Population Growth and Life History Traits
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What is the precautionary principle proposed by Rachel Carson?
It suggests that we should 'look before you leap' and consider potential consequences before taking action.
What are the six ecologically productive areas used to calculate ecological footprints?
1. Land suitable for crops 2. Pasture 3. Forest 4. Ocean 5. Built-up land 6. Fossil energy land.
What does the ecological footprint measure?
It measures how fast we consume resources and generate waste compared to how fast nature can absorb our waste and generate resources.
What is the predicted range of the human population by the year 2050?
Predictions range from 7.3 to 10.7 billion people.
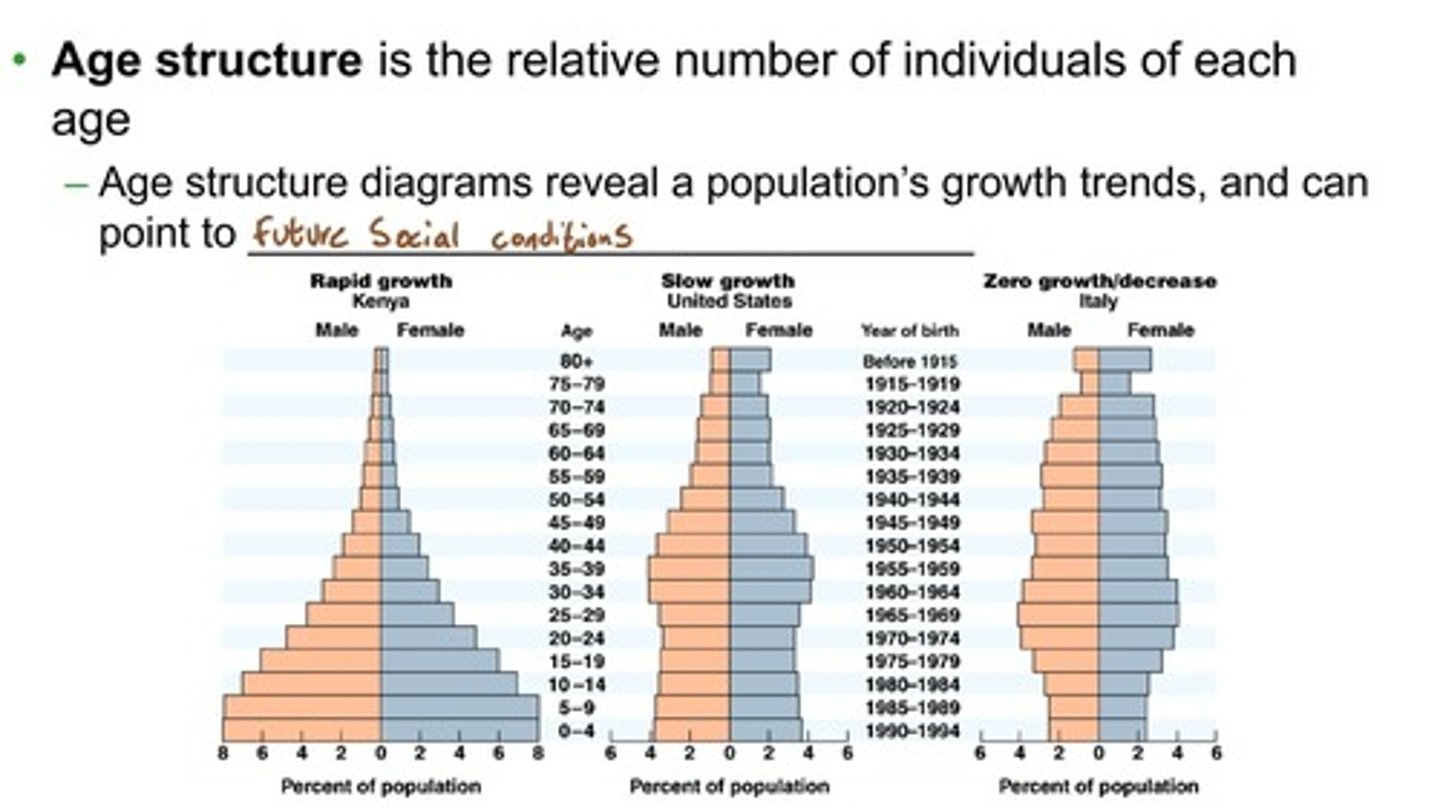
What is the significance of age structure in population studies?
