mandible, TMJs and nasal bones
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
hyoid bone
small U-shaped bone situated at the base of the tongue (about level of C3)
accessory bone of axial skeleton—not a facial or cranial bone
only bone in the body that does not articulate with another bone
muscles that attach to the hyoid bone help control the actions of the tongue, pharynx, larynx, and mandible.
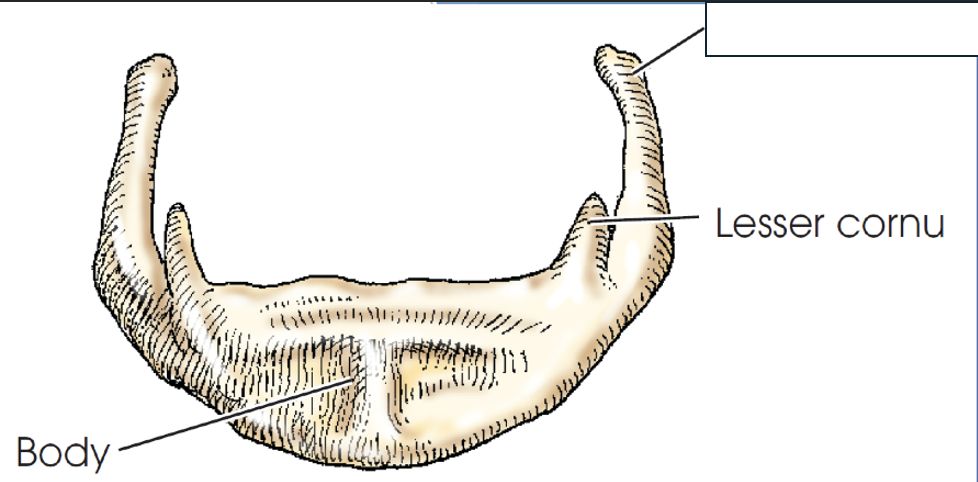
what anatomy is this?
greater cornu
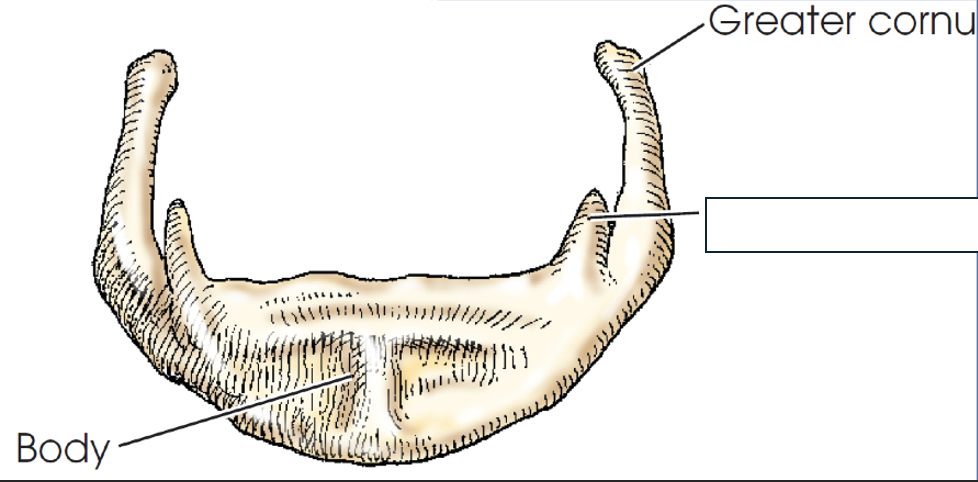
what anatomy is this?
lesser cornu
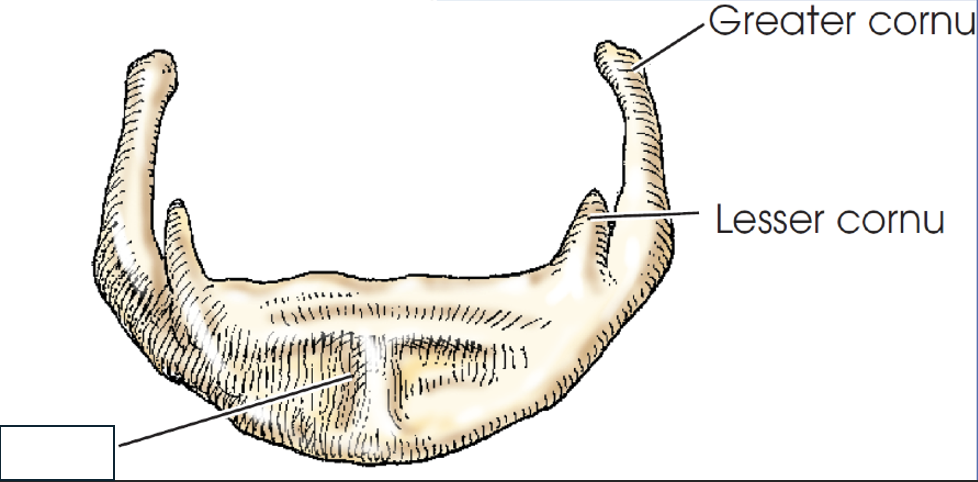
what anatomy is this?
body
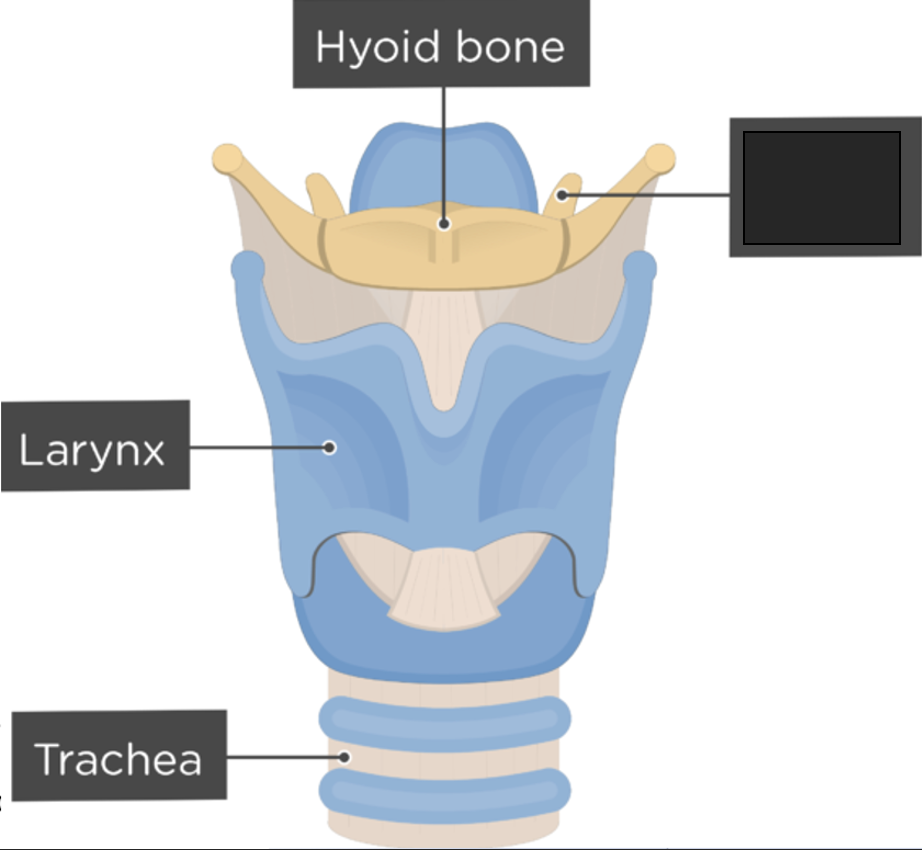
what anatomy is this?
lesser cornu
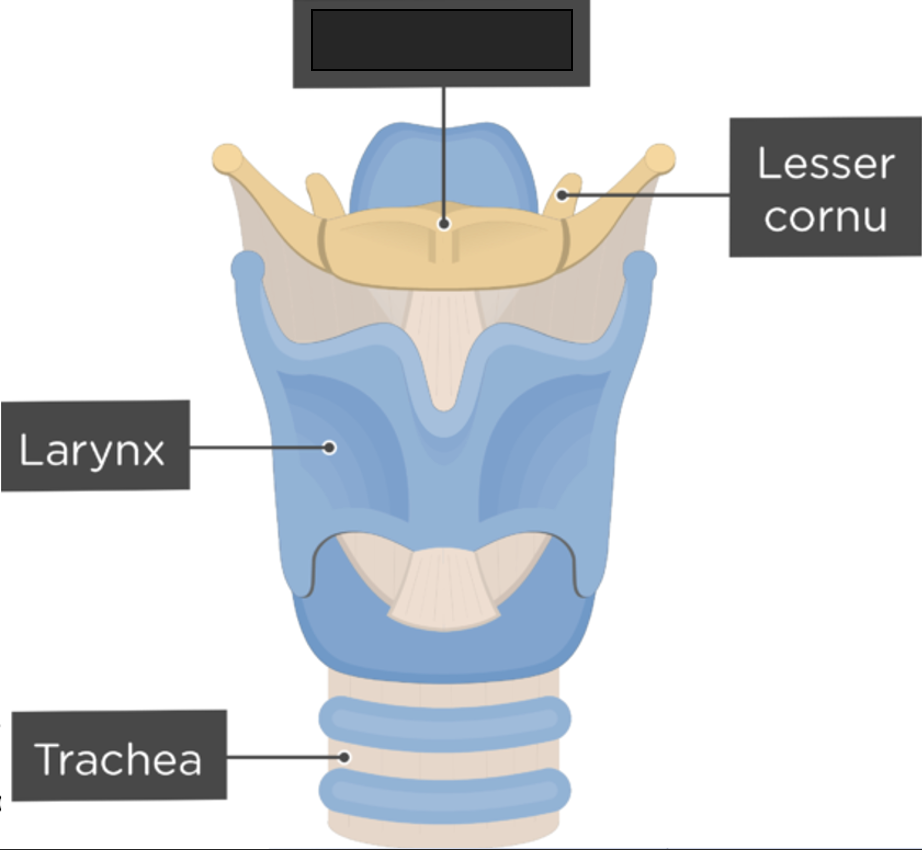
what anatomy is this?
