L8 Antigens and Immune regulation
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Immunogen
Substance that induces a specific immuner esponse
antigen (Ag)
substance that reacts with the products of a specific immune response
Hapten
Non-immunogenic, but can react with the products of a specific immune response
Epitope (antigenic determinant)
Portion of the antigen that combines with the products of a specific immune respons
Antibody (Ab)
protein that is produced to an immunogen and which reacts with an antigen
Factors influencing immunogenicity
Contibution of the antigen
Foreigness
Size, large > small
Chemical composition
Physical form, solubility, naitve or denatured
Degradability
Factors influencing immunogenicity
Contirbution of the biological system
Genetic factors
Age
Factors influencing immunogenicity
Method of administration
Dose, optimum
Route, e.g. subcutaenous, intravenous
AdjuvantsC
Chemical nature of immunogens
Proteins
Polysaccharides
Nucleic acids
Lipids
Haptens
An incomplte immunogen, which is unable to induce an immune response, but can react with components of the immune system (e.g. antibodies)
Haptens are small molecules (<10 kDa)
Haptens need to be boudn to a carrier molecule to induce an immune response (hapten-carrier model)
Carrier - hapten
INjection with, antibodies formedS
hapten-carrier conjugate:
antibodies to hapten, antibodies to carrier, antibodies to conjugate of hapten and carrier
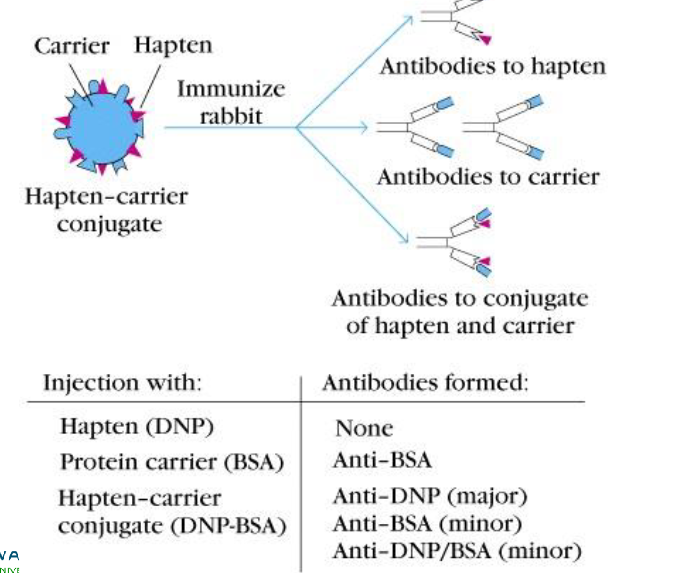
Protein + haptne
hapten induced conformational change
ahpten cross-linked conjugate
multi-hapten conjugate
addition of hapten (alpha-gal( to enhance vaccine potential
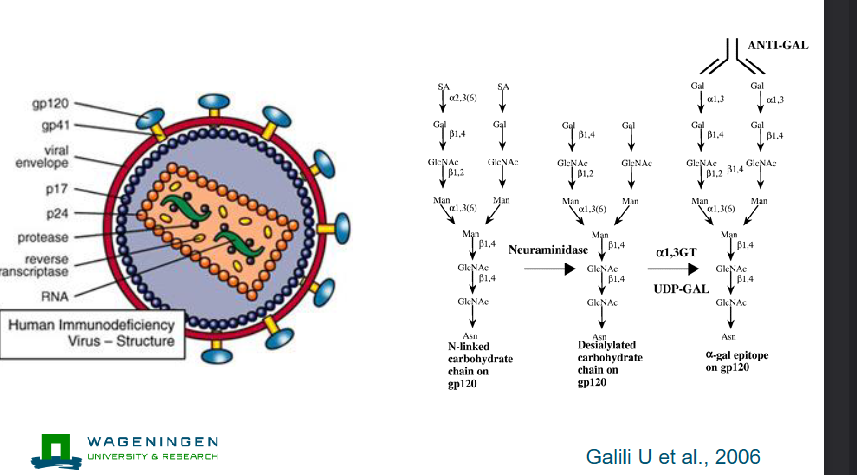
Alpha-gal as hapten
Knock-out mouse has no alpha-gal epitopes and therefore high levels of alpha-gal antibodies
WT mouse has alpha-gal epitopes and therefore no alpha-gal antibodies
Immunization with GP120 or GP120-alpha-gal

Mechanism immune enhancement by haptens
Anti alpha-gal immunoglobulins form immune complexes with GP120alpha-gal
Immune complexes are more effciently internalized by APC (enhanced antigen presentation)
APC cause increased Thelper cell activation resulting in more antibodies and cytotoxic T cells
Primair
Val, glu, ser, pro, gly, etc
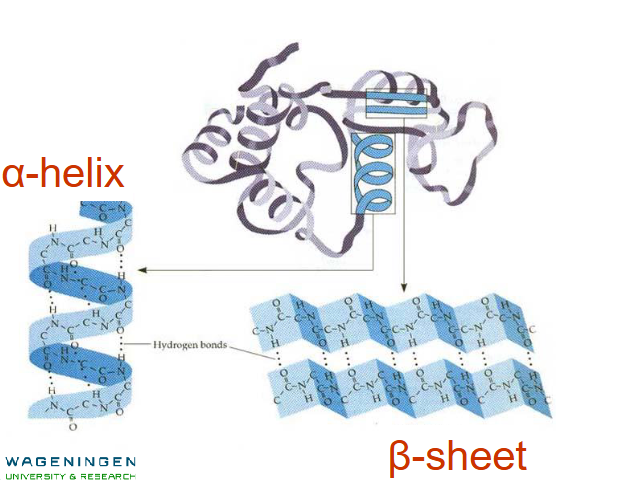
Secondari
Alpha helix, or beta sheet
Tertiar
Domain
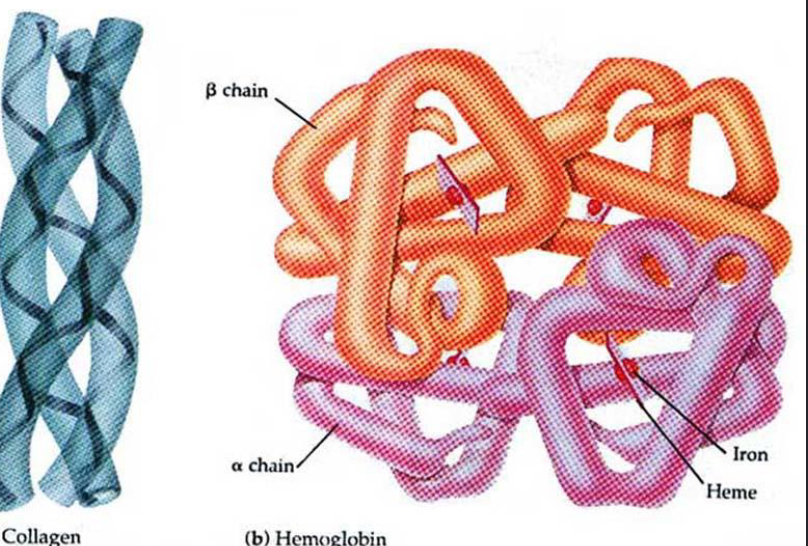
Quarternair
Protein