Age structure reveals a population's growth trends and can indicate future social conditions.
What does the Demographic Transition Model suggest about human populations?
It suggests that a regional human population can exist in one of two configurations: high birth and death rates or low birth and death rates.
What are the stages of the Demographic Transition Model?
1. Stage 1: High birth & death rates 2. Stage 2: High birth rates, decreasing death rates 3. Stage 3: Decline in birth rates 4. Stage 4: Low and stable birth & death rates.
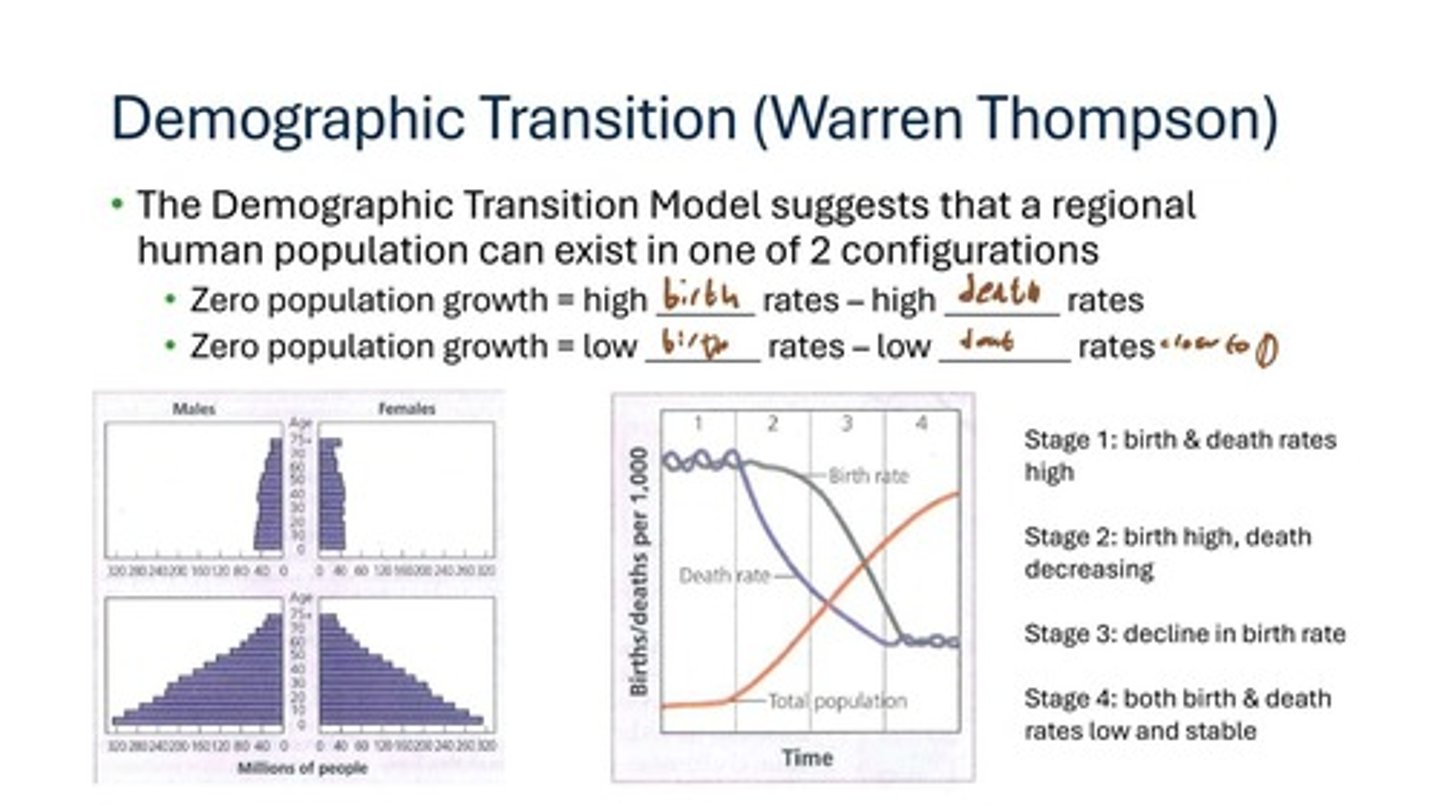
What might cause the human population to cease growing rapidly?
Factors could include resource limitations, changes in social conditions, or shifts in birth and death rates.
What is Earth's carrying capacity for humans?