hyoid bone
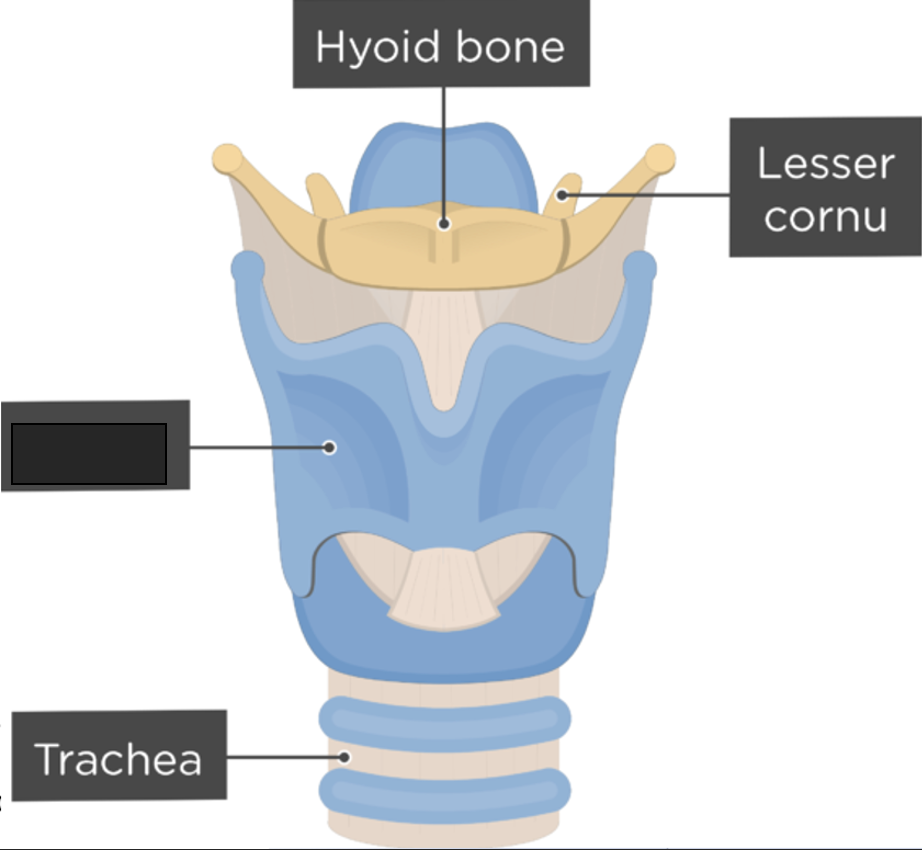
what anatomy is this?
larynx
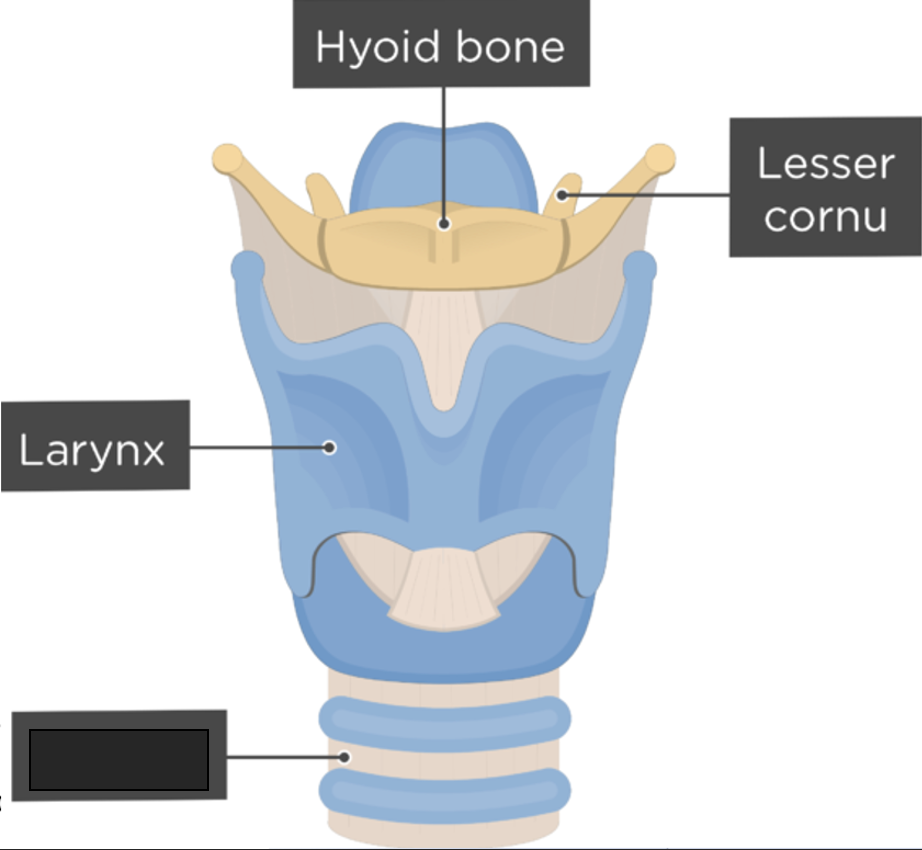
what anatomy is this?
trachea
nasal bone
two small, thin bones that form “bridge of nose”
form superior bony wall of nasal cavity
vary in size and shape in individuals
located anteriorly and superiorly to frontal processes of maxillae
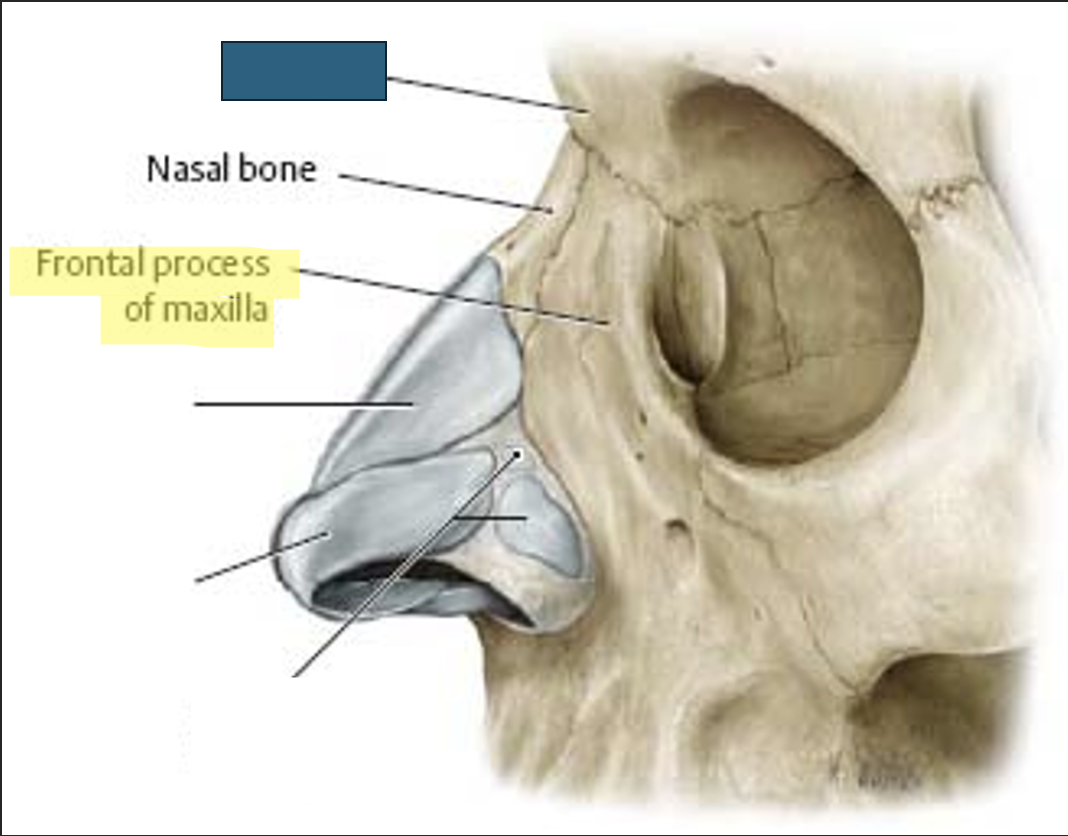
what anatomy is this?
glabella
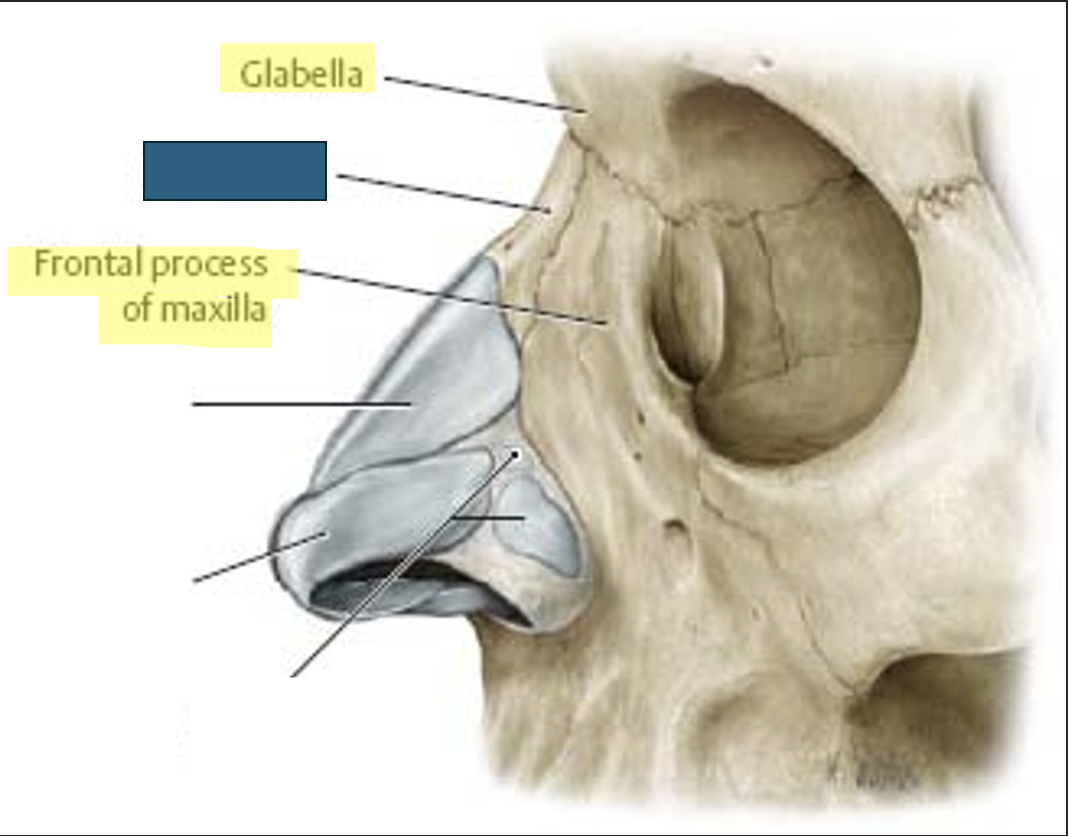
what anatomy is this?
