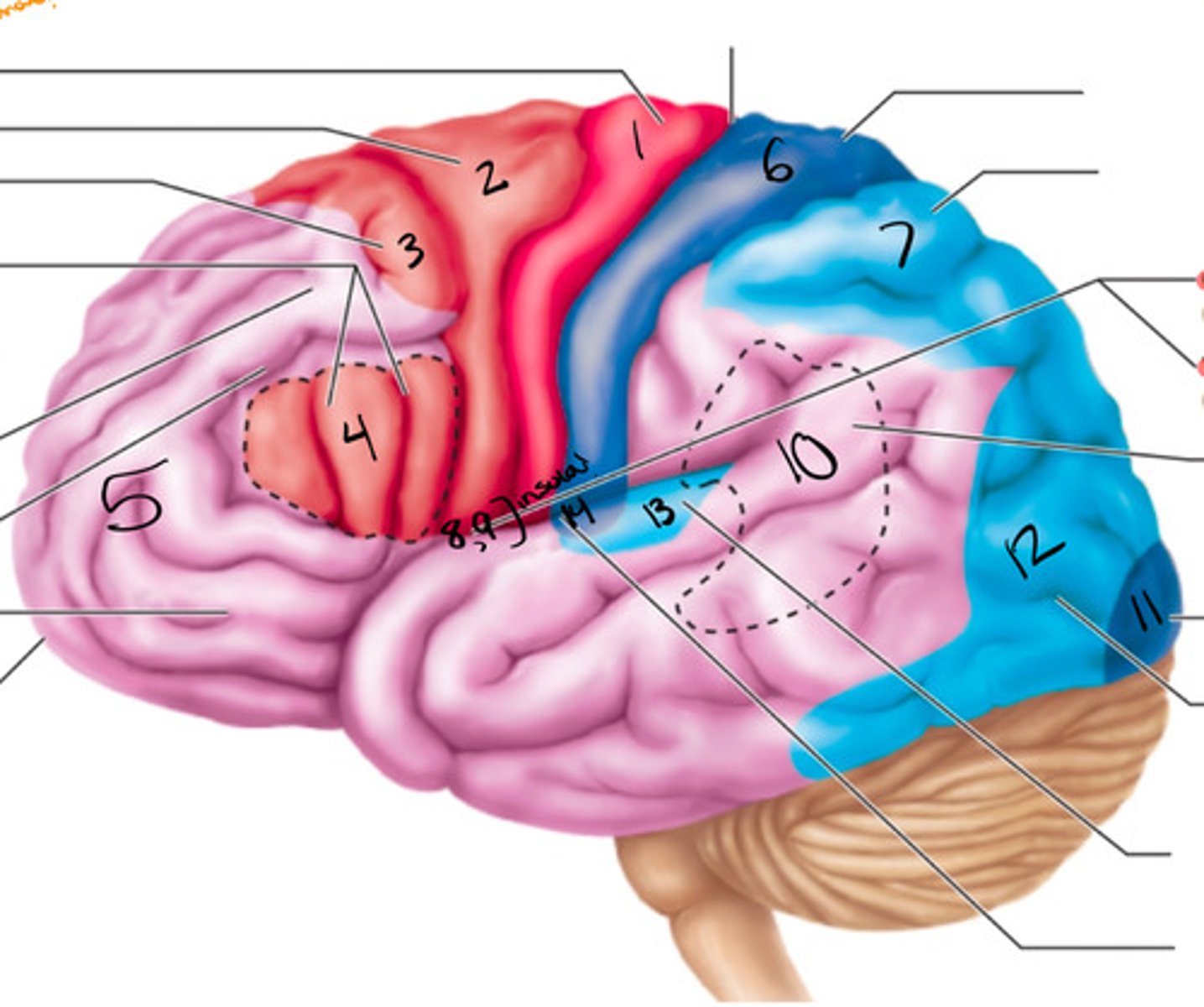
bro as area
what structure is labeled by #4?
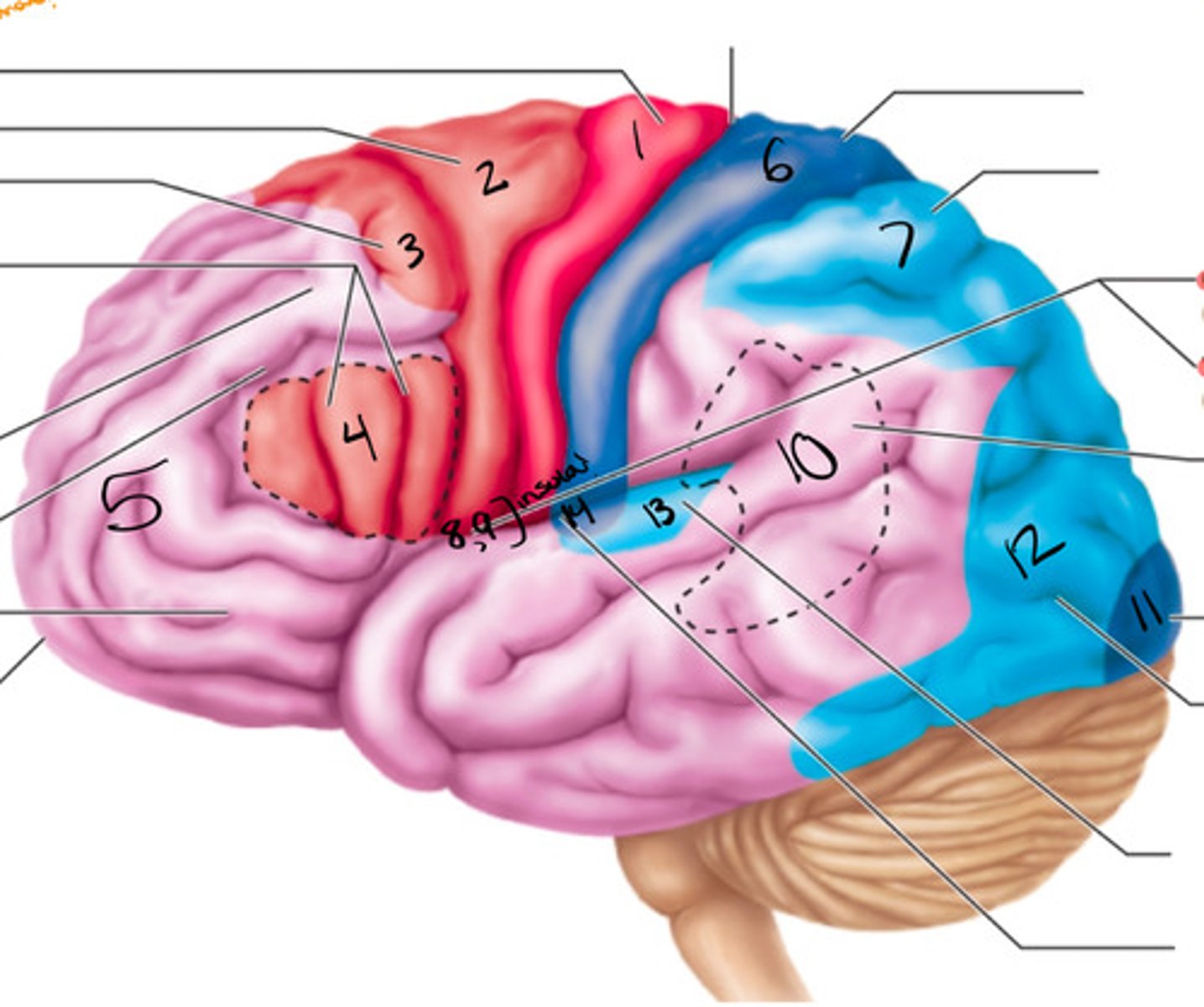
anterior association area (prefrontal cortex)
what structure is labeled by #5?
