BIOS1101 Practical Exam
1/80
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Darwinian demon
A hypothetical organism that maximises evolutionary fitness by having unlimited resources and no limitations on reproduction, survival, or lifespan.
Formula for identifying similarity between species (percentage)
no. same amino acids / total amino acids * 100
e.g. no. same amino acids = 23
total amino acids = 30
overall similarity = (23/30)*100 = 77%
what are coelomates? + phylum examples
Coelomates are animals that possess a true coelom, a fluid-filled body cavity completely lined by mesoderm. Examples include chordates, and annelids.
what are acoelomates? + phylum examples
Acoelomates are animals that lack a coelom, instead having a solid body without a fluid-filled cavity. Examples include Platyhelminthes.
what are pseudocoelomates? + phylum examples
Pseudocoelomates are animals that have a body cavity called a pseudocoel, which is not fully lined by mesoderm. Examples include Nematodes.
what is diploblasty?
having two tissue layers (endoderm and ectoderm)
what is triploblasty?
having three tissue layers (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm)
what evolutionary advantage can bilateral symmetry provide?
allows more direct and mobile movement
advantage of a coelom?
provides a space for organs in an organism
Phylum porifera:
are they symmetrical?
how many tissue layers (diploblast or triploblast)?
coelomate, acoelomate or pseudocoelomate?
do they have a skeleton?
are they segmented?
not symmetrical
zero tissue layers (neither)
acoelomate
yes - fibres of calcium carbonate, silica or spongin
not segmented
Phylum Cnidaria:
are they symmetrical?
how many tissue layers (diploblast or triploblast)?
coelomate, acoelomate or pseudocoelomate?
do they have a skeleton?
are they segmented?
yes - radial symmetry
two - endoderm and ectoderm (diploblast)
acoelomate
no skeleton
not segmented
Phylum Platyhelminthes:
are they symmetrical?
how many tissue layers (diploblast or triploblast)?
coelomate, acoelomate or pseudocoelomate?
do they have a skeleton?
are they segmented?
yes - bilaterally
three - endo, ecto, meso (triploblast)
acoelomate
no skeleton
no segmentation
Phylum nematoda:
are they symmetrical?
how many tissue layers (diploblast or triploblast)?
coelomate, acoelomate or pseudocoelomate?
do they have a skeleton?
are they segmented?
yes - bilaterally
three (triploblast)
pseudocoelomate
no skeleton
no segmentation
Phylum annelida:
are they symmetrical?
how many tissue layers (diploblast or triploblast)?
coelomate, acoelomate or pseudocoelomate?
do they have a skeleton?
are they segmented?
yes - bilaterally
three (triploblast)
coelomate
yes - hydroskeleton
yes
phylum arthropoda:
are they symmetrical?
how many tissue layers (diploblast or triploblast)?
coelomate, acoelomate or pseudocoelomate?
do they have a skeleton?
are they segmented?
yes, bilaterally
three (triploblast)
coelomate
yes - exoskeleton
yes
phylum mollusca:
are they symmetrical?
how many tissue layers (diploblast or triploblast)?
coelomate, acoelomate or pseudocoelomate?
do they have a skeleton?
are they segmented?
yes - bilaterally
three (triploblast)
coelomate
some have external (shells) e.g. snails — some have reduced internal (mantle) e.g. octopus
no segments - only chitons
3 common traits among all molluscs?
muscular foot, visceral mass (containing organs), and mantle (secretes shell)
phylum echinodermata:
are they symmetrical?
how many tissue layers (diploblast or triploblast)?
coelomate, acoelomate or pseudocoelomate?
do they have a skeleton?
are they segmented?
yes - radial
three (triploblast)
coelomate
yes - endo
not segmented
phylum chordata:
are they symmetrical?
how many tissue layers (diploblast or triploblast)?
coelomate, acoelomate or pseudocoelomate?
do they have a skeleton?
are they segmented?
yes - bilateral
three (triploblast)
coelomate
yes, internal - can be bony, or cartilaginous
kind of
name 3 types of mammals and what makes them unique
-marsupial - have a pouch
-placental - live birth
-monotreme - lay eggs
skeletal muscle tissue: location + what do they help with?
connect to the skeleton - help with voluntary muscle movements e.g. bending your arm
skeletal muscle tissue: how can you identify them?