There is a wide range of estimates, often based on food availability and agricultural limits.
What is an ecological footprint in terms of land area?
It is the aggregate land area required for various categories of resource consumption and waste generation.
How does the ecological footprint vary among different countries?
Countries have different ecological footprints based on their consumption patterns and available ecological capacity.
What does a population pyramid indicate about a population?
It shows the distribution of various age groups, which can indicate growth trends and potential future demographics.
What is the relationship between ecological footprints and sustainability?
A larger ecological footprint indicates greater resource consumption and waste generation, which can threaten sustainability.
What is the implication of a zero population growth scenario?
It indicates a balance where birth rates equal death rates, leading to a stable population size.
What factors can influence the ecological capacity of a region?
Factors include resource availability, land use practices, and environmental policies.
What is the role of agriculture in determining Earth's carrying capacity?
Agriculture limits assumptions on available food amounts, affecting estimates of carrying capacity.
How does the concept of multiple constraints relate to ecological footprints?
It acknowledges that humans face various limitations beyond just food, such as water and energy resources.
What does the term 'built-up land' refer to in ecological calculations?
It refers to land that has been developed for urban or industrial use, impacting ecological footprints.
What are the implications of high ecological footprints for a country?
High ecological footprints suggest unsustainable resource use and potential environmental degradation.
How can the ecological footprint inform policy decisions?
It can guide resource management and sustainability efforts by highlighting areas of excessive consumption.
What does the term 'fossil energy land' mean in the context of ecological footprints?
It refers to the land area required to produce fossil fuels consumed by a population.
What significant event in human history occurred around 1650 that affected population size?
The Plague, which took 34 million lives.
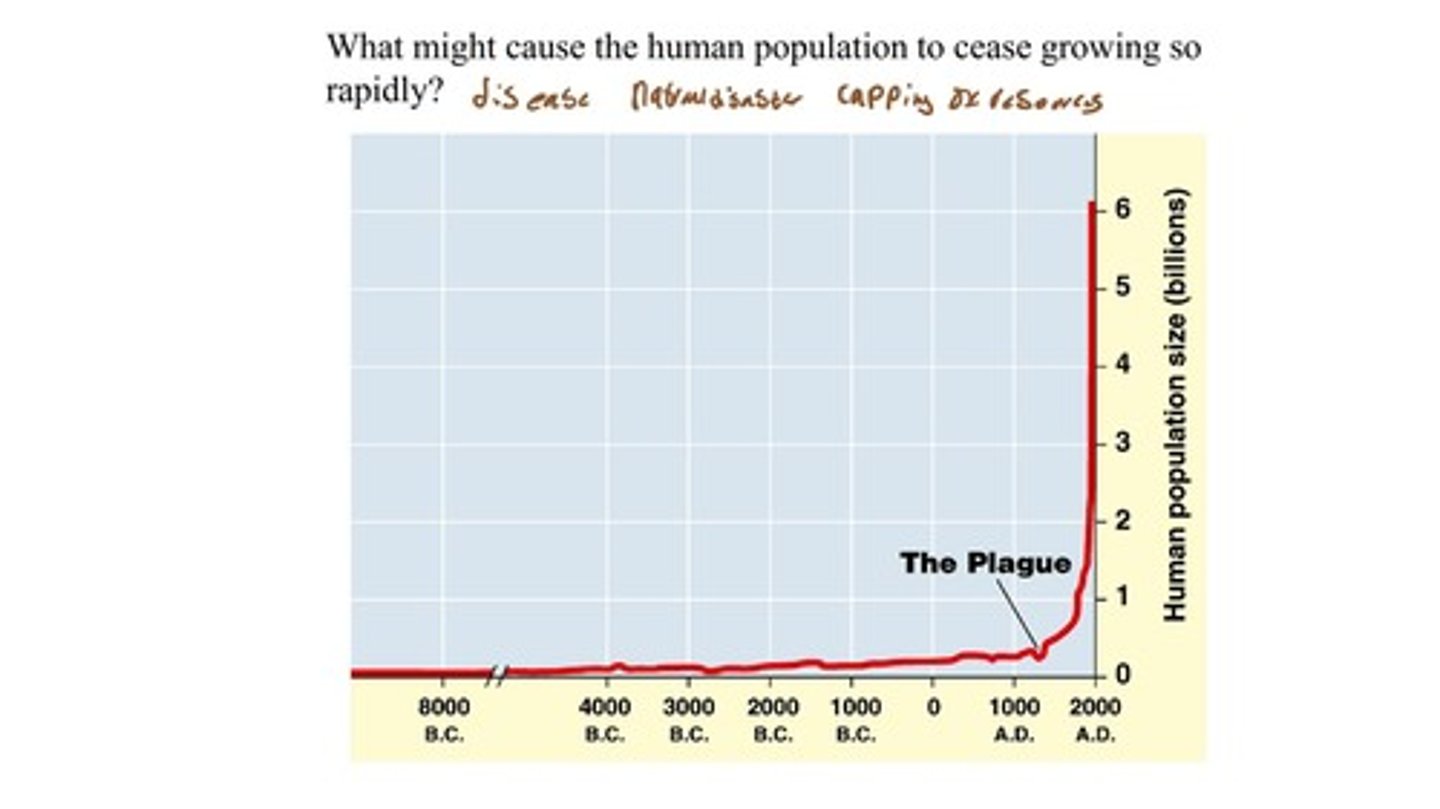
How has the human population changed since the Plague?