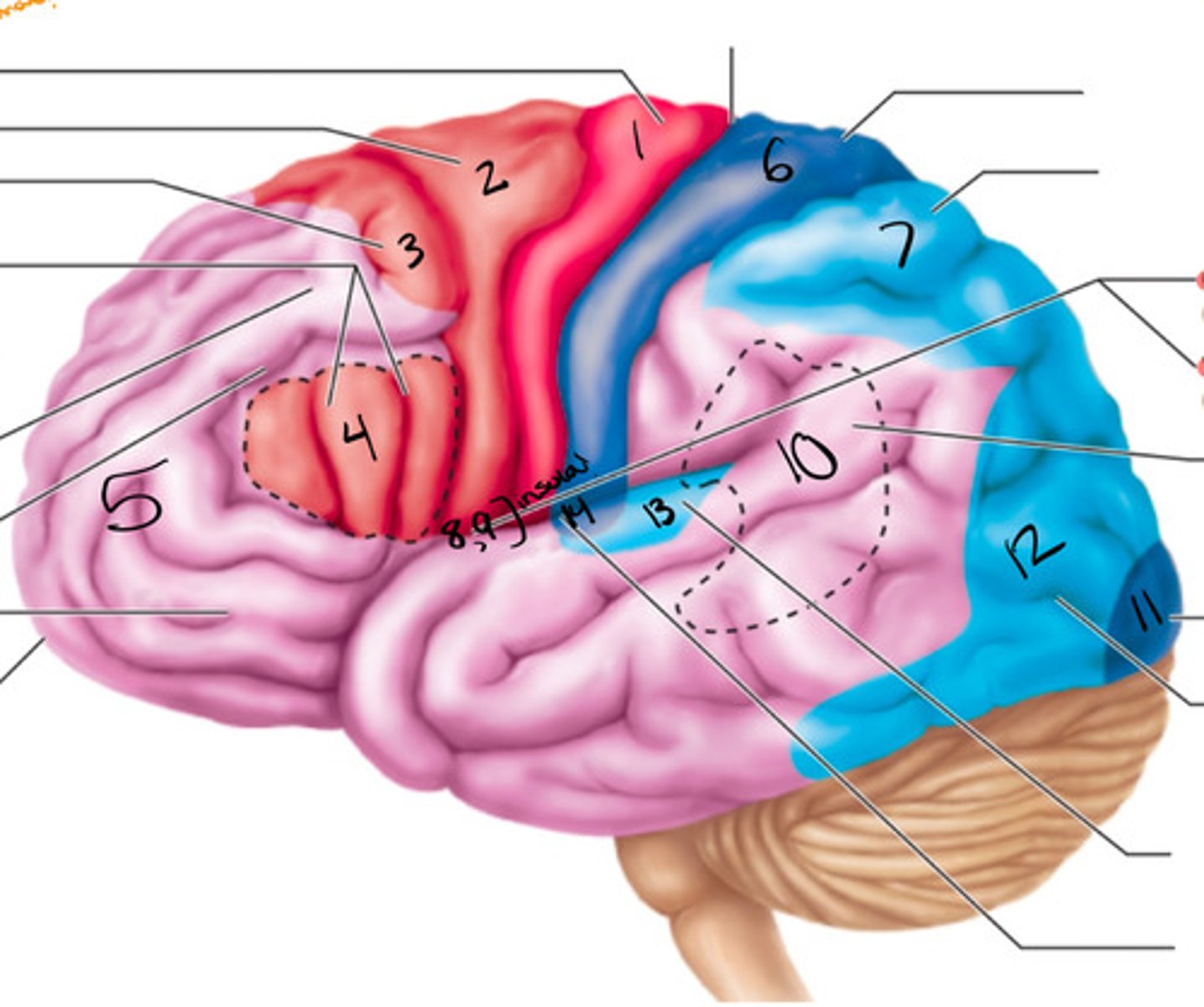
primary somatosensory cortex
what structure is labeled by #6?
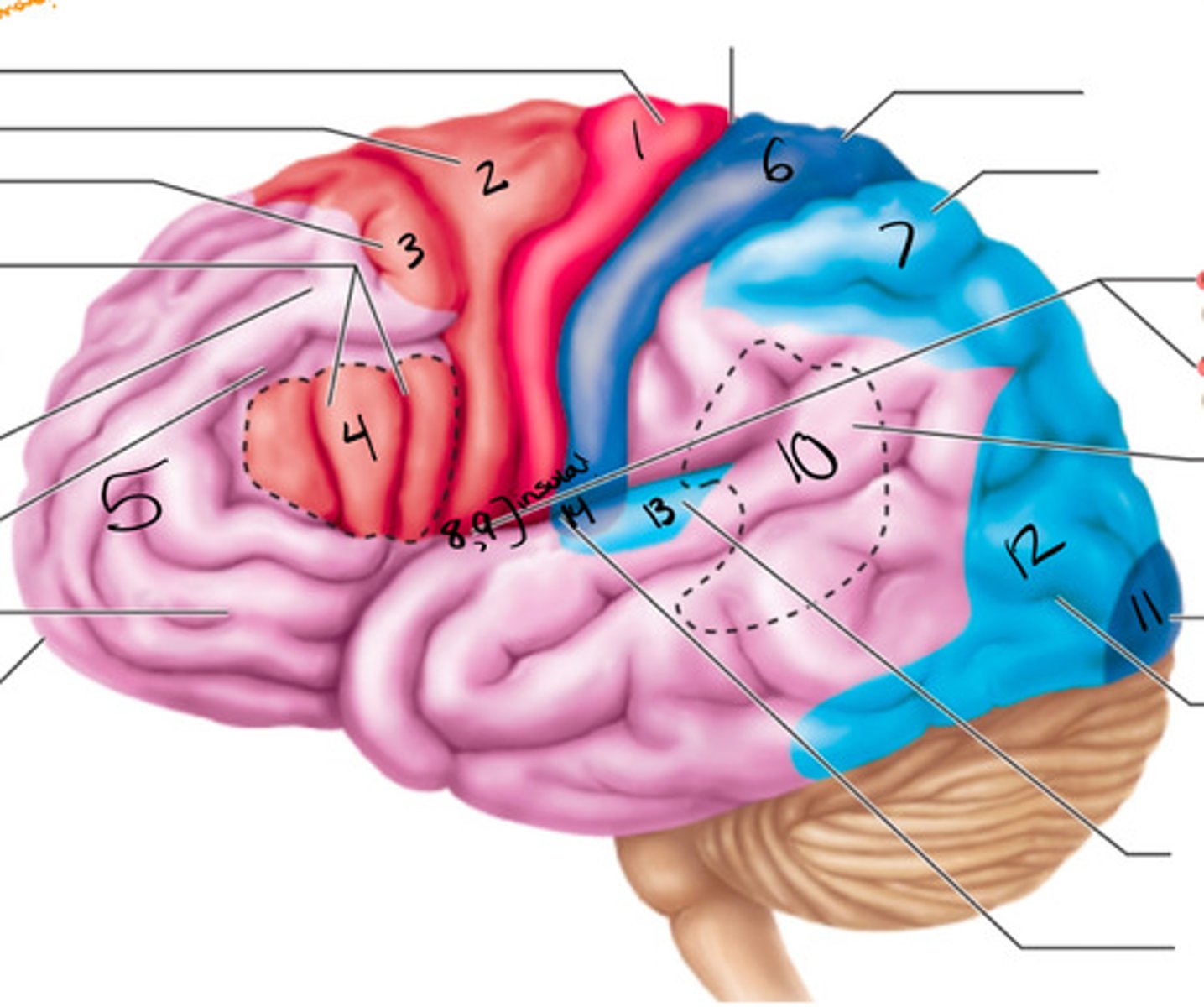
somatosensory association cortex
what structure is labeled by #7?
