Biology – Semester 1
1/388
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
389 Terms
cell division
cell reproduction; two "daughter cells" are produced that are genetically identical to each other and to the "parent" cell; replaces damaged or lost cells, permits growth, and allows for reproduction
Chromosomes
tightly coiled strands of long DNA molecules in a cells nucleus that appear when the cell is ready to divide
Asexual Reproduction
single-celled organisms reproduce by dividing in half, and the offspring are genetic replicas of the parent (inherit all of their chromosomes from 1 parent); no fertilization of an egg by a sperm, uses Mitosis
Sexual Reproduction
requires fertilization of an egg by a sperm, use Miosis
Eukaryotic Chromosomes
# it has depends on species; located in the nucleus; made up of chromatin which is composed of DNA which coils around histone proteins to form nucleosomes which interact with one another to form coils and supercoils that make up chromosomes
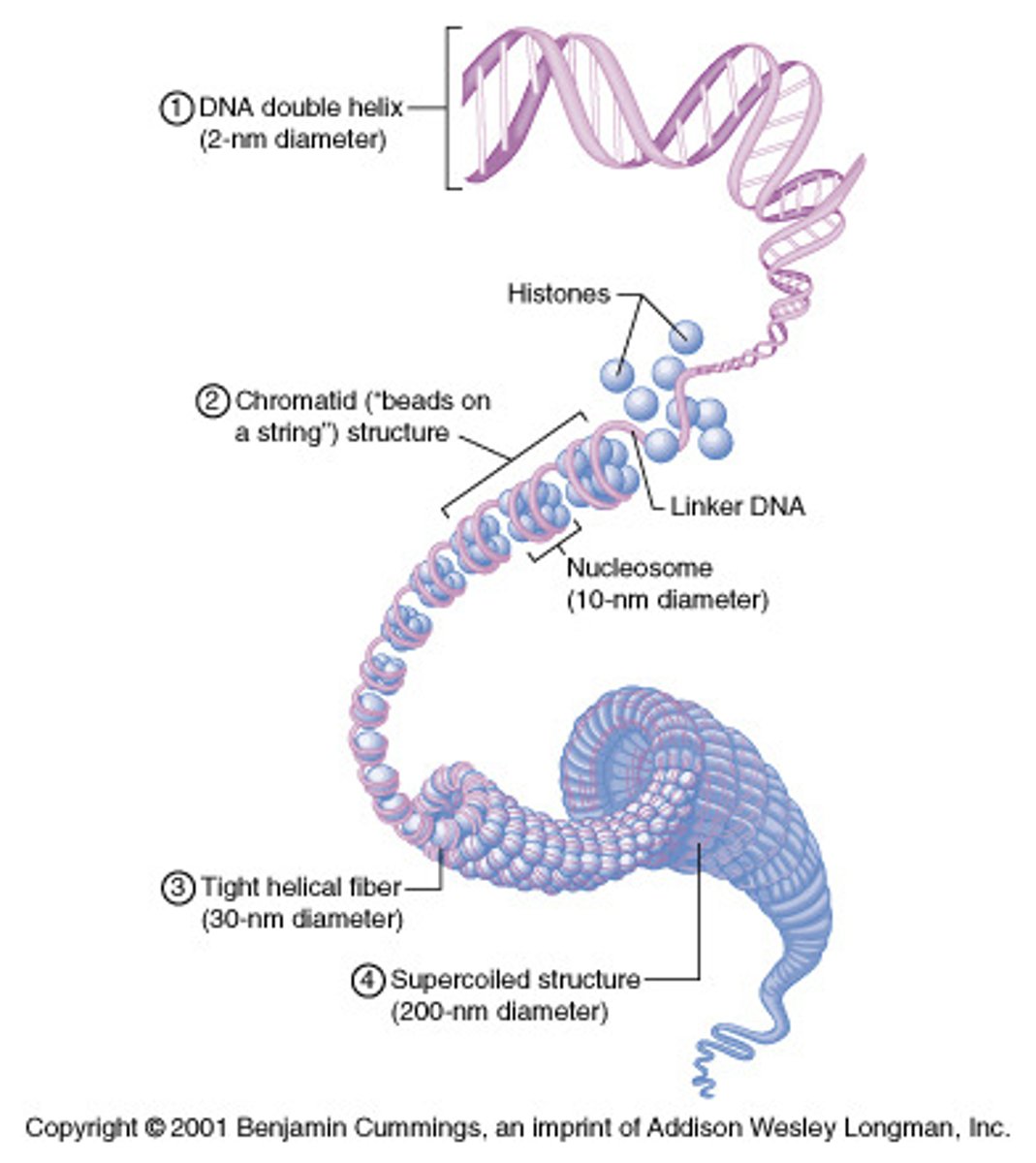
