Lesson 11: Feeding
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Why are toads toothless
Their diet is mostly insects
Teeth aren’t good at grabbing something small like an insect
Catch prey in long sticky tongue instead
Also bulk feeding

Invertebrates that do bulk feeding
Lack true teeth but have toothlike structure made of chitin (carb material that makes up exoskeleton of insects)
No dentin or enamel
following are examples of invertebrates that lack true teeth

Bulk feeding: Cnidearians (eg. Portuguese man of war)
Giant float, gas filled bladder that helps them float on ocean
Tentacles (up to 30m)
Fish that get caught, are paralyzed by stinging cells on tentacles
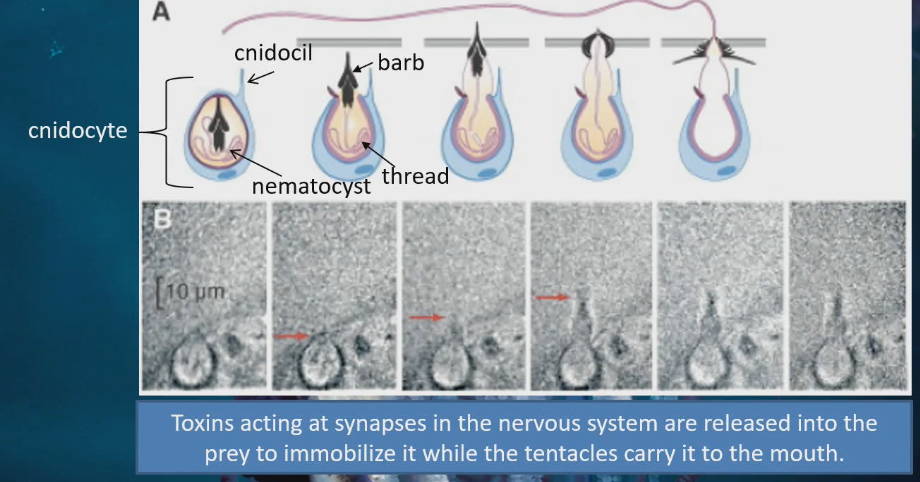
Stinging cells or cnidocyte on Cnidarians
2 parts
Cnidocil or trigger
Fish has to brush up against this for cell to sting it
Trigger to detect prey
nematocyst inside the trigger has 2 parts of its own
Barb : sharp pointy part, penetrates through body wall of fish
Thread : enter into fishes body through the opening that the barb has created, and it comprised of toxins. Toxins acting at synapse in the nervous system are released into prey to immobilize it while the tentacles carry it to mouth.
when Cnidearians (eg. Portuguese man of war) eats the prey with all the toxins, why isn’t it impacted by the same toxins that killed its meal
Toxins are entirely protein based