-striations (need to contract and extend very fast)
-nuclei off to the side
cardiac muscle tissue: location + what do they help with?
in the heart - handles lots of pressure from blood being pumped by heart
cardiac muscle tissue: name 3 features of cardiac muscles
-striations
-intercalated discs
-branched out (to cover entire heart)
cardiac muscle tissue: 1 visual difference between vein and artery cross section?
-artery - thick wall, circular
-vein - thin wall, infinity shaped (wider on sides, thinner in middle)
smooth muscle tissue: function? + examples of location/function
responsible for involuntary muscle movement e.g. digestion (intestines), blood pressure regulation (veins, arteries)
smooth muscle tissue: why aren’t they striated?
no fast contractions occur where there are smooth mucles
epithelial tissue: where would you find simple squamous epithelium?
in smooth muscles - lungs, veins, arteries
epithelial tissue: describe the form of simple squamous epithelium + why this is useful
thin, once cell thick - allows for gas exchange
epithelial tissue: where would you find simple cuboidal epithelium?
intestines (but less so), glands, testes, ovaries
epithelial tissue: describe the form of simple cuboidal epithelium + why this is useful
cuboid - gaps in between each cell for excretion
epithelial tissue: where would you find simple columnar epithelium?
intestines, oviduct
epithelial tissue: describe the form of simple columnar epithelium + why this is useful
columnar - good for absorbtion
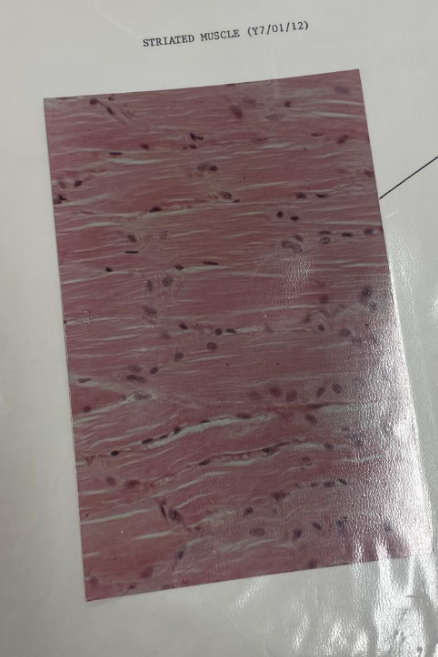
what is this? what is the line pointing to?
skeletal muscle tissue
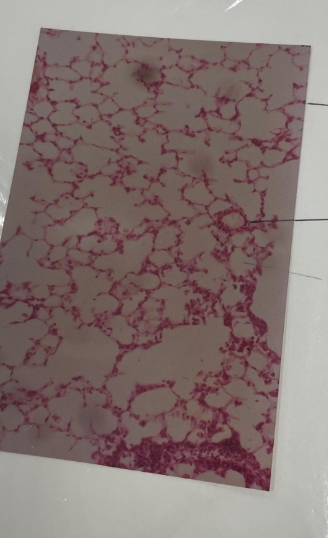
what is this? what are the lines pointing to?
