DNA Replication and the Human Genome Overview
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
uta biol 1441 dna replication
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
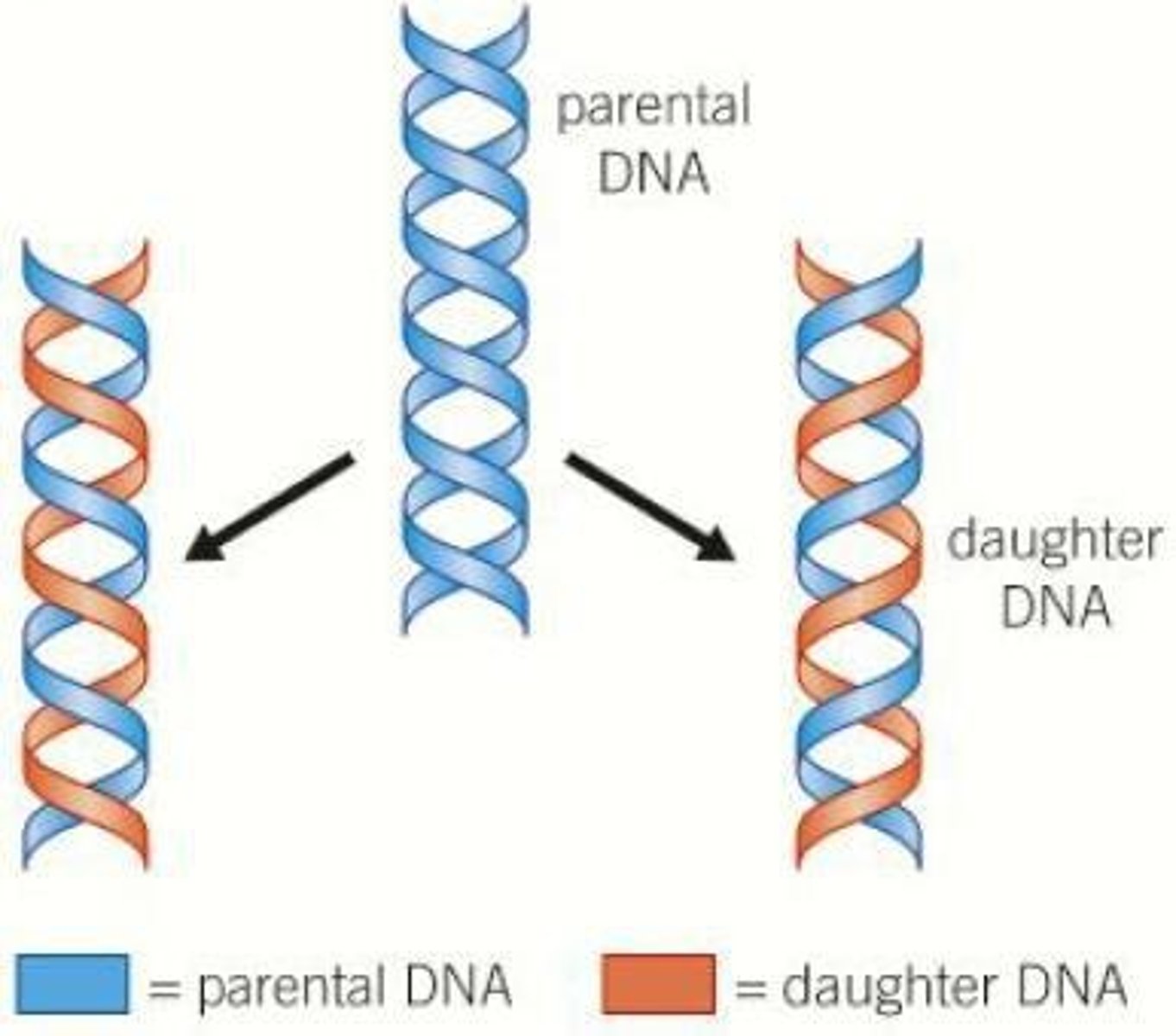
Semiconservative replication
Each new DNA strand contains one original strand.
