4.4 GENETIC DIVERSITY AND ADAPTATION
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
GENETIC DIVERSITY:
Number of different alleles of genes in a population
HPW IS GENETIC DIVERSITY BETWEEN SPECIES MEASURED?
Differences in base sequences of DNA.
Differences in base sequence of mRNA.

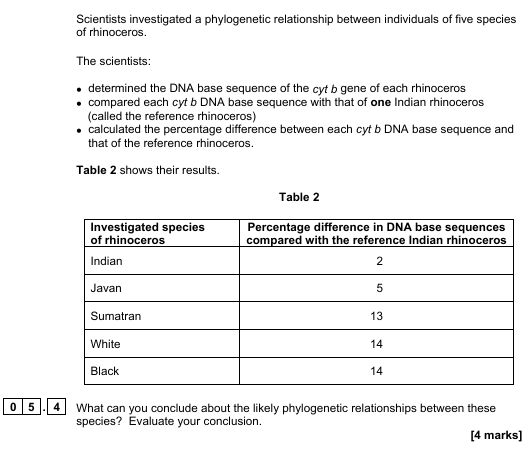

DESCRIBE HOW ORGANISMS ARE GROUPED IN A PHYLOGENETIC CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM?

HOW DO ALLELES ARISE?
Mutation.
POPULATION:
Same species in an area/ habitat at a given time.
That can interbreed.
IMPORTANCE OF GENETIC DIVERSITY?
WHAT IS IT A RESULT OF?
Enables natural selection to occur.
(With certain alleles having a selective advantage over others.)
RESULT OF:
Mutations.
Meiosis.
Random fusion of gametes.
REDUCING GENETIC DIVERSITY?
Genetic bottleneck, large number of population dies, some alleles are lost —> reduces ability to survive —> can’t adapt (—> abnormalities in offspring).
Founder Effect, only a few individuals in a new area.
New group may evolve differently to old.
WHAT IS EVOLUTION?
Change in allele frequency over many generations in a population
Occurring through natural selection.
EXPLAIN PRINCIPLES OF NATURAL SELECTION IN THE EVOLUTION OF POPULATIONS?
MARIA

FACTORS THAT DRIVE NATURAL SELECTION:

WHAT DOES NATURAL SELECTION RESULT IN?
Species that are better adapted to their environment.
THREE TYPES OF ADAPTATIONS?
Anatomical.
Physiological.
Behavioural.
STABILISING AND DISRUPTIVE:
WHAT DOES DISTUPTIVE RESULT IN?
Stabilising prevents change.
Average phenotype selected against both extremes.
DISRUPTIVE:
Both extremes of a phenotype have a selective advantage over those in the middle, so both are selected,
Most important in bringing about evolutionary change and thus speciation.
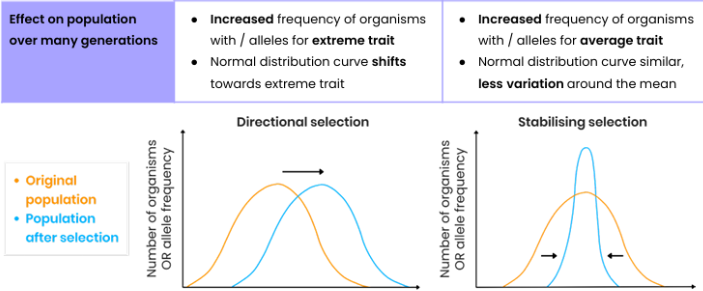
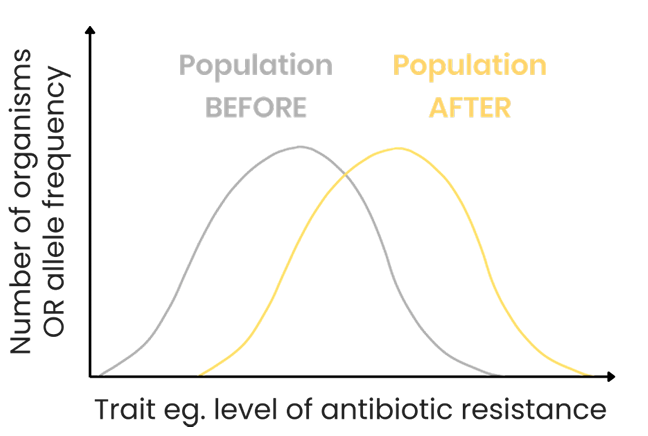
DIRECTIONAL SELECTION:
One extreme has a selective advantage.
Frequency of this allele increases and frequency of the other extreme’s allele decreases.
EXPLAIN HOW ANALYSING RIBOSOMAL RNA CAN HELP DETERMINE PHYLOGENIC RELATIONSHIPS?
Compare the DNA base/nucleotide sequence;
More closely related (species) the more similar the genes/DNA;
WHY DOES ANALYSING GENES CODING FOR RIBOSOMAL RNA ALLOW FOR PHYLOGENETIC RELATIONSHIPS TO BE STUDIED BETWEEN ALL CELLULAR ORGANISMS?
All (cellular organisms) have ribosomes
OR
All (cellular organisms) have ribosomal RNA/rRNA;