15 - Weather Reports and Forecast
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Where can a pilot find what weather briefing services are available at a particular location?
CFS
During radio communications the pilot addresses the FIC as
RADIO
What are the 4 main FISE freq
123.275 MHz
123.375 MHz
123.475 MHz
123.55
The weather term CAVOK used in an ATIS means?
Visibility 6 miles or more, no cloud below 5 000 feet, no cumulonimbus, precipitation, thunderstorms, fog, or drifting snow.
Pilots can get information during the en route portion of flight from a FSS using the FISE frequency. (T/F)
FSS is for aerodrome operations. FIC is for flight planning and en route.
Correct answer is False
For a long range flight it would be best to contact?
AWBS
The primary purpose of the ATIS is to
reduce frequency congestion.
VOLMETs are available during the
North Atlantic crossings.
NOTAM, RSC, and CRFI are included in advisories for a period of . . . . . hr for domestic traffic, and . . . . . hr for international traffic, after dissemination by means of telecommunication.
12, 24
Pilots are required to tune in the ATIS prior to making initial contact with ATC / FSS.
If ATIS is available, all pilots should use it, not mandatory (required).
The correct answer is 'False'.
A NOTAM is a timely notice concerning the establishment, condition, or change of any
Aeronautical facility
Aeronautical hazard
Aeronautical service
NOTAMs are not usually issued more than . . . . . days in advance.
14
The first four characters of the Q Line of a NOTAM identify the
location indicator of the FIR
Which would require the issuance of a NOTAM?
NBD will be undergoing maintenance.
Control tower frequency change.
Snow clearing operations.
K0001/13 NOTAMN
Q) CZYZ/QMRLR/IV/NBO/A
A) CYAM B) 1307311800 C) 1307312000
D) DAILY 1800-2000
E) SAULT STE.MARIE ALL AD LGT U/S
Which is the incorrect statement about the NOTAM?
a. Valid from 31 July 2013 at 18:00 local till 31 July 2013 at 20:00 local.
b. Valid from 31 July 2013 at 18:00 UTC till 31st July 2013 at 20:00 UTC.
c. K0001/13 is the NOTAM continuity number.
d. All aerodrome lights are unserviceable for CYAM.
NOTE: the question is asking INCORRECT or NOT correct.
The correct answer is: Valid from 31 July 2013 at 18:00 local till 31 July 2013 at 20:00 local.
G0012/19 NOTAMN
Q) CZWG/QXXX/IV/NBO/A
A)CKB7 B)1905040900 C)1305112300
ROBLIN ARCAL LGT DURATION REDUCED TO 7 MIN
Which is the correct statement about the NOTAM?
Select one:
a. This is a new NOTAM.
b. Valid from 4 May 2019 at 09:00 local till 11 May 2019 at 23:00 Local.
c. Valid from 5 April 2019 at 09:00 local till 5 November 2019 at 23:00 local.
d. Valid from 5 April 2019 at 09:00 UTC till 5 November 2019 at 23:00 UTC.
The correct answer is: This is a new NOTAM.
Why do we have NOTAMs available?
To increase communication.
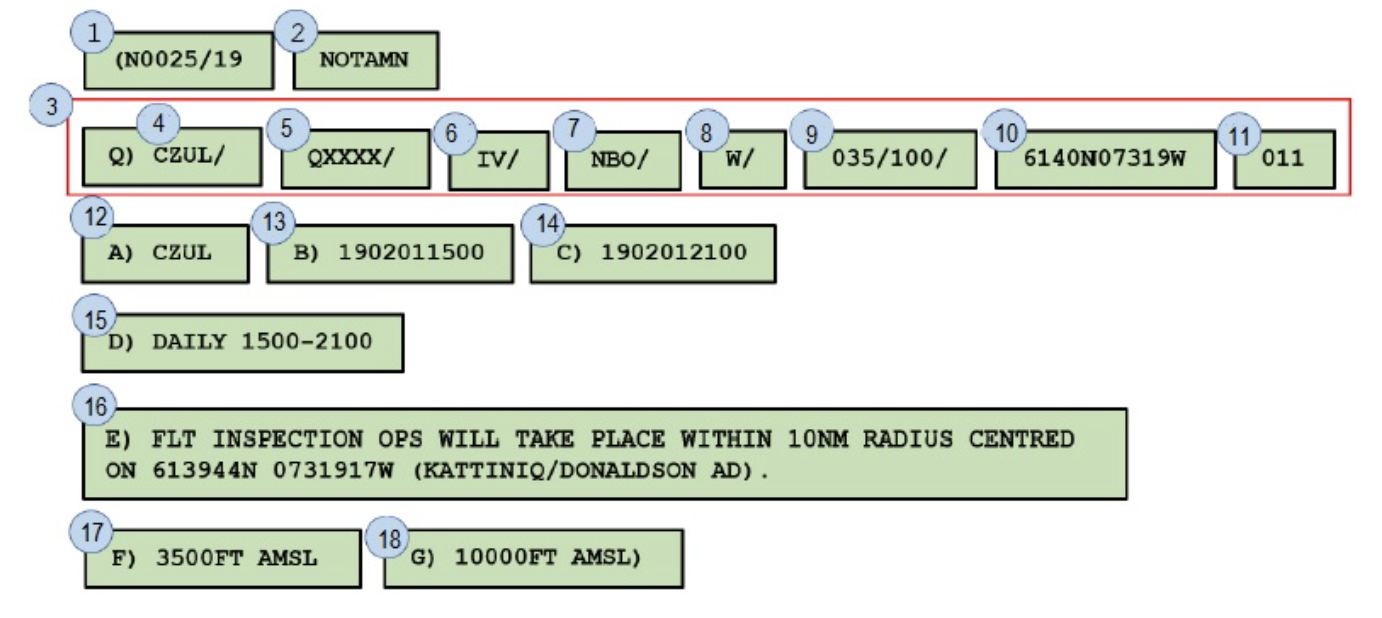
Item 9 indicates the geographical coordinates of the NOTAM affected area. (T/F)
False
C0079/19 NOTAMN
Q) CYWG/QMRLC/IV/NBO/A
A) CYWG B) 0606151330 C) 0606151600
E) RWY 13/31 CLOSED DUE MAINTENANCE
After approximately a hour on the ground at St. Andrews the weather has improved. The flight to Winnipeg International Airport's ETA is 16:45 Z. According to the NOTAM runway 13/31 Is/will be ______
will be available at the ETA.