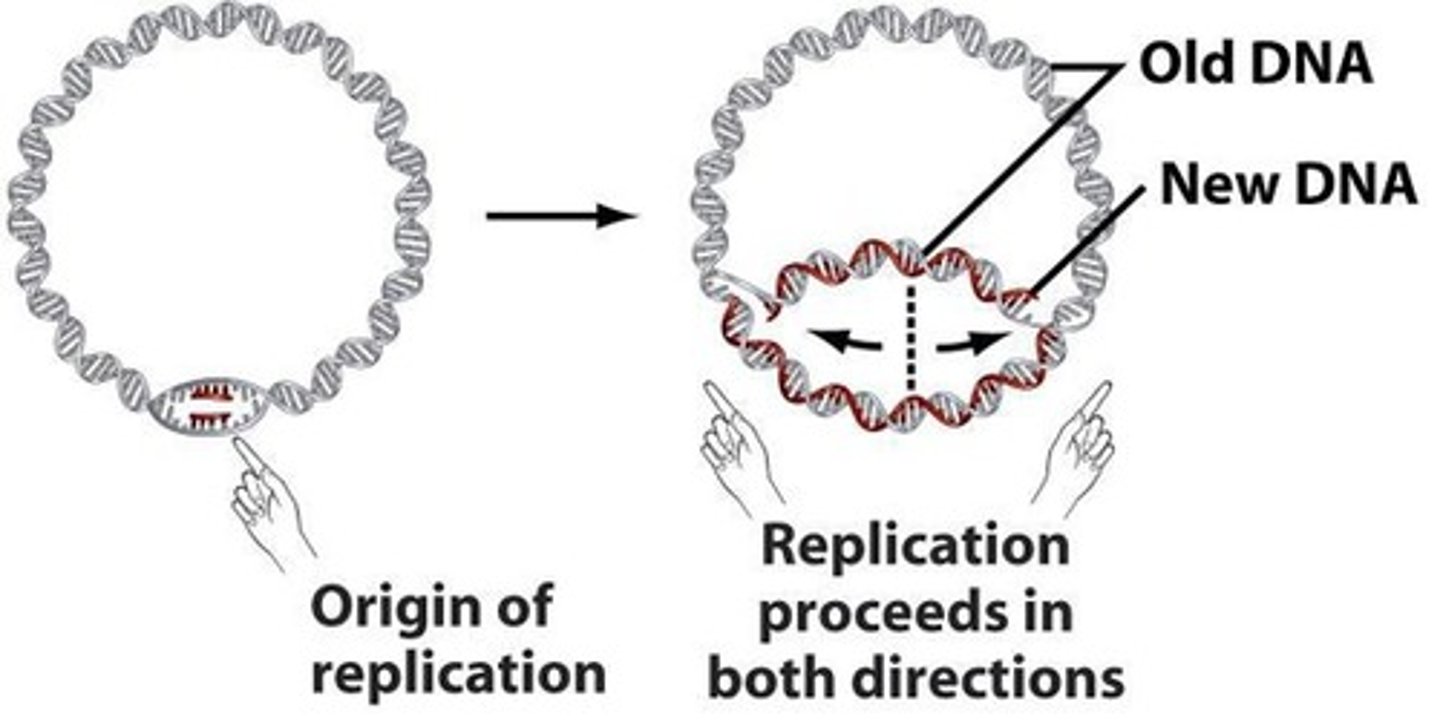
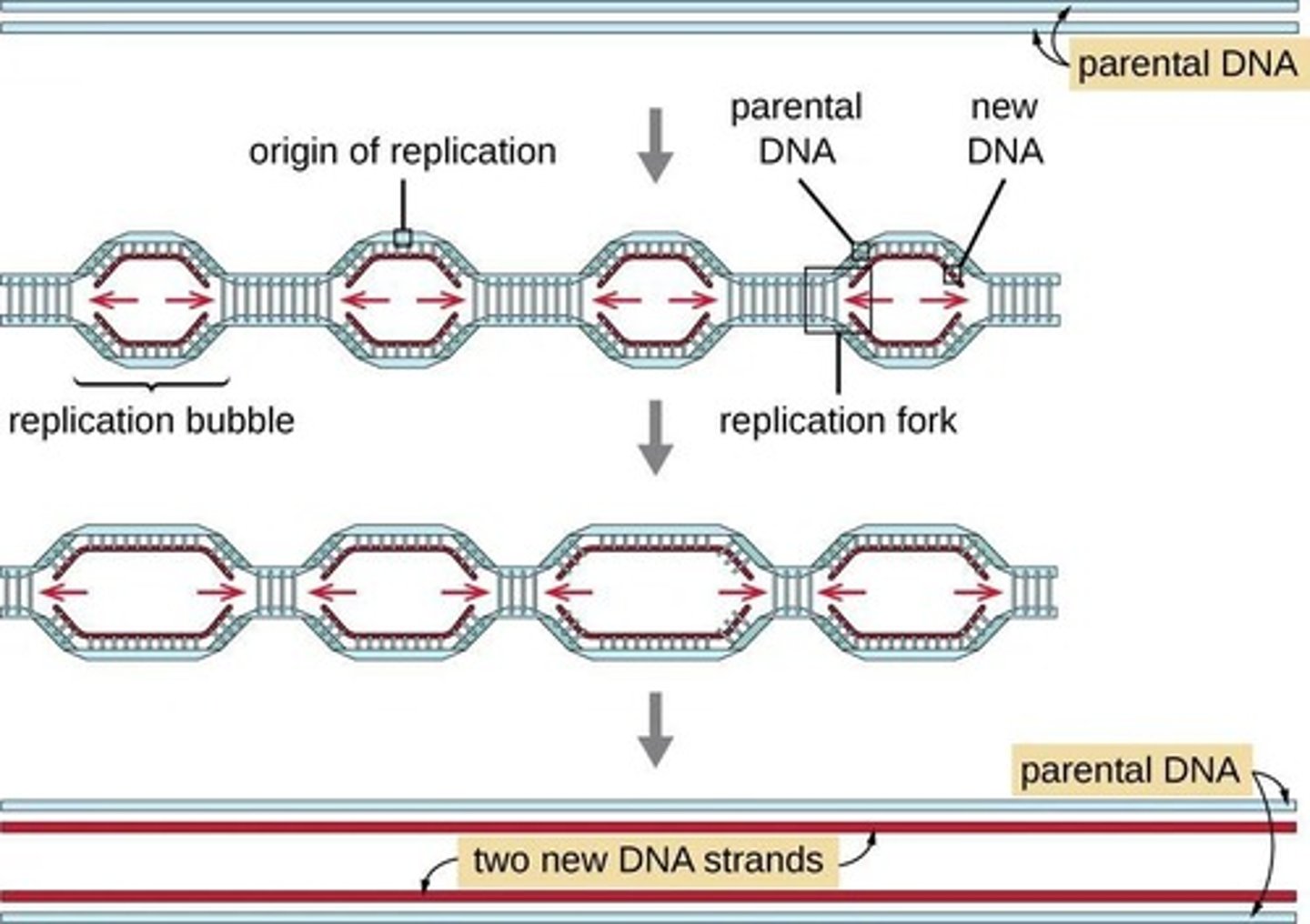
Origins of replication
Sites where DNA replication begins.