Lung tissue
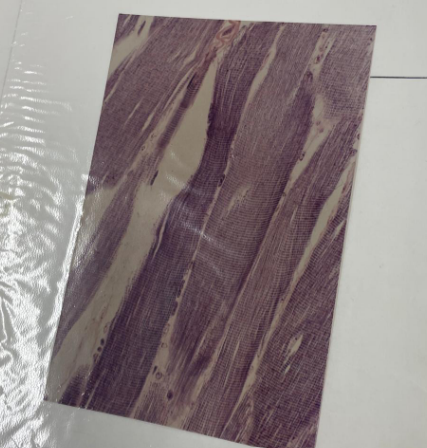


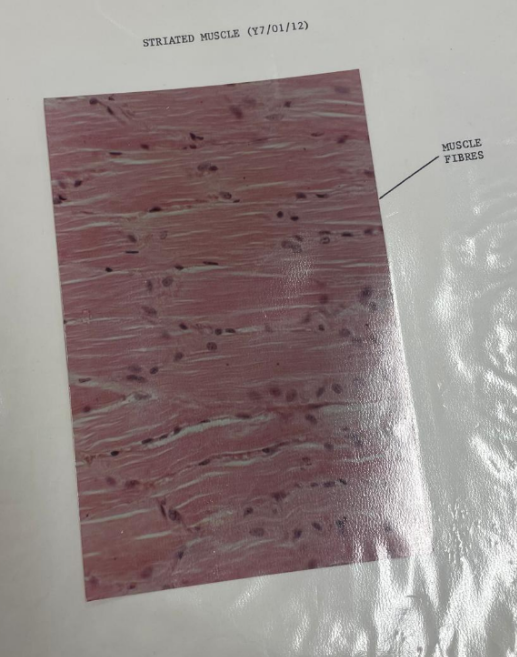
what is this? what is the line pointing to?
striated muscle tissue

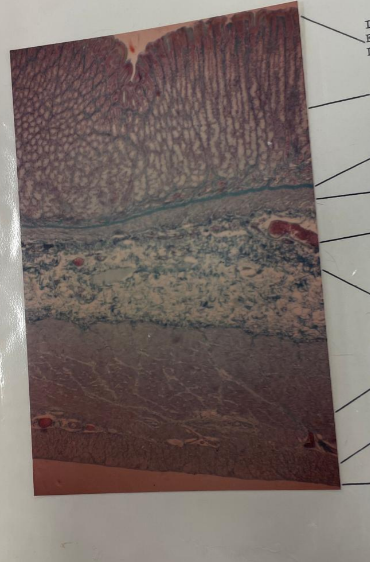
what is this? what are the lines pointing to? (name at least 3-4)
stomach
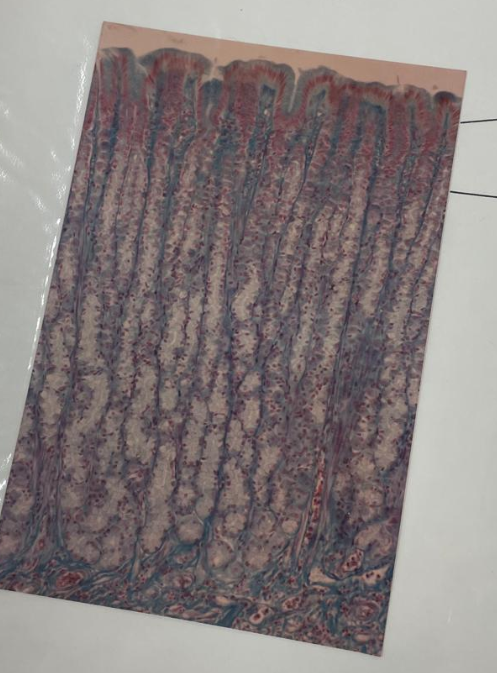


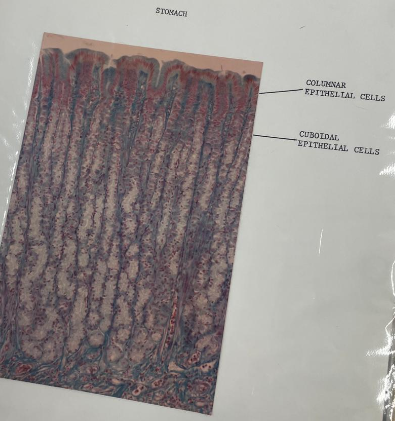
what is this? what epithelial cells are the lines pointing to?
stomach
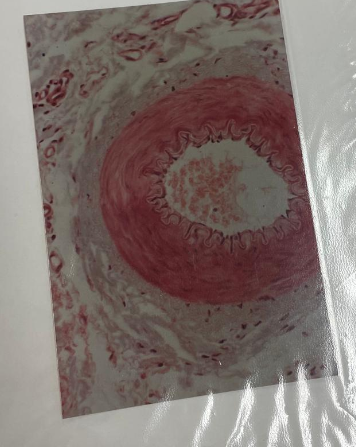
what is this?