nasal bone
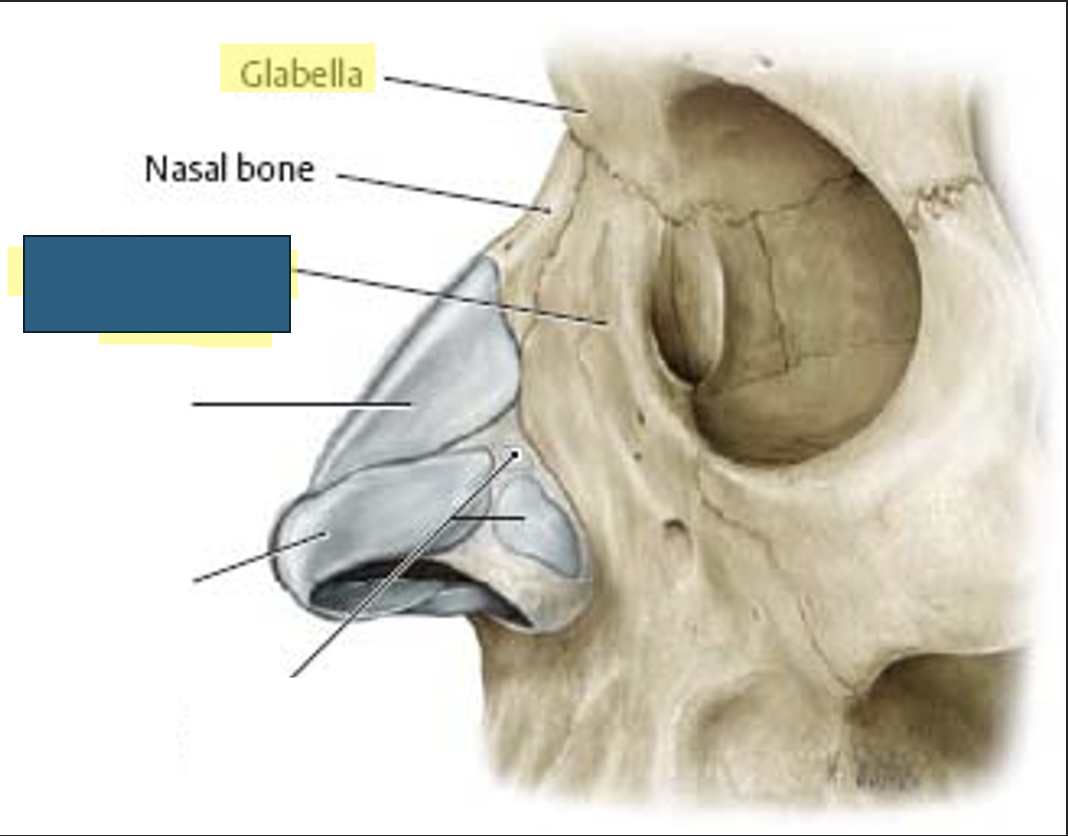
what anatomy is this?
frontal process of maxilla
nasal bone articulations
(midsagittal plane)
superior - frontal bone
posterosuperior - perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
on each lateral side - maxillae
what are the essential projections for the nasal bones?
parietoacanthial (waters)
PA axial (caldwell)
lateral (both left and right)
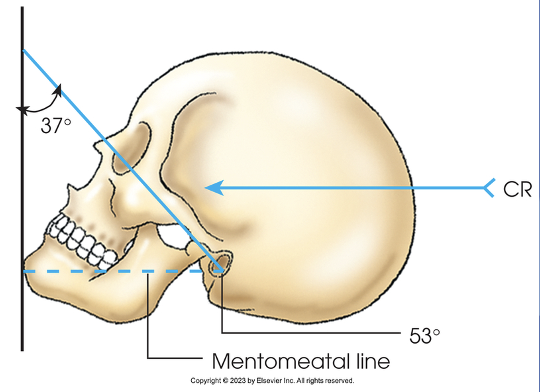
baselines for parietoacanthial (waters) nasal bones
MML perpendicular to IR
central ray for parietoacanthial (waters) nasal bones
exits nasion
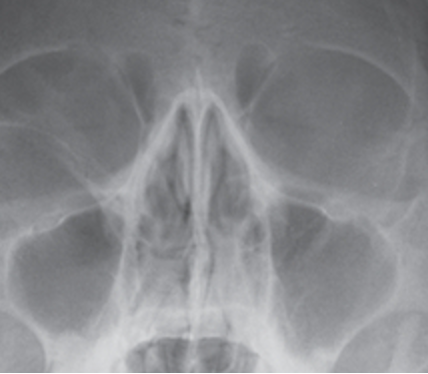
structures shown/ evaluation criteria for parietoacanthial (waters) nasal bones
tangential view of mid-nasal and distal nasal bones, with little superimposition from glabella
PETROUS RIDGES INFERIOR TO MAXILLARY SINUSES
no tilt or rotation
what projection is this?
parietoacanthial (waters) nasal bone
PA axial (caldwell) nasal bone baseline
OML perpendicular to IR
central ray for PA axial (caldwell) nasal bone
15 degrees caudal; exit nasion
structures shown/ evaluation criteria for PA axial (caldwell) nasal bone
nasal septum
PETROUS RIDGES IN LOWER 1/3 OF ORBITS
no tilt or rotation
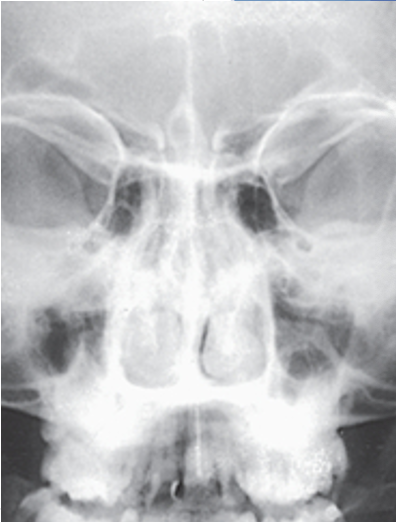
what projection is this?
PA axial (caldwell) nasal bone
lateral nasal bone baselines
IPL perpendicular to IR
adjust flexion of neck to place IOML parallel with the floor
lateral nasal bones central ray
perpendicular to bridge of nose
enters at a point 1 inch distal to nasion
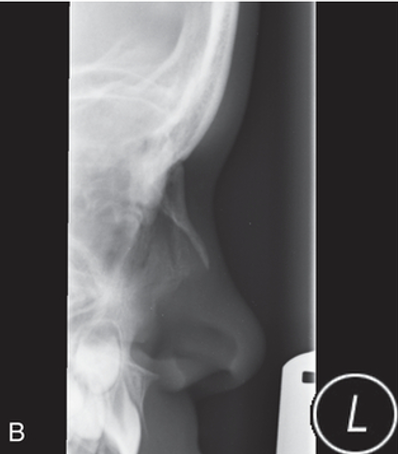
what projection is this?
left lateral nasal bone
mandible
largest and densest bone of the face
single bone, but at birth to approximately 1 year of age it is 2 bones that eventually fuse
body: curved horizontal portion
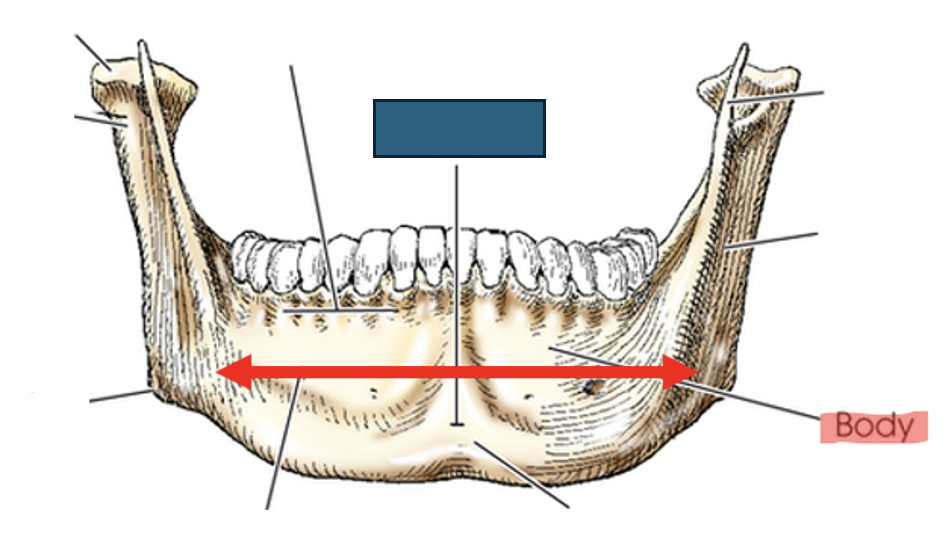
what anatomy is this?
symphysis
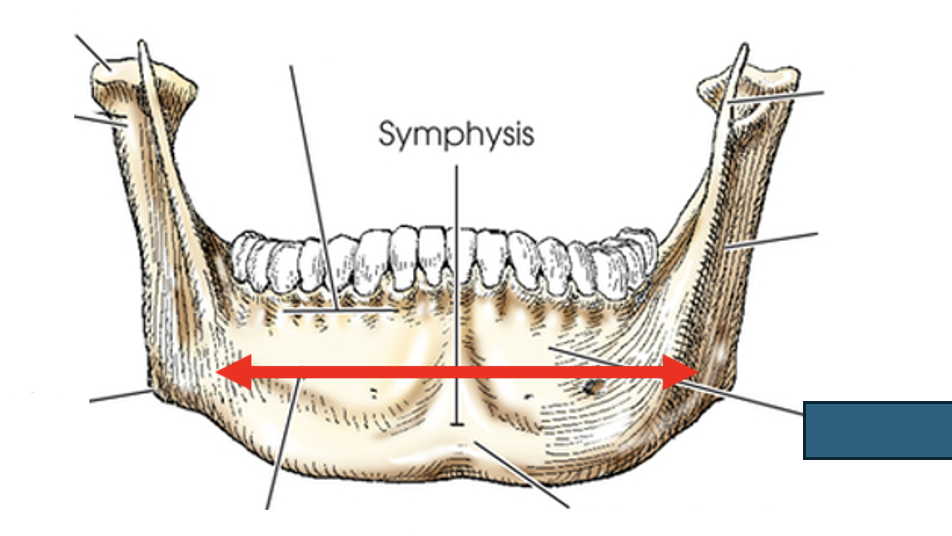
what anatomy is this?