Replication bubbles
Spaces formed as DNA strands separate.
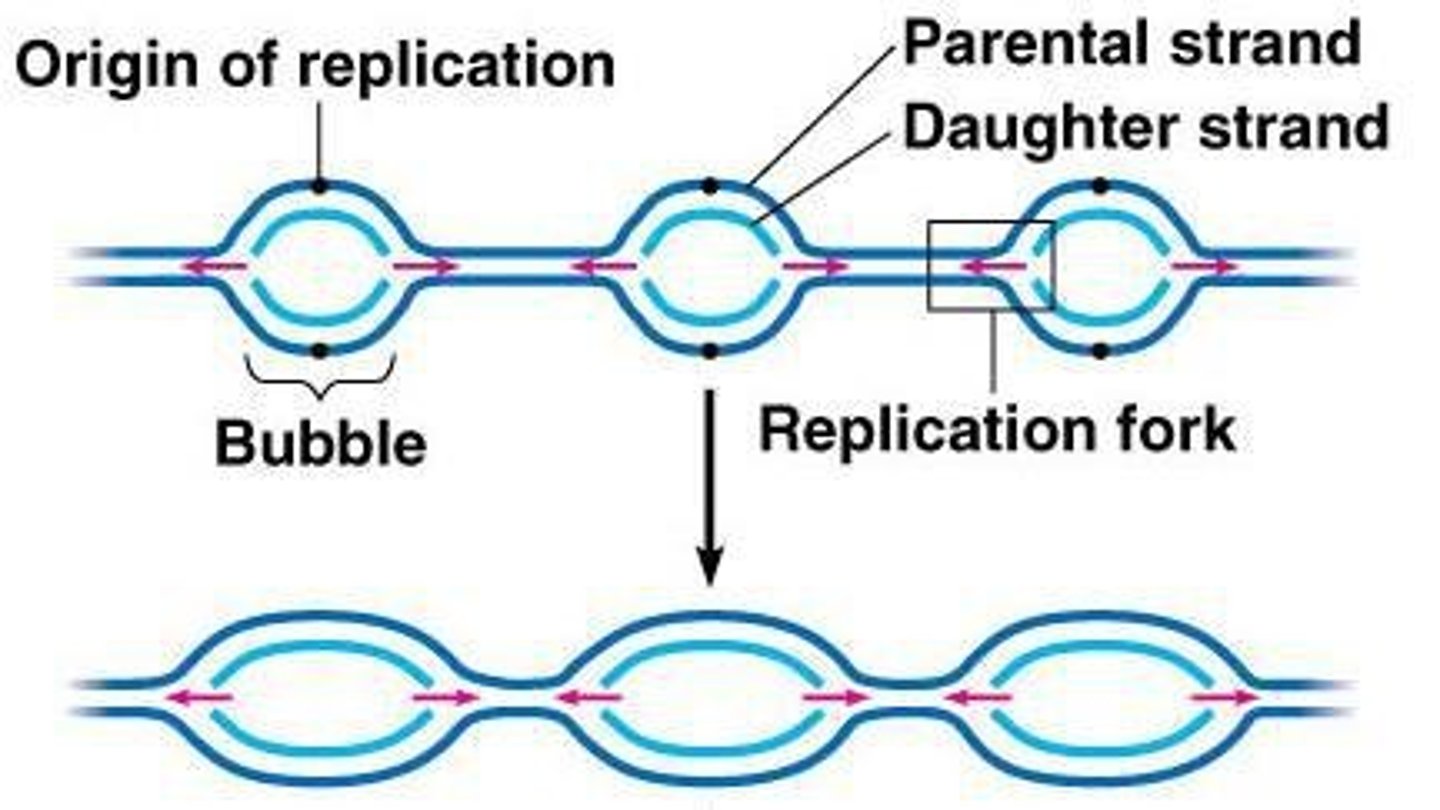
Replication forks
Edges of replication bubbles where DNA unwinds.