When a NOTAM is replaced what type of NOTAM is issued?
NOTAMR
A METAR reports winds in
knots and true.
METAR CYQT 210300Z 36008KT 5SM RA BR OVC021 15/14 A2952 RMK NS8 SLP999=
The cloud height as reported in the METAR is
2 100 feet AGL.
Visibility is reported in a METAR in
statute miles
SPECI CYQK 090310Z 33005KT 10SM -RA FEW034 BKN044 OVC080 14/13 A2980 RMK SC2SC5AC2 SLP095=
When was the SPECI issued?
On the 9th day of the month at 03:10 Zulu.
When the conditions stated by a METAR change significantly before the next reporting period, what occurs?
A SPECI is issued.
METAR CYBR 210100Z 34010KT 15SM FEW030 BKN150 16/13 A2995 RMK SC2AC2 SLP147=
The METAR reports the wind direction and speed as
340°T at 10 KT.
How is visibility reported in a METAR?
Prevailing visibility near ground level.
R25/2000FT/N
The RVR report indicates the
10-minute average runway visual range is 2 000 feet and this value is not changing.
The abbreviation used to describe hail is
GR
Not an obscuration to visibility is
SM
The cloud coverage amount for a BKN is
5 to less than 8 oktas.
Two cloud layers exist. The first layer covers 2/8th of the sky from 2 000 to 2 500 feet ASL. The second layer covers 3/8th of the sky from 5 000 to 6 000 feet ASL.
These layers would be reported on a METAR with a field elevation of 1 000 feet ASL as
In a METAR (and TAF) the layers add together. Remarks in the METAR gives cloud type and coverage for each layer.
The cloud layer at 1 000 feet AGL is FEW covering 2/8th of the observed sky. The next cloud layer at 4 000 feet AGL combined with the lower cloud layer is BKN covering 5/8th (2/8 + 3/5) of the sky, as observed from the ground.
The correct answer is: FEW010 BKN040.
METAR CYVR 180700Z 21009KT 15SM FEW020 SCT060 BKN170 03/M01 A2981 RMK SC1SC2AC2 SLP096=
The METAR reports the ceiling as
In a METAR (and TAF) the layers add together. Remarks in the METAR gives cloud type and coverage for each layer. The first layer in the remarks is 1/8 and the second layer is 2/8. Because the layers add together the second layer totals 3/8 which is a scattered layer. The third layer is only 2/8 also, but adding the previous layers it totals 5/8 which gives a broken layer making it the ceiling.
Only 5/8 coverage or more (BKN or 8/8 OVC) is considered a ceiling. VV (Vertical Visibility) is also a ceiling for VFR.
The correct answer is: 17 000 feet AGL.
METAR CYQK 211300Z 35006KT 15SM FEW006 FEW045 M14/M16 A2991 RMK SF1SC1 SLP135=
The METAR reports the dew point as
-16°C.
METAR CYHD 211100Z AUTO 36007KT 9SM CLR 12/11 A2982 RMK SLP107=
With regards to the METAR, A2982 refers to the
altimeter setting
METAR CYHD 211100Z AUTO 36007KT 9SM CLR 12/11 A2982 RMK SLP107=
The reported sea level pressure in the METAR is
1010.7 mb
Weather reports that are automatically generated and reported are
sometimes fallible and should not always be trusted.
UACN10 CYQT 211234
WG
UA /OV CYQT /TM 1234 /FLDURD /TP C208 /TB LGT TB /RM APCH RWY 07
The PIREP decodes as
PIREP over Thunder Bay at 12:34 Z, filed during a descent by a Cessna 208, reported light turbulence on approach to runway 07.
A TAF is a forecast that gives the expected weather within . . . . . NM of the airport and is typically issued . . . . . times per day.
5, 4
Wind shear is included in the TAF when it is predicted that it may affect an aircraft within . . . . . feet AGL.
1 500 ft AGL
Visibility in a TAF that is greater than . . . . . are coded as . . . . .
6 SM, P6SM
The precipitation code signifying heavy rain showers is
+SHRA.
With regards to a terminal aerodrome forecast, a TEMPO is issued when the forecast weather is expected to last less than
an hour or if reoccurring for a total time of less than half the TEMPO period.
When the weather is expected to change gradually over a period of time and then remain the same, the change group used is
BECMG.
When the probability is 50% that a hazard to aviation may occur during a specified time the weather change group used is
TEMPO, FM or BECMG.
BECMG 1523/1602
The weather change group interprets as between
the 15th day at 23:00 Z and the 16th day at 02:00 Z the following weather elements will gradually change.
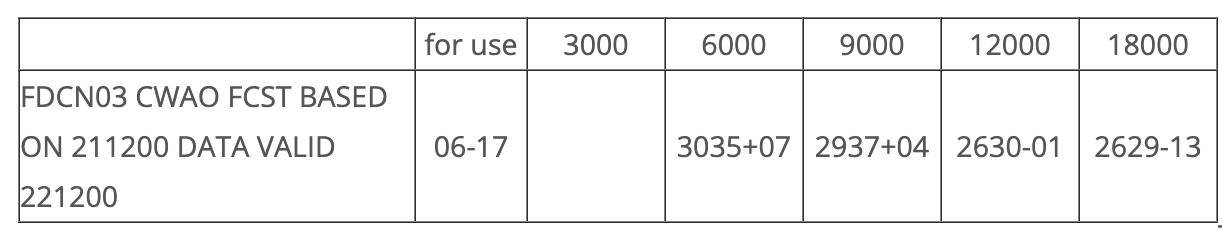
expected winds for 11:00 Z at 7 500 feet is
You are looking for upper winds at 11:00 Z - this falls between the given FD forecast window valid 06 - 17Z.