When they get into digestive system of Portuguese man of war, they get digested like proteins, so they are hydrolyzed by the predator when it consumes prey
This is why protein based medications cannot be taken orally Like insulin
If you did take insulin orally it would just get digested and you wouldn’t get any of the benefits
injecting insulin orally the toxin bypasses the digestive system making it effective
Deposit feeding
Investing food items contained within the solid material that the animal lives in or on
Crabs that eat mud they lived on
Earthworms eat the dirt as they crawl through it
Snails
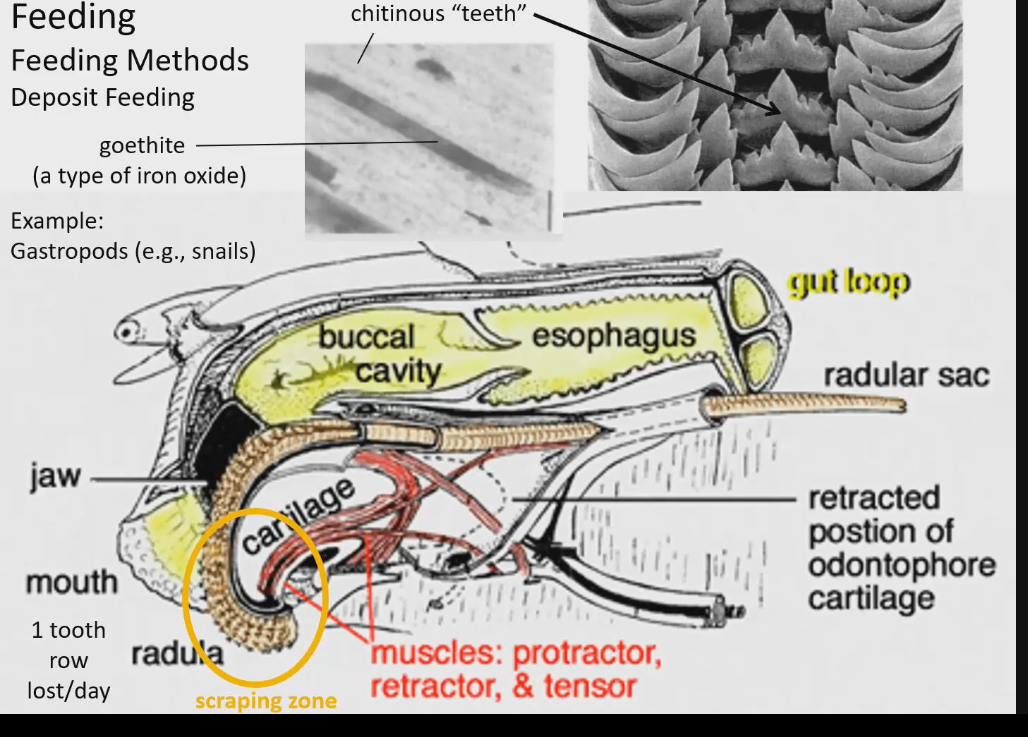
snails as deposit feeders
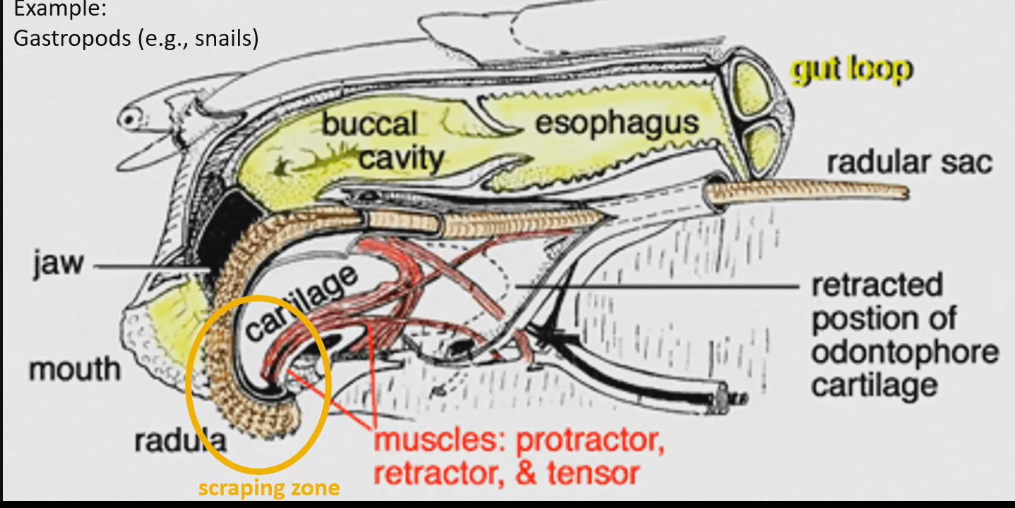
Radula → tongue like thing with teeth like structure that scrapes surface they are crawling on like glass of aquarium
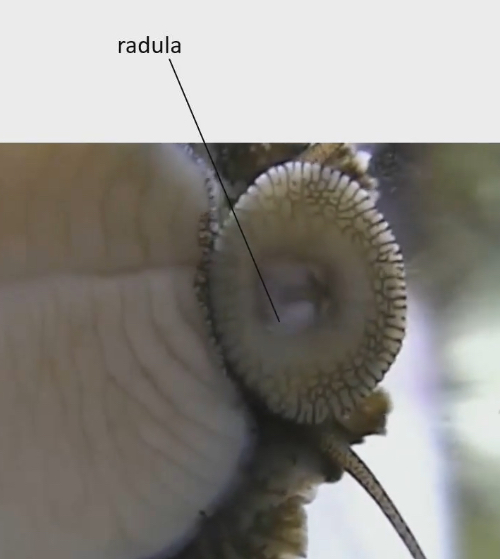

Radula structure
Brown thing in picture
Larger than we initially thought, scrapping zone is what we see on outside
Protractor muscles that stick radula out, retractor pulls it back in, and a tensor operate the function
Not true teeth on radula of snail
Made of chitin and mineral deposits embedded (goethite: a type of iron oxide that makes the tooth really strong)
No enamel and dendrite
Shape of not true teeth used to be the way that snails were classified. Until research showed that shapes of teeth can change within snail group based off diet
Raudla is always loosing teeth because of the scrapping of surfaces