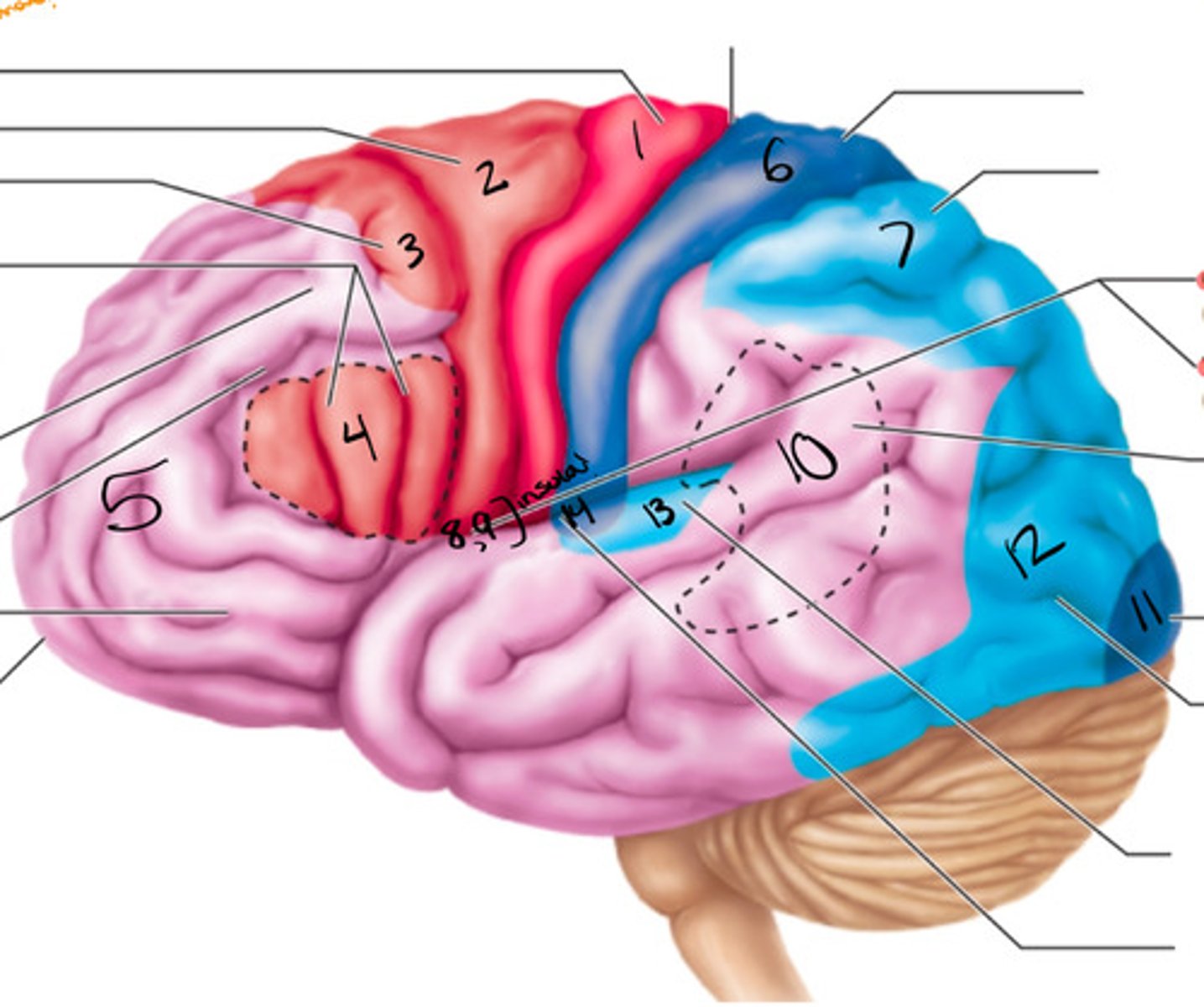
gustatory cortex and vestibular cortex
what structure is labeled by #8 and #9?
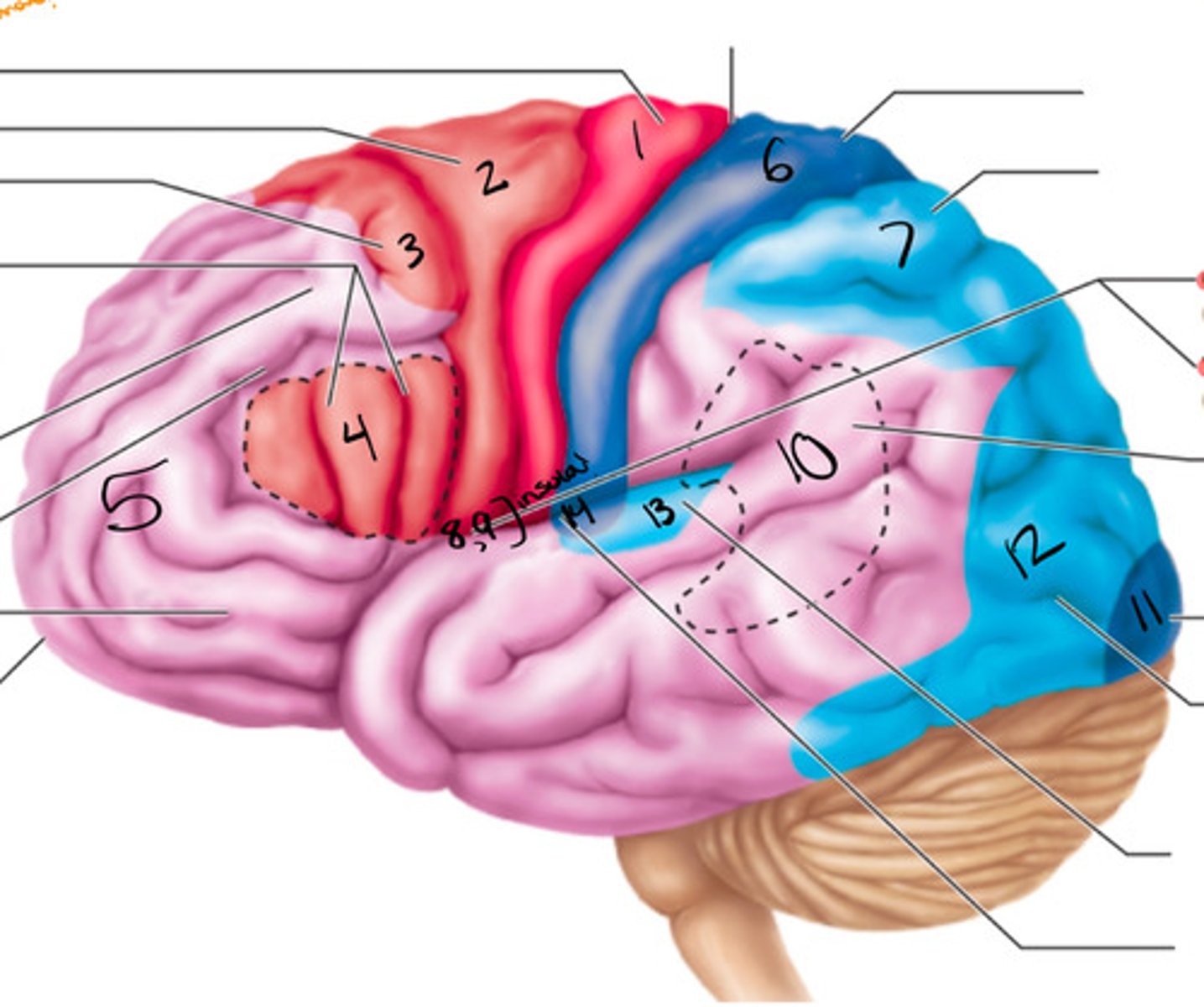
wernickes area
what structure is labeled by #10?