Sister Chromatids
two copies of a duplicated chromosome containing identical genes
Centromere
Where two sister chromatids are joined together tightly, a narrow "waist"
The Cell Cycle
The ordered sequence of events that extend from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent cell to its own division into two cells; Interphase (90%) & Mitotic phase (10%)
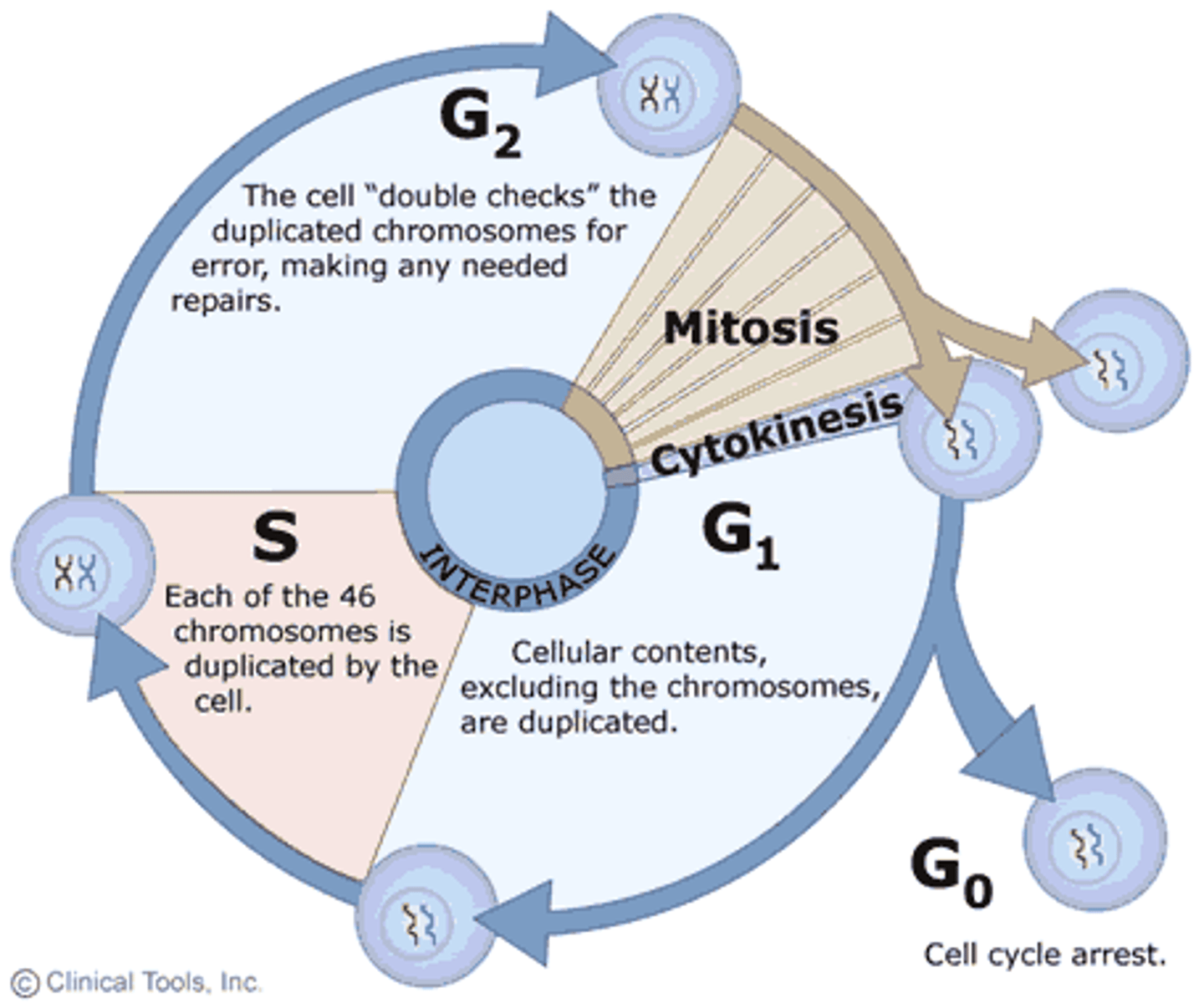
Interphase
90% of the cycle, cell performs normal functions, double everything, and grows in size, chromosome duplication ; G1=growth, S=sister chromosomes form, G2=cell organelles duplicate
Mitotic (M) phase
Part of the cell cycle were the cell is actually dividing; includes Mitosis and Cytokinesis= two genetically identical daughter cells
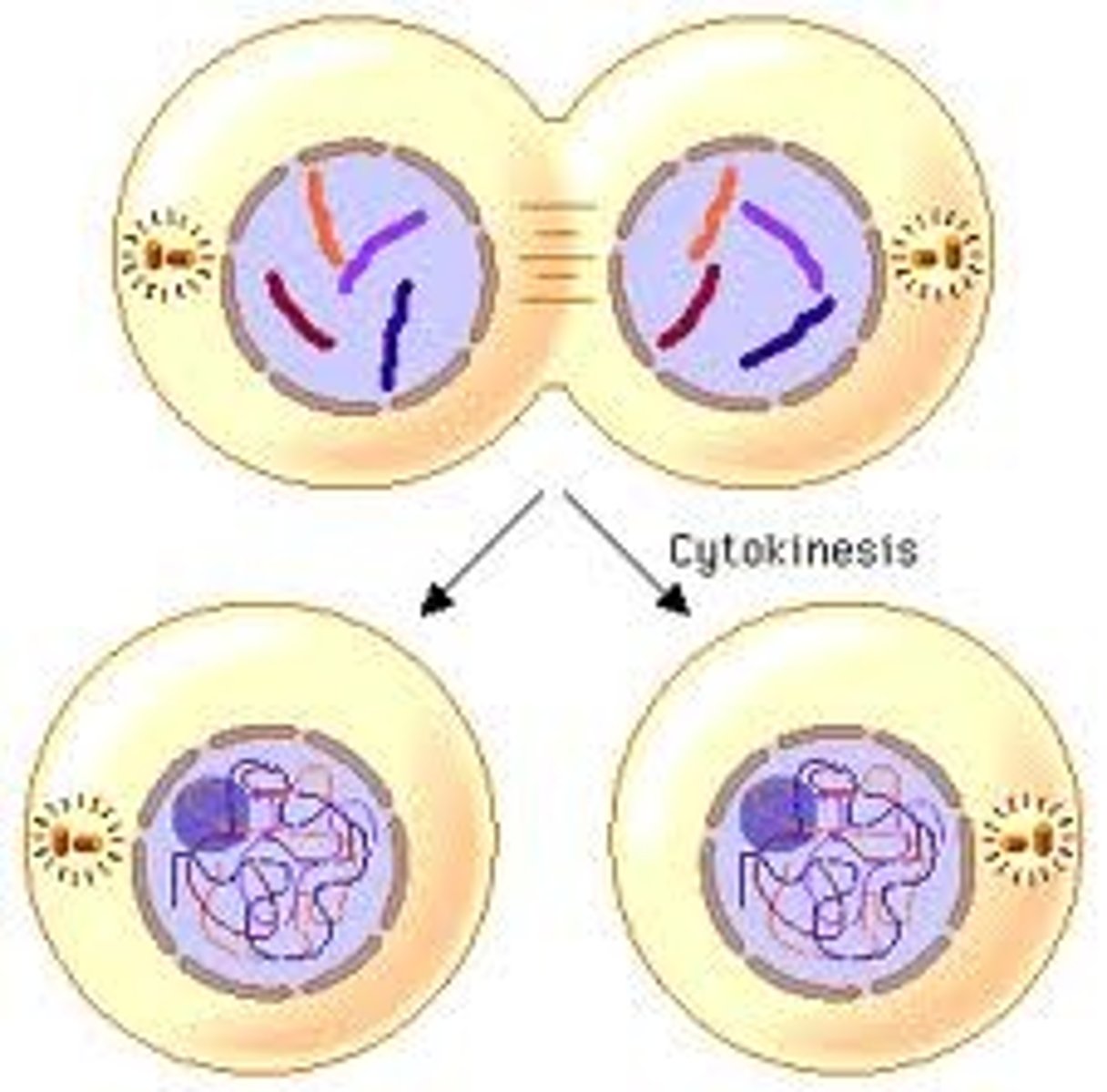