You want altitude of 7 500 feet but are only given 6000 and 9000. 7 500 feet is in the middle so we can average the direction and speed of both 6000 and 9000 winds separately.
This gives us the following:
For direction: (30 + 29) / 2 = 295° true.
For speed: (35 + 37) /2 = 36 knots.
The correct answer is: 295°T at 36 KT.
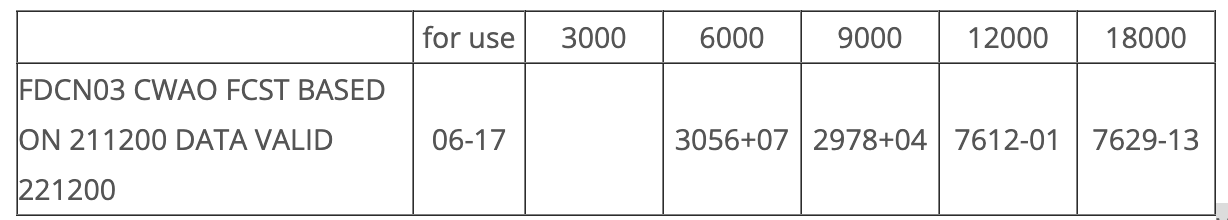
What are the expected winds for 11:00 Z at 12 000 feet?
76 - 50 = 26 which is 260°
12 + 100 = 112 knots
The correct answer is: 260°T at 112 KT.
An AIRMET is?
a GFA revision
The GFA forecast is valid for altitudes below
24 000 feet.
The GFA is issued . . . . . times daily and consist of . . . . . charts each.
4, 6
For an extended forecast period the GFA includes an IFR outlook located
on the 12-hour clouds and weather chart comments box.
All heights on a GFA are measured as . . . . . unless noted.
ft ASL