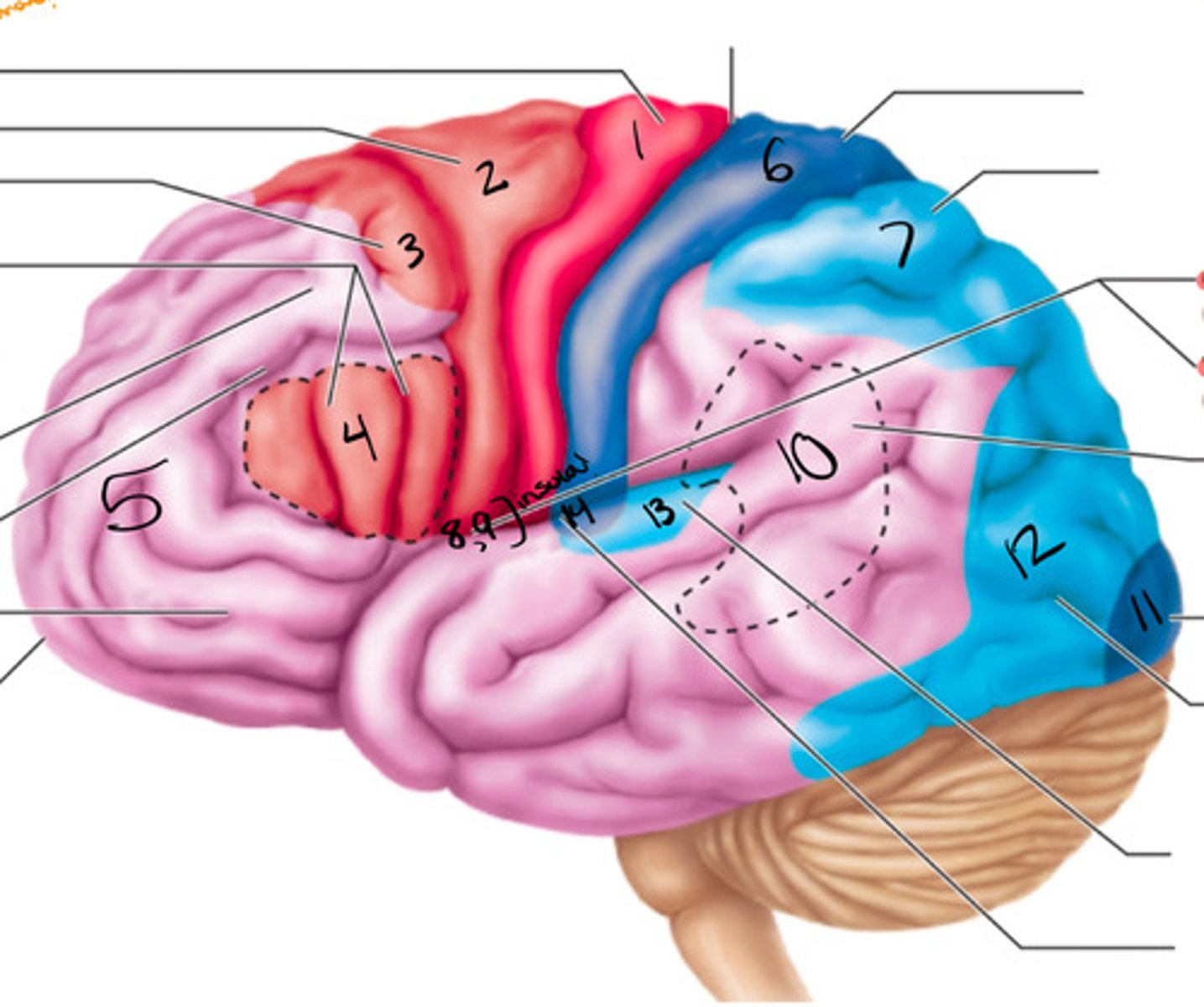
primary visual cortex
what structure is labeled by #11?
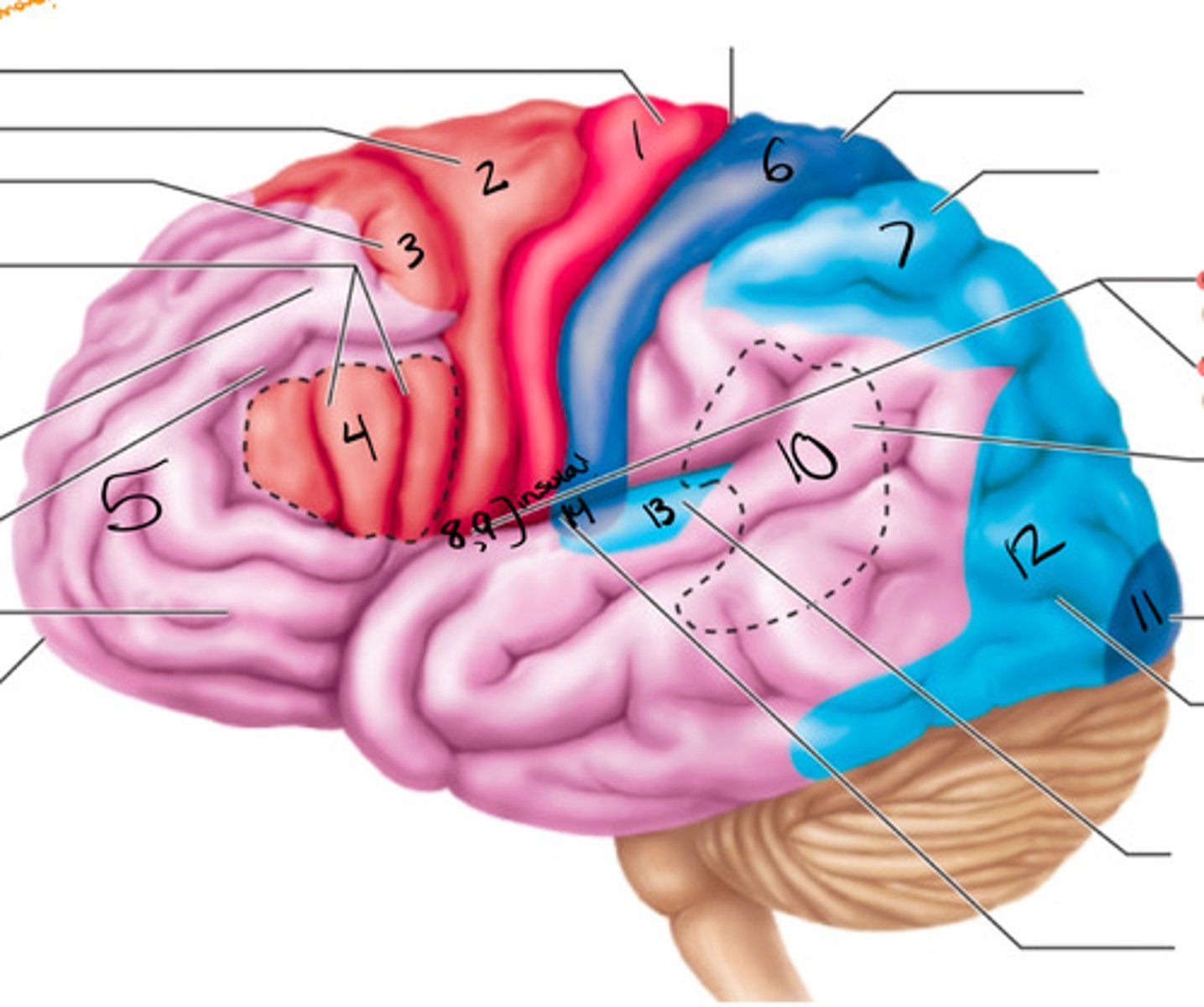
visual association area
what structure is labeled by #12?