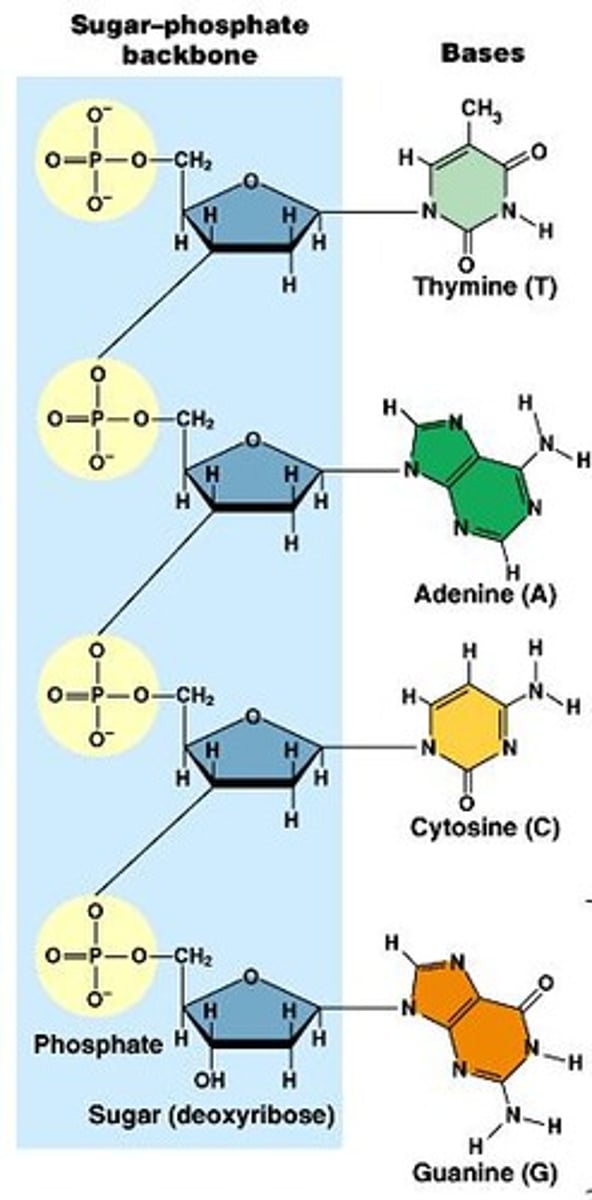
Nucleotide
Building blocks of DNA, composed of sugar, phosphate, base.
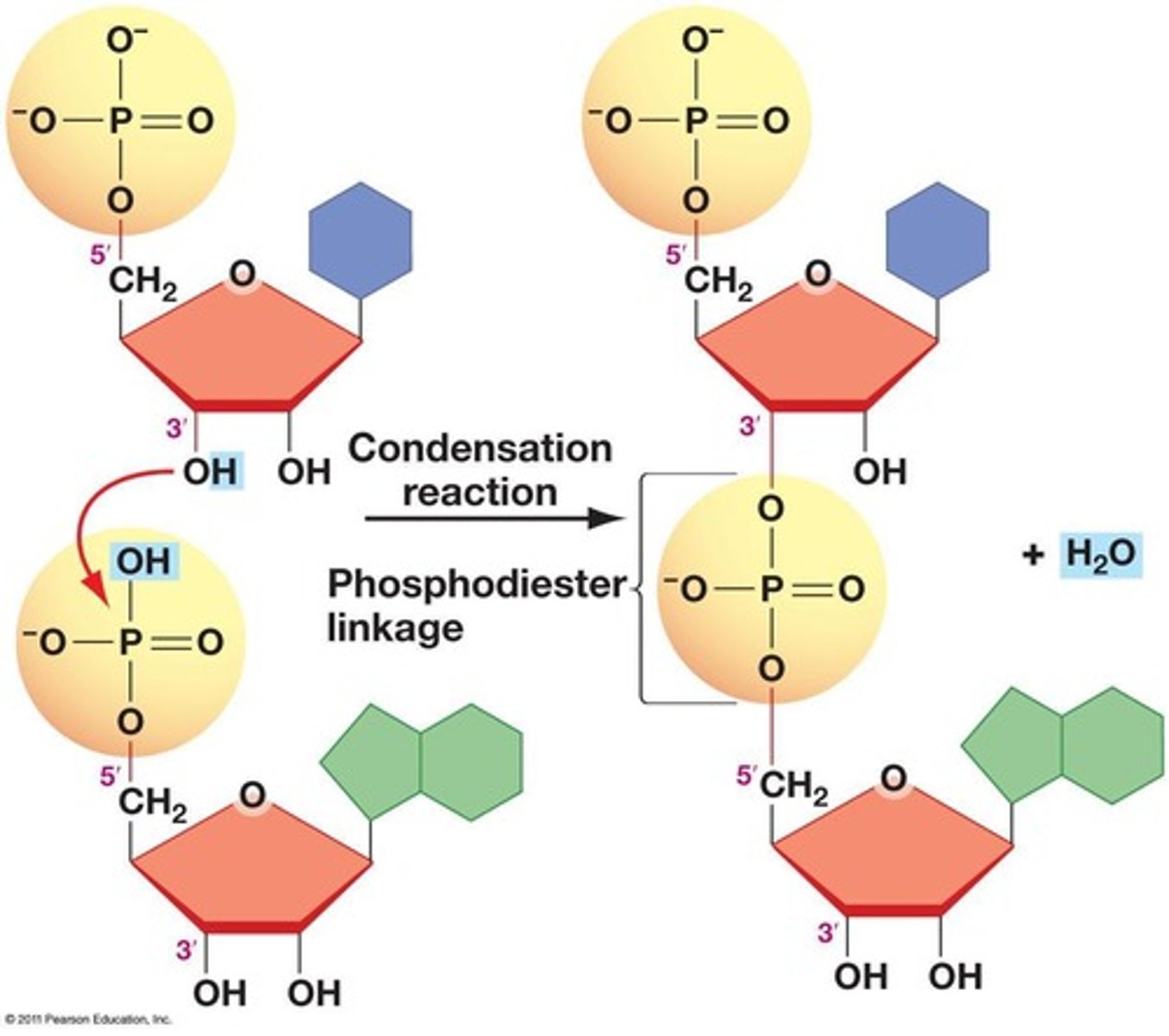
Phosphodiester bond
Links nucleotides in the DNA backbone.