artery

what is this?
vein
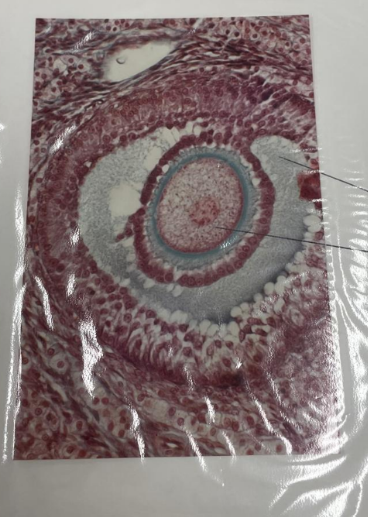
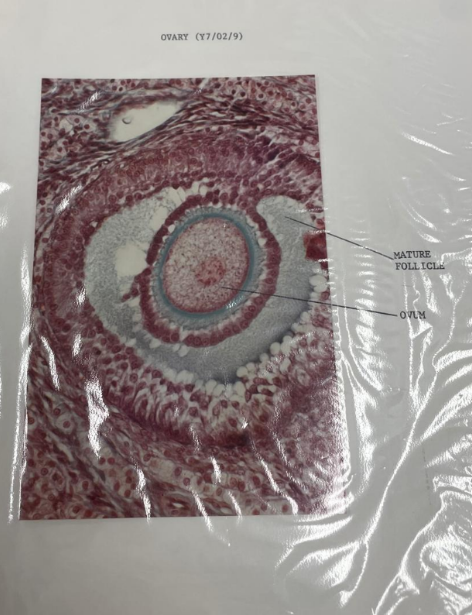
what is this? what are the lines pointing to?
ovary
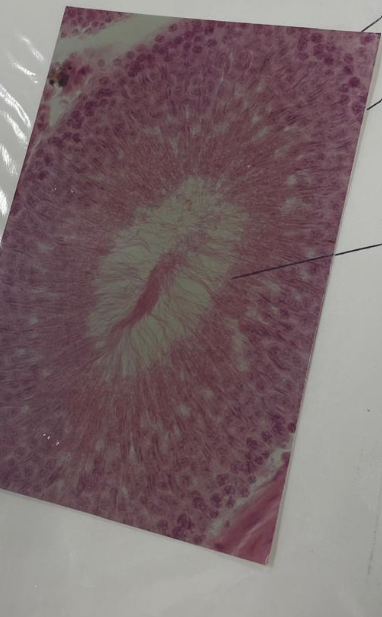
what is this?
testis

what is this?
cardiac muscle
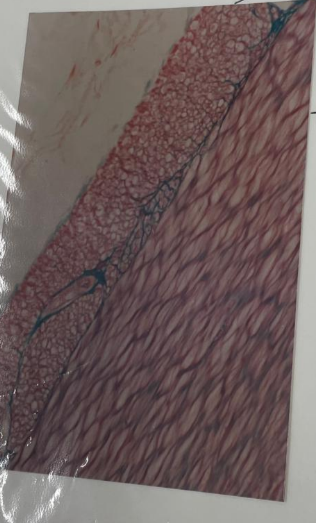
what is this?
smooth muscle
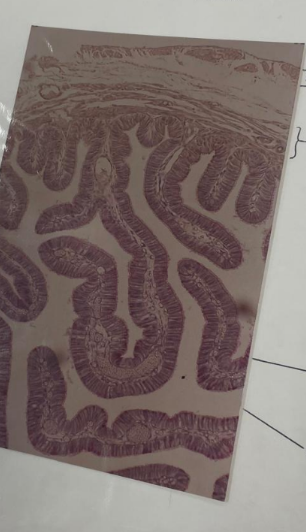
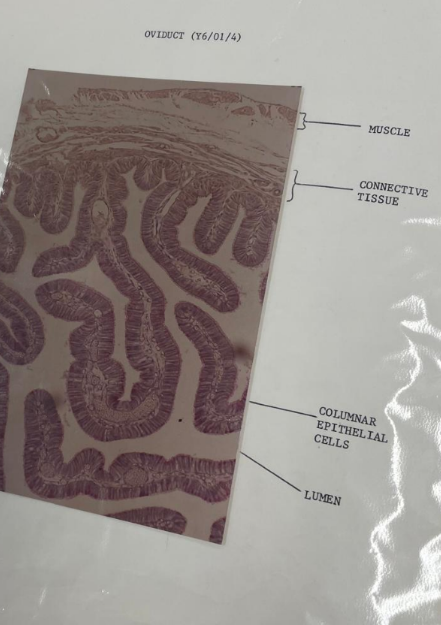
what is this? what epithelial cells can you see?