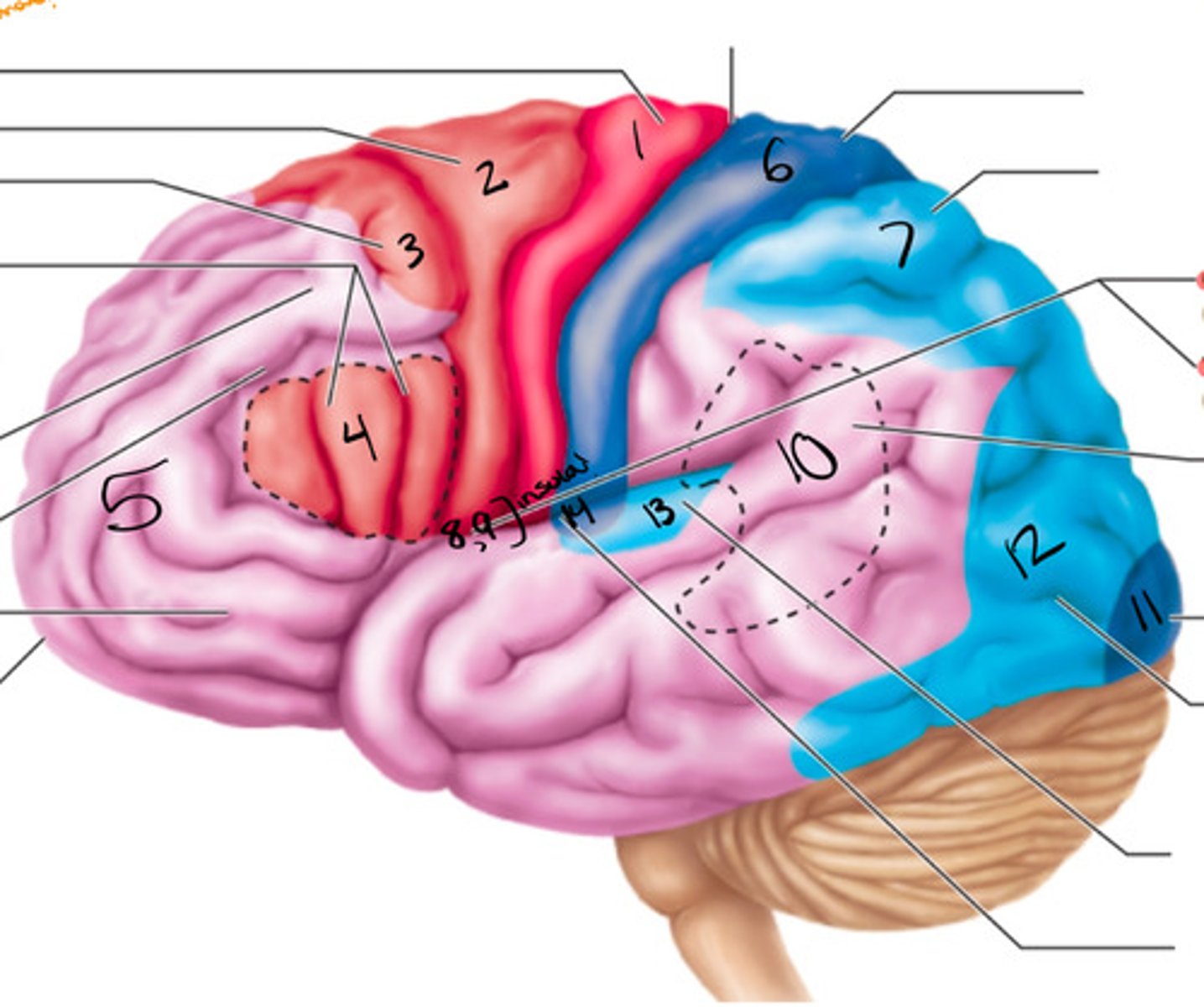
primary motor cortex (pre-central gyrus), premotor cortex, broca's area, frontal eye field
what are the 5 motor areas?
auditory association area
what structure is labeled by #13?
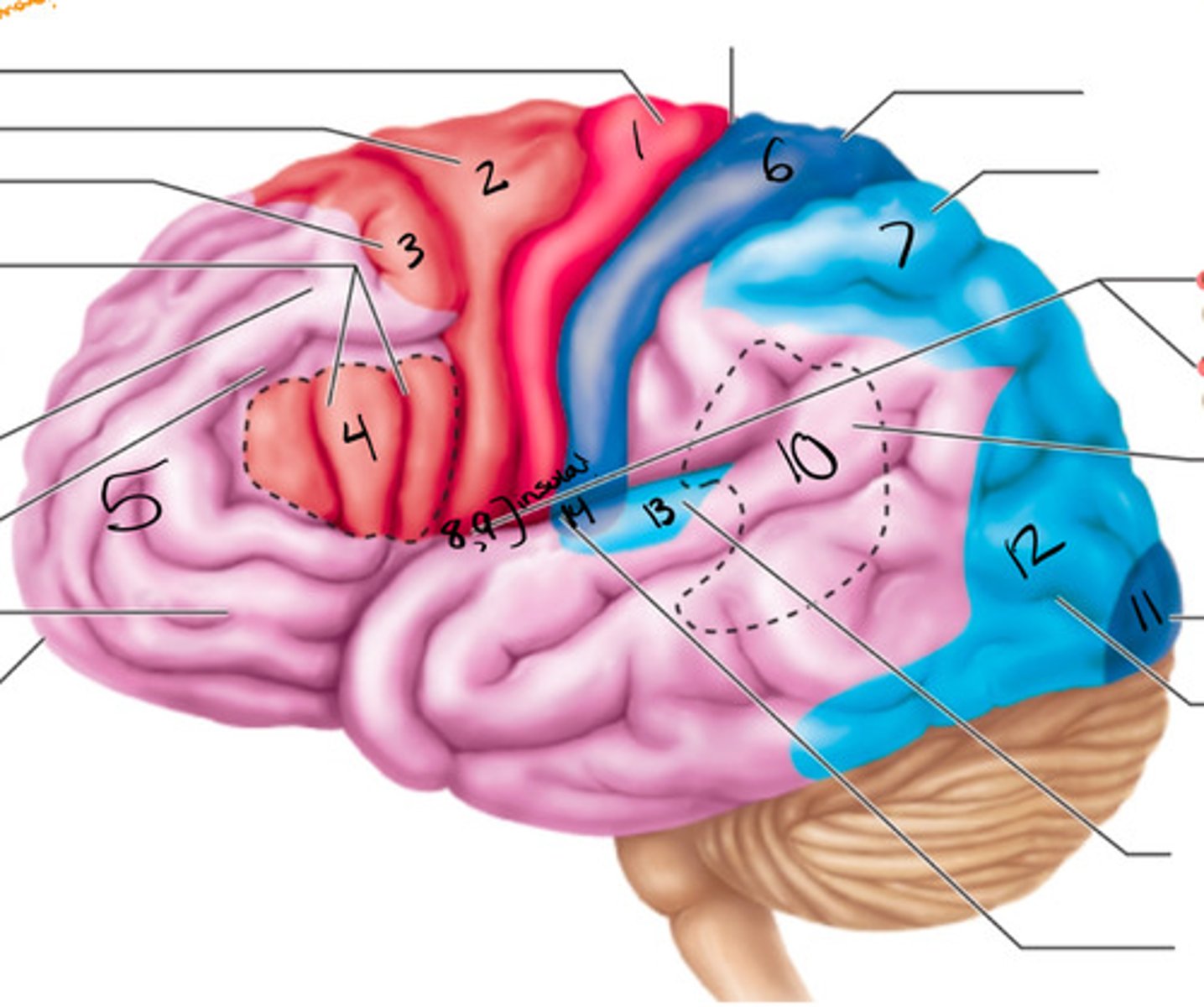
primary auditory cortex
what structure is labeled by #14?