Mitosis
The nucleus and its contents, most importantly the duplicated chromosomes, divide and are events distributed, forming to daughter nuclei
Cytokinesis
The cytoplasm is divided into two
4 STAGES OF MITOSIS
1. Prophase: Nuclear membrane gone
2. Metaphase: Chromosomes line up in the middle
3. Anaphase: Chromosome go apart (yay! :))
4. Telophase: Pinching and growing apart of soon to be 2 cells
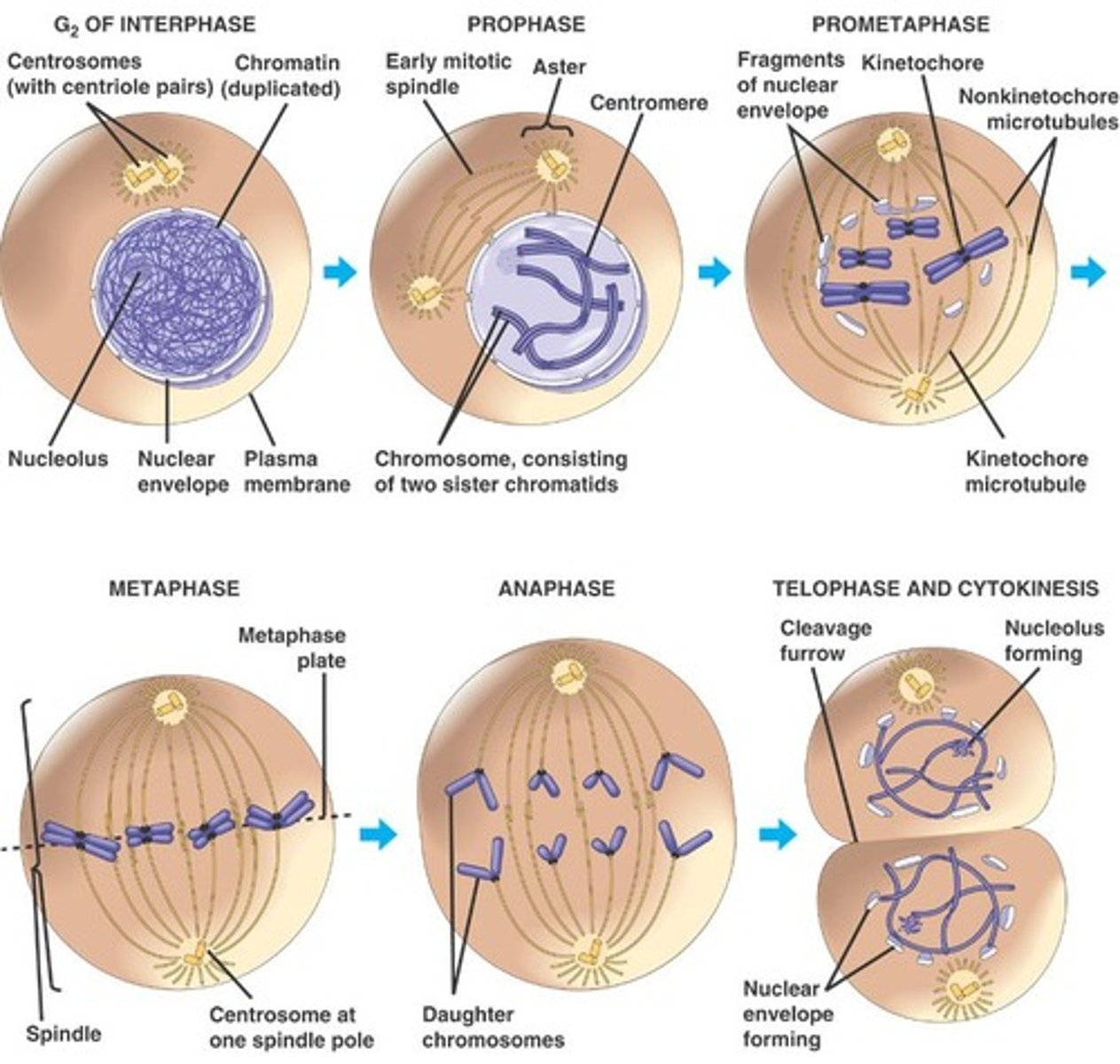
Cleavage furrow
An indentation at the equator of a cell during telophase (pinching)
Cell Plate
disk containing cell wall material that develops in plant cells during cytokinesis, eventually dividing the cell into two daughter cells
Cell Control System
Consists of specialized proteins, which send "stop" and "go-ahead" signals at certain points during the cell cycle
Cancer
Disease of the cell cycle, cells do not respond normally to the cell cycle control system, a malignant tumor