The scraping zone communicates to radula sac the kind of food it’s eating so that new growth of teeth re the right shape. This shape is changing based off diet
Suspension feeding
Investing organic material suspended in fluid
Larger particles
Filter to remove food particles from water
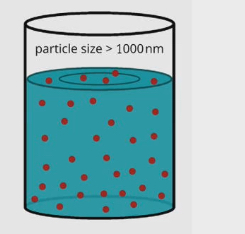
Solution
a liquid mixture in which the minor component (the solute) is uniformly distributed within the major component (the solvent)
Smaller particle size so they dissolve
Salt and water
Can’t use filter to get salt out of water

Sponges are filter feeding
Openings at top of sponge called oscula
Pores on side of sponge
Water comes into sponge through the pores and comes out through oscula that is lined with cells who can do the filtering of water from food
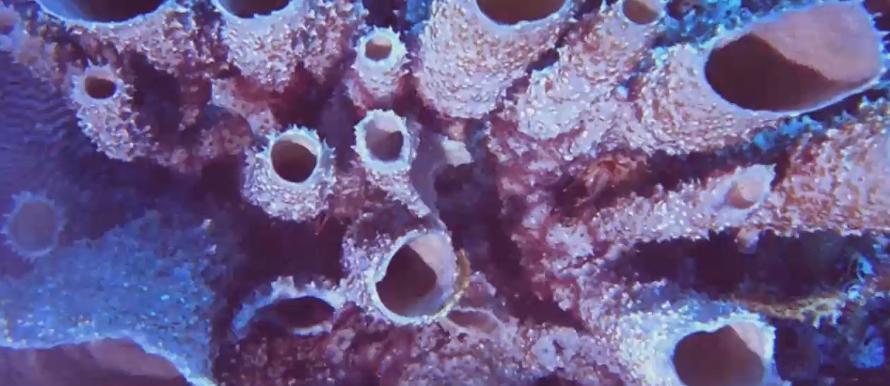
Sponge diagram
Water will leave body through osculum
Water and food will come into sponge through pores that are also made up of living cells called porocytes
Lining the spongocoel is choanocytes that do the actual filter feeding
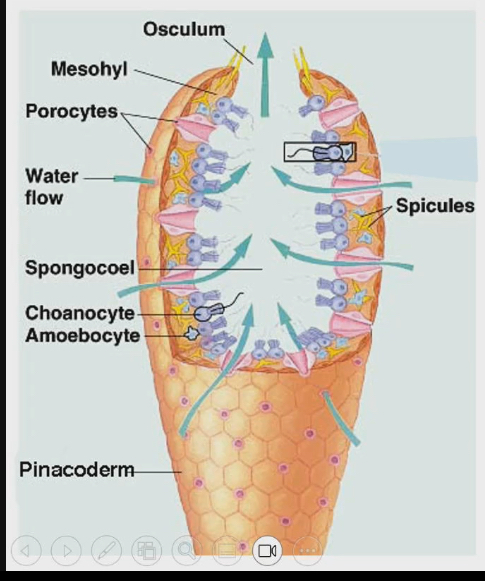
choanocytes up close
Have a collar that looks like a mesh = filter where water can exit, but the holes in collar are too small for the food to escape
Mucus is coating the collar. Water won’t stick to the mucus so it will pass through, but the other particles will