voluntary movement
What is the function of the primary motor cortex?
planning of movement
What is the function of the premotor cortex?
production of speech
What is the function of broca's area?
working memory for spatial tasks, executive area for task management, working memory for object-recall, solving complex/multitask problems
What are the four functions of the anterior association area (prefrontal cortex)
sensory
What is the parietal lobe primarily responsible for?
primary sensory cortex (post-central gyrus), somatosensory association cortex, visceral sensory area, frontal eye field
What are the 4 main sensory areas?
somatic sensation, taste, equilibrium, speech/language, vision, hearing
What are the 6 main functions of the sensory areas?
primary somatosensory cortex & somatosensory association cortex
What are the two main structures related to somatic sensation?
receiving information on touch, pressure, pain, and temperature
What is the function of the primary somatosensory cortex?
can't feel, numbness
What would happen if your primary somatosensory cortex was damaged?
process, store, and integrate sensory information
What is the main function of the somatosensory association cortex?
insula
Where are the gustatory cortex & vestibular cortex located?
perception of taste
What is the function of the gustatory cortex?
conscious awareness of balance
What is the function of vestibular cortex?
understanding language
What is the function of wernicke's area?
primary visual cortex & visual association area
What are the two main structures of the occipital/vision region?
receives visual information
What is the function of the primary visual cortex?
interpret visual stimuli from primary visual cortex
What is the function of the visual association area?
auditory association area & primary auditory cortex
What are the two structures of the temporal/hearing region?
interprets sounds
What is the function of the auditory association area?
receive and process auditory information
What is the function of the primary auditory cortex?
visual, auditory, vestibular, olfactory, gustatory
What are the 5 special sense areas?
control of movement & amount of force
What is the function of basal nuclei (ganglia)?
caudate nucleus, putamen, globes pallidus
What makes up the basal nuclei?
sub-thalamic nuclei, substantial nigra
What two structures support the basal nuclei?
GABA, Dopamine, Glutamate
What are the 3 neurotransmitters involved with the basal nuclei?
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
what are the 3 structures of the diencephalon?
sort information, relay
What is the function of the thalamus?
vital for body homeostasis, control the ANS, emotional response, body temp, food intake, thirst, circadian rhythm, endocrine functions
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
secretes melatonin (sleep inducing signal, sleep-wake cycle)
What is the function of the epithalamus?
midbrain, pons, medulla
What are the 3 structures in the brain stem?
motor control, eye movement, visual & auditory processing
what are the functions of the midbrain?
superior cerebellar peduncles, superior colliculi, inferior colliculi, substantial nigra, red nuclei
What are the 5 structures of the midbrain?
superior cerebellar peduncle
what structure is labeled by #8?
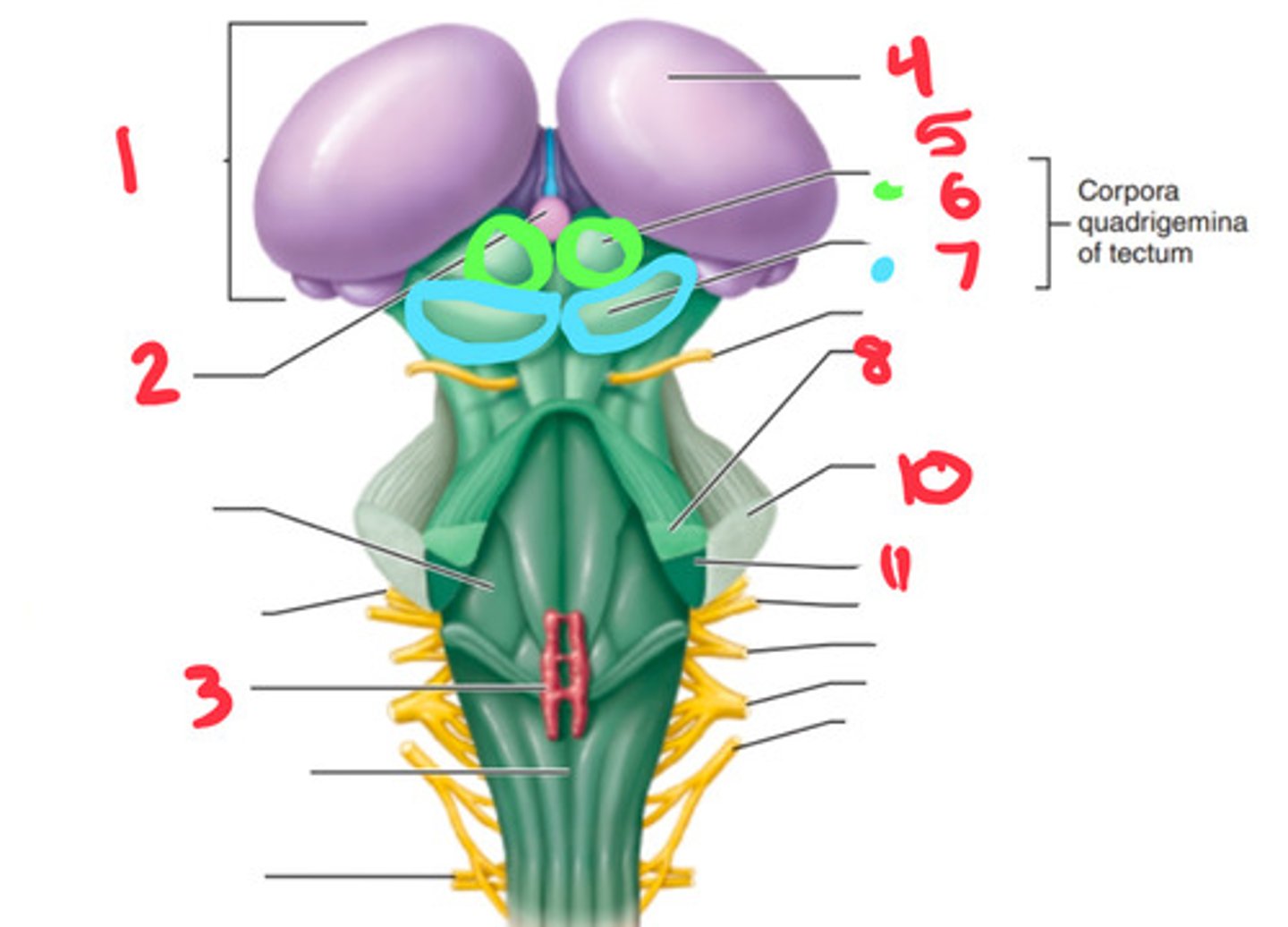
superior colliculus
what structure is labeled by #6?