body
rami (ramus)
two vertical portions on each side of body; terminates in “U” shaped notch
mandibular notch
concave area at top of ramus
each have two processes
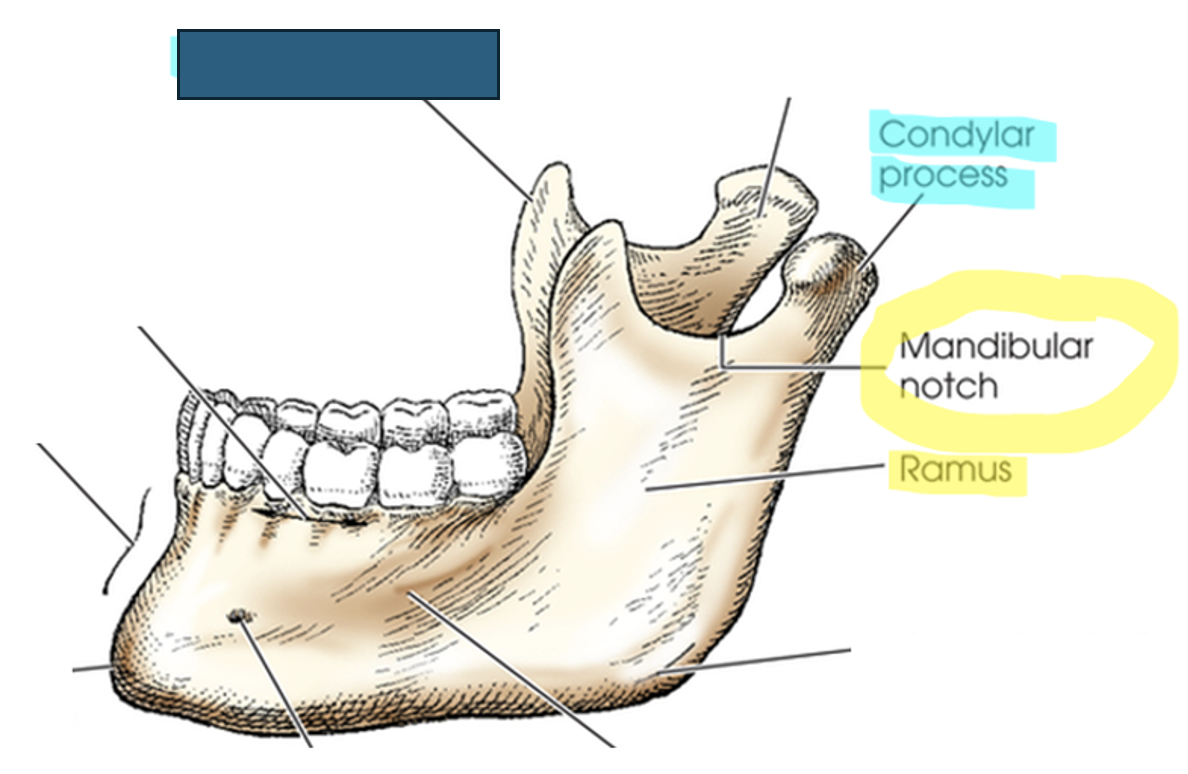
what anatomy is this?
coronoid process
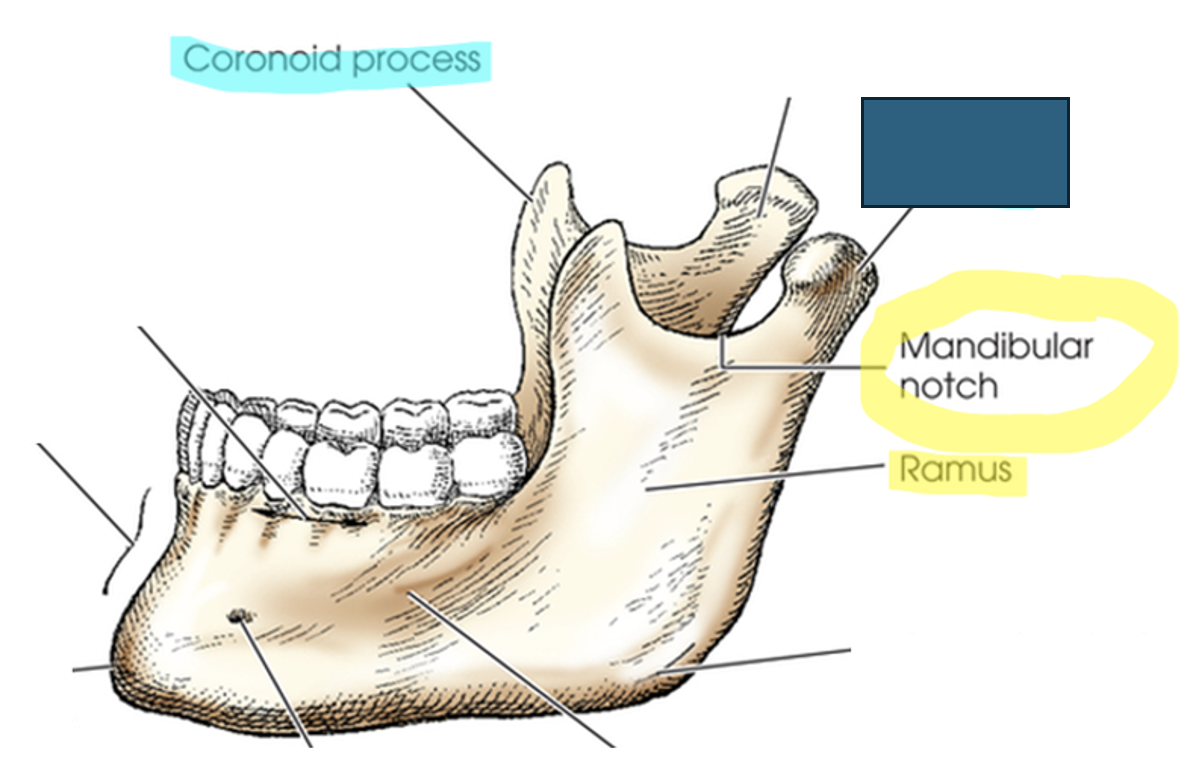
what anatomy is this?
condylar process
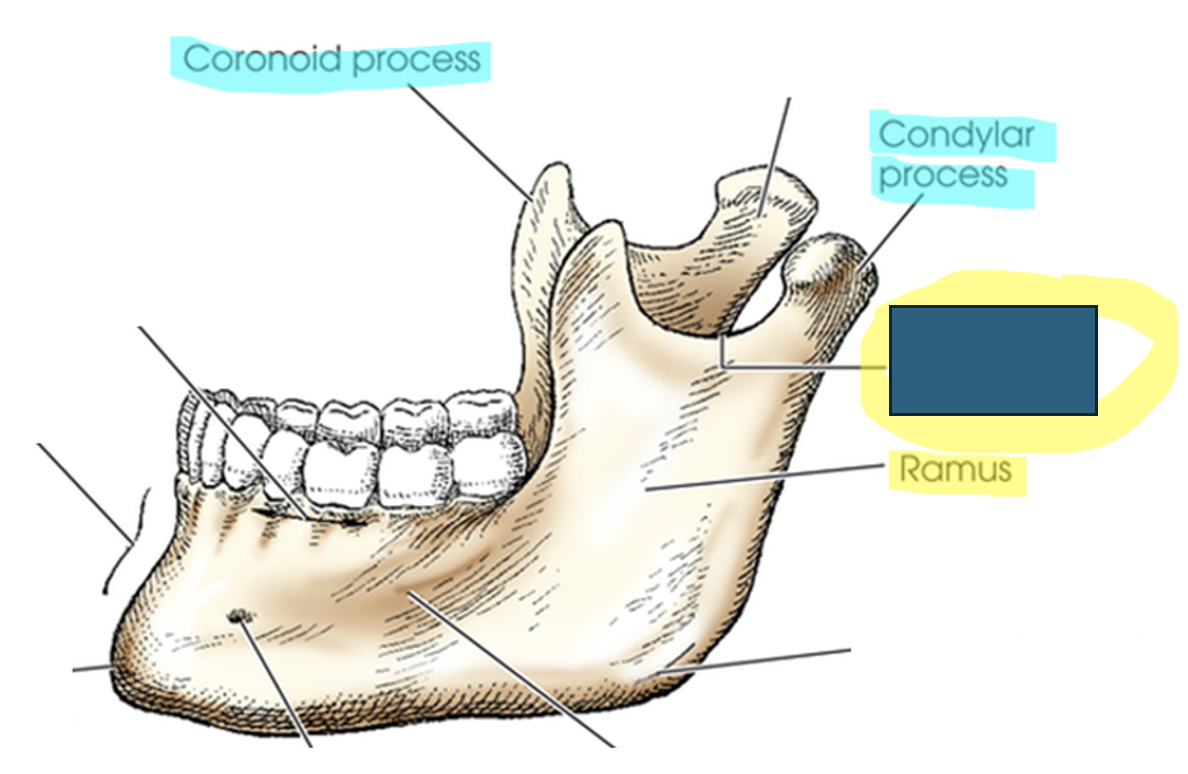
what anatomy is this?
mandibular notch
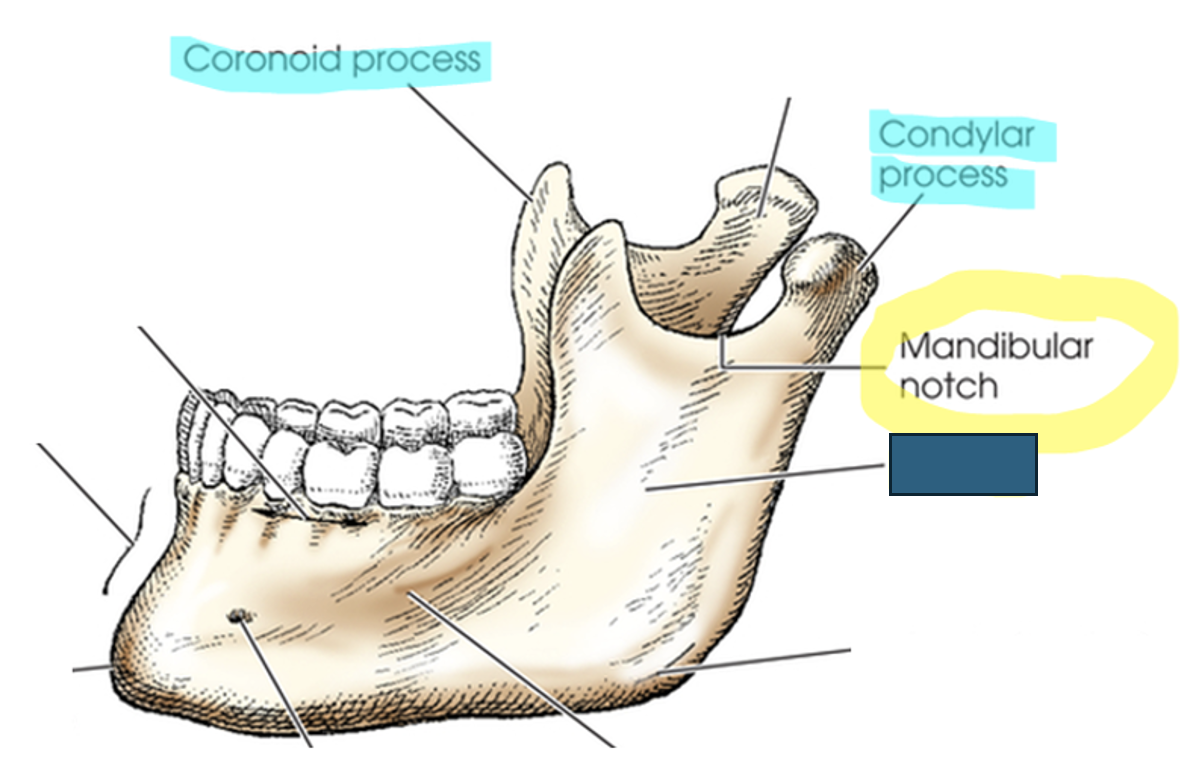
what anatomy is this?
ramus
coronoid process
anterior process on top of ramus; serves for muscle attachment– can’t be easily felt
condylar (condyloid) process
posterior process that forms TMJ, only movable skull joint.