Marginal VFR weather conditions are determined according to ceilings between
1 000 to 3 000 feet AGL and/or visibility between 3 to 5 SM.
The motion of synoptic features on the GFA will be indicated when movement is expected to be
5 KT or more
When the visibility forecast by a GFA meets or exceeds . . . . . it is indicated as . . . . .
6SM, P6SM
An area of fog reducing visibility on the GFA to 1/4 SM would be indicated on the GFA by
enclosing it with a dashed orange line.
Areas of light icing could be found on the
ICG TURB & FZLVL chart comments box.
The height of the freezing level on a GFA is measured in . . . . . and is indicated by contour lines every . . . . .
feet ASL, 2 500 feet.`
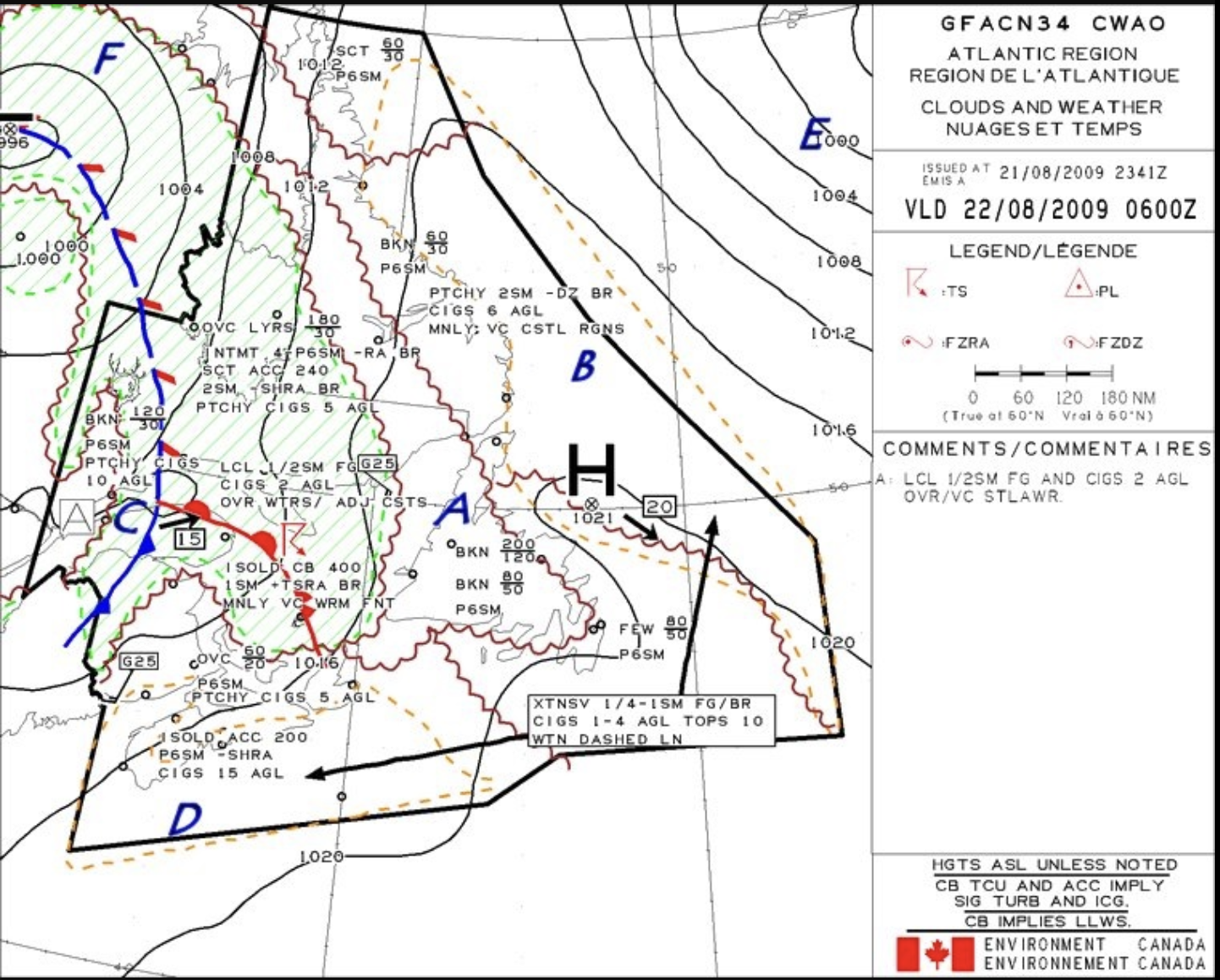
Ceiling in area A is forecast to be
5 000 Ft ASL
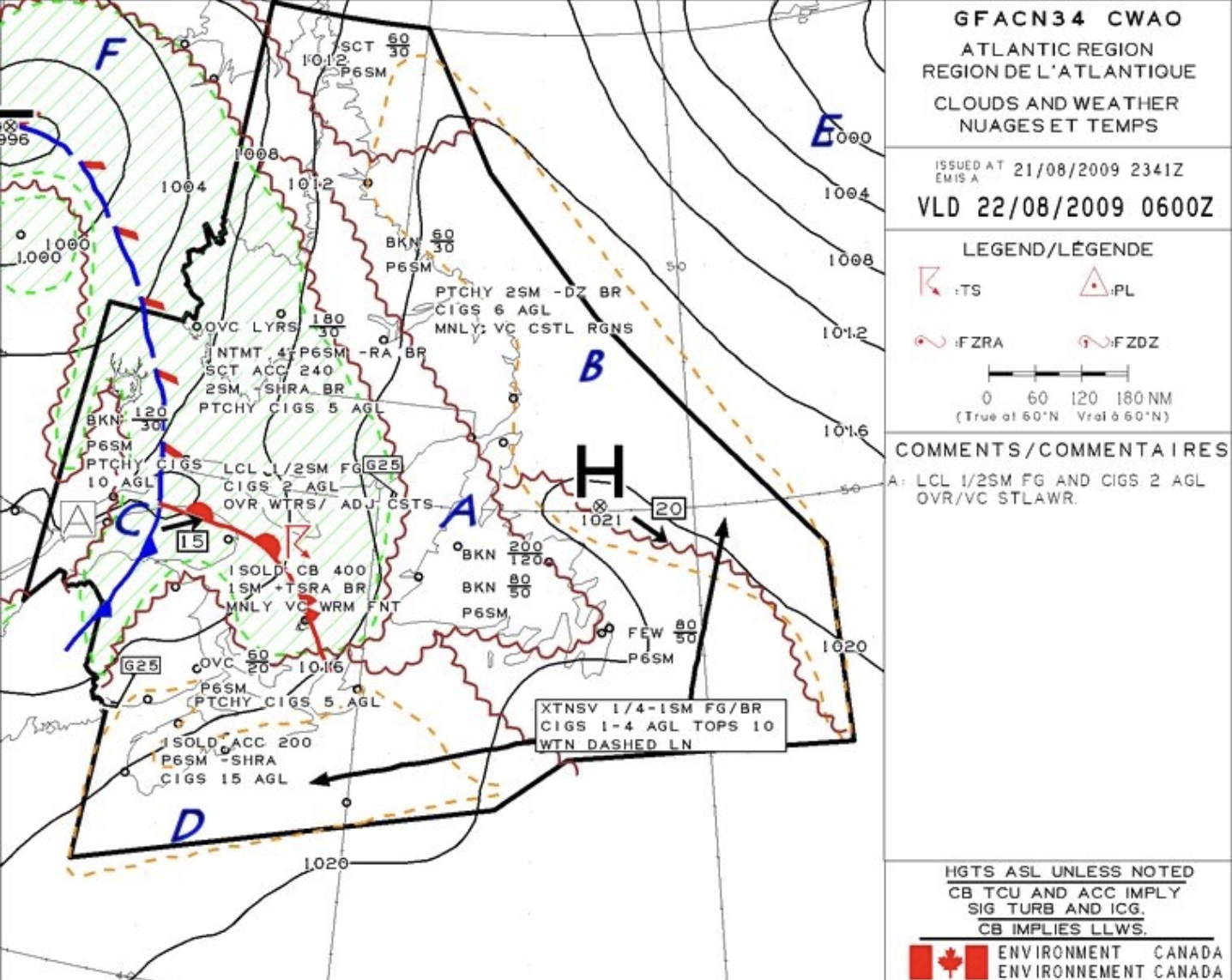
What does region B specify is happenign?
Obstruction to vision due to fog and mist.