The human population has increased rapidly after the Plague.
What is the trend of human population growth over the last three centuries?
The human population has been growing exponentially.
What is the trade-off between seed number and seed size?
There is a trade-off where increasing seed number may decrease seed size.
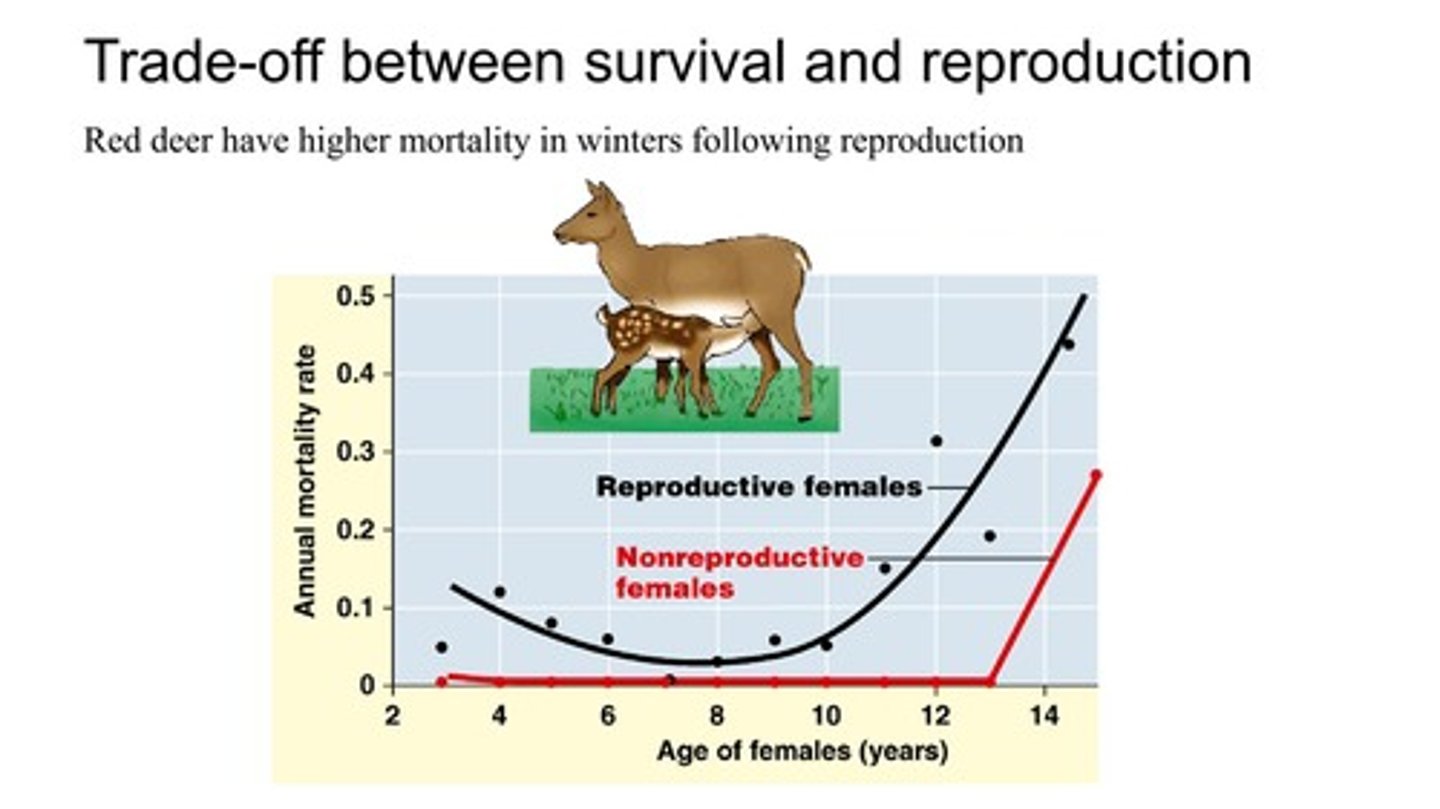
What is the trade-off between survival and reproduction observed in red deer?