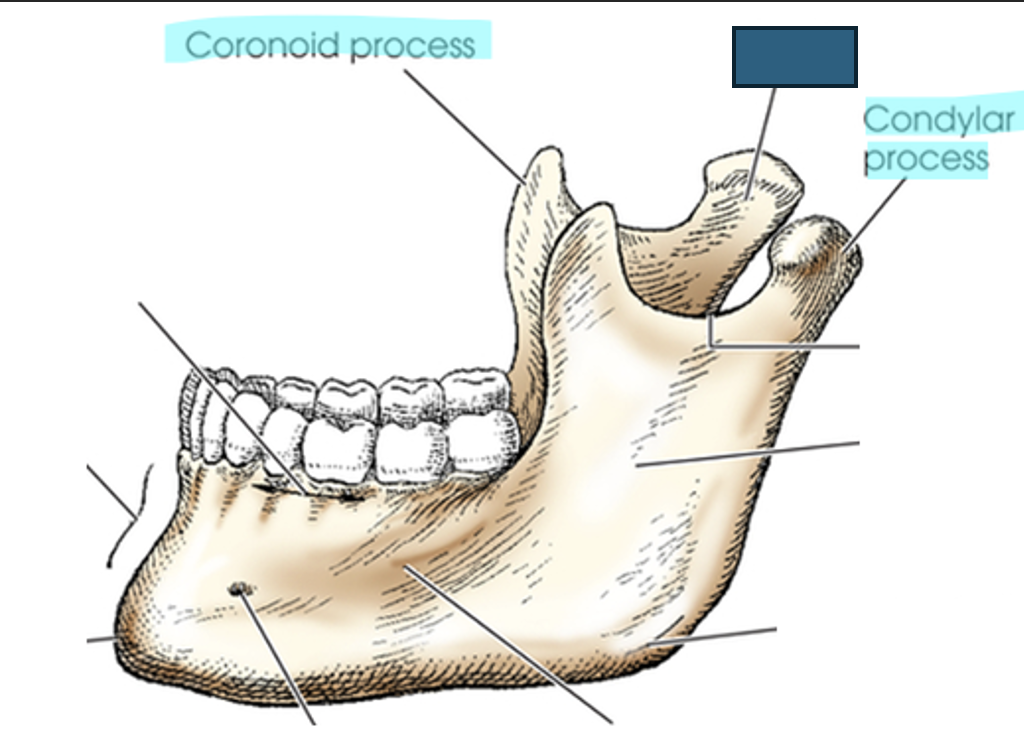
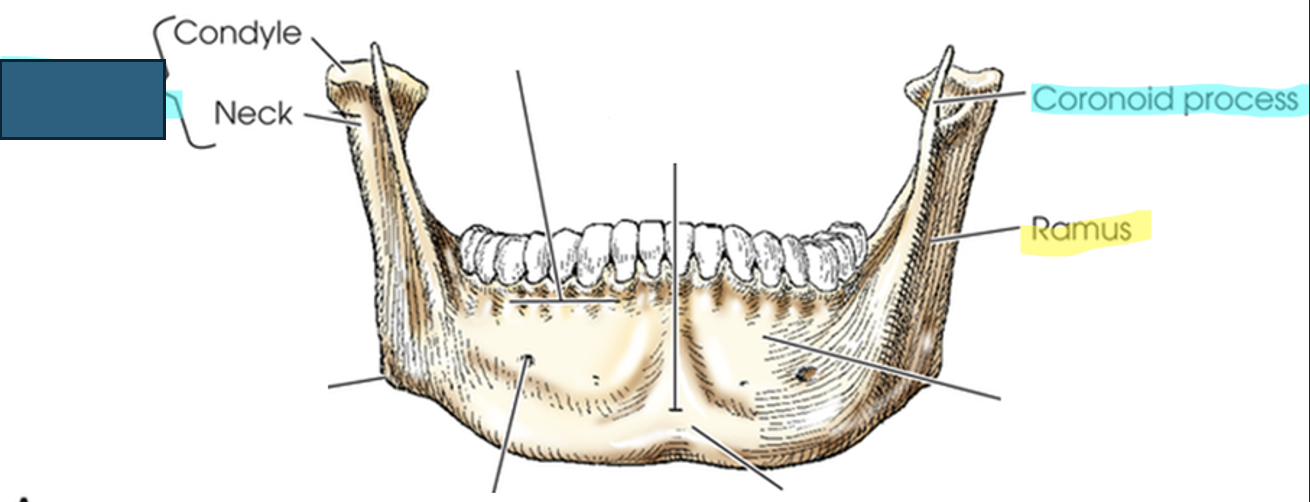
what anatomy is this?
neck
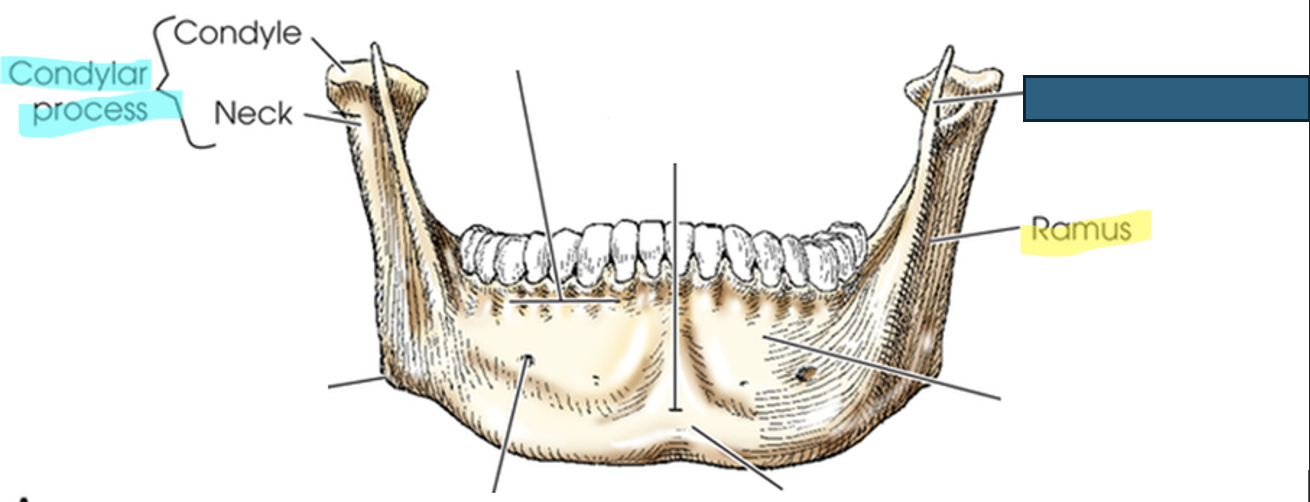
what anatomy is this?
coronoid process
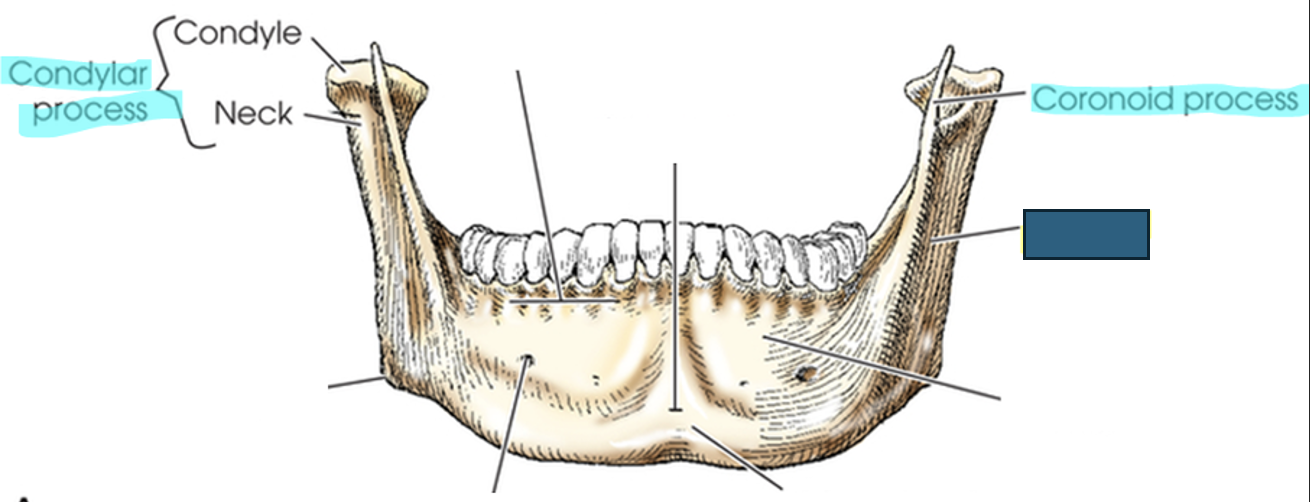
what anatomy is this?
ramus
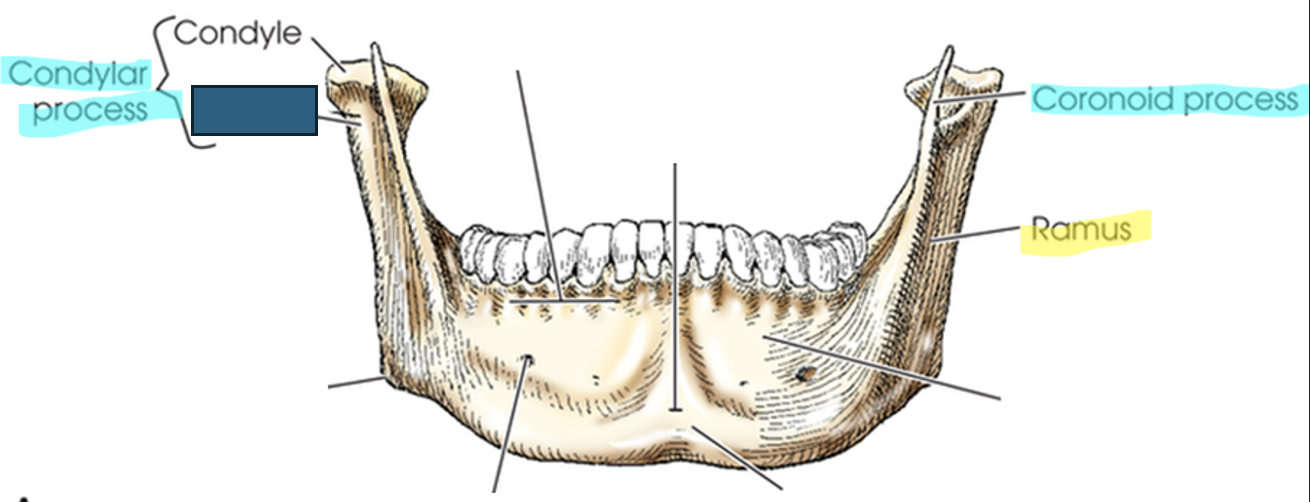
what anatomy is this?
