Parent Material - Envirothon
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Alluvium
deposited by stream/rivers, undeveloped profile (since recent), well sorted
Marine sediments
settled out of sea → by current and tides (but also constantly modified byt eh current ad tides)
Ablation till
loose, permeable till deposited during the downwasting (melting>flow → receeding) of glacier; Coarse, deominated by snad, gravel, cobbles, stones
Glaciomarine deposits
deposits by glaciers of glacially eroded sediment taken from marine environments; High in silt and clay
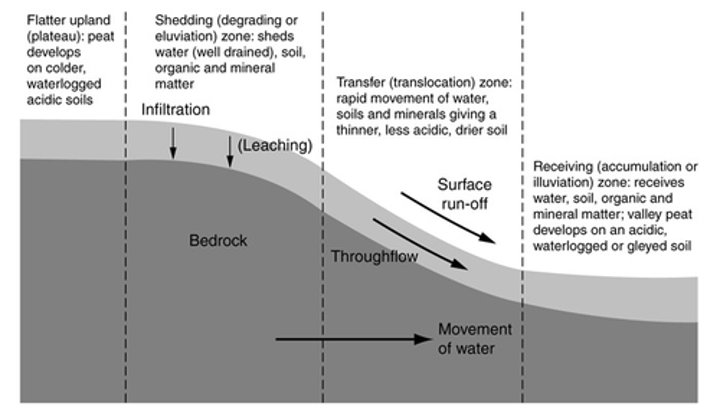
3 features of topography that matter
slope, aspect, catena
Slope:
steeper =
level soil =
expressed as percent
Steeper = more erosion (faster moving water??)
Level soil = more developed (more leaching of water and chemicals??)
Aspect
direction relative to sun
Aspect effect
N Hem =
S hem =
N Hem: northern/eastern slopes fact away from sun more so darker, cooler, wetter → deeper soil (more decomposition) w/ lots of OM
Catena
a bunch of soils near each other by have different horizon types, sequences, thickness because of its position to/in the water table
Parts of catena (4)
Summit: above 4 feet water table
Well drained obviously
Shoulder: watertable is 3-4 feet below surface
Most well drained
Backslope: water table 2-3 feet
Ehh drained
Footslope: Water table 2 feet bwlow
Poorly drained of course
two factors of climate
vegetation and percipitation & temp
vegetation impact
less = less org material → prbly light in color and a thinner O layer
percip & temp impact
Less precipitation = less chem weathering → coarse soil & chemical leaching → darker or non existant e layer?
Airid soils
warm/wet climate = more decomposition & organic matter
MA climate features & impact
mod temp & perc → OM can accumulate, slightly acidic soils (bases leached away), frost = break rock fragments (loamy sands)
MA parent material history, majority of parent material, other comon parent materials (5)
During 2-14kya it was covered in ice (Pleistocene glaciation)
Most parent materials are glacial, primarily till (sometimes eolian over till
Other common: glaciofluvial, lacustrine, marine, recent alluvium, recent organic.
How do microorganisms impact parent material?
break down OM, soil fertitllity via nitrogen fixation, products humus
How do bioturbation impact parent material? (2)
big animals mix soil so soil is permeable
Excretions also help aggregate soil & improve structure & conserve nutrients so there is less leaching
How do hardwoods and softwoods impact parent material
Hardwoods take up bases and return to soil
Softwoods: take up less bases so bases leach more → soil more acidic
How do grasses arreas impact parent material?
thicker, darker surface layer + moisture cause grase roots hold onto soil + decompose slowly → A layer nutrient rich
How does wind throw parent material?
uproots trees which mixes up soil
How does time impact parent material? (2)
over time the, the soil forming facors become more defined
how long does it take to create 1" of top soil?
500-1000 years
Older soils have... (4)
Older soil has more defined profiles
Older soil more likely to have E layer
Older soil has thicker A/B
Older soil has more clay
MA soil formation (time)
Massachusetts: most soils formed since last glaciation (inceptisols) → little weathering and profile development so under <10% clay
Write a FRQ answering how the 5 parent factors impact MA's soil
lol u got to do this work yourself
Soil def
unconsolidated organic and mineral material on the surface of the earth that is capable of supporting plants.
(note: actual definitions have a lot of wiggle room since soils are dynamic and can differ a lot → no concrete definition)
5 soil factors
the action of climate, plants, and organisms (animals + people) on parent material in different topographic location over time
CLORPT
Parent material
uncoscolidated organic and mineral material that the soil is formed from (does not include consolidated bedrock)
Why do we care about parent material
INFLUENCES RATE OF WEATHERING AND RATE OF FORMATION
Residuum
produced by weathering of rock
How to ID residuum
Used when the soil properties match the ones of the underlying rock and modification via movement
Where does alluvium occour?