Red deer have higher mortality in winters following reproduction.
What are the two reproductive strategies discussed in the notes?
Semelparity and iteroparity.
What is semelparity?
A reproductive strategy where organisms reproduce once and produce a large number of offspring, after which they die.

What is iteroparity?
A reproductive strategy where organisms reproduce multiple times, producing fewer offspring per episode.
What factors influence the evolution of semelparity vs. iteroparity?
Factors include acquisition of energy by the parent and survival of the offspring.
In what type of environments is semelparity selected?
Unpredictable environments.
In what type of environments is iteroparity selected?
Stable or predictable environments.
What is an example of a semelparous organism mentioned in the notes?
The agave plant.
What is the significance of life history traits?
They are products of natural selection that influence reproductive strategies.
What is the mortality rate of reproductive females in the age graph provided?
The annual mortality rate is shown to be between 0.1 and 0.5 depending on age.
What are K-selected organisms characterized by?
K-selected organisms are density-dependent, sensitive to population density, and live and reproduce around the carrying capacity (K).
What are r-selected organisms characterized by?
r-selected organisms are density-independent, exhibit high rates of reproduction, and thrive in variable environments with population densities fluctuating well below K.
What does the logistic growth model account for?
The logistic growth model accounts for the carrying capacity (K) of an environment, showing how population growth slows as it approaches K.
What is the relationship between population density and life history traits?
Population density and environment affect life history traits through natural selection.