oviduct - columnar
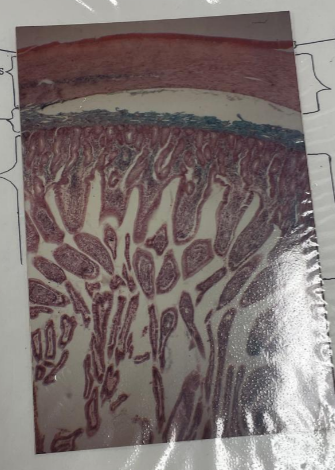
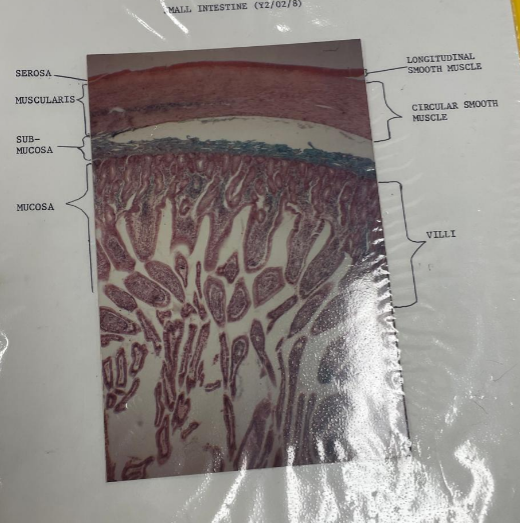
what is this?
small intestine

is this wood from an angiosperm or a gymnosperm? why?
angiosperm - because its porous (has vessels)
what are traits associated with plants in an aquatic environment?
-flagellated sperm
-simple diffusion for nutrient uptake
-rhizoids
what are traits associated with plants in a moist terrestrial environment?
-stomata
-rhizoids
-flagellated sperm
-photosynthetic gametophytes
-spores
what are traits associated with plants in a dry terrestrial environment?
-stomata
-woody tissue
-roots
-pollen
-seeds
-vascular tissue
-waxy cuticle
rhodophyte algae:
what colour?
are they plants?
depth found? (deepest, middle, shallowest)
red algae
not really?
deepest (~250m)
Phaeophyta:
what colour?
are they plants?
depth found? (deepest, middle, shallowest)
brown algae
technically protists
middle (~200m)
chlorophyta:
what colour?
are they plants?
depth found? (deepest, middle, shallowest)
green algae
most plant-like out of all three algae
shallowest (150m)
what is this? what are the missing words? what type of plant?
a gametophyte and sporophyte - bryophyte (moss)
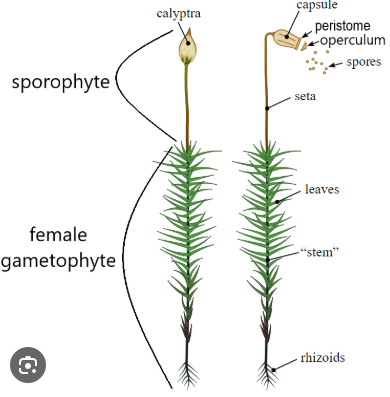
what are the archegonia in bryophytes?
-egg-bearing organ with long neck
-extends beyond the venter
-capped at tip with cover cells
what are the antheridia in bryophytes?