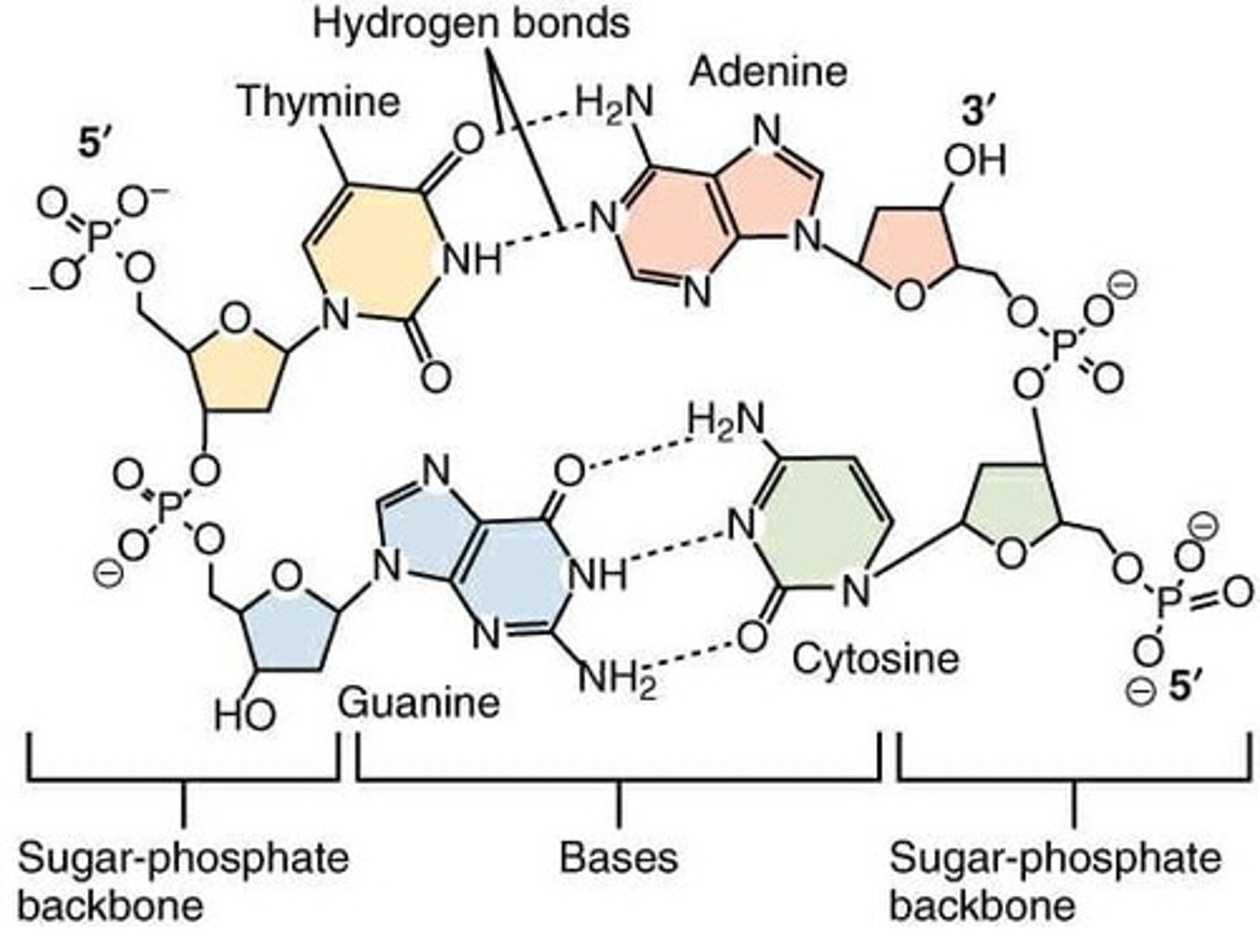
Hydrogen bonds
Connect complementary nitrogenous bases in DNA.
Leading strand
Synthesized continuously towards the replication fork.

Lagging strand
Synthesized discontinuously in Okazaki fragments.
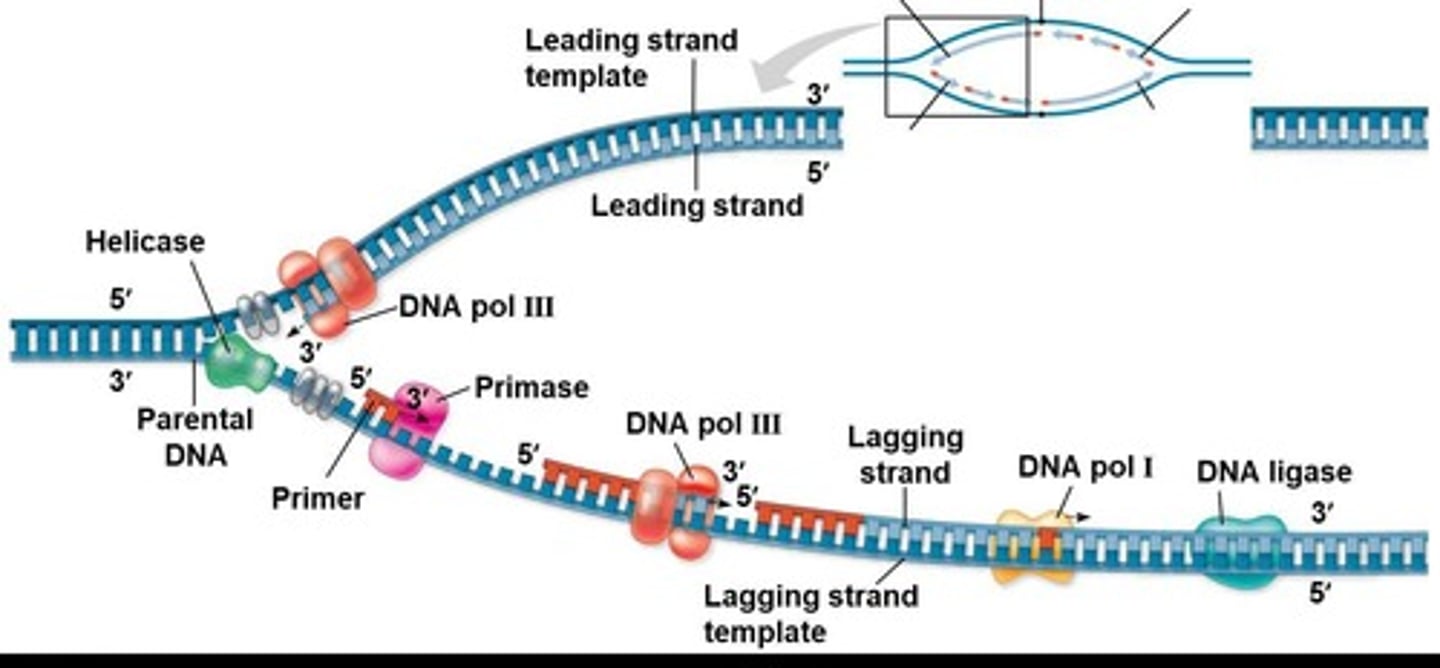
DNA Polymerase III
Enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands.
