Fundamentals of Computer Networks
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
What is a computer network?
Two or more computers connected together to share resources and data
2
New cards
What are the advantages of a computer network?
* Being able to share hardware such as printers and scanners
* Centralised and often automatic backup of files
* Software can be installed and updated centrally, rather than on several machines
* Software can be bought using a site licence which can save organisations money
* Allows easy sharing of files
* Improved communication between network users and devices
* Centralised and often automatic backup of files
* Software can be installed and updated centrally, rather than on several machines
* Software can be bought using a site licence which can save organisations money
* Allows easy sharing of files
* Improved communication between network users and devices
3
New cards
What are the disadvantages of a computer network?
* The equipment required such as hubs/switches and other cabling can be expensive
* It will usually require a network manager to have oversight and maintain the system
* There is a big reliance on the main server so if this goes down, people won’t be able to access their files on the server, and may not be able to communicate with one another
* Connections can be slow - particularly if using the wrong setup which leads to several data collisions
* Worms and viruses can spread quickly through network connections
* Hacking is a threat, and if one connection is compromised, then they could have access to the whole network
* It will usually require a network manager to have oversight and maintain the system
* There is a big reliance on the main server so if this goes down, people won’t be able to access their files on the server, and may not be able to communicate with one another
* Connections can be slow - particularly if using the wrong setup which leads to several data collisions
* Worms and viruses can spread quickly through network connections
* Hacking is a threat, and if one connection is compromised, then they could have access to the whole network
4
New cards
What is a Personal Area Network (PAN)?
Networks centred around an individual, allowing individual devices to connect to other pieces of hardware within a 10m radius e.g. using Bluetooth
5
New cards
What is a Local Area Network (LAN)?
Networks that usually cover relatively small geographical areas and are often owned and controlled/managed by a single person or organisation
6
New cards
What is a Wide Area Network (WAN)?
Networks that usually cover a wide geographic area and are often under collective or distributed ownership - the Internet is the biggest example of a WAN
7
New cards
What is a wired network?
A network that makes use of a number of different types of cable to connect devices together
8
New cards
When would fibre optic cables be used?
To use very little space, have a higher bandwidth than copper and have the connection not be easily intercepted
9
New cards
When would copper cables be used?
To be bent, cheap and be able to power some devices directly without the need of a separate power source
10
New cards
What is a wireless network?
A network that uses a wire-free connection such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi to connect devices together
11
New cards
What are the advantages of a wireless network?
* Cheap set-up costs as one wireless access point can be used to connect a large number of devices
* Nodes are not tied to a specific location
* Easy to connect new devices without new hardware
* Nodes are not tied to a specific location
* Easy to connect new devices without new hardware
12
New cards
What are the disadvantages of wireless network?
* There can be interference on the network, particularly through walls or obstructions
* Tend to be slower and less stable connections
* Many more security risks, as anyone is able to find the connection, and if the appropriate security features such as firewalls and authentication are not in place, people can use this connection to access all other devices on the network
* Tend to be slower and less stable connections
* Many more security risks, as anyone is able to find the connection, and if the appropriate security features such as firewalls and authentication are not in place, people can use this connection to access all other devices on the network
13
New cards
What is a star topology?
A network that consists of a central hub/switch that all other devices are connected to using their own cables, often used if there are lots of devices or if speed or security is an important factor to consider
14
New cards
What is a bus topology?
A network that consists of one long cable with terminators at either end, which all the nodes on the network are connected to by their separate cable, often used when there are only a few computers or if cost and expertise are limiting factors
15
New cards
What type of topology is this?
Star
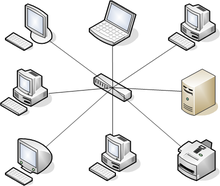
16
New cards
What type of topology is this?
Bus
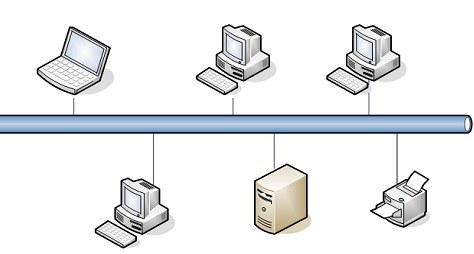
17
New cards
What is a network protocol?
An agreed way of communicating over a network
18
New cards
What is Ethernet?
A family of related protocols which deal with how data is sent along ethernet cables
19
New cards
What is Wi-Fi?
A family of related protocols rather than a single protocol and Wi-Fi is a trademark while the generic name for networks of this nature is WLAN
20
New cards
What is TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)?
A protocol that addresses packets and tracks them through the network to make sure that they arrive safely at their destination and if any packets don’t arrive where they are supposed to be, they are resent by the sender
21
New cards
What is UDP (User Datagram Protocol)?
A protocol that addresses packets and sends them through the network and if any packets don’t arrive where they are supposed to be, they are not resent by the sender
22
New cards
What is IP (Internet Protocol)?
A protocol that manages the addressing of the data packets, and is responsible for adding the sender and receiver IP addresses to each packet, as well as determining which data packets are addressed for that machine, working alongside TCP to ensure that data is sent securely across the internet
23
New cards
What is HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)?
A protocol that is responsible for sending requests for and receiving web pages, underlying the World Wide Web
24
New cards
What is HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)?
A protocol that is responsible for sending requests for and receiving web pages, underlying the World Wide Web and provides an encrypted version of HTTP for more secure web transactions
25
New cards
What is FTP (File Transfer Protocol)?
A protocol used to upload or download (i.e. transfer) files between computers and the internet
26
New cards
What is SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)?
A protocol used by mail servers to send and receive mail from all other mail servers around the world
27
New cards
What is IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol)?
A protocol that controls the download/upload of emails to and from the mail server, creating a copy of the email on the device that you have, but also leaving a copy on the mail server so that it can be viewed on other devices as well
28
New cards
Why is network security important?
Because with more devices than ever connected to different networks, hacking and corporate espionage on the rise, and increasingly sophisticated ways of people stealing data, it is really important to secure networks as much as possible against attack
29
New cards
What is authentication?
Methods that are used to make sure a user is who they say they are e.g. the use of password protected accounts, security dongles, or biometric measures such as fingerprints or facial recognition
30
New cards
What is encryption?
Turning data into an unreadable format that can only be understood by using a key to decrypt it, meaning that if a device in a network is stolen, the thief cannot simply remove the hard drive and take all the data from it as they will need to also have access to the key to make the data readable
31
New cards
What is a firewall?
A network security device that monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and decides whether to allow or block specific traffic based on a defined set of security rules
32
New cards
What is MAC address filtering?
Allowing devices to access or be blocked from accessing a network based on their physical address embedded within the device’s network adapter
33
New cards
What is the application layer?
Where the network applications, such as web browsers or email programs, operate
34
New cards
What protocols operate on the application layer?
* HTTP
* HTTPS
* SMTP
* IMAP
* FTP
* HTTPS
* SMTP
* IMAP
* FTP
35
New cards
What is the transport layer?
Sets up the communication between the two hosts and they agree settings such as the size of packets
36
New cards
What protocols operate on the transport layer?
* TCP
* UDP
* UDP
37
New cards
What is the internet layer?
Addresses and packages data for transmission, and routes the packets across the network
38
New cards
What protocol operates on the internet layer?
IP
39
New cards
What is the link layer?
Where the network hardware such as the NIC (network interface card) and OS device drivers is located