Cilia on collar will push mucus and particles to cell body where phagocytosis occurs. Choanocytes will ingest trapped food particles intracellularly
Digestion occurs in amoebocytes
Choanocytes of a single flagellum to create water current when there is no flowing water
baleen whales also do filter feeding
2 key structures
Throat pleats : grooves in body surface that expand size of mouth to take in as much water and suspended food as possible. But they don’t want to have this large surface area all the time when they are not eating
Baleen: actual filtering structure to separate the water and particles. Looks hairlike, it’s comprised of keratin, the same protein that makes up our hair. Slits between keratin hairs, that are large enough for water to go through but small enough that food particles can’t
open mouth expands as large as it can. Animal will lunge and water and suspended particles will enter mouth. Then it will close its mouth, not completely, then pushes tongue to roof of mouth. This forces all the water out and through baleen back into the ocean. Tongue to lick inner surface of baleen to get all the food particles, and swallow
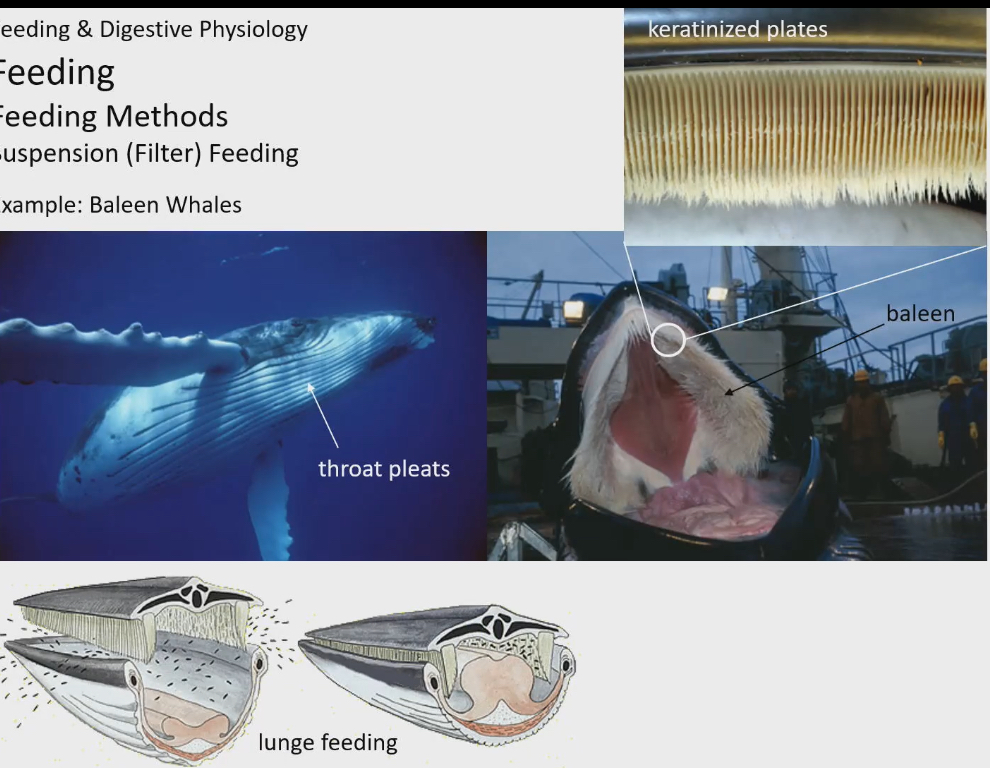
Lunging done by baleen whales to filter feeding is an expensive mechanism
Whales need to make sure there is enough food in the water before they lunge to justify the cost of this process
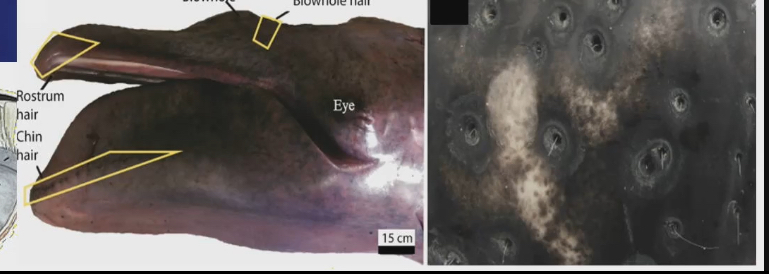
They can detect food in the water by sensory hairs on rostrum (nose) and chin. Sensory hairs can detect vibrations in water and density of food in water before they feed