Tumors
Abnormally growing masses of body cells
Benign Tumor
Tumors that have not spread into surrounding tissue
Malignant Tumor
Tumors that have spread to other parts of the body and interrupt body functions
Metastasis
Spread of cancer cells beyond their original site of orgin
Radiation Therapy
damages DNA and disrupts cell division
Chemotherapy
Use of drugs to disrupt cell division
Meiosis
Sexual reproduction, fertilization and produces offspring that contain a unique combo. of genes from their parents
Somatic Cell
A typical human body cell that has 46 chromosomes
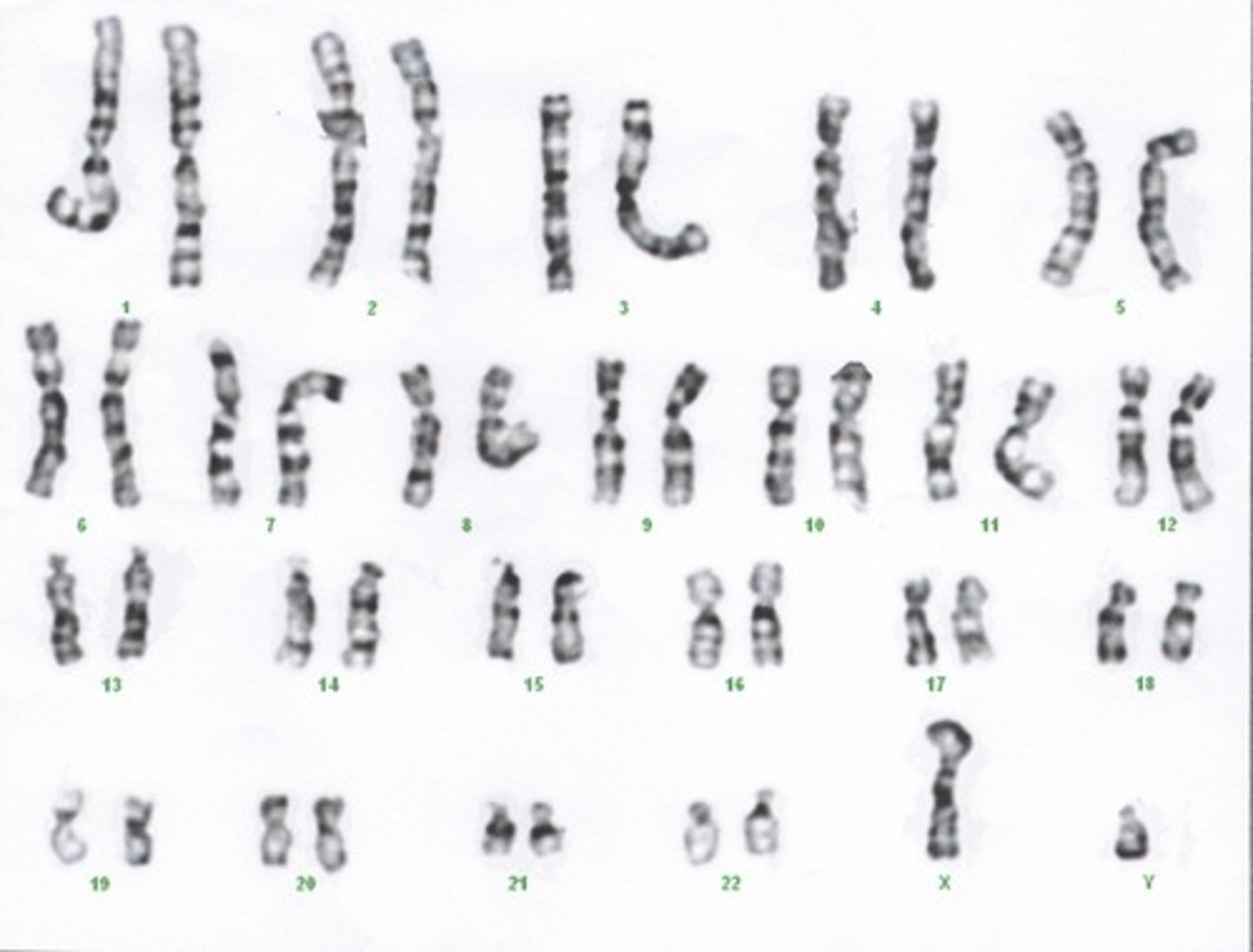
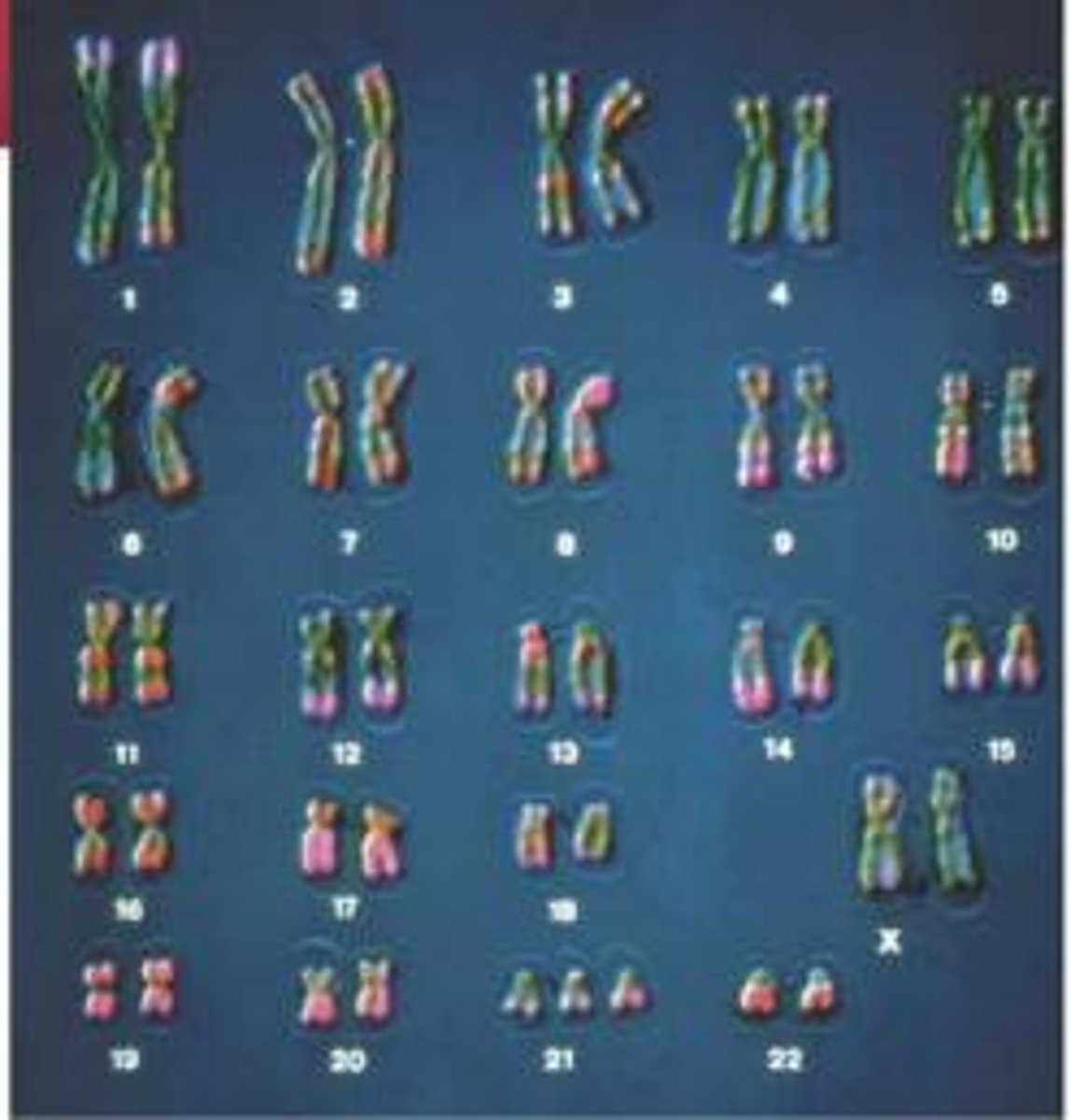
Karyotype
An image that reveals an orderly arrangement of chromosomes
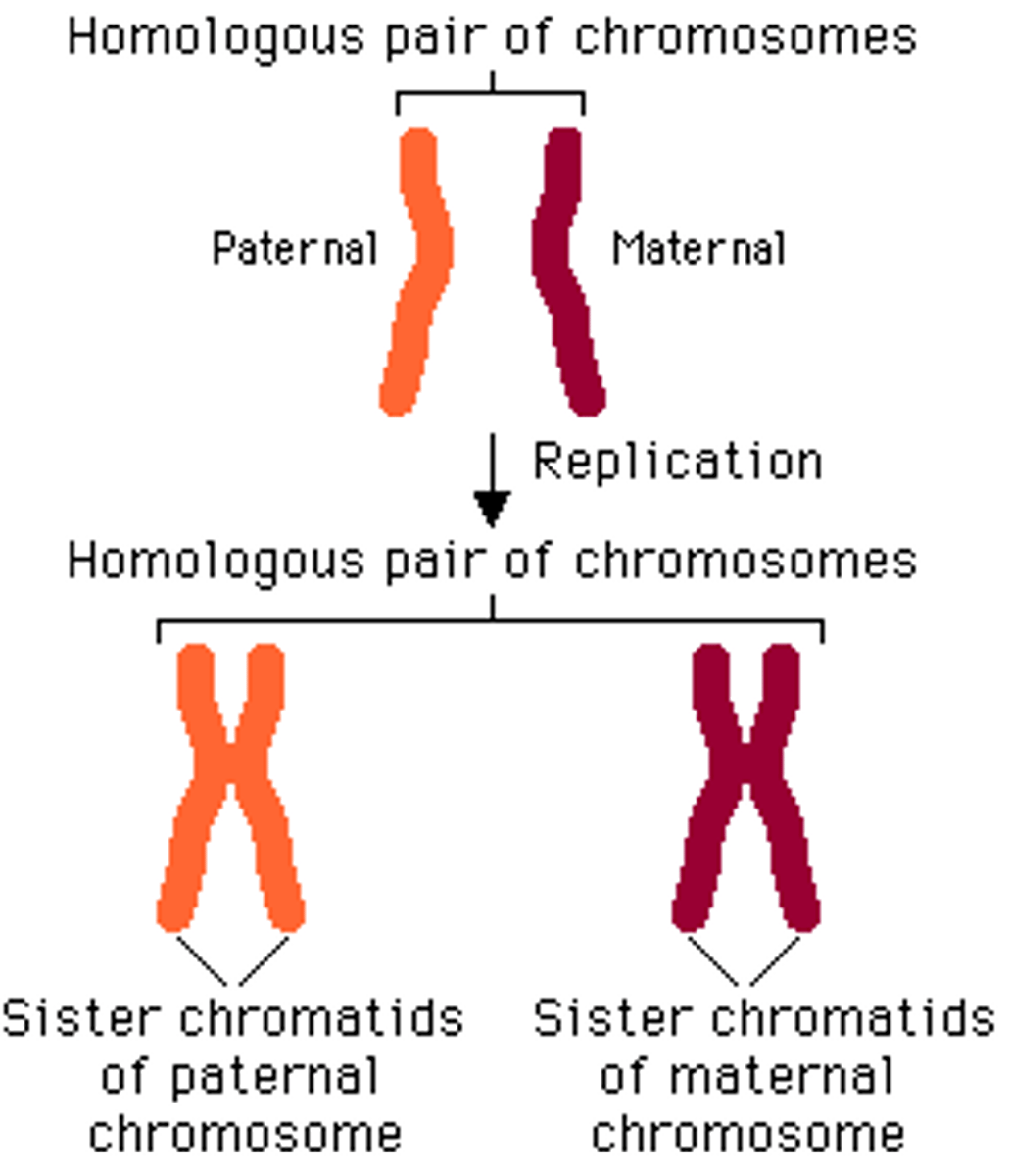
Homologous Chromosomes
Matching pairs of chromosomes that can possess different versions of the same genes.