Typically occurs in old/new terraces & active flood plains, basins & bottomlands periodically flooded
Luastrine deposits
settled out material in lakes. Well sorted?
Beach deposits
former shorelines of sea and lakes, sorted in low ridges; Sandy, gravely, cobbly, stony
Folian
wind carried material → typically silty or very fine sand (super light, type of eolian material)
Colluvium
mss of soil material/fragements at base of slopes
Talus
Accumulation of rock fragments at base of slope
Organic material
accumulation of peat and muck from deposites of plants; 16+ inches of organic deposits (otherwise developed mineral material)
Where does OM occour?
Typically in wet area where the plant remains are decomposed rapidly → marshes, swamps
Till
directly depostied via ice (no water), unstratified, hetergenous mixture of clay, silt, sand, gravel, boulders, stone
Types of till
Ablation and lodgement/basal till
Lodgement/basal till
denst, compact, impermeable till that was crushed by the glacier; deposited beneath moving glaciers; Sandy or loamy
Glaciofluvial deposits (collectively, glacial outwash)
material transported by glacier, deposited during melting of glacier (Sorted) & Includes deposits via streams & rivers from the ice melt
Glaciolacustrine deposits
luastrine deposits but from glacial lakes; Stratified or laminated; Fine clay to sand (ie contains silt)
Varves
alternating depostitions related to season's glacial ice melt; Have drianed by now
How do varves form?
Mass of ice compressed land
Glacial beach deposits
gravel and sand from beaches of glacial lakes (mixture depends on deposits of orginal glacier)
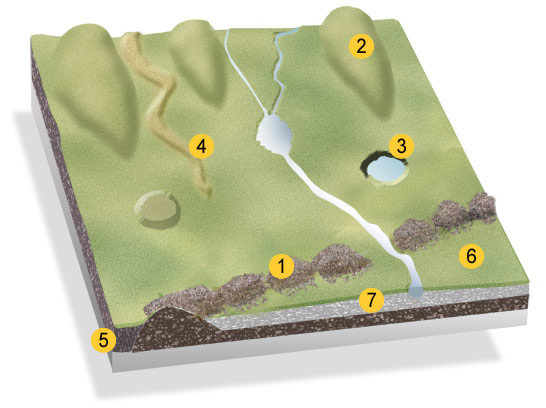
What is feature 1? What is it’s purpose?
A moraine
Piles of rock & sedimented deposited when a retreating glacier melts
types of moraines (4)
Terminal moraines are found at the terminus or the furthest (end) point reached by a glacier.
Lateral moraines are found deposited along the sides of the glacier.
Medial moraines are found at the junction between two glaciers.
Ground moraines are disorganised piles of rocks of various shapes, sizes and of differing rock types.
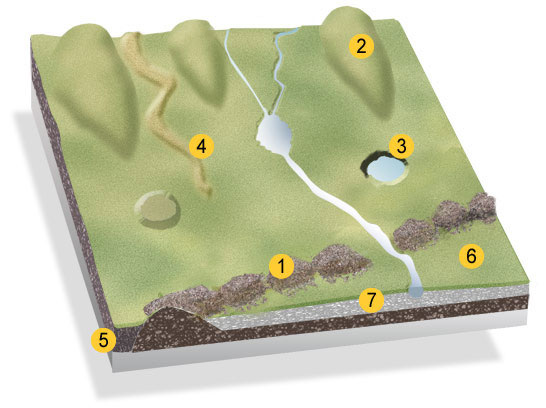
What is feature 2?
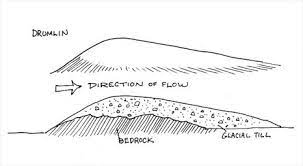
A drumlin
Smooth elongated oval hill made of glacial sediment. Long axis parallel to glacial flow, tail points in direction of flow
floodplaine
Nearly level plain bordering stream or river, subject to flooding
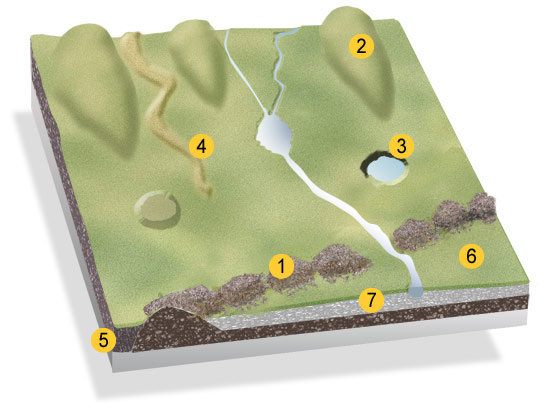
What are the rest of the features 3 & 6
3: Kettle Hole
6 is an Outwash Plain
Escarpment
countinuos cliff
glacial lake
Former glacial lake
Low lying
Level
Parent material with strata of silt-clay-fine sand