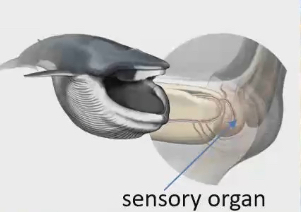
Sensory organ between 2 lower jaw bones there is a sensory organ on baleen whale
Coordinates feeding events
Help relay sensory info of hairs back to the brain
Involved in coordinating movement of tongue and expansion of throat plates
2 classes of whales
All whales are a part of order catacea
Baleen whales belong to suborder mysticeti → no teeth
Another suborder odontoceti that feed by bulk feeding with teeth that are all the same shape → swallow food whole, teeth just used to grab food.
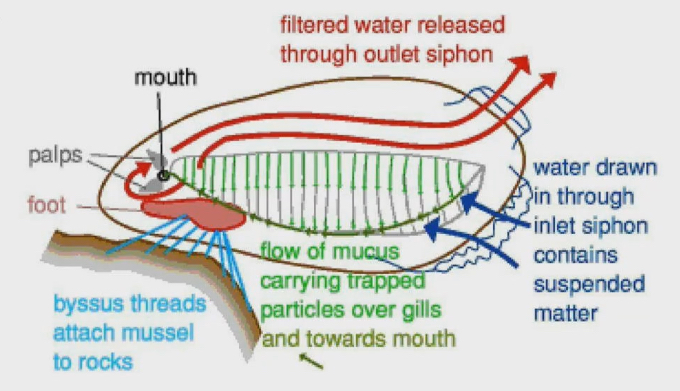
Bivalve mollusc
2 openings that allows water to come in and water come out
Filters sometimes get clogged. So clams can close openings if they sense something like sand coming in their direction that could clog their filter
Water drawn in through inlet siphon contains suspended matter
Flow of mucus carry trapped molecules over gills and towards mouth
Mucus and gills act as the filter
Byssus threads attach mussel to rocks
Filtered water released through outlet siphon
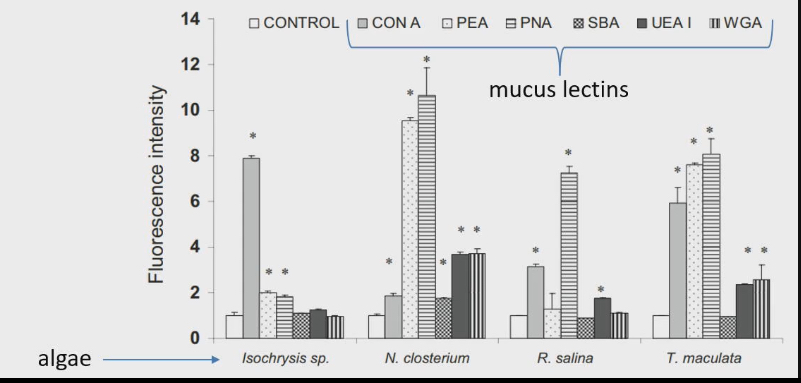
Mollusc can control the food they eat by changing proteins in their mucus
Lectins bind to carbs
For each species of algae how well does it bind to the different type of lectins
Filter feeders can selectively eat certain foods better than others
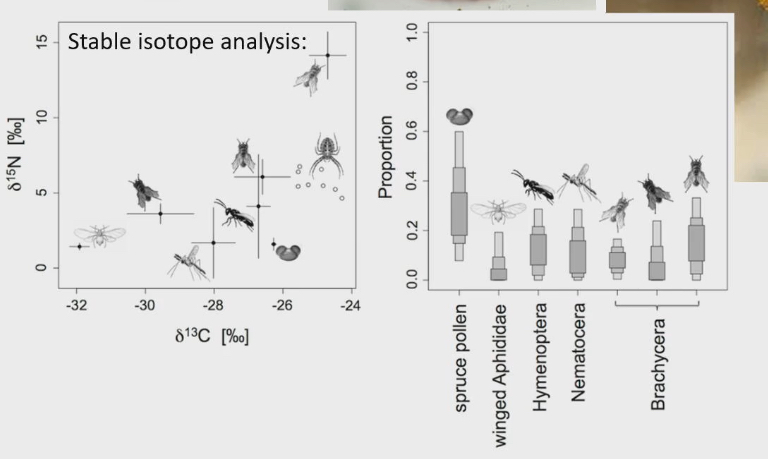