-sperm-bearing organ with outer row of sterile (non-sperm forming) cells enclosing inner fertile cells, each of which becomes a sperm
describe the fertilisation process of bryophytes
sperm from antheridium fertilises in archegonia
sporophyte grows from female gametophyte
spores released from mature capsule in sporophyte
spores grow into filamentous protonema
young gametophytes grow from protonema

what is this? what are the missing words? what type of plant?
sporophyte and gametophyte in a fern

describe the fertilisation process in ferns
sperm use flagella to swim to archegonia (archegonia uses attractants to attract the sperm)
zygote develops into sporophyte/gametophyte
then into mature sporophyte
then into sporangium that contains the pollen
describe the fertilisation process in gymnosperms
occurs in cone where the developed seed is exposed
what are the sporophyte and gametophytes in gymnosperms?
-sporophyte - the tree
-gametophyte (male) - pollen
-gametophyte (female) - within the ovule
what are the sporophyte and gametophytes in angiosperms?
-sporophyte - the flower
-gametophyte (male) - pollen
-gametophyte (female) - within the ovule
describe the fertilisation process in angiosperms
once pollen grain reaches the stigma, it makes a pollen tube down the style to the ovary
two sperm cells enter - one fuses to an egg cell (to make a zygote - 2n) and the other to 2 polar nuclei (to make an endosperm - 3n)
embryonic development begins - the ovule becomes a seed
what are the 2 nuclei present in a mature pollen grain?
tube nucleus and generative nucleus
what is the role of synergid and antipodal cells in the development of an embryo?
-synergid - attracts the pollen tube through the micropyle (opening to the ovule)
-antipodal - unknown but may help develop the endosperm
simple fruit:
no. of carpels/ ovaries?
no. of flowers?
examples?
1 carpel
1 flower
blueberry, cherry, peaches, sunflower
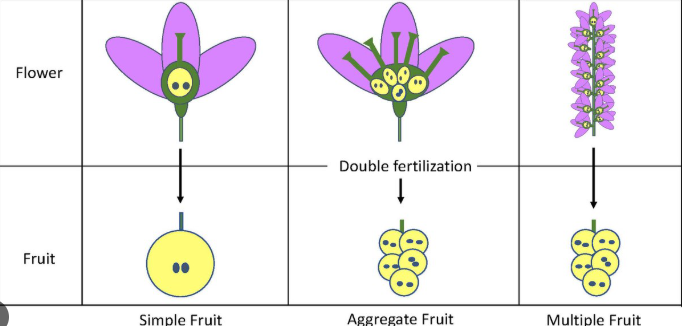
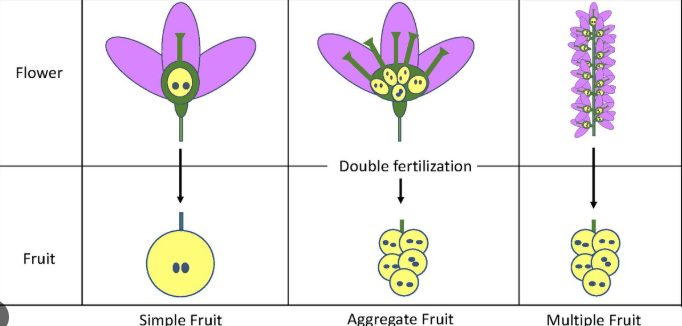
aggregate fruit:
no. of carpels/ ovaries?
no. of flowers?
examples?
several
1 flower
strawberry, raspberry
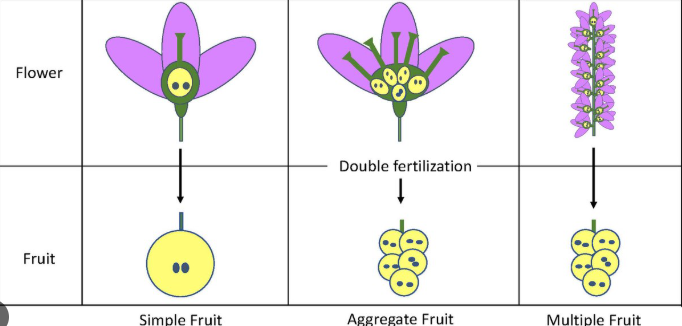
multiple fruit:
no. of carpels/ ovaries?
no. of flowers?
examples?
several
several flowers
pineapple, fig
what makes a fruit an accessory fruit? + examples
a fruit that is made from tissues separate from the carpel e.g. apples (made from hypanthium) and strawberries (made from receptacle)
what hormone is responsible for the ripening of the fruit?
ethylene
what environmental factors trigger germination?
water availability, oxygen, temperature, and light
what hormones are associated with seed dormancy and germination in plants?