neck
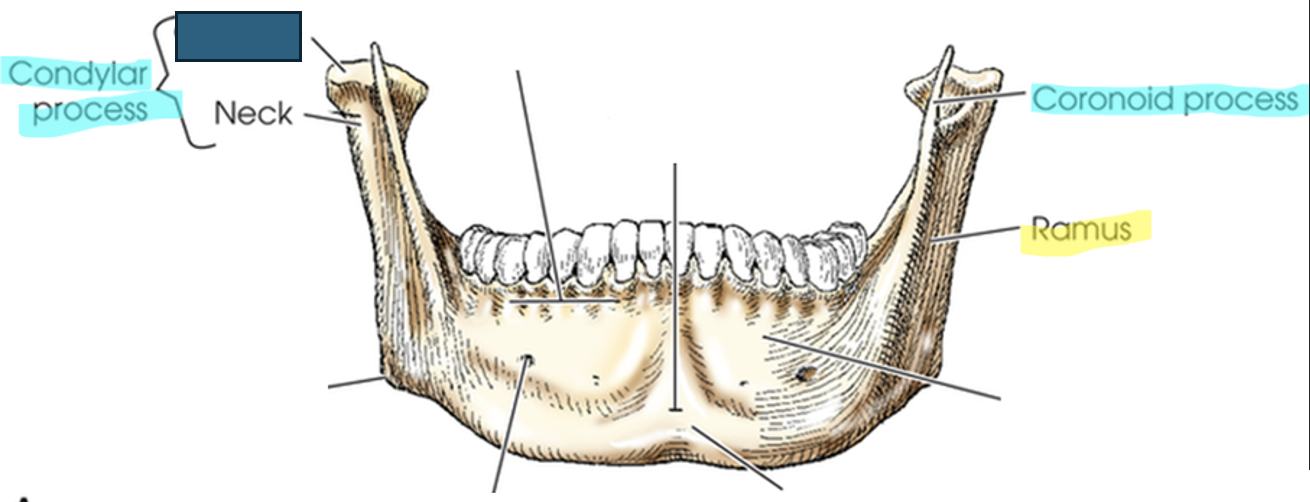
what anatomy is this?
condyle
what anatomy is this?
condylar process
angle of mandible (gonion)
where body and ramus meet
symphysis
most anterior and central part where left and right halves of mandible fuse
alveolar portion (process)
superior border of body; consists of spongy bone that supports roots of teeth
mental foramina
small openings on each side; transmit nerves and blood vessels (for lower teeth)
mental protuberance
anterior, triangular prominence
essential projections (mandible)
PA (for rami and body)
PA axial (for rami and body)
Axiolateral oblique
AP axial (towne)
PA (modified waters)
Submentovertex (SMV)
PA axial mandibular rami central ray
20 to 25 degrees cephalad to exit acanthion
what projection is this?
PA mandibular rami - closed mouth
what projection is this?
PA axial mandibular rami - open mouth
structures shown for PA/PA axial mandibular rami
mandibular body and rami
central part of body not well shown due to superimposed spine
shows medial or lateral displacement of fragments in fractures of the rami
PA Axial evaluation criteria
condylar processes of rami visible
PA Axial mandibular body central ray
30-degree cephalic angle midway between TMJs
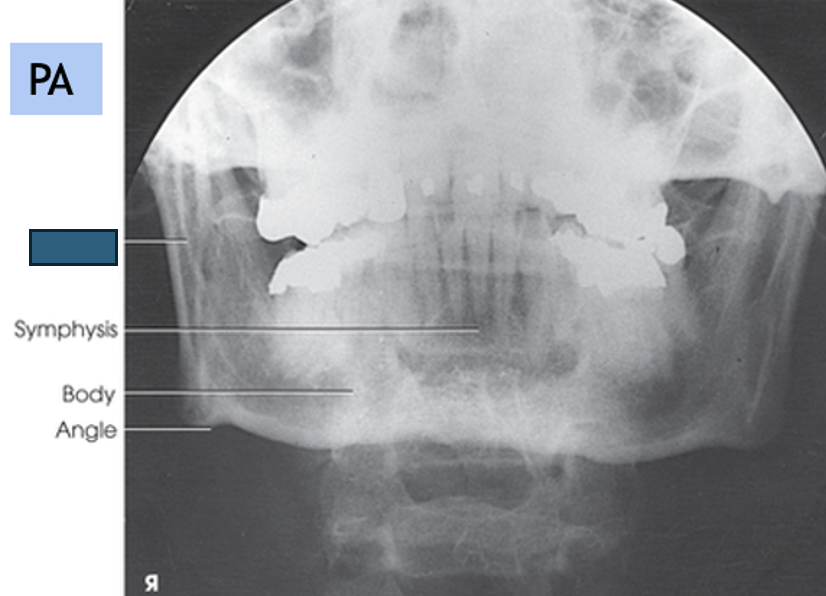
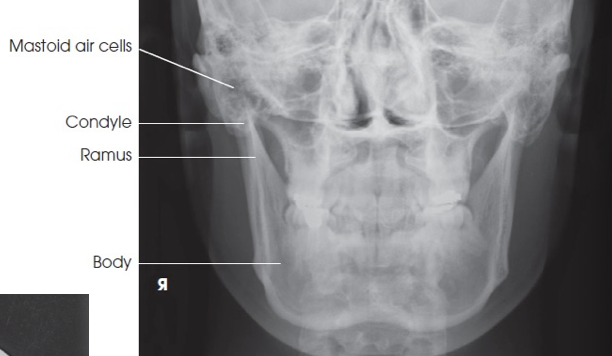
what anatomy is this?
ramus
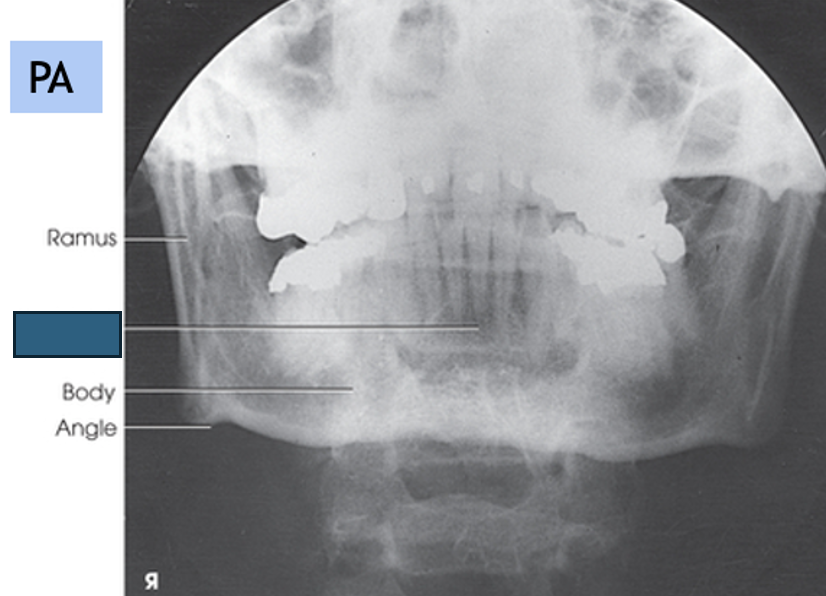
what anatomy is this?
symphysis
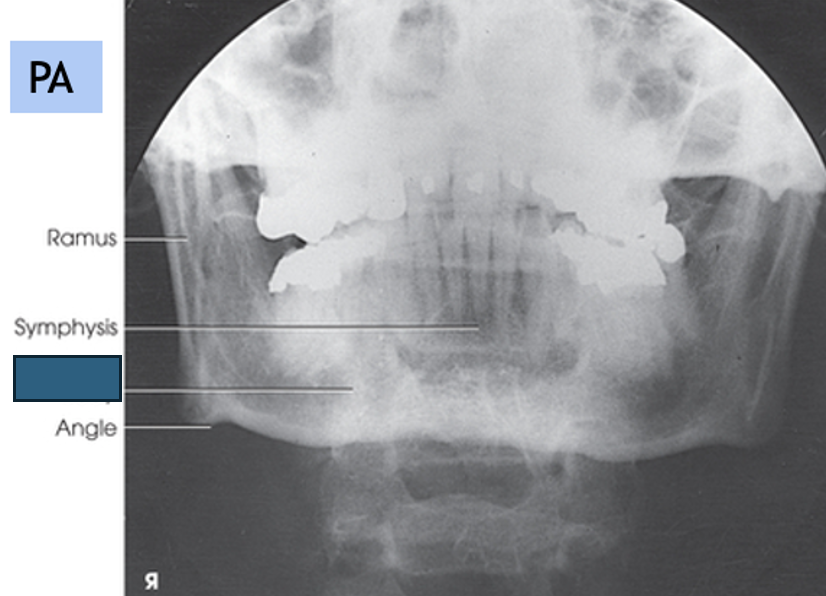
what anatomy is this?
body
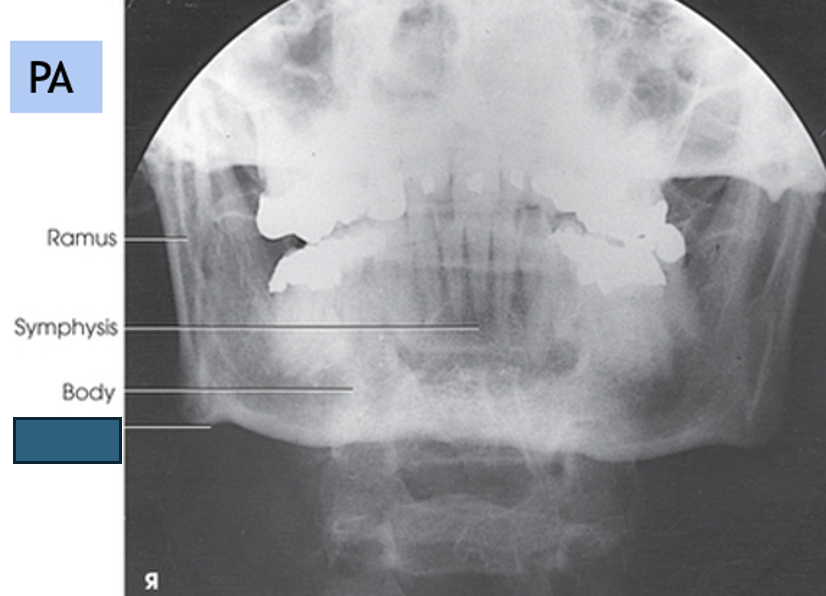
what anatomy is this?