Sex Chromosomes
Determine a persons sex, Father Chromosomes determine the sex
Males=XY
Female=XX
autosomes
The remaining chromosomes found in both male and females (everything but XX, XY)
Diploid Organisms
Body cells contain two sets of chromosomes/ pairs of homologous chromosomes
Haploid Organisms
A cell with a single chromosome set, has only one member of each pair of homologous chromosomes
Fertilization
A haploid sperm fuses with a haploid egg
Zygote
A fertilized egg
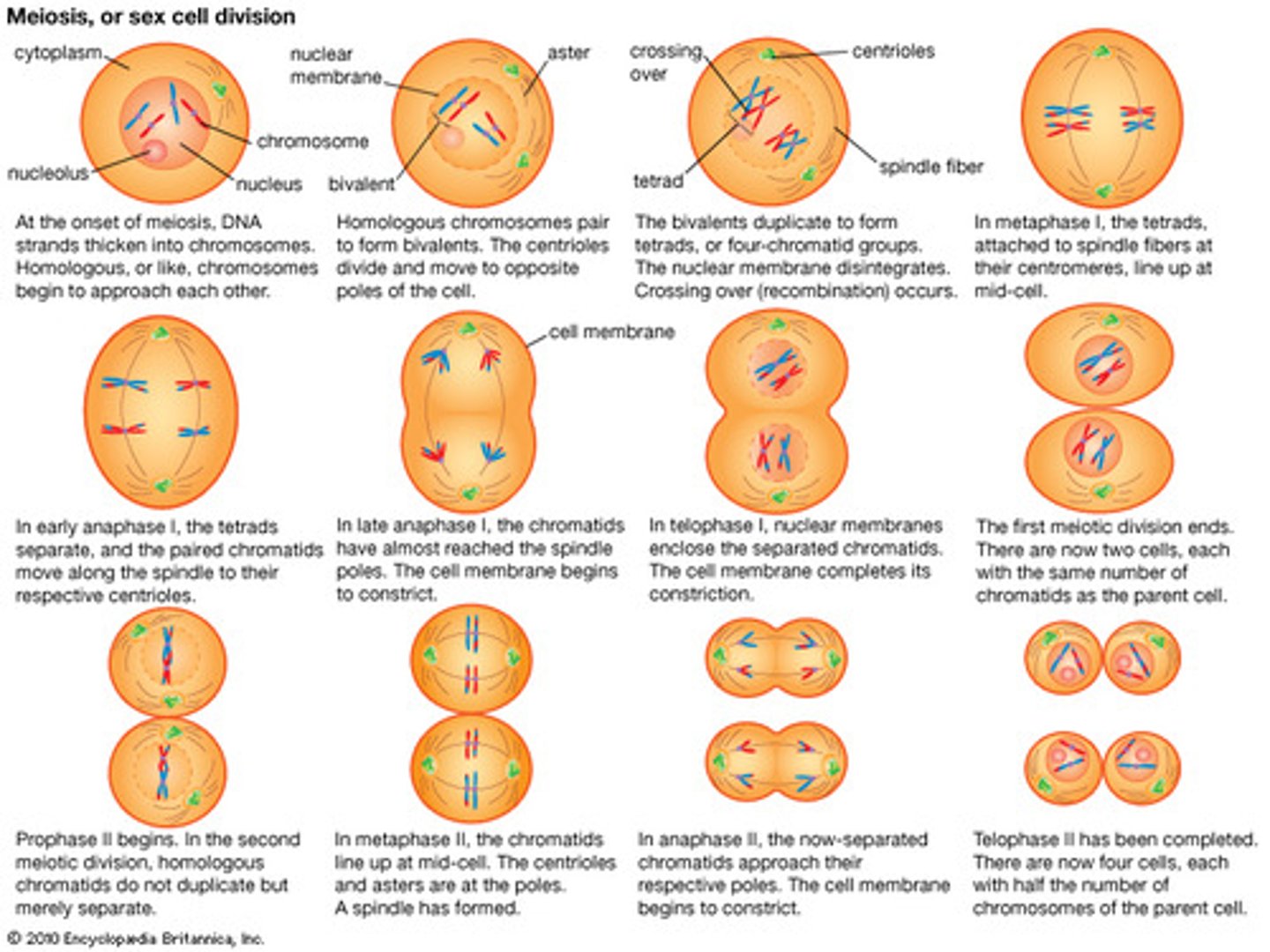
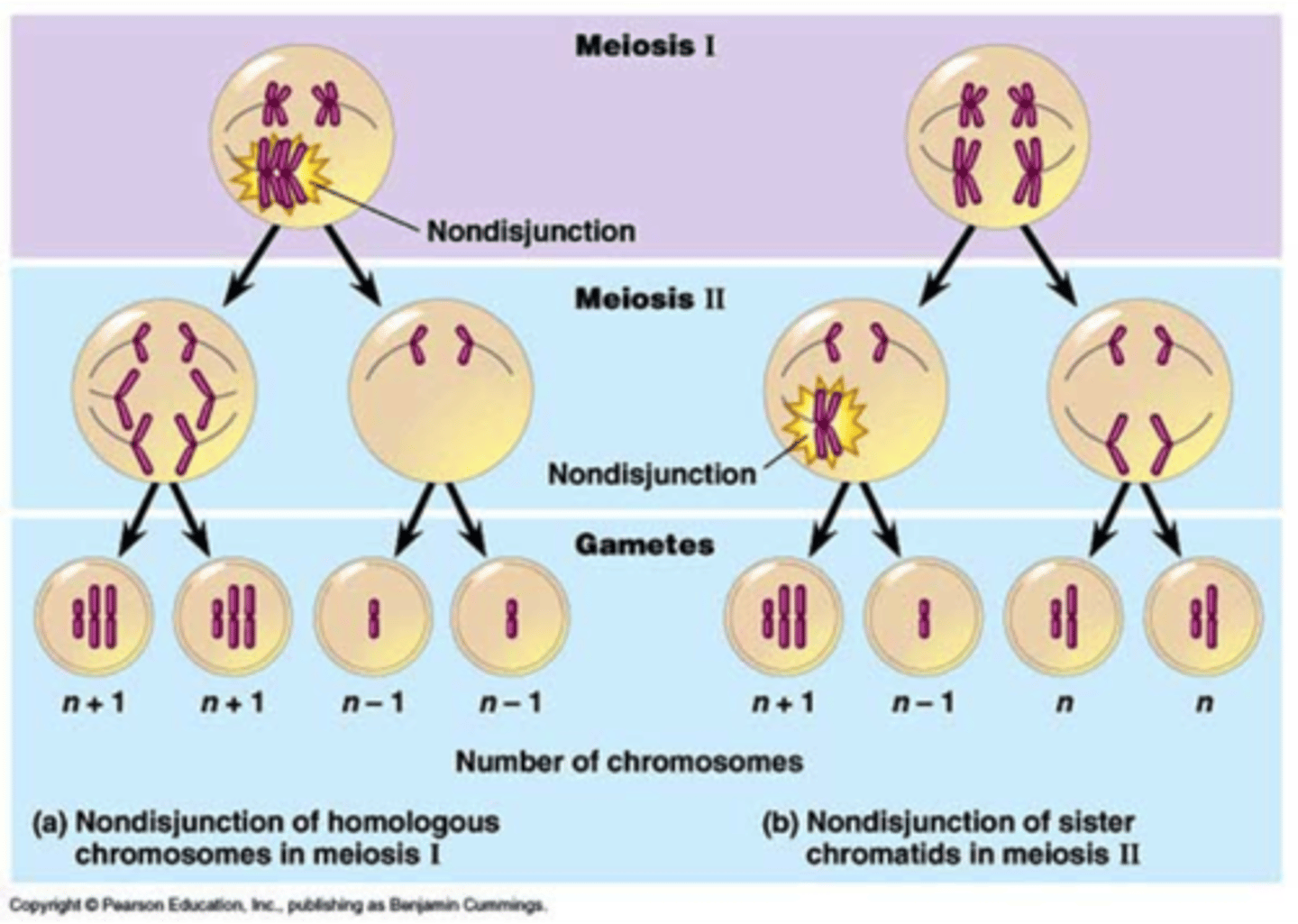
How Meiosis Halves chromosome number
LOOK AT PIC
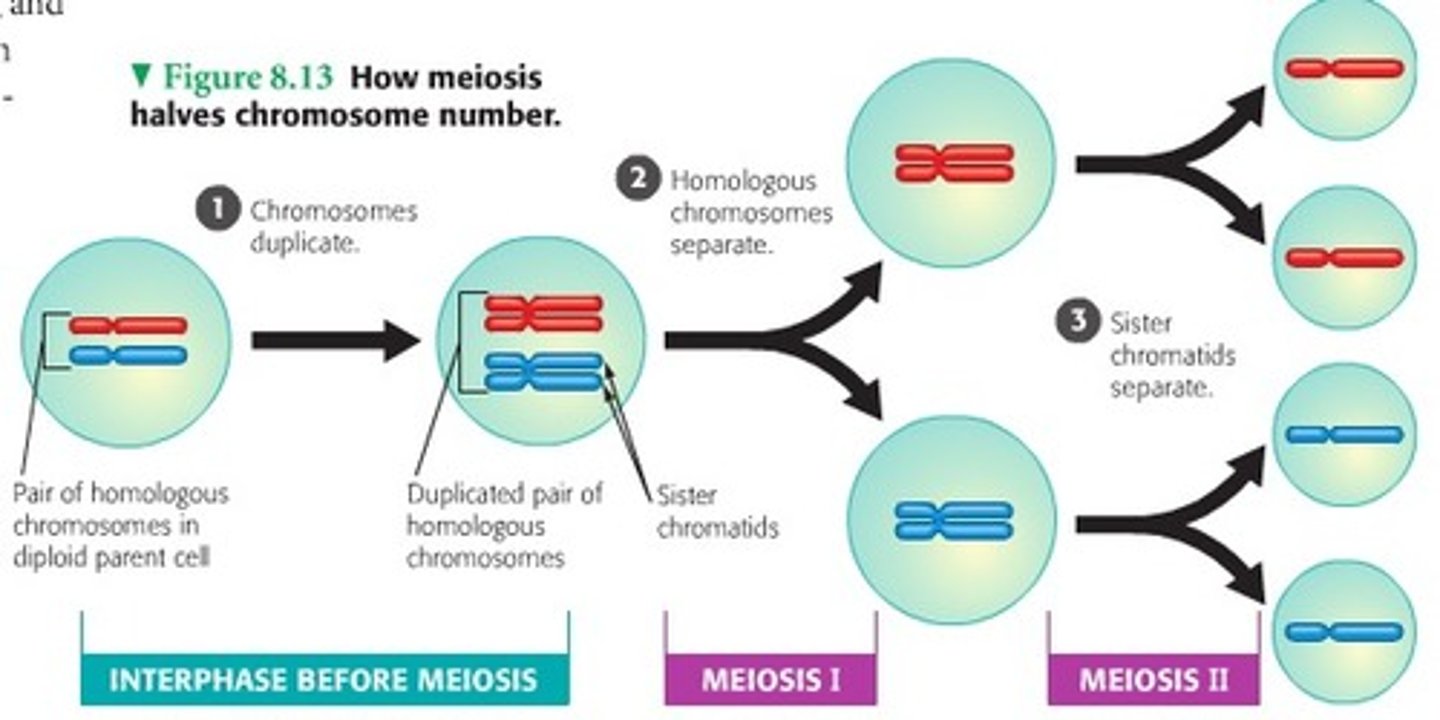
Process of Meiosis
LOOK AT PIC
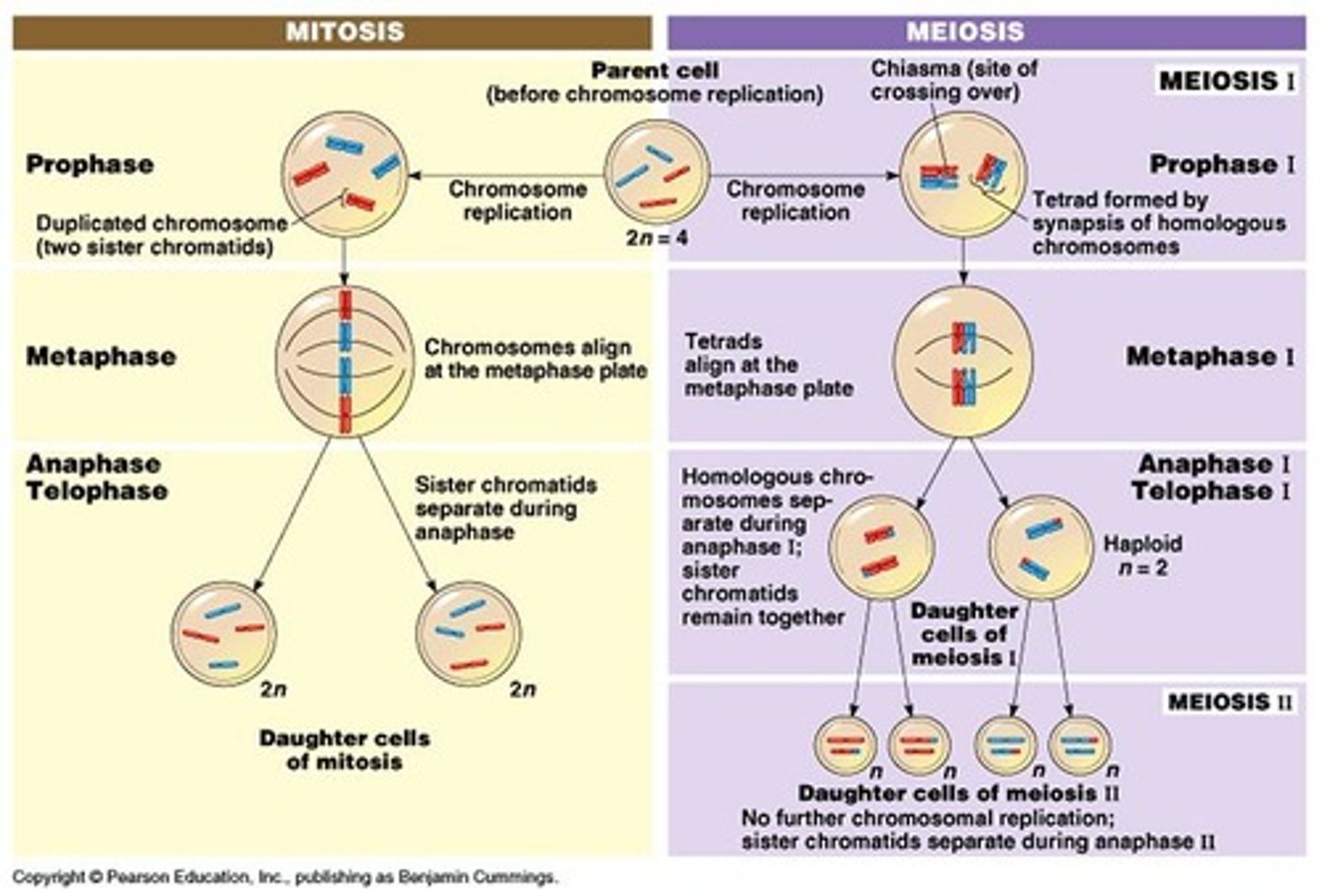
Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis
LOOK AT PICK
Independent Assortment of Chromosomes
Every chromosome pair orients independently of all others at metaphase I. We can't predict which chromosomes (genes) organisms will end up with
Random Fertilization
Human eggs are fertilized randomly, 70 trillion different possible chromosome combination (wooooowwww)
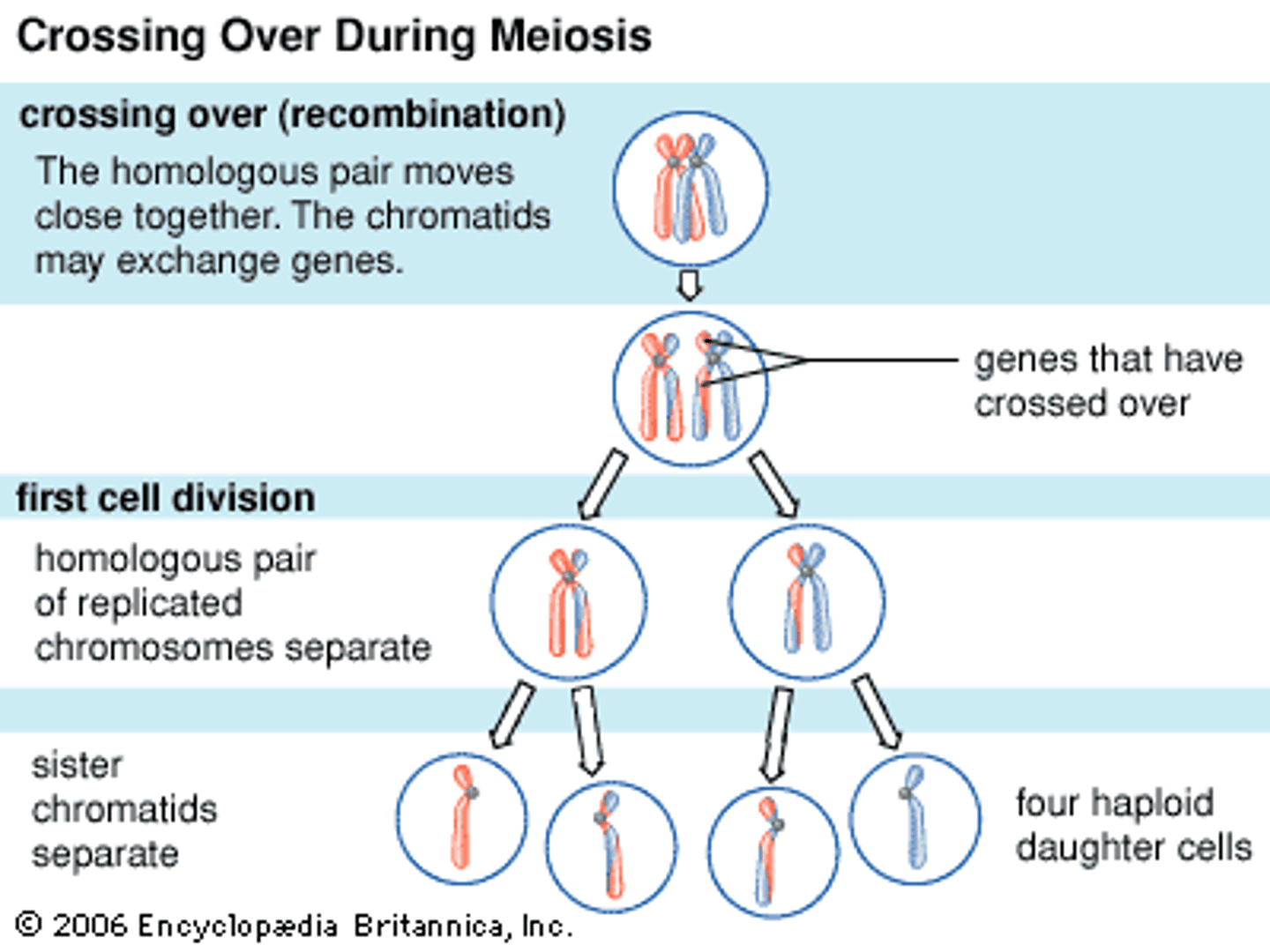
Crossing over
The exchange of corresponding segments between non sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes which occurs during prophase I of meiosis; creates more variations
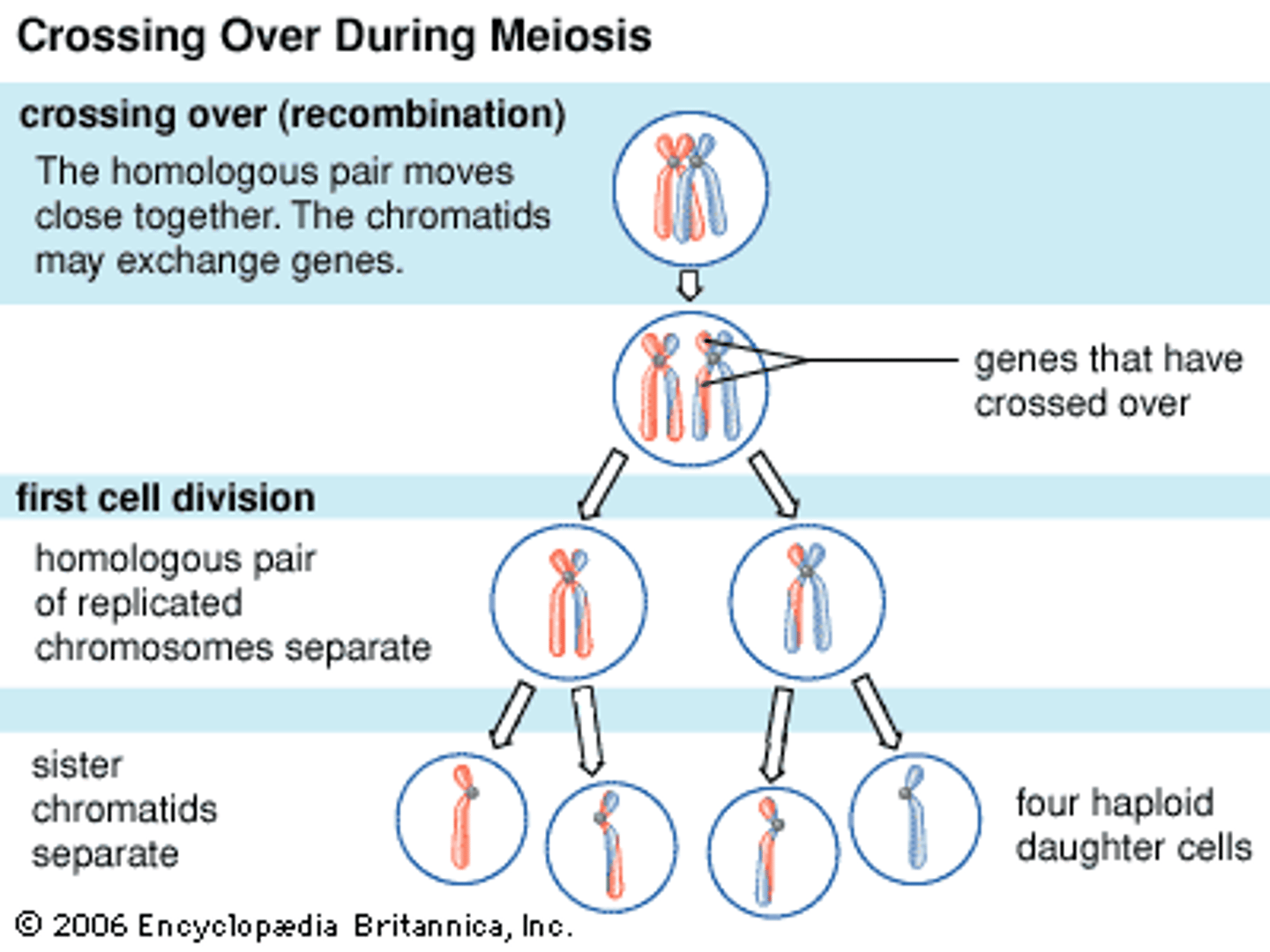
Genetic recombinations
The production of gene combinations different from those carried by the chromosomes; combine genetic information from different parents because of crossover
Nondisjunction
The members of a chromosome pair fail to separate at anaphase, producing gametes with a incorrect number of chromosomes
Trisomy 21/ Down Syndrome
Individual has an extra chromosome 21, 1 out of every 700 children
Heredity
the transmission of traits from one generation to the next
The science of genetics has ancient roots dating back to the Greek physician
Hippocrates
genetics
the scientific study of heredity
character
a heritable feature that varies among individuals