Seocondary structure
Quaternary structure
Immune function and dysfunction (pathology)
Foreing antigen from pathogen
immune activation, recovery from infection
Tolerance, persistent infection
Foreign antigen from environemnt (harmless)
tolerance, remain healthy
immune activation, allergic disease
Self antigen
tolerance, remain health
Immun activation, autoimmune diseases
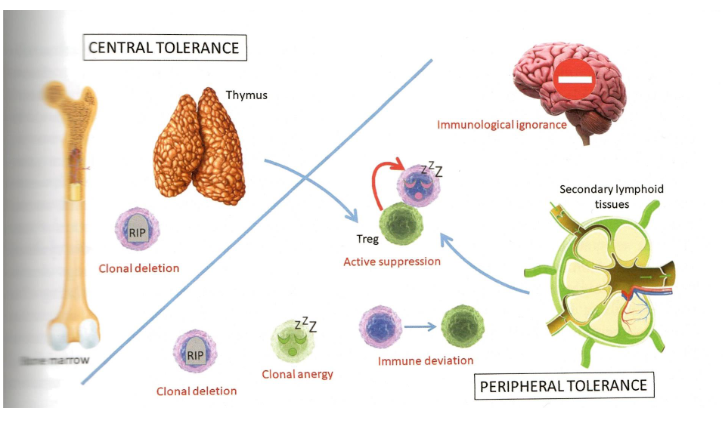
Tolerance, central and peripheralS
Immunoregulation
Communication between immune cells
Tolerance
Antigens
immunoglobulins, idotypic networks
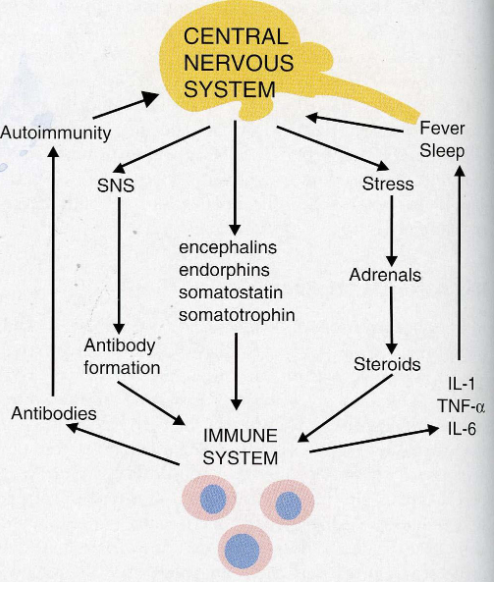
Neural regulation
Regulatory T cells, hygiene hypothesis
Tolerance
Immunological tolerance is the lack of an adaptive response to a specific antigen
T cell tolerance
Neg en pos selection (central tolerance in thymus)
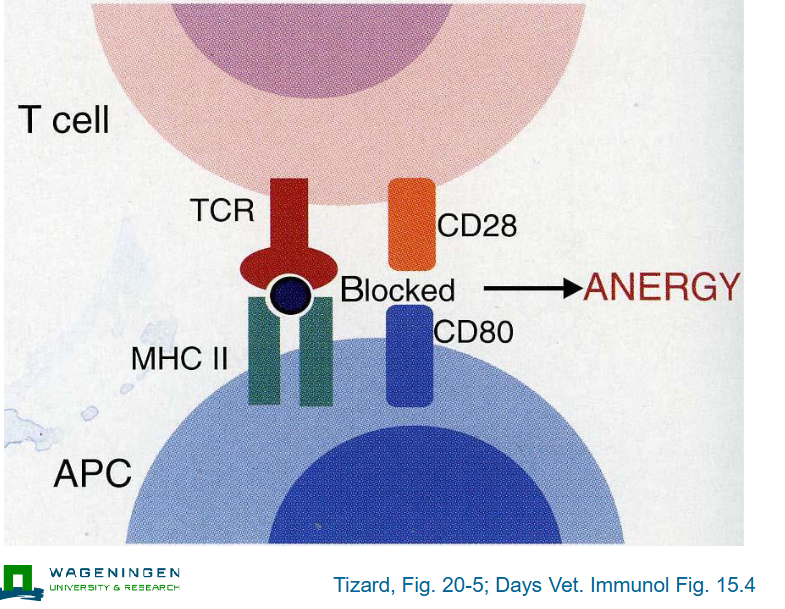
T cell anergy (absence of co-stimulation)
B cell tolerance
clonal abortion (central tolerance in bone marrow)
clonal anergy
Tolerance of T and B cells - schematic

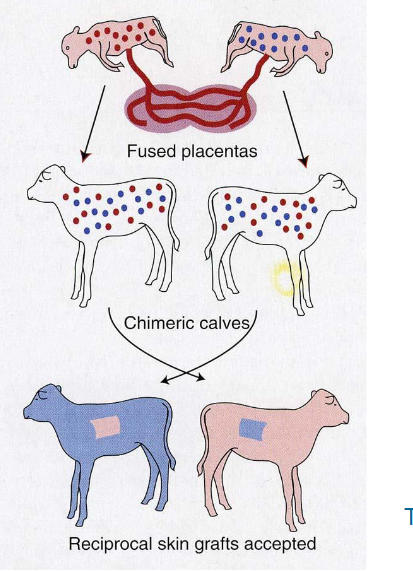
Mucosal tolerance (oral tolerance)
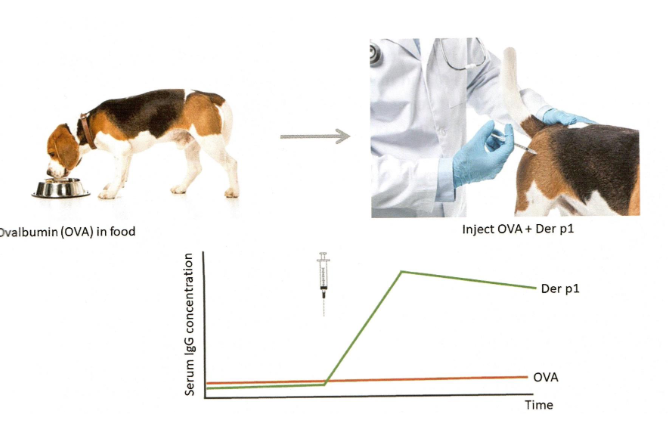
Oral tolerance in broilesr

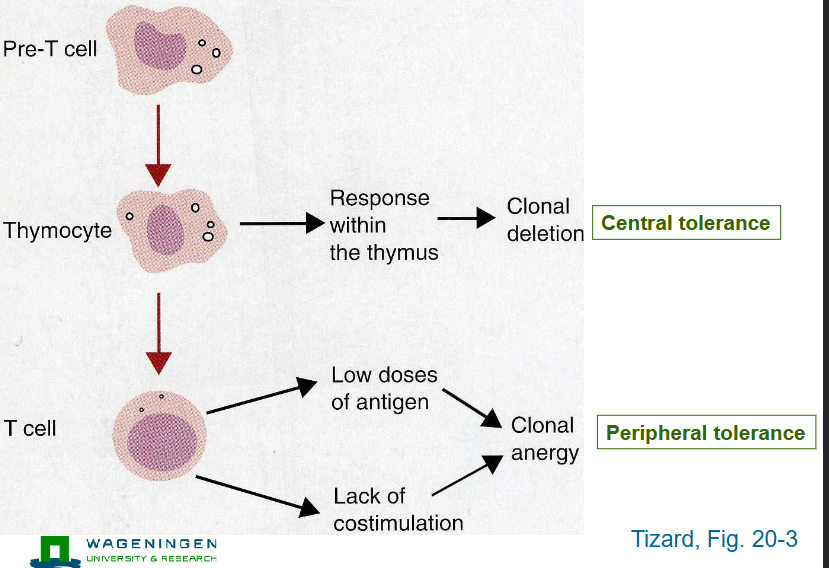