angle
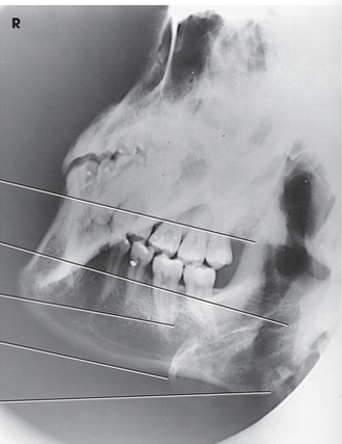
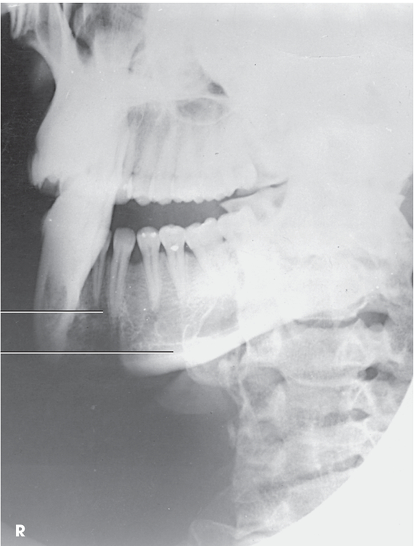
how much should you rotate the head to see the ramus in an axiolateral oblique mandible?
true lateral - 90 degrees
how much should you rotate the head to see the body in an axiolateral oblique mandible?
30 degrees toward the IR
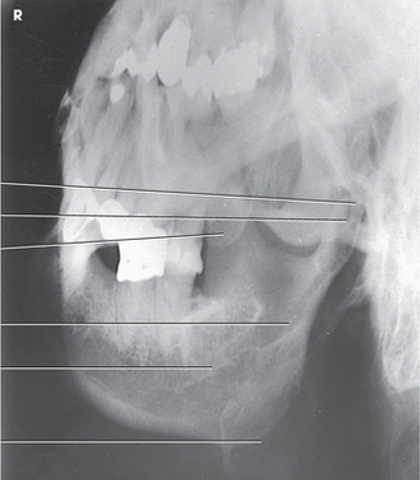
how much should you rotate the head to see the symphysis (mentum) in an axiolateral oblique mandible?
45 degrees toward IR
central ray for axiolateral oblique mandible
angled 25° cephalad (FOR ALL) to pass directly through the mandibular region of interest
evaluation criteria for axiolateral oblique mandible
no overlap of the ramus by opposite side of mandible
no elongation or foreshortening of ramus or body
no superimposition of the ramus by the cervical spine
what projection is this?
axiolateral oblique (body)
what projection is this?
axiolateral oblique (ramus)
what projection is this?
axiolateral oblique (symphysis)
central ray for AP axial (towne) mandible
35-40 degrees caudal
centered to glabella to pass through each rami
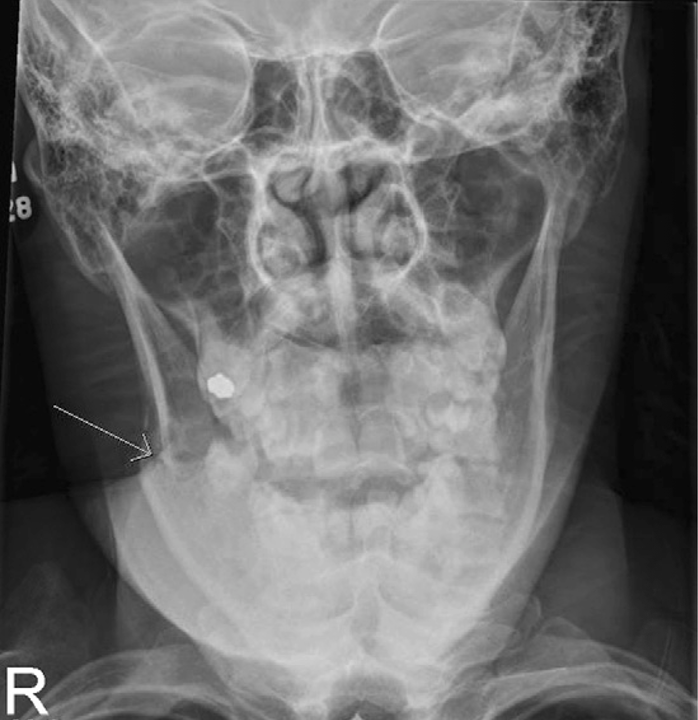
what projection is this?
AP Axial (towne) mandible
PA (modified waters) baseline
OML 55 degree angle with the IR
where are the petrous ridges in a PA (modified waters)
just below the inferior border of the orbits at a level midway through the maxillary sinuses
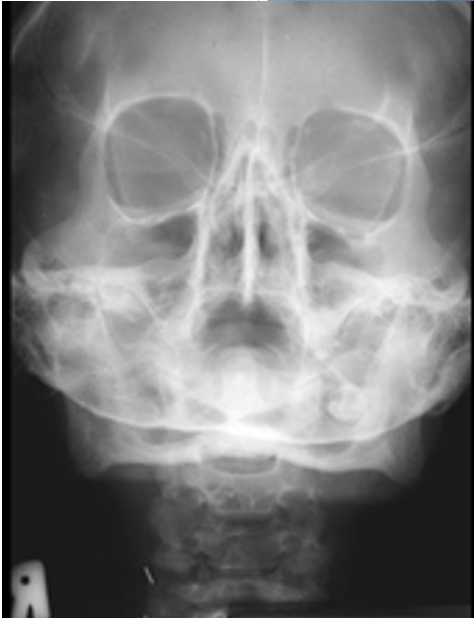
what projection is this?
PA (modified waters)
central ray for submentovertex (SMV) mandible
centered midway between mandibular angles
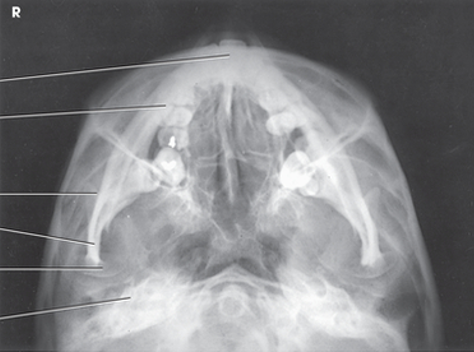
what projection is this?
submentovertex (SMV) mandible
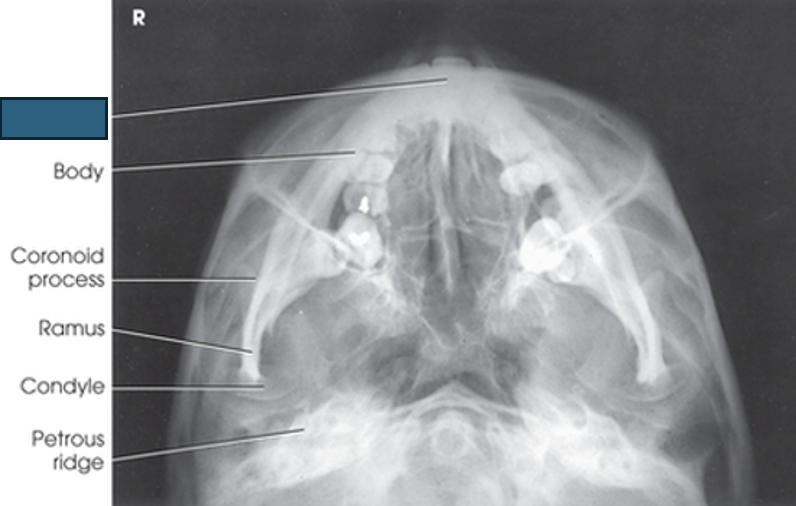
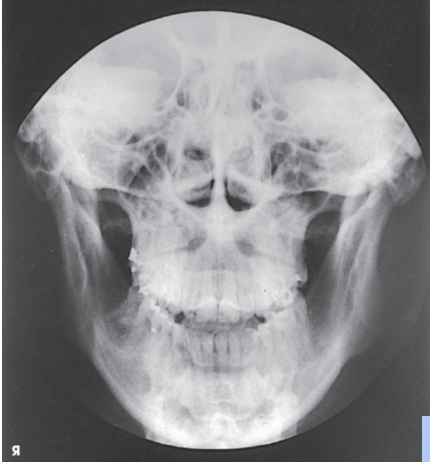
what anatomy is this?
symphysis
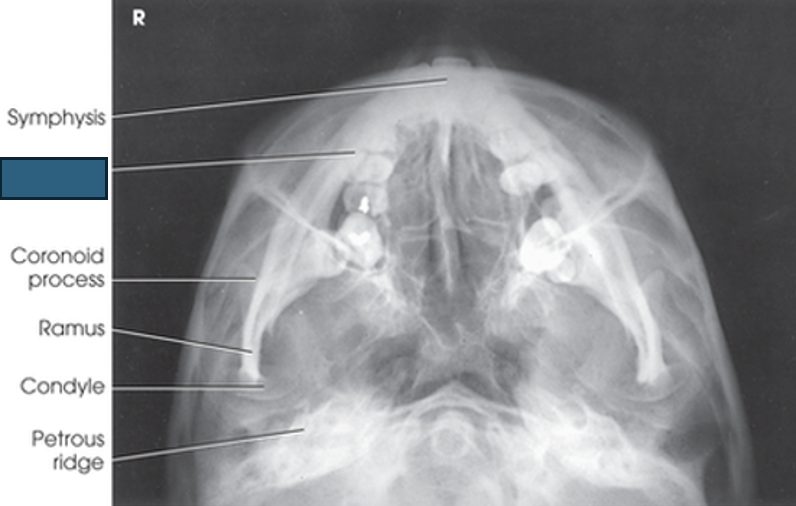
what anatomy is this?