What does an organism's life history encompass?
An organism's life history is the product of evolved traits that affect reproduction and survival.
What is the trade-off faced by organisms regarding resources?
Limited resources mandate trade-offs between investments in reproduction and survival.
What is an example of a population that exhibits regular boom-bust cycles?
The lynx and snowshoe hare populations cycle on a ten-year basis.
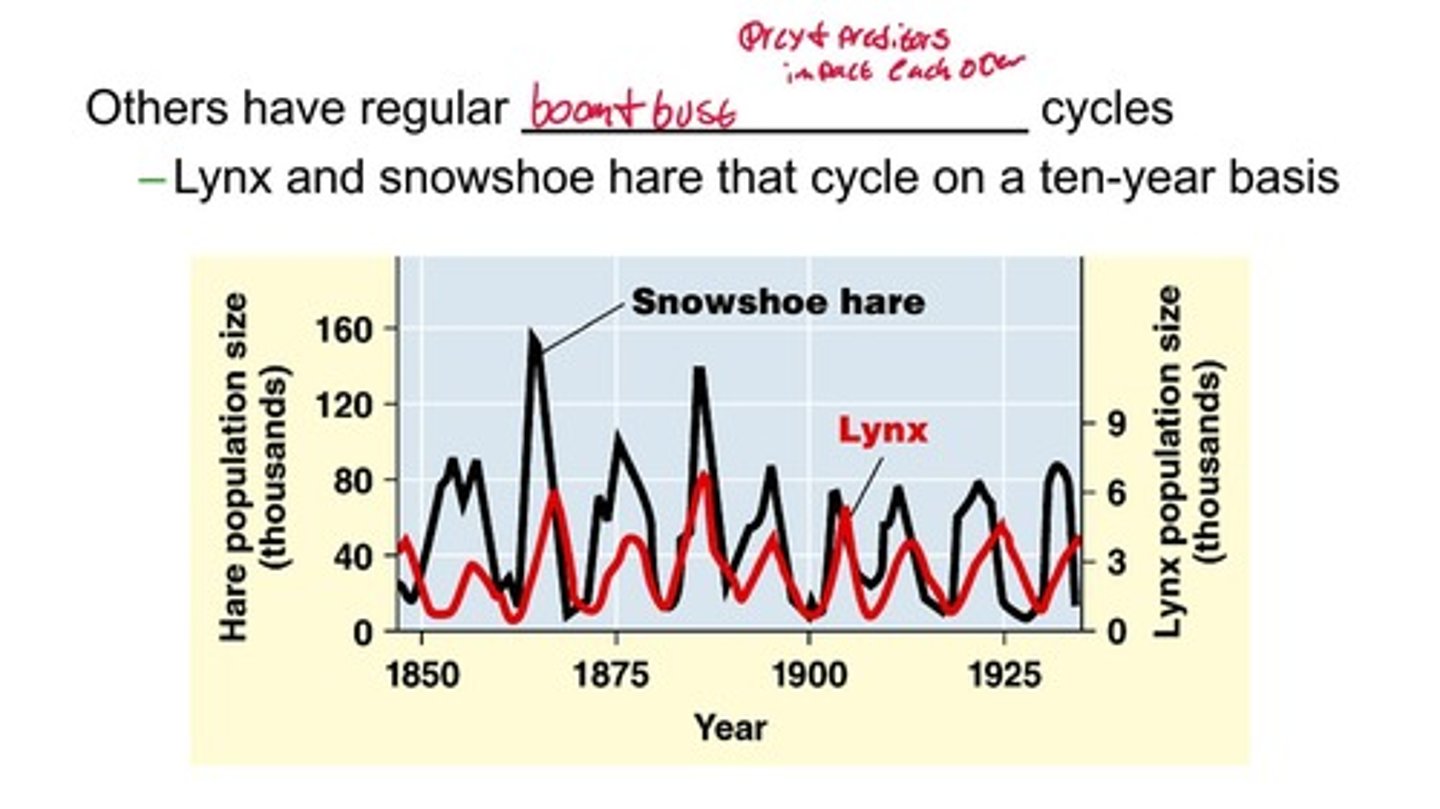
What factors can cause populations to fluctuate erratically?
Populations can fluctuate due to various biotic and abiotic influences.
What is carrying capacity (K)?
Carrying capacity (K) is the maximum population size that an environment can sustain.
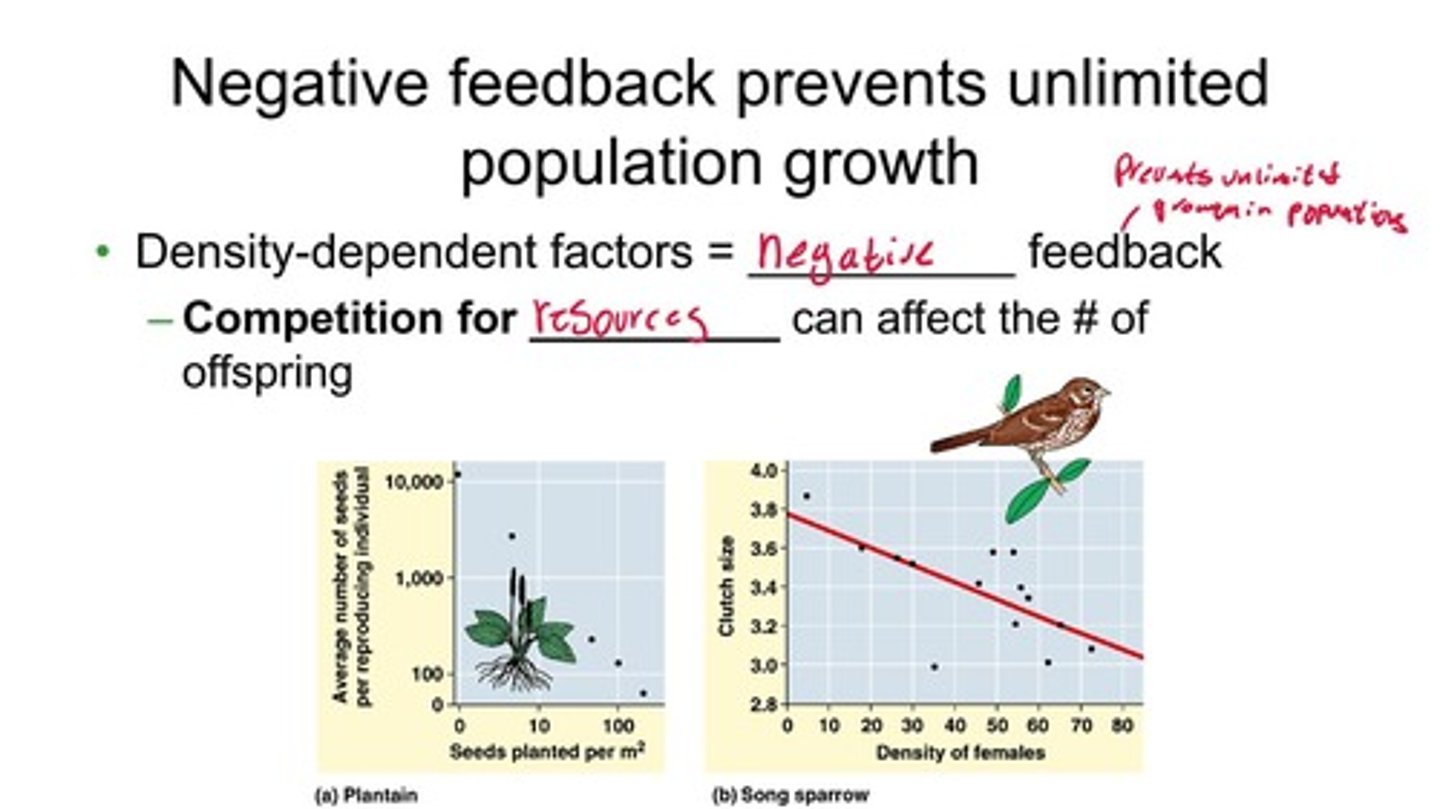
What are density-dependent factors?
Density-dependent factors are negative feedback mechanisms, such as competition for resources, that can affect the number of offspring.
What is demographic stochasticity?
Demographic stochasticity refers to random variations in population dynamics that can affect population growth.
What are density-independent factors?
Density-independent factors, such as natural disasters, limit population size without being influenced by the population density.
What are examples of density-independent factors?
Examples include fire, flood, drought, and severe weather events.
Why might the logistic model not fit all populations?
The logistic model does not fit all populations because actual population dynamics can be influenced by various factors not accounted for in the model.
What is the significance of year-to-year data in population analysis?
Year-to-year data helps in analyzing population change and understanding fluctuations.
What is the impact of negative feedback on population growth?
Negative feedback prevents unlimited population growth by regulating the number of offspring based on resource availability.