Terrestrial filter feeders
Orb weaver spiderlings
Pollen gets trapped and filtered by spider webs
Researchers wondered if this was because older spiders eat insects, little spiders eat pollen, and no competition for resources
To test this used stable isotope analysis (common to find out what kind of food an animal eats)
Hypothesis was correct, pollen was main food of baby spider
Stable isotope
Not radioactive isotope
Ex. 3 major isotopes of carbon 12 (stable), Carbon 13 (stable), carbon 14 (radioactive)
stable isotope
What is ratio of carbon 12 : carbon 13 and also the ratio of nitrogen 14 : nitrogen 15 in animal
Then you do same thing for all the potential things they could eat (ex. All the things caught in their web like pollen, insects)
Then you are what you eat, carbon and nitrogen ratios in predator will be similiar to the ratio of the food they eat
Pollen is too big for the consumption to be accidental. They need to digest it outside of body then eat it
Fluid feeding
Ingesting liquids that contain organic molecules in solution
Ex. Lamprey
Lamprey
Fish that are jawless
Instead they have oral disc on head that is like a suction cup, they use it to attach themselves to a fish’s body, cut fish up, and then drink their blood
Toothlike structures to get fish good grip on fish. Not true teeth, made of keratin (what our fingernails are composed of)
Make a larger circular flesh wound and feed on blood that flows out