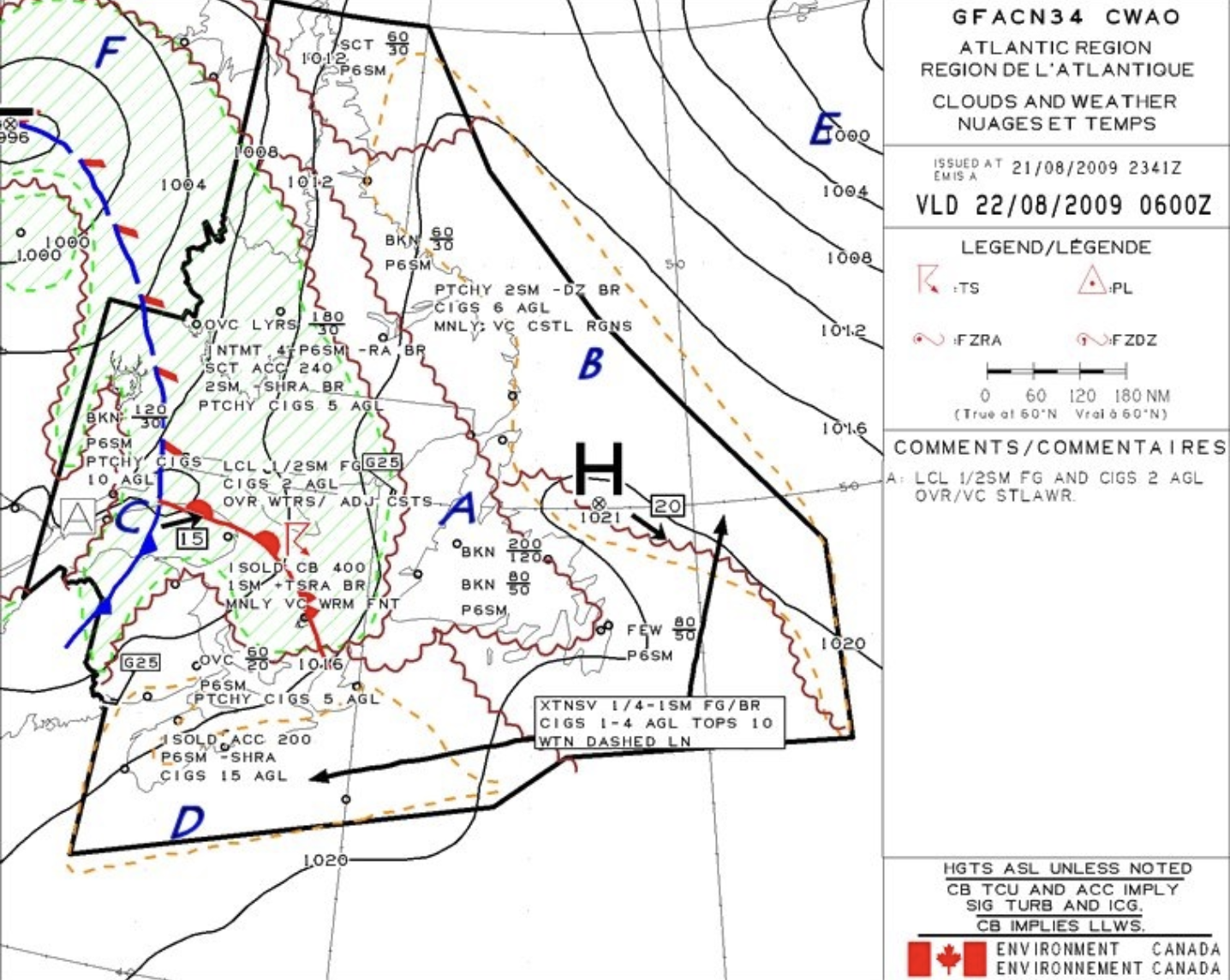
The occluded front moving in region C is moving
East at 15KT
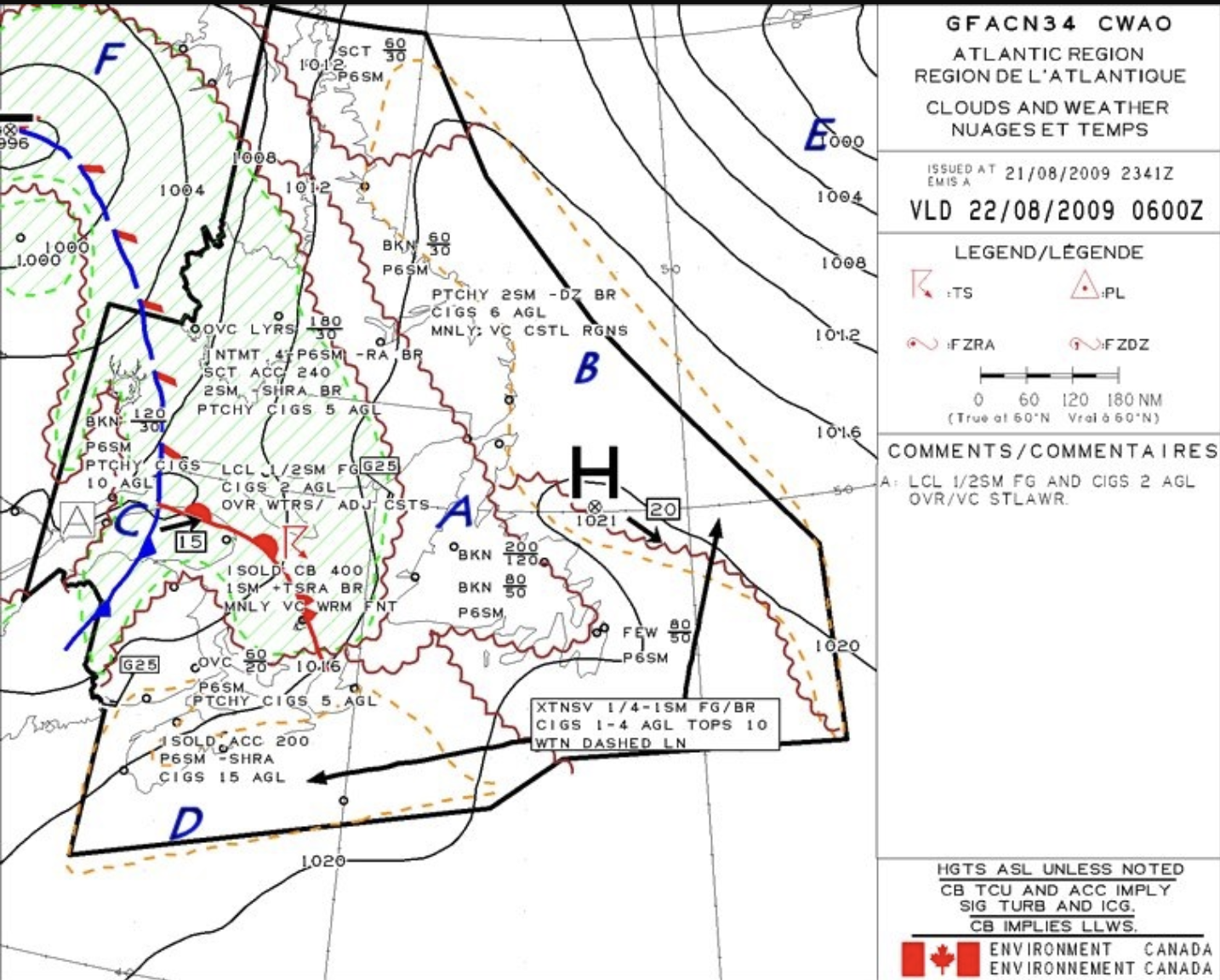
The region that has the greater wind speed is
The closer the isobars, the greater the pressure gradient, resulting in stronger winds.
