Plant Anatomy, Photosynthesis, and Cell Biology: Key Concepts for Biology Students
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Cuticle (Cutin)
A waxy coating that helps prevent water loss on plants
Trichomes
Cellular outgrowth that may reduce water loss
Vein
The part of the plant that contains the xylem and phloem
Lower Epidermis
Dermal layer with many stomata
Palisade Parenchyma
The part of the mesophyll that is very ridged and contains most of the chloroplast of the cell.
Midrib
Supports vein and leaf blade, found going down the length of a leaf.
Spongy Parenchyma
The part of the mesophyll that is very open and hollow which allows for gas to be exchanged in the leaf. Oxygen goes out while CO2 is brought in.
Upper Epidermis
Dermal layer with few stomata
Mesophyll
Most photosynthesis takes place here
Vascular Tissue
Xylem and Phloem
Xylem
Conducts water and minerals throughout the plant
Phloem
transports sugars (food) and amino acids
Guard Cells
Cells found flanking the stoma that open and close when need to adjust the rate of gas exchange, and regulate water loss.
Stoma
A small opening generally found at the bottom of a plants leaves that allows for gas exchange
Stomata
Multiple stoma
How does energy enter most ecosystems?
As sunlight
An organism that can make its own food is called a:
Producer (autotroph)
An organism that gets energy by breaking down organic matter such as wastes and dead organisms is called a:
Decomposer
The first organism in a food chain is always a:
Producer
The organism that eats the producer is a:
First-level consumer (Herbivore)
The organism that eats a first-level consumer is called a:
Second-level consumer (Carnivore)
A diagram made up of many food chains is called a(an):
Food Web
The energy in food is released through the process of:
Respiration
The energy released in0 the process known as cellular respiration is stored in the carrier molecule known as:
ATP
What organelles found in plant cells capture energy from the sun to make food?
The Chloroplasts
What is the name of the process in which cells break down simple food molecules such as sugar and release the energy these molecules contain?
Cellular Respiration
What is the name of the organelle where aerobic respiration takes places, converting simple sugar molecules into usable energy?
The Mitochondria
What form of respiration does not require the presence of oxygen?
Anaerobic Respiration
Does respiration take place only in animal cells?
No, it takes place in both animal and plant cells.
What form of respiration releases more ATP, Anaerobic or Aerobic respiration?
Aerobic Respiration.
What consumers only eat plants?
Herbivores
What consumers only eat other animals?
Carnivores
What consumers eat both plants and animals?
Omnivores
What consumers eat only animal and plant remains?
Scavengers
The Light Reaction occurs in the:
Thylakoids
The Calvin Cycle (Dark Reaction) occurs in the:
Stroma
Leaves are very thin and flat:
To maximize sunlight capture
There are air spaces between the mesophyll cells to:
Capture/exchange gases
The epidermis secretes cuticle to:
To prevent drying out
Why does water travel up the xylem of a plant if there is not any heart to pump the water around?
Xylem tubes are so small that water is able to travel up using capillary action. Water evaporates (sweats) out of the leaves of a plant (partially through the stomata) and the charge of the water evaporating pulls up more water at the bottom of the plant.
Cell Membrane
Regulates what goes in and out of a cell using enzymes, phospholipids, and specific proteins
Ribosomes
Responsible for protein synthesis by converting mRNA into amino acids. Generally attached to the endoplasmic reticulum
Amyloplast
Converts sugars into starch and stores it for later use, generally found in non photosynthetic cells
Chloroplast
Primary location for where photosynthesis takes place
Golgi apparatus
Packages and transports proteins and lipids in and out of the cell
Cell wall
Provides structure to plant cells
Nucleus
Contains cells genetic material
Endoplasmic reticulum
Responsible for protein, lipid, and steroid synthesis and folding
Mitochondria
Converts sugar into ATP
Cytoplasm
A liquid material that houses the organelles of a cell
Stroma (Chloroplast)
Where the Calvin Cycle takes place
Interior membrane (Chloroplast)
Regulates the passage of substances between the chloroplast and the rest of the cell
Thylakoids (Chloroplast)
Location of the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis takes place
Exterior Membrane (Chloroplast)
Regulates the passage of substances between the chloroplast and the exterior of the cell
Granum (Chloroplast)
A stack of thylakoids
Where is the chloroplast located?
Within the cytoplasm
What are the four function of a leaf?