(ex. flower color)
trait
a variant of a character (ex. purple, white flowers)
heritable factors
today we call genes
self-fertilize
the eggs of one plant are fertilized by the sperm of the same plant (e.g., pea plants)
cross-fertilization
process by which sperm from one flower's pollen fertilizes the eggs in a flower of a different plant
true-breeding
organisms that produce offspring identical to themselves if allowed to self-pollinate
hybrids
the offspring of two different purebred varieties
genetic cross
the cross fertilization of two different purebred varieties (also called hybridization)
P generation
the true-bred parent generation
F1 generation
the hybrid offspring of two different P generations
F2 generation
the offspring of two F1 generations
Monohybrid Cross
a cross where the parent plants differ in only ONE character (like the color of the flower)
Mendelian Principles
1. There are alternative versions of genes that account for variations in inherited characteristics
2. For each inherited character, an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent.
3. If two alleles of an inherited pair differ, then one determines the organism's appearance (Dominant) and one has no noticeable effect (recessive)
4. Law of segregation: A sperm or egg carries only one allele for each inherited character because the two alleys for a character separate from each other during the production of gametes
alleles
the alternative versions of a gene; an organism inherits two alleles, one from each parent
homozygous
organism that has two identical alleles for a gene
heterozygous
when there are two different alleles for a gene
dominant allele
the allele that determines the phenotype and organism's appearance; written in uppercase
recessive allele
the allele that has no noticeable affect on phenotype or organism's appearance; written in lowercase
Mendel's law of segregation
A sperm or egg carries only one allele for each inherited character because the two alleles for a character separate from each other during the production of gametes