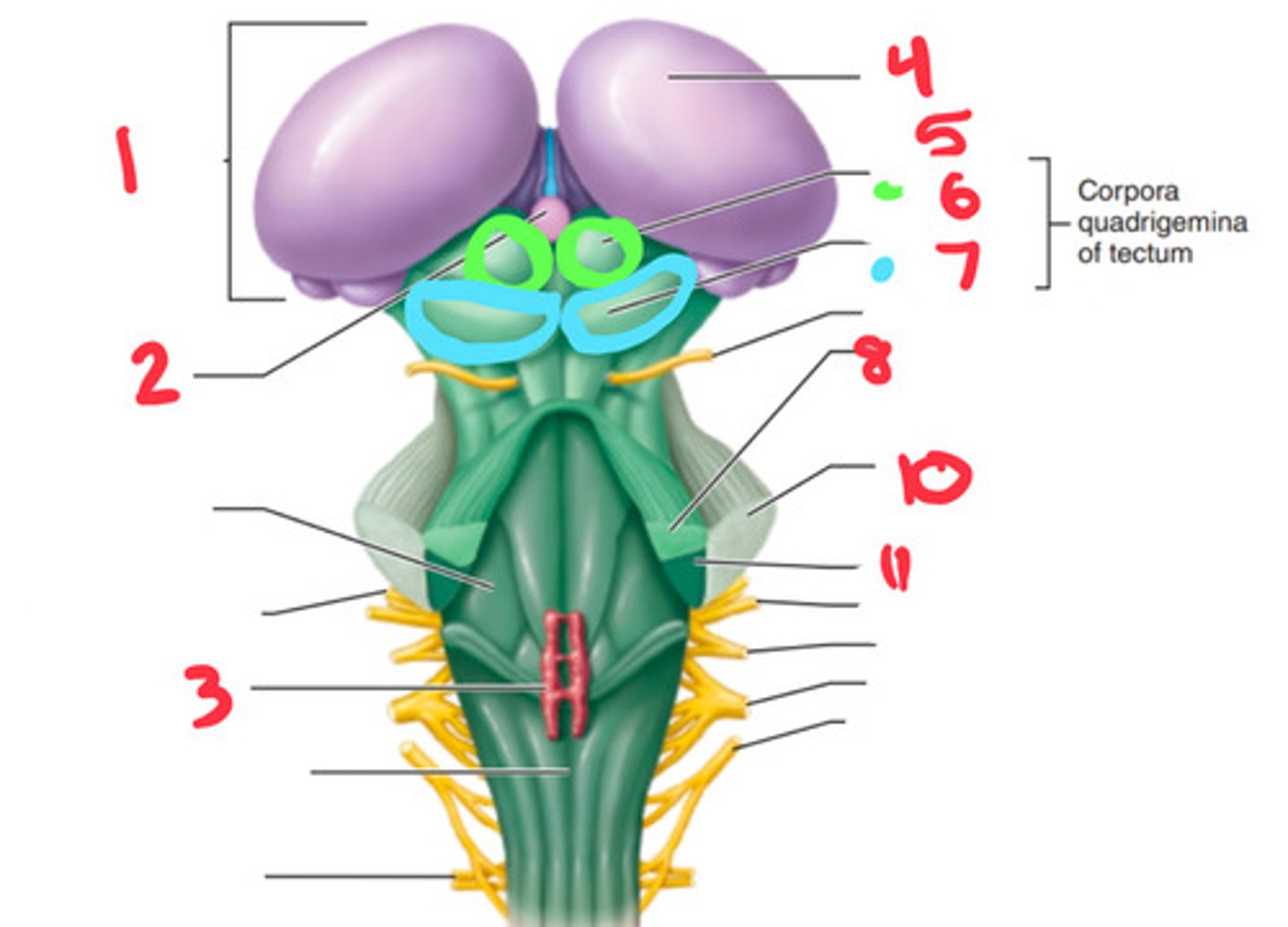
inferior colliculus
what structure is labeled by #7?
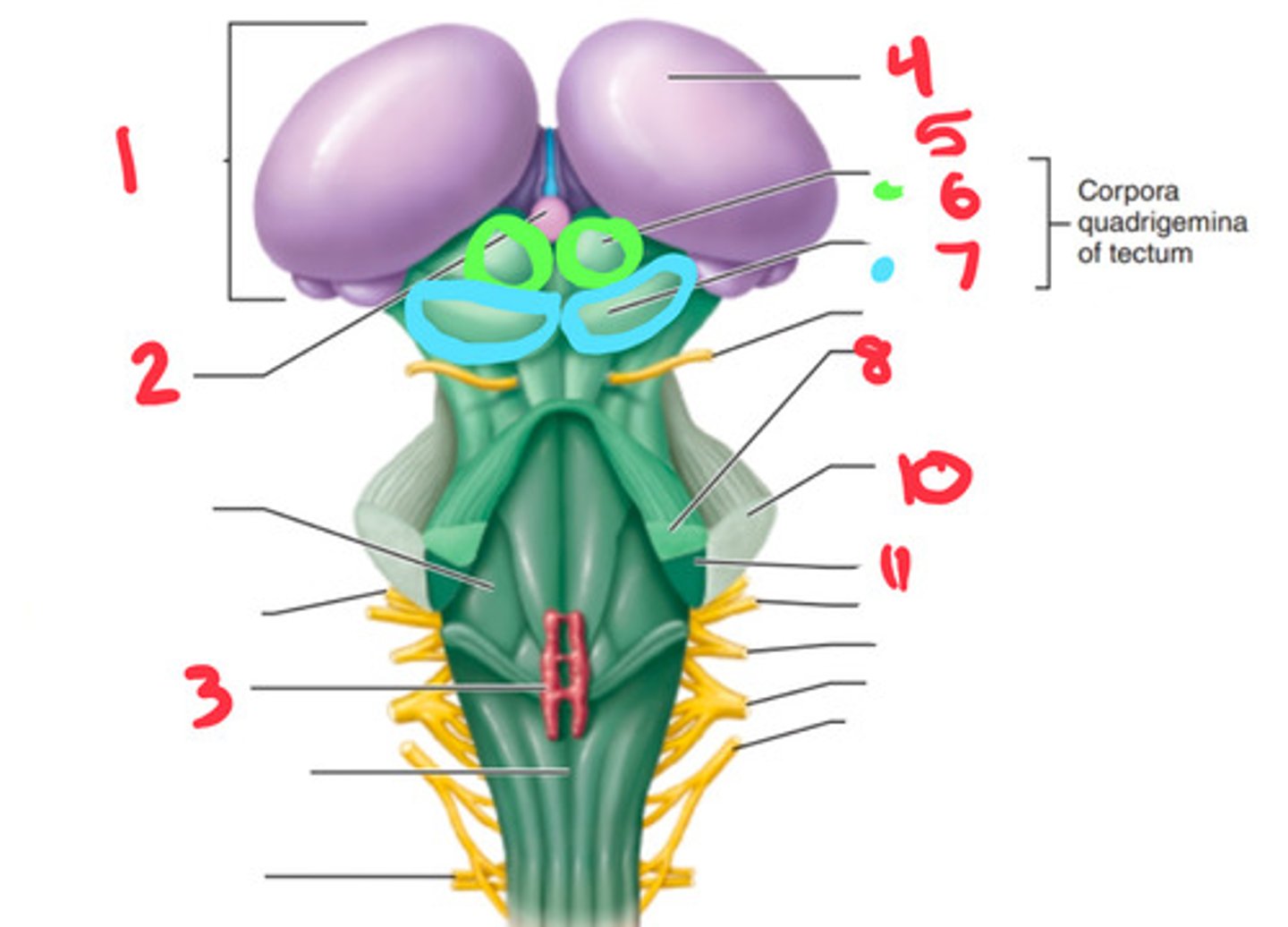
middle cerebellar penducle
what structure is labeled by #10?