What is environmental stochasticity?
Environmental stochasticity refers to unpredictable environmental changes that can impact population sizes.
What does the term 'natural selection' imply in the context of life histories?
Natural selection implies that certain life history traits are favored based on their effectiveness in reproduction and survival in specific environments.
What role does competition play in population dynamics?
Competition for resources can limit population growth and affect the number of offspring produced.
How does population density influence environmental resistance?
As population density increases, the intensity of environmental resistance also increases, affecting growth rates.
What does the term 'carrying capacity' indicate about a population?
Carrying capacity indicates the maximum sustainable population size that an environment can support without degrading.
What is the relationship between predators and prey in population dynamics?
Predators and prey impact each other's populations, often leading to cyclical patterns in their sizes.
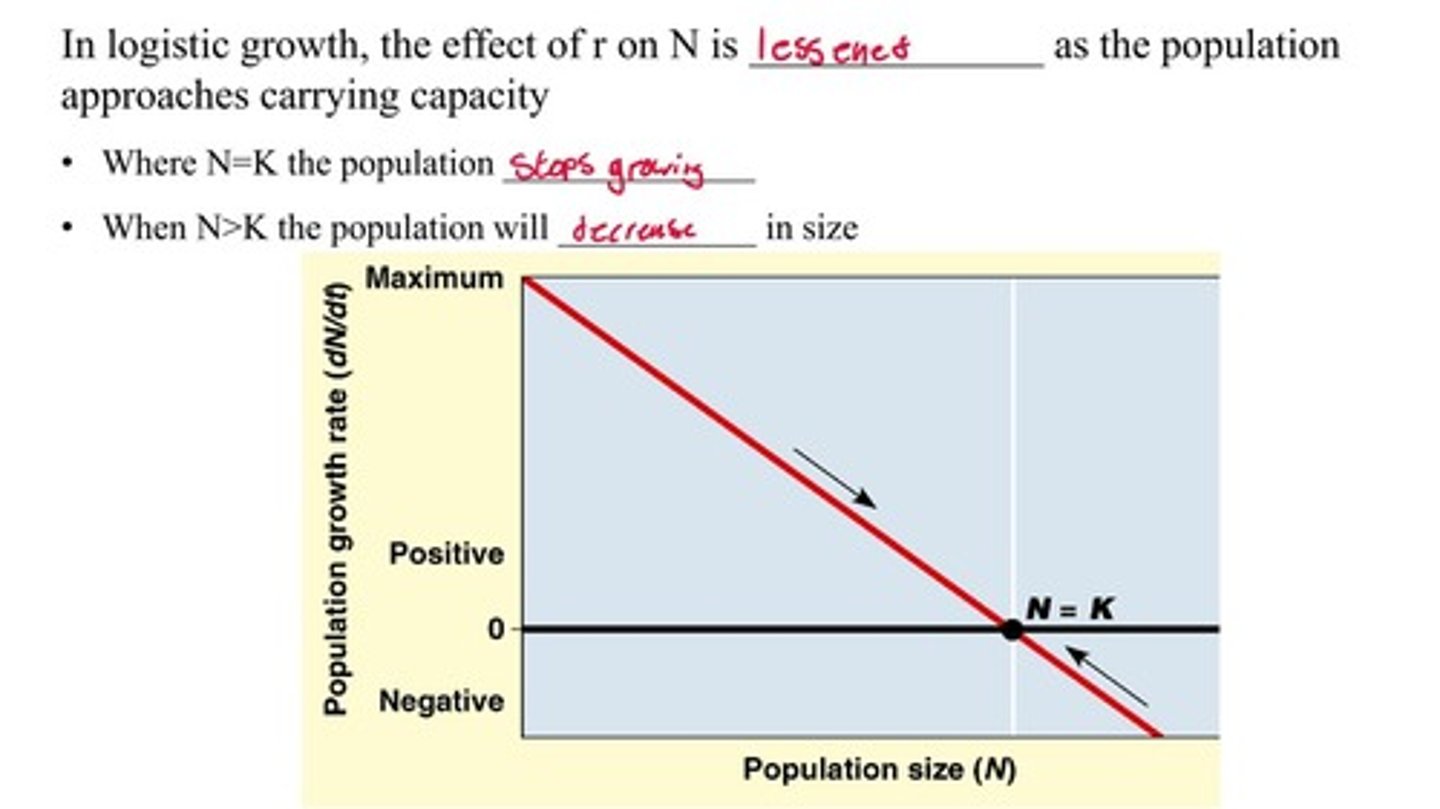
What is the shape of the curve representing logistic growth?
The resulting curve is S-shaped.
What happens to population growth when N equals K?
The population stops growing.
What occurs when N is greater than K?
The population will decrease.
What does K represent in population dynamics?
K represents the carrying capacity, which is the maximum sustainable population size an environment can support.
How does carrying capacity affect population growth?
Carrying capacity imposes constraints on population growth and slows the growth rate as the population size approaches K.
What is the equation for logistic growth?
dN/dt = rN (K-N/K) where N is the population size.
What is demographic stochasticity?
Variations in birth and death rates that affect population growth.