Punnett Square
a diagram used to determine the possible offspring from a cross
phenotype
an organism's physical appearance
genotype
an organism's genetic makeup
dihybrid cross
mating between parental organisms with two differing traits
locus (loci)
a specific location of a gene along the chromosome
Mendel's law of independent assortment
states that the inheritance of one character has no effect on the inheritance of another
testcross
a mating between an individual of dominant phenotype but unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual to determine the unknown genotype
rule of multiplication
A statistical rule stating that the probability of two independent events occuring together is the product of their individual probabilities. (e.g., 1/2 * 1/2 = 1/4)
rule of addition
A rule stating that the probability that an event can occur in two or more alternative ways is the sum of the separate probabilities of the different ways. (e.g., 1/4 + 1/4 = 1/2)
wild-type traits
traits that are not necessarily specified by dominant alleles but are seen more often in nature
pedigree
A chart or "family tree" that tracks which members of a family have a particular trait
carriers
parents; people who carry a trait, esp a disorder
cystic fibrosis (CF)
A hereditary disorder characterized by excess mucus production in the respiratory tract; most common life-threatening genetic disease in the US
inbreeding
a mating between close blood relatives
Huntington's disease
rare disease, affects motor and memory, is inherited disease that does not manifest until midlife.
amniocentesis
(pregnancy) extraction by centesis of amniotic fluid from a pregnant woman (after the 15th week of pregnancy) to aid in the diagnosis of fetal abnormalities
chorionic villus sampling
sampling of placental tissues for prenatal diagnosis of potential genetic defects
ultrasound imaging
A technique for examining a fetus in the uterus. High-frequency sound waves echoing off the fetus are used to produce an image of the fetus.
