chemistry unit five
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
activation energy
minimum amount of energy needed to initiate a chemical reaction
collision theory
theory that says particles must collide in order to react
reaction rate
rate in which reactants are converted into products
spontaneous reaction
reactants have more free energy
nonspontaneous reaction
products have more free energy
ΔGrxn
less then 0
ΔGrxn
more than 0
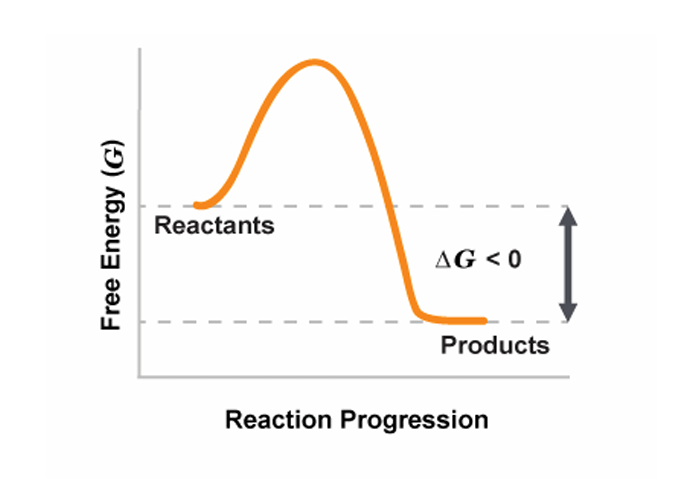
spontaneous reaction
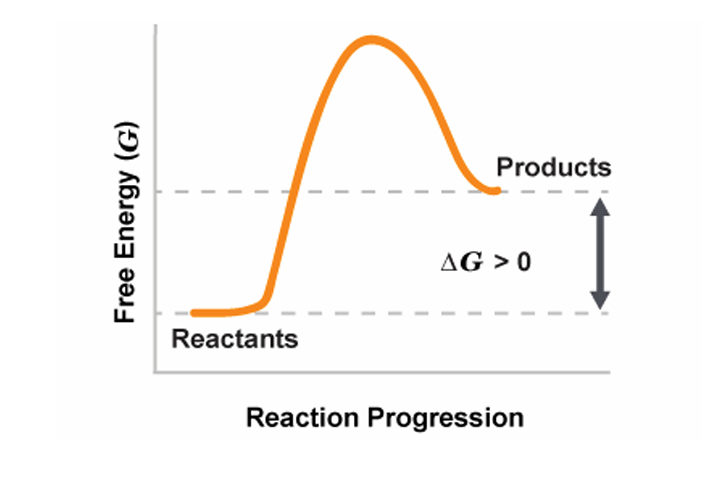
nonspontaneous reaction
EA
activation energy
the greater the activation energy
the less likely the reaction is to happen
chemical bonds
rearrange the atoms in molecules by making/breaking bonds
self sustaining reactions arere
spontaneous
reaction rates depend on
activation energy
high activation barriers result in
low rates
low activation barriers result in
high rates
reaction rate is NOT determined by
ΔGrxn
every reaction begins with
collision of molecules/particles
kinetic theory
molecules at a given temperature have different speeds
maxwel - boltzmann distribution
describes the distribution of speeds among particles
conditions for a reaction to occur
molecules/particles must collide and be effective
conditions for effective collisions
collisions must be energetic and in the correct orientation
factors that increase frequency or energy will
increase reaction rate
factors that decrease frequency or energy will
decrease reaction rate
temperature represents a distribution of what type of energy?
kinetic
temperature increases
reaction rate increases
higher reactant concentration leads to
more frequent collisions
frequent collisions lead to
increases rate of reactions
to make a gas faster you must
add reactants and decrease volume
increasing pressure also increases reaction rates IF
reactants contain more moles of gas than the products
reactions occur at the
surface
increasing surface area increases
particles available for reaction
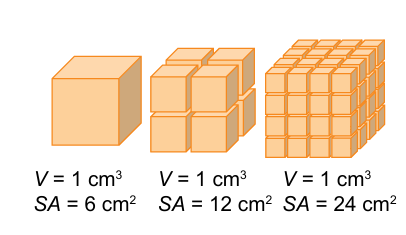
reversible reaction
balanced reaction
reactants are on the
left side
products are on the
right side
forward reaction
left to right
reverse reaction
right to left
dynamic equilibrium
forward and reverse reaction being equal
when there are more reactants than products
reactants are favored and lies to the left
when there are more products than reactants
products are favoured and lies the right
K eq
equilibrium constant
equilibrium constant
ratio of the amount of reactant and product
equilibrium constant expression
Keq = [products]^[coefficients] / [reactants]^[coefficients]
appears in equilibrium expression
gases and aqueous species
does not appear in an equilibrium expression
pure solids and liquids
the value of Keq is
different for each reaction system
Keq depends on
pressure, temperature, and volume of system