Inject lamphredin which is like a anticoagulant (prevents blood from clogging), local anaesthetic (prevents fish from feeling pain), immune suppression
prevents the fish from relizing that they are being fed on so lamprey can get the most blood as possible
Although fish is not ingested, up to due 60% will die due to lamprey inflected wounds

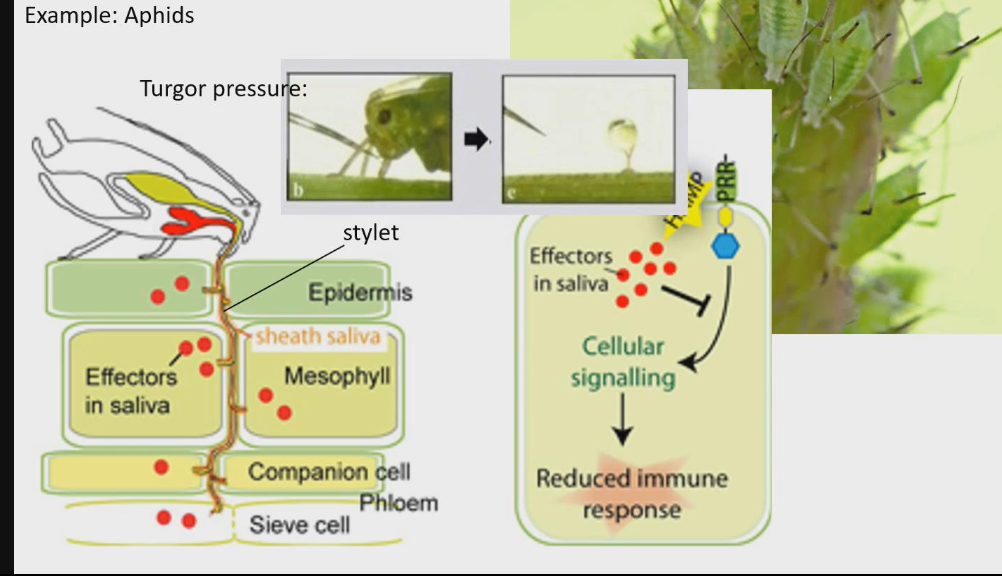
aphids
Fluid feeder
Feed on sap or phloem of the plants
Stilt, long tube that gets through all the layers of tree until it gets to the phloem
Not like a straw because aphids don’t need to suck because phloem is under turgor pressure
Effectors in saliva are being injected into the plant so that the plant doesn’t start any kind of immune response, stopping the aphids meal
Don’t directly kill the plant, but cause enough damage to decrease evolutionary fitness
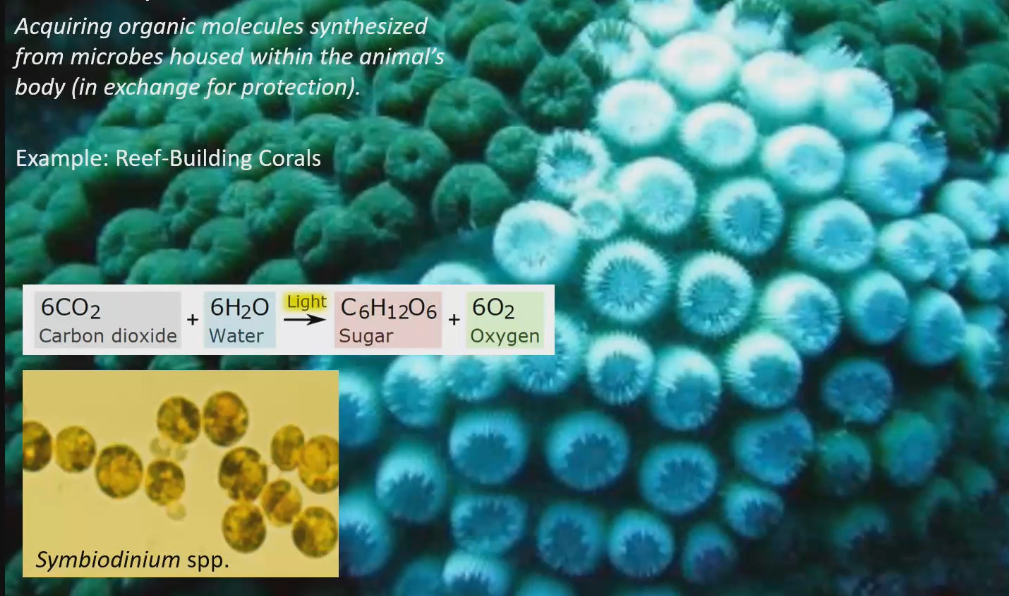
microbial symbiosis
Acquiring organic molecules synthesized from microbes housed within the animal’s body (in exchange for protection)
Ex. Reef building corals
Photosynthetic algae symbiodinium spp harboured in body
Corals protect green algae, in return symbiodinium does photosynthesis and provides sugar to the corals
White part of corals means its gone through ‘coral bleaching’. It’s gotten rid of symbiodinium, and so coral is white because thats the colour of the skeleton of the corals. Sometimes symbiodinium Get kicked out of coral because if there is so much heat or light, they do so much photosynthesis they produce so much ROS → no net benefit for corals