What is environmental stochasticity?
Variations in environmental conditions such as fire, flood, and drought that affect population growth.
What is the Allee effect?
A phenomenon where low population density prevents healthy males and females from finding one another, affecting reproduction.
What factors can lead to small populations being susceptible to extinction?
Genetic drift, inbreeding, reduced pollinator visitation in plants, and disrupted social structures in animals.
What does the equation dN/dt = 1.0N represent?
Exponential growth of a population.
What is the significance of carrying capacity (K) in population dynamics?
It indicates the maximum stable population size that an environment can support due to limited resources.
What happens to the growth rate as the population size approaches carrying capacity?
The growth rate slows down.
What is the relationship between births and deaths when a population stabilizes at K?
Births will equal deaths, resulting in r = 0.
What is stochasticity in the context of population dynamics?
Stochasticity refers to randomness that can affect birth and death rates.
What is the impact of climate variability on population dynamics?
Climate can introduce unpredictability, affecting population growth rates.
What is the maximum sustainable population size called?
Carrying capacity (K).
What can limit population growth indefinitely?
Populations cannot grow exponentially forever due to resource limitations and environmental constraints.
What is the effect of small population sizes on genetic diversity?
Small populations are more susceptible to genetic drift and inbreeding.
What are life history traits?
Characteristics that influence an organism's schedule of reproduction and survival.
What are the learning objectives mentioned in the notes?
Factors affecting population growth, life histories, and human population growth.