-abscisic acid (ABA) - growth inhibitor and seed maturation
-gibberellin - growth promotion
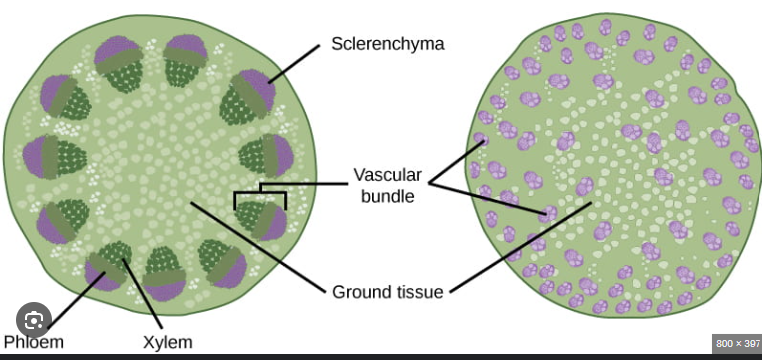
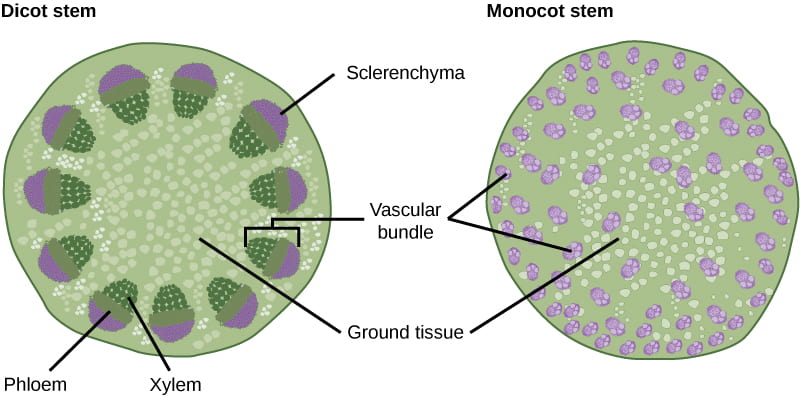
which is the monocot and which is the eudicot stem cross section?
left - eudicot
right - monocot
if, when in presence of hydrogen peroxide, a stigma bubbles/fizzes, what does this mean?
it means the stigma is ready for fertilisaiton
name the 4 tropism’s plants use to survive in their environments and what each does
-phototropism - makes a plant grow towards light
-gravitropism (negative) - makes roots grow downward
-gravitropism (positive) - makes plants grow upward
-thigmotropism - makes plant wrap around nearby objects/plants for stability
-hydrotropism - helps roots grow in the direction of water
what plant hormone mediates gravitropism and phototropism? how does their reaction affect the plant?
auxin - they always fall in response to gravity. if they detect a change in light or orientation of the plant, they will perform cell elongation on the opposite side (e.g. will elongate cells on the underside of a plant in response to it falling)
which plant tissues are lignified?
sclerenchyma and xylem
why does the phloem have a companion cell
it accompanies the xylem and forms the vascular bundle
what forces pull water through xylem vessels?
capillary action (cohesion and adhesion), hydrostatic pressure, and diffusion pressure
how do vascular bundles provide support the stem of a plant?
lignified xylem keeps stem (and plant) upright
why is the palisade mesophyll tightly packed? why is the spongy mesophyll loosely packed?
-palisade mesophyll is tightly packed to maximise light absorption for photosynthesis
-spongy mesophyll is loosely packed to facilitate gas exchange