Without symbiodinium, corals can get food through bulk feeding through mesenterial filament
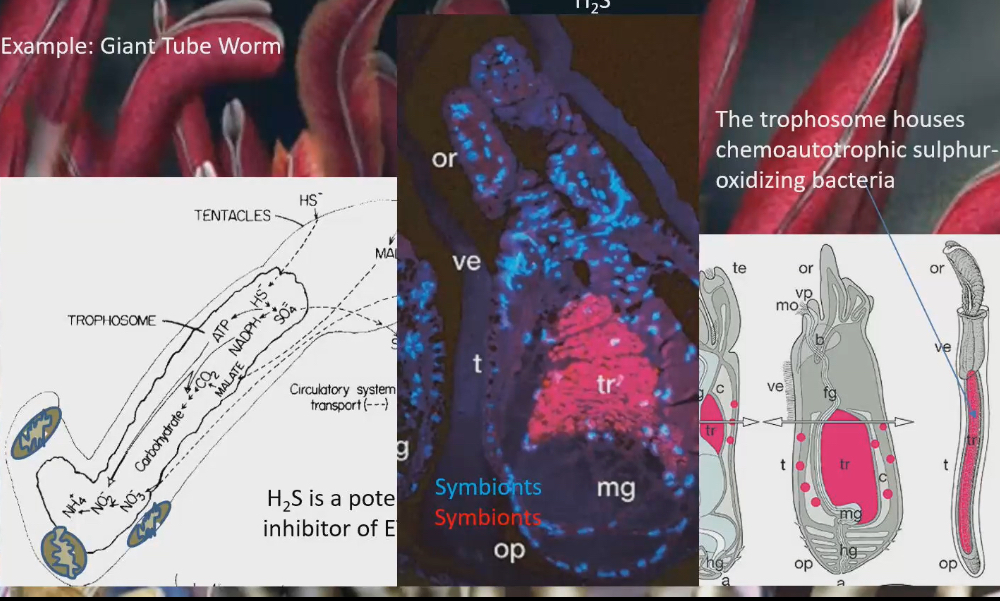
giant tube worm
Microbial symbiosis
Hydrothermal vents
Black smokers, super hot mineral rich water comes out of ocean crust
As soon as it hits the cold ocean water above, all the minerals precipitate out
most of species that live in hydrothermal vents are endemic (meaning they are found in no other environments except in hydrothermal vents
Giant tubes are endemic to hydrothermal vents
sticking out of tube is red gills. Gills are red because of hemoglobin. They have 2 hemoglobin, one that binds H2S (one of the minerals in hydrothermal vents)
In tube worms they have a structure called trophosome that houses chemoautotrophic sulphur-oxidizing bacteria. Bacteria oxidized H2S, to get energy from it, use energy to build sugar to give to tube worms
H2S is also an inhibitor to ETC. only way to survive in hydrothermal vents as an aerobic species is to have this bacteria that binds the H2S, to not only send it to trophosome to use it for food, but also to ensure H2S doesn’t get anywhere near mitochondria
To trophosome in a baby tube worms, they are born with a gut, that degenerates as it grows older and trophosome grows in. Trophosome are acquired through their skin and body wall