Yes there is a wind indication north of the D, but that is because it is in the domain. Area E is not in the domain but the isobars are a lot closer so that is where stronger winds are. Being outside the domain there is no information given. So based on the isobar spacing E is where the strongest winds are, whether or not a wind indicator is present.
The correct answer is: E.
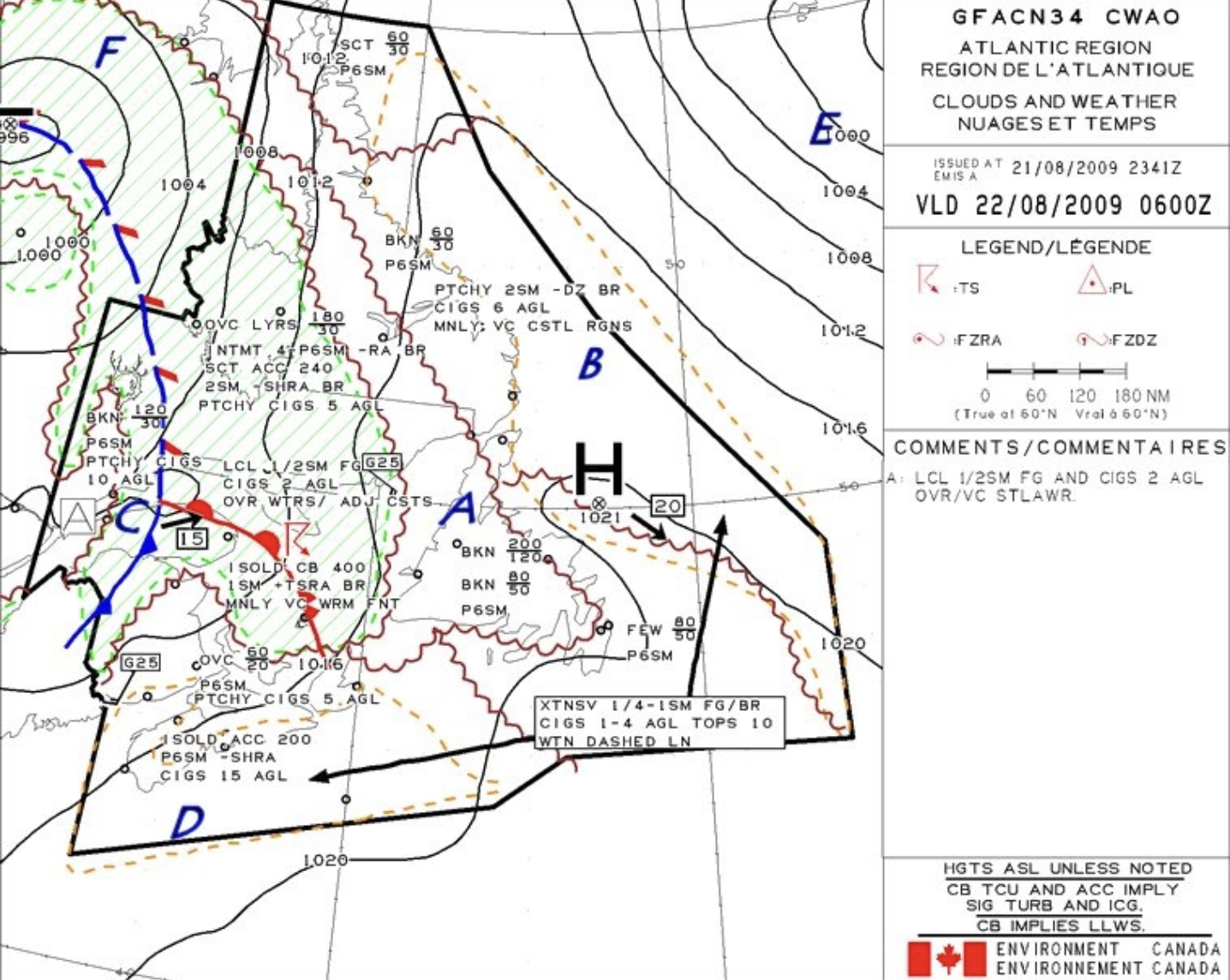
Region F on the GFA chart indicates the meteorological phenomena of
showery precipitations
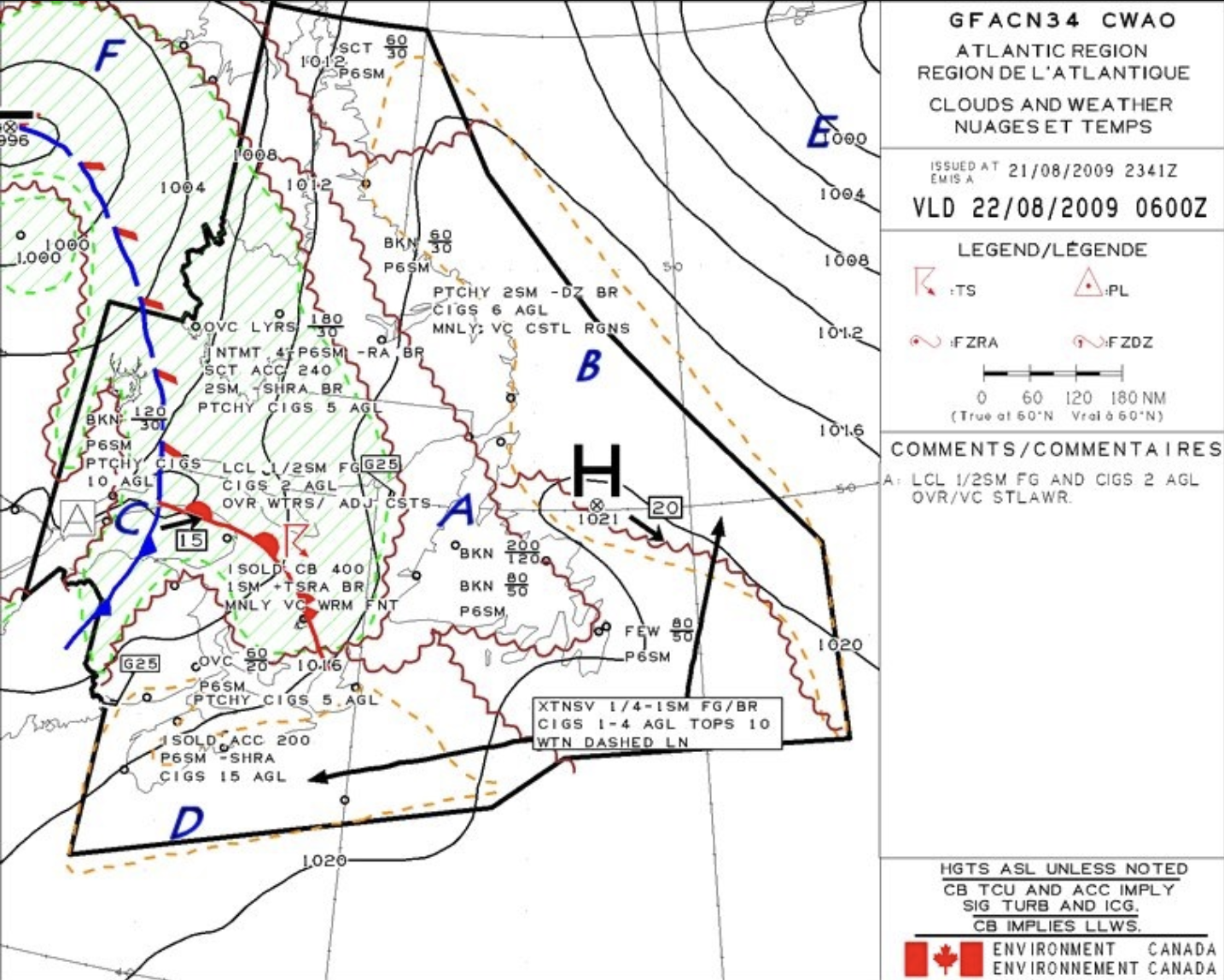
The clouds associated with region D in the GFA are
25% or less coverage altocumulus castellanus clouds topping at 20 000 feet ASL.
Upper level weather charts are issued
two times daily at 00:00 and 12:00 Z.
To view the upper level weather map based at 18 000 feet refer to the
500 mB chart.
The term OCNL refers to cloud coverage
between 25 to 50%.
A surface analysis chart provides
actual weather as observed from the surface to any height and pressure patterns surface to 3 000 feet AGL.
Surface prognostic charts are
forecasts issued 48 and 36 hours before valid time.

This surface prognostic chart symbol is used to identify
rain showers

This surface prognostic chart symbol is used to identify areas of
drizzle

This surface prognostic chart symbol is used to identify areas of
Ice pellets
Reggarding upper level charts, which statement is false?
Select one:
a. Shows reported conditions aloft of wind speed and direction, temperatures, frontal positions, and pressure systems.
b. Gives a picture of the extent of weather systems, cloud levels, and thunderstorms.
c. Indicates past weather conditions.
d. Shows reported conditions at the surface of wind speed and direction, temperatures, frontal positions, and pressure systems.
FALSE: Shows reported conditions at the surface of wind speed and direction, temperatures, frontal positions, and pressure systems.
The 700 mB chart level is equivalent to a pressure altitude of 10 000 feet ASL.
True
An advantage of polar orbiting satellites over geostationary satellites is
the level of detail in the image captured.