body
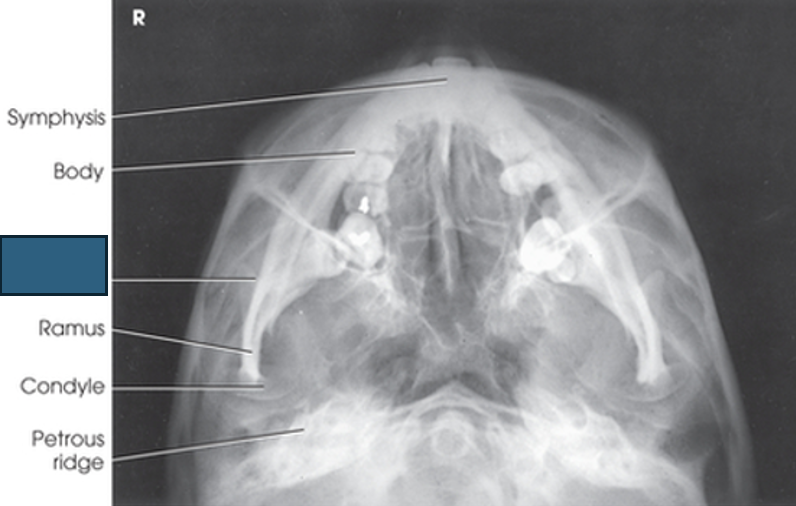
what anatomy is this?
coronoid process
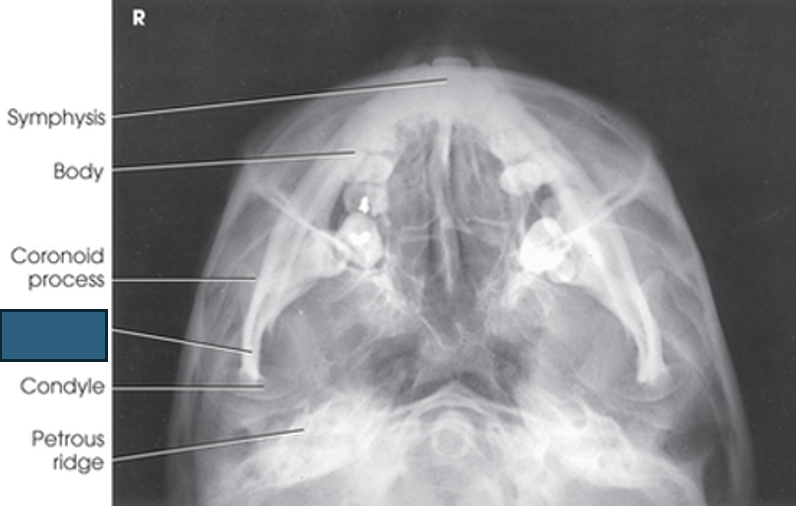
what anatomy is this?
ramus
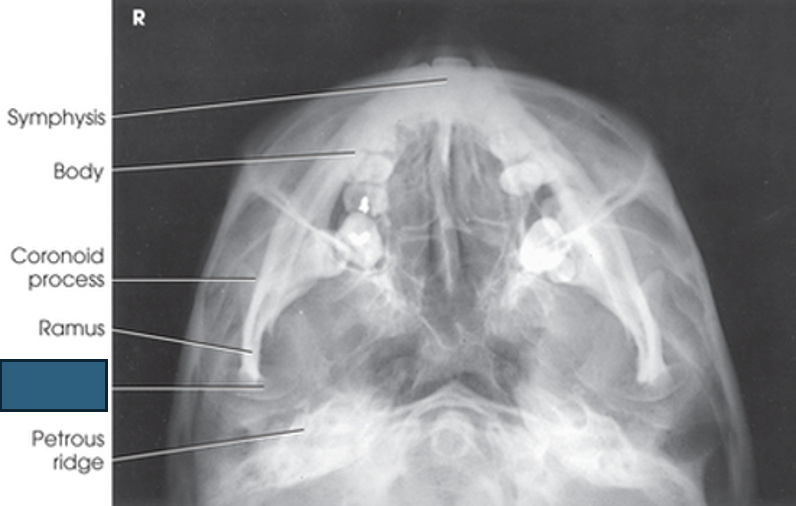
what anatomy is this?
condyle
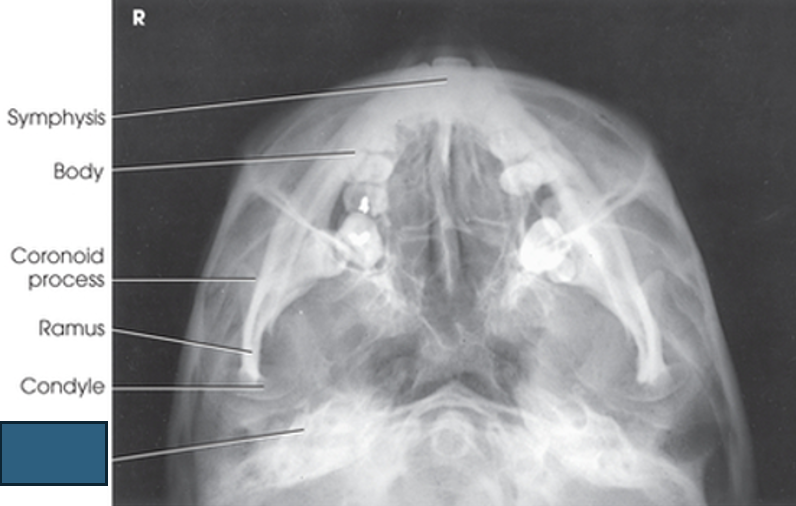
what anatomy is this?
petrous ridge
essential projections for temporomandibular Joints (TMJs)
axiolateral (modified Shuller)
axiolateral oblique (modified Law)
AP axial (Modified Towne)
what type of joint is the TMJ?
SYNOVIAL, hinge type joint
mandibular fossa
on temporal bone; articulates with condyloid process of mandible
articular tubercle
bony prominence on temporal bone, directly anterior to mandibular fossa
central ray for axiolateral TMJs
angle 25-30 degrees caudad
enters about ½” anterior and 2” superior to EAM FURTHEST from IR
evaluation criteria for axiolateral TMJs
condyle in mandibular fossa (closed-mouth)
condyle inferior to the articular tubercle (open-mouth)
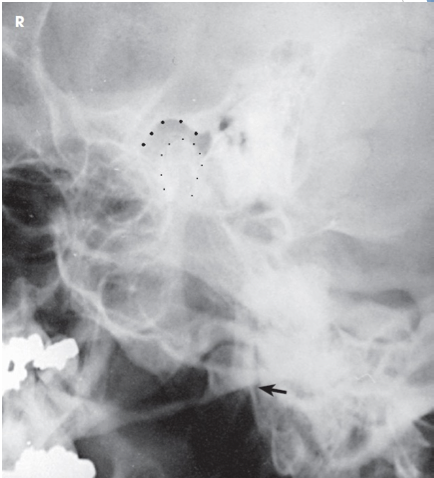
what projection is this?
closed mouth axiolateral TMJs
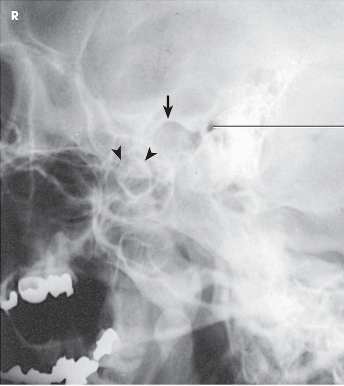
what projection is this?
open mouth axiolateral TMJs
AP axial TMJ baseline
OML perpendicular to IR plane
central ray for AP axial TMJs
angled 35 degrees caudad
centered midway between TMJs, entering a point 3” above nasion
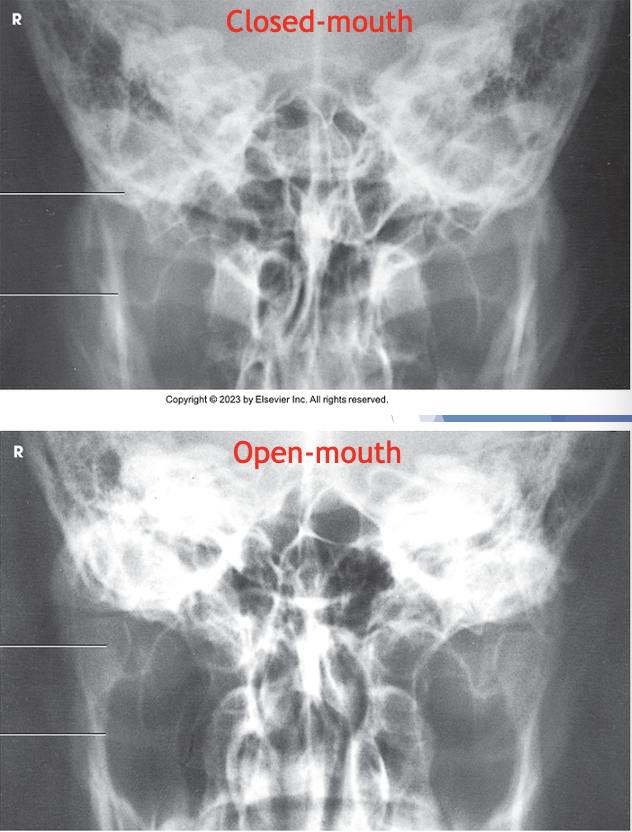
what projection is this?
open and closed mouth AP axial TMJs
central ray for axiolateral oblique TMJs (modified law)
angled 15° caudad
exits through TMJ closest to IR
enters approximately 1½ inch superior to upside EAM
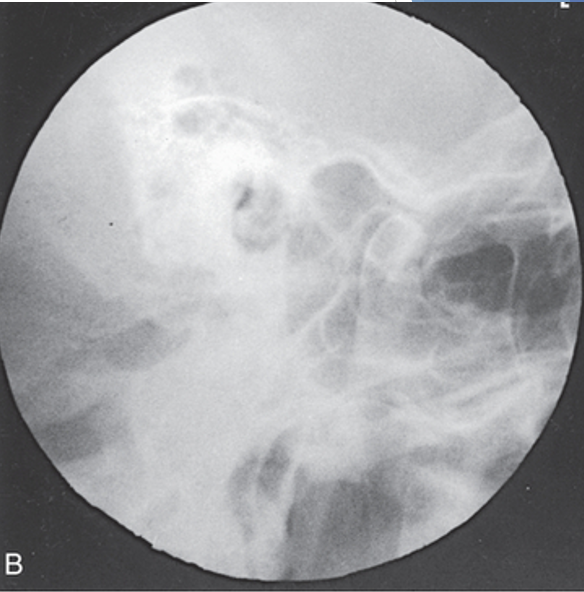
what projection is this?
axiolateral oblique TMJs (modified law)
structures shown for axiolateral oblique TMJs (modified law) open and closed mouth
Open-mouth – mandibular fossa and inferior and anterior portion of the condyle
Closed-mouth – fractures of the neck and condyle of the ramus