1) Gas exchange
2) Cool the plant
3) Photosynthesis
4} Food storage
Equation for Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 (oxygen) ---------> 6CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6H2O (water) + energy (ATP)

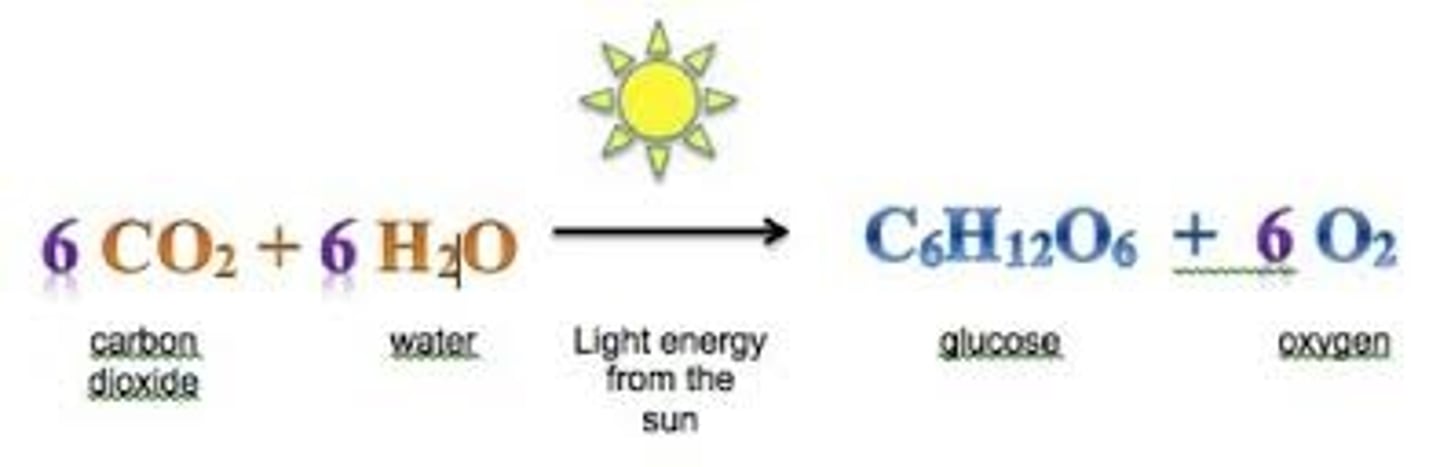
Equation for Photosynthesis
6CO2 (6 carbon dioxide) + 6H2O (6 water) + energy (Sun light) -------> C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 (6 oxygen)
Petal
A type of leaf that surrounds that reproductive parts of a flower, primarily severing to attract pollinators through their color, shape and scent
Stamen
the male fertilizing organ of a flower, typically consisting of a pollen-containing anther and a filament.
Anther
the part of a stamen that contains the pollen.
Filament
The filament is the stalk that supports the anther and makes it (the anther) more visible/accessible to pollinators
Pistil
the female organs of a flower, comprising the stigma, style, and ovary
The Stamen consists of the following:
anther and filament
the Pistil consists of the following:
Stigma, style, and ovary
Stigma
the topmost, sticky part of the pistil that is designed to catch pollen
Ovary
produces ovules, protects them until fertilization , and that develops into a fruit or seed
Sepal
protects the developing flower bud from physical damage and dehydration before it opens, provides support for the petals
receptacle
provides structural support, ensuring that the different parts of the flower are correctly positioned for pollinations and reproduction
Pedicel
a small stalk-like growth that supports a flower, found at the base of the flower
What is the root word use when describing parts of the fruit?
Carp
What must ALL fruits have in the to be a fruit?
Seeds
What are the three parts of a seed?
Endosperm, seed coat, embryo

Do do gymnosperms have fruits?
No
What must happen (what process(es) has to have happened) in order for a flower to become a fruit?
Pollinations and fertilization
What three tissues make up the pericarp?
Exocarp, Endocarp, and Mesocarp
What is the pericarp?
The part of a fruit formed from the wall of the ripened ovary; the part of a fruit that develops from the ovary wall of a flower after fertilization and encloses the seed
What is another name for seed coat?
Testa
Does the light-independent reaction, or Calvin cycle, need to be done exclusively at night?
No, the Calvin cycle can be done at any time, but is most commonly done at night.
Where does most photosynthesis take place?
in the mesophyll between, the two epidermal layers
What part of the plant conducts food?
Phloem
What part of the plant conducts water and minerals?
Xylem
What dermal layer has the most stomata?
The lower epidermal layer
Do leaves have true top and true bottoms?
Yes`
Lumen
indie the individual thylakoid
Monocots have:
have one cotyledon (seed leaf), parallel leaf veins, fibrous roots, and flower parts in multiples of three
Dicots
have two cotyledons, net like leaf veins, a taproot, and flower parts in multiples of four or fives
Cotyledon
an embryonic leaf in seed bearing plants, one mor more of which are the first leaves to appear from a germinating seed. They are not photosynthetic and serve as a food source for the young germinating plant
Vascular bundles
A strand of specialized vascular tissue in plants that contains the xylem and phloem of the transport of water, minerals, and food
Tap Root
the main root of a plant that grows vertically downward, from which smaller lateral roots branch out of, it serves to anchor the plant and reach deep water sources
Fibrous root
a dense, fibrous root system with many thin branching roots that grow from the base of the stem, unlike a tap root system with a single main root. They are found in most monocots like grasses, corn, and wheat
Root hairs
not visible to the naked eye, responsible for water absorption and nutrient absorption
Zone of maturation
a region in a plat root where cells stop dividing and begin to specialize into different tissues to further support plant growth
Apical meristem
The growing point of a root (where cell division occurs)
Root Cap
a hard root mass that protects the apical meristem
Apical bud
the primary growing point at the tip of a pant, responsible for vertical growth and releases a hormone (auxin) to discourage the growth of lower, lateral buds.
Internode
a section of a plant stem that lengthens to increase height between nodes
Lenticel
small, pore like structures on the stems and trunks of woody plants, as well as on the skin of some fruits and other organs. They re a type of pore that allows for gas exchange between the internal tissues of the plants and the atmosphere. Important for when a plant does not have leaves.