achondroplasia
a form a dwarfism where the head and torso develop normally, but the arms and legs are short
complete dominance
the dominant allele has the same phenotypic effect whether present in one or two copies
incomplete dominance
F1 generation hybrids fall between the phenotypes of the two parents ( white chicken + black chicken = all gray chicks)
ABO blood groups
Involve 3 allele of a single gene, produce 4 phenotypes
codominant
both alleles are expressed in heterozygous inviduals (like AB blood versus just A or just B)
pleiotropy
when one gene influences several characters
sickle-cell disease
disease that makes red blood cells produce abnormal hemoglobin proteins
polygenic inheritance
the additive effects of two or more genes on a single phenotypic character (opposite of pleiotropy)
chromosome theory of inheritance
states that genes are located at specific positions on chromosomes and that the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis and fertilization accounts for inheritance patterns
linked genes
Genes located on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together in genetic crosses.
sex-linked gene
a gene located on a sex chromosome
linkage map
genetic map that shows the location of genes on a chromosome
sex chromosomes
X and Y chromosomes = determine sex of an individual
red-green colorblindness
a common sex-linked disorder that is caused by a mafunction of light-sensitive cells in the eyes
hemophilia
a sex-linked recessive trait that causes those affected to bleed excessively when injured
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
A human genetic disease caused by a sex-linked recessive allele; characterized by progressive weakening and a loss of muscle tissue.
Nucleotide
The sub-unit of nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) consisting of a sugar, phosphate and a nitrogenous base.
Sugar-phosphate Backbone
A repeating pattern of sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate that make up the sides of the DNA ladder.