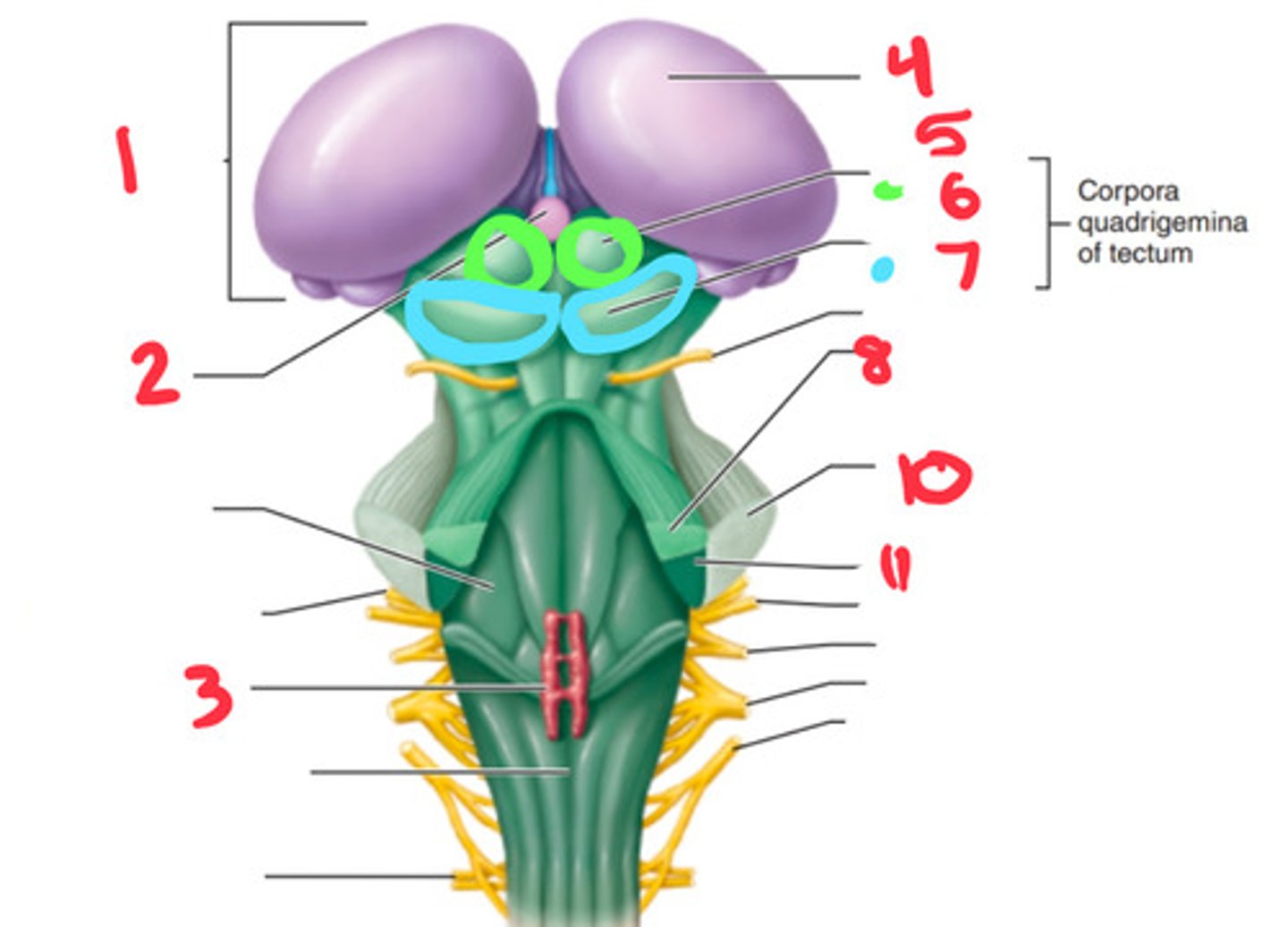
inferior cerebellar penducle
what structure is labeled by #11?
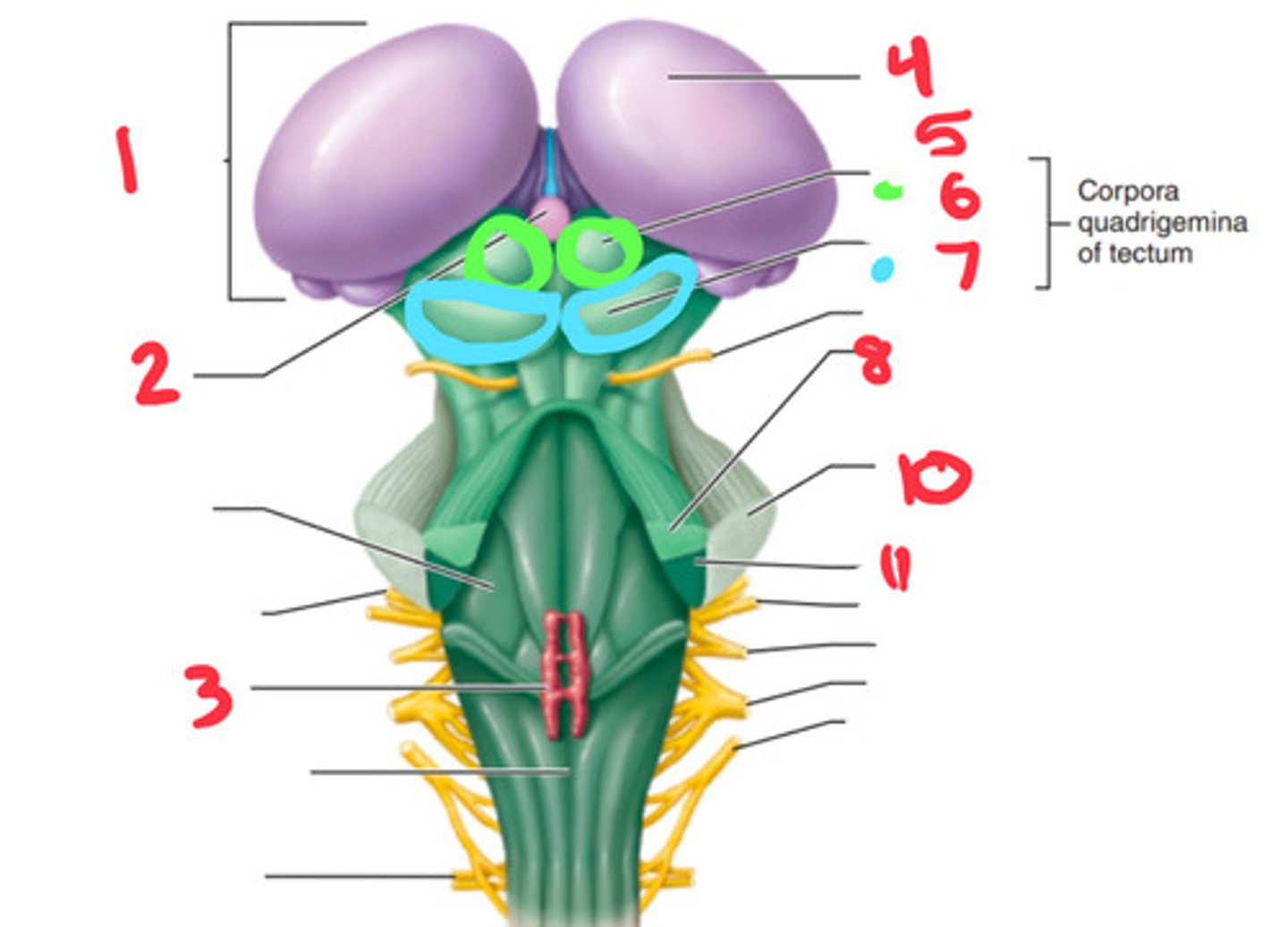
medulla
the inferior cerebellar penducle is apart of what part of the brain?
midbrain
the superior cerebellar penducle is apart of what part of the brain?
vision reflex & eye tracking
What is the function of the superior colliculi?
auditory reflex, startle reflex
What is the function of the inferior colliculi?
basal nuclei with movement, dopamine
What is the function of the substantial nigra?
limb flexion pathways
What is the function of red nuclei?
breathing
What is the function of the pons?
longitudinal tract (brain & spinal cord) and transverse tract (pons & cerebellum)
What makes up the pons?
autonomic activity of heart and lungs
What is the function of the medulla?
cardiac center, respiratory center, cochlear nuclei
What are the 3 important nuclei of the medulla?
decussation (info crosses to the other side of the brain)
What happens in the medulla?
inferior cerebellar peduncle
What structure is located in the medulla?
provides the precise timing and appropriate patterns of muscle contractions
What is the function of the cerebellum?
subconsciously, ipsilateral
how does the cerebellum function?