Nucleotide excision enzymes
Repair enzymes that correct DNA errors.
Okazaki fragments
Short DNA segments on the lagging strand.
3' end
Has a hydroxyl group, where nucleotides are added.
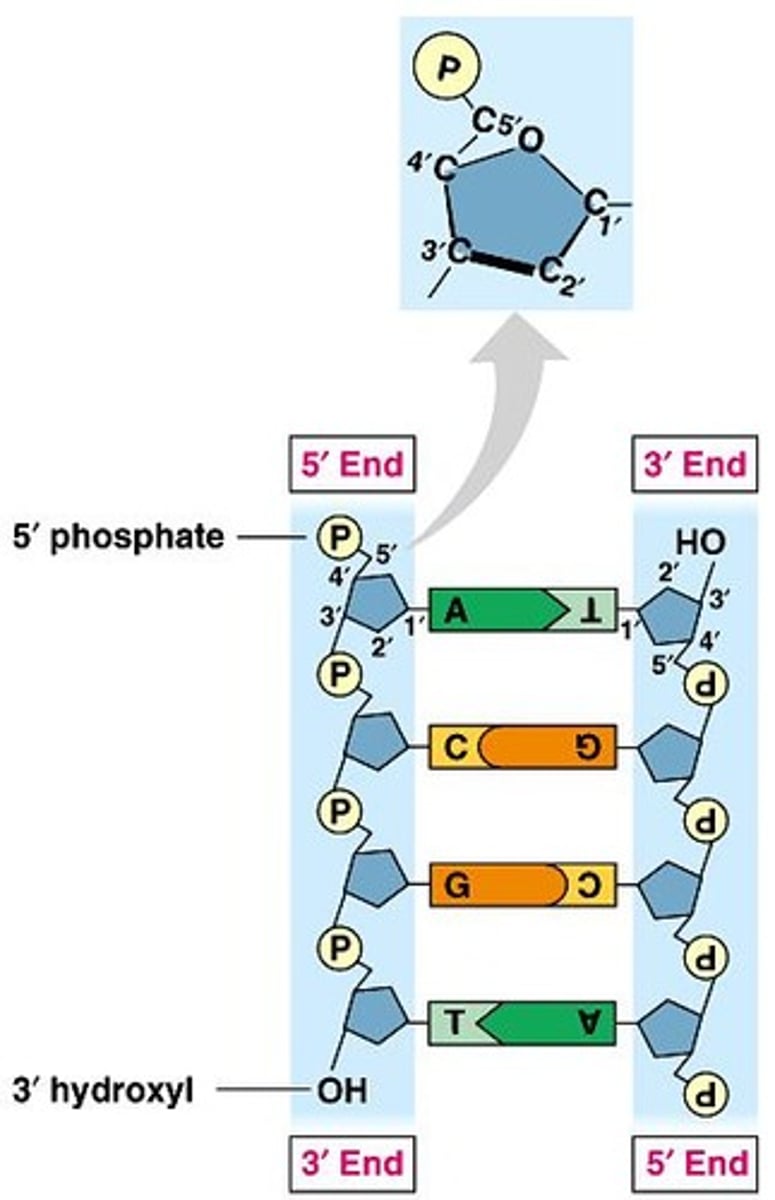
5' end
Has a phosphate group, starting point for synthesis.
Antiparallel strands
Strands run in opposite directions in DNA.