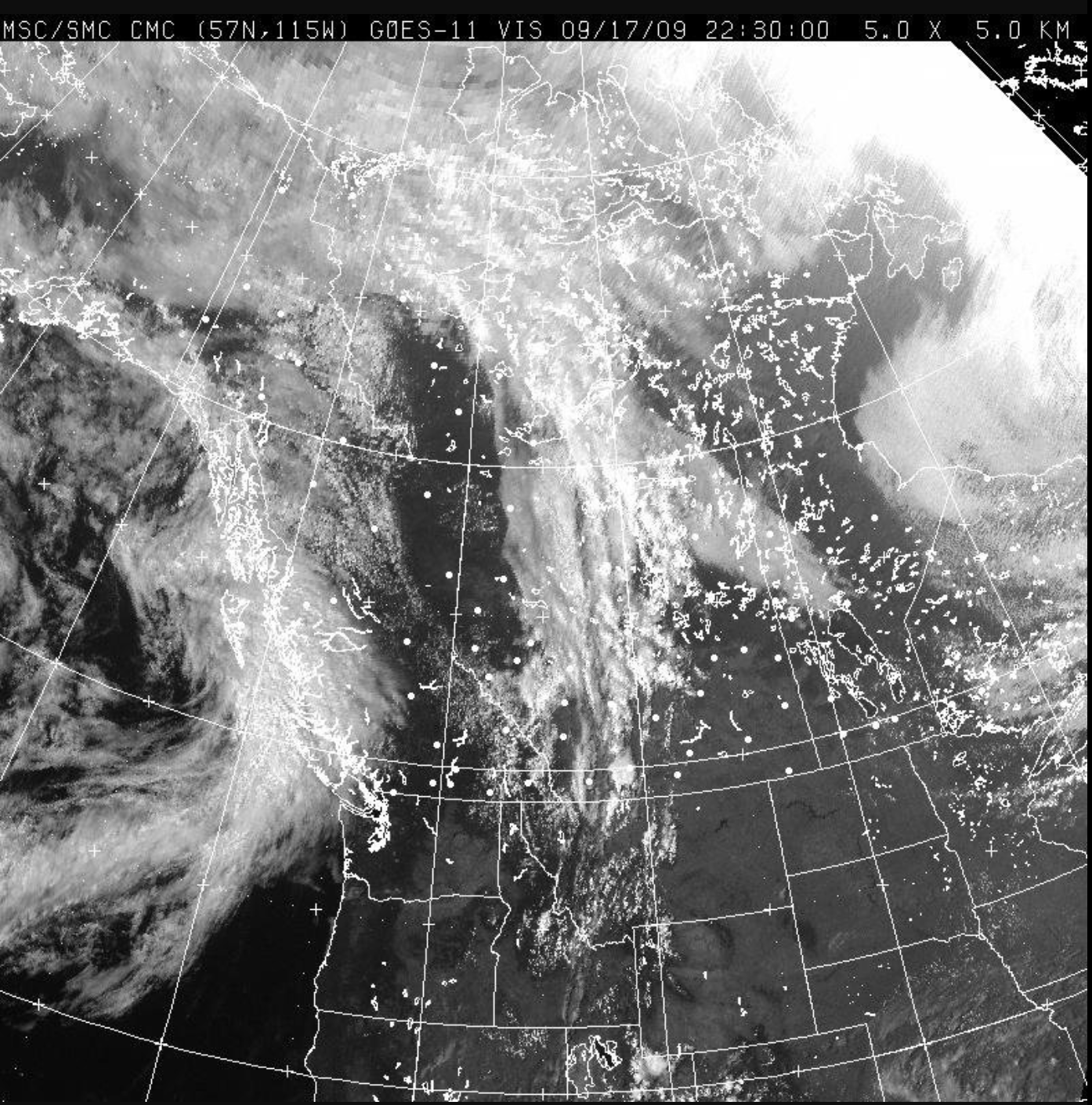

This satellite image is a
geostationary visible satellite image.
Infrared satellite images are able to detect the temperature emitted by all objects above
-272°C.
On an infrared satellite image, colder temperatures are depicted as . . . . . and correspond to . . . . . altitudes.
brighter, higher
Polar orbiting satellites circle the earth . . . . . times per day.
14
The smallest object (resolution) that can be identified from an infrared image is
4km
Which is not an advantage of visible over infrared images?
Ability to capture relevant data around the clock.
Which statement does not describe geostationary satellites? Select one:
a. Orbit above the equator at an altitude of 36 000 km.
b. Move west by two time zones per orbit.
c. Travels at more than 11 000 km/h.
d. Takes one day to complete an east to west orbit.
Polar Orbiting Satellites "appear" to move west by two time zones per orbit.
The correct answer is: Move west by two time zones per orbit
Clouds are better defined on IR charts. (T/F)
False
Regarding visible satellite images it is incorrect that
Select one:
a. banks of fog are readily recognized.
b. cumuliform clouds are not readily seen.
c. at low sun angles the clouds can take on a 3D appearance.
d. thunderstorms can be detected.
Question is asking INCORRECT.
The correct answer is: cumuliform clouds are not readily seen.
The purpose of weather radar is to detect
Remember weather radar does not detect thunderstorms directly but rather by detecting precipitation. Thunderstorms, having immense amounts of precipitation, are therefore great candidates for identification on the radar display.
The correct answer is: thunderstorms.
When an iso-echo contour display indicates a thin white band surrounding the iso-echo hole, the phenomena most closely associated is
turbulence.
Weather radar is able to detect
rain
What is the reason for weather radar attenuation?
Near cells blocking radar feedback from distant cells.
Which scope patterns would indicate the presence of hail shafts?
Finger-like protrusions, Hooks & Scalloped edges
It is advisable to avoid large storm cells that are changing shape rapidly by
20 NM.
It is incorrect regarding attenuation that
Select one:
a. under certain conditions the the emitted signal can be absorbed by a large area of moisture.
b. attenuation is caused by radome icing.
c. the display may not accurately depict what lies ahead.
d. the weather radar depends on the transmitted signal bouncing off something and returning to the antennae.
attenuation is caused by radome icing.
Rainfall gradient and turbulence are high when rainfall increases or decreases rapidly over a
short horizontal distance.
A black-hole on the weather radar display will most likely represent
the hard core of a thunderstorm cell.
Airborne weather radar can see water best in its solid form. (T/F)
False
Another word for a lightning detector is
Spherics devices.
The advantage of a stormscope compared to radar is
lower cost
It is not true regarding ADS-B that it
Select one:
a. is a ground based system.
b. includes METARs and TAFs.
c. is superior to XM weather radar.
d. currently is a free service.
Question is asking NOT true.
The correct answer is: is superior to XM weather radar.
It is incorrect regarding radar detection that radar
Select one:
a. detectors have fewer moving parts than lightning detectors.
b. detects the presence of rain.
c. provides more detail then lightning detectors.
d. is better for predicting where the turbulence will be.
Question is asking INCORRECT.
The correct answer is: detectors have fewer moving parts than lightning detectors.
XM weather receives weather information from
a satellite receiver.