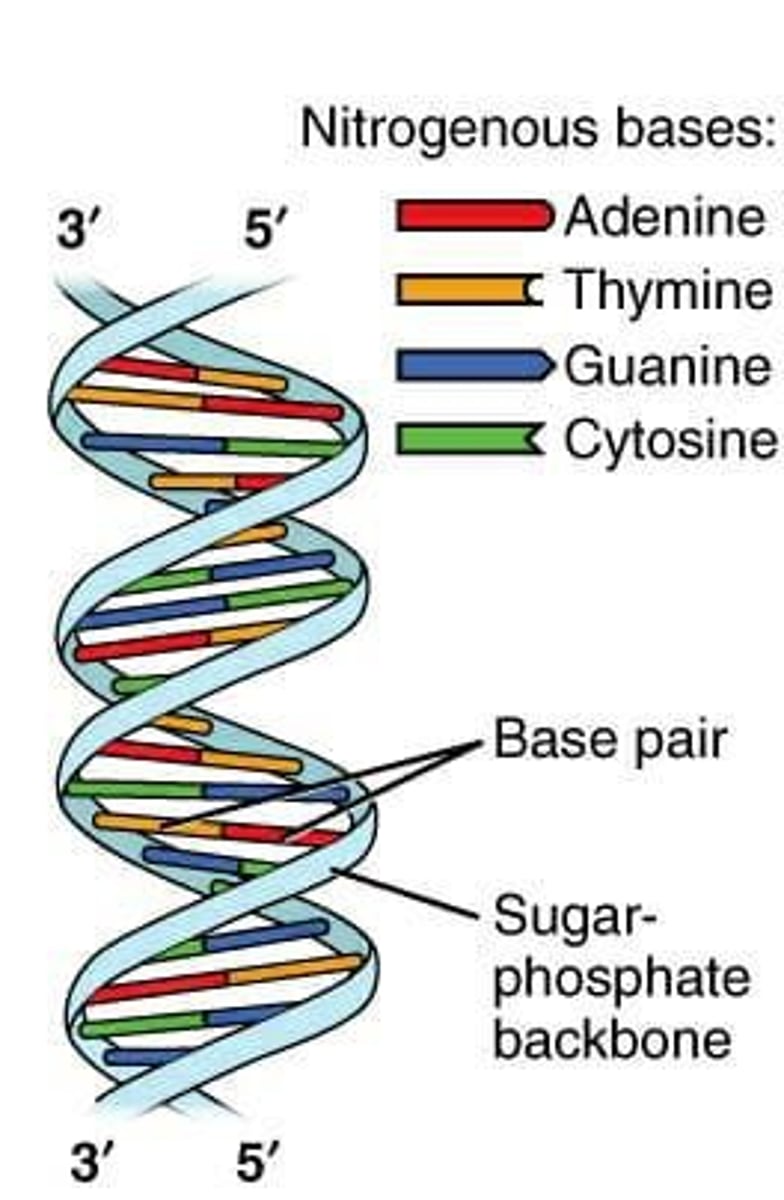
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Molecule carrying genetic instructions for life.
Human genome
Complete set of DNA in human cells.
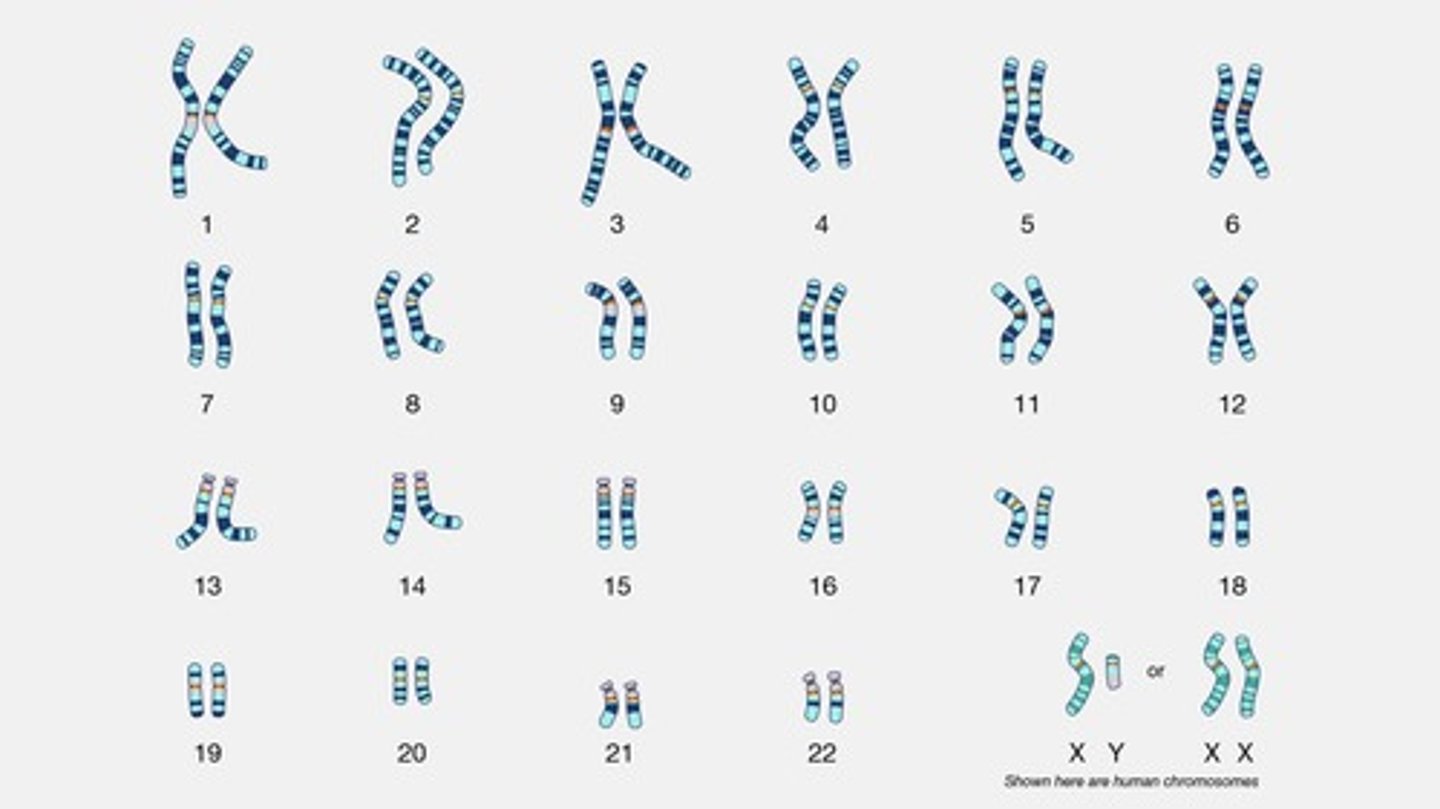
Chromosomes
Structures containing DNA coiled around proteins.
Autosomes
Chromosomes regulating general body functions.
Sex chromosomes
Chromosomes determining sex and related traits.
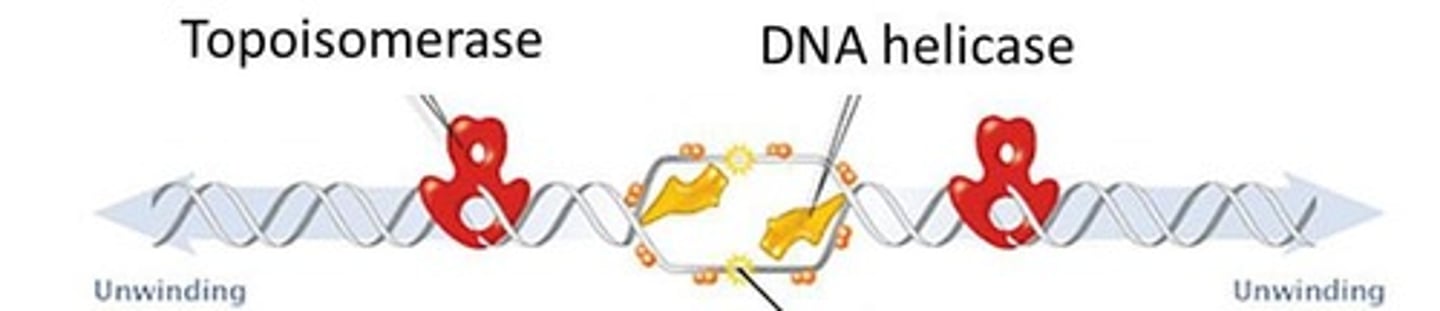
DNA helicase
Enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix.
Topoisomerase
Relieves strain ahead of the replication fork.
RNA primer
Short RNA segment initiating DNA synthesis.
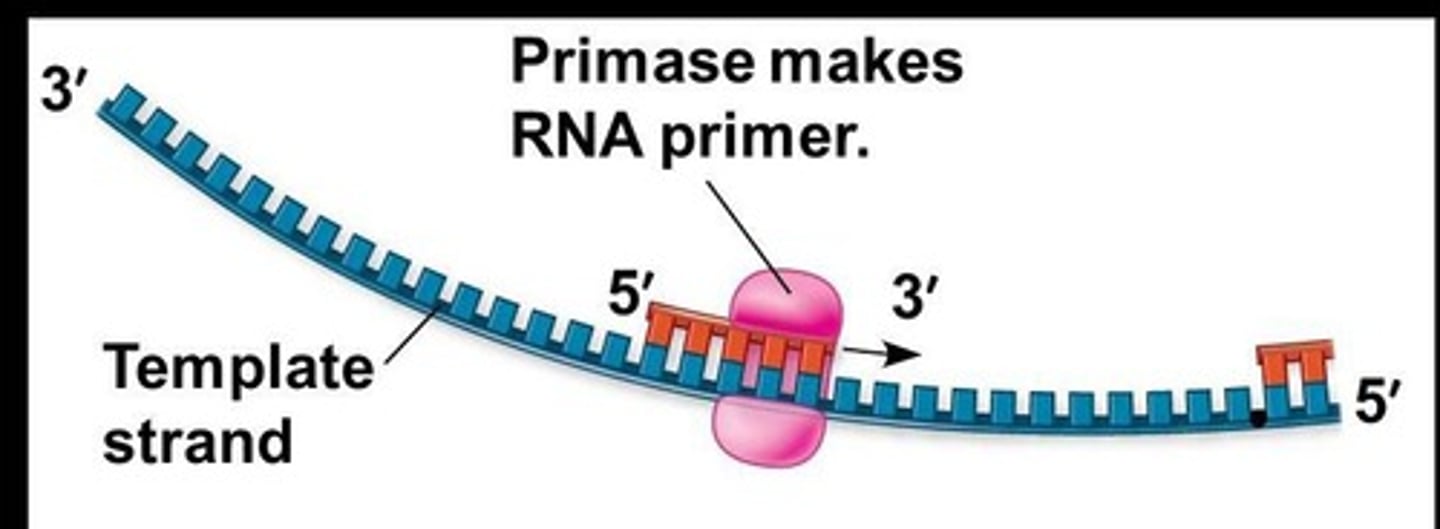
Primase
Enzyme that synthesizes RNA primers.
Template strand
Original DNA strand used for replication.
Complementary strand
New DNA strand formed based on template.
Karyotype
Visual representation of an organism's chromosomes.
DNA proofreading
Process ensuring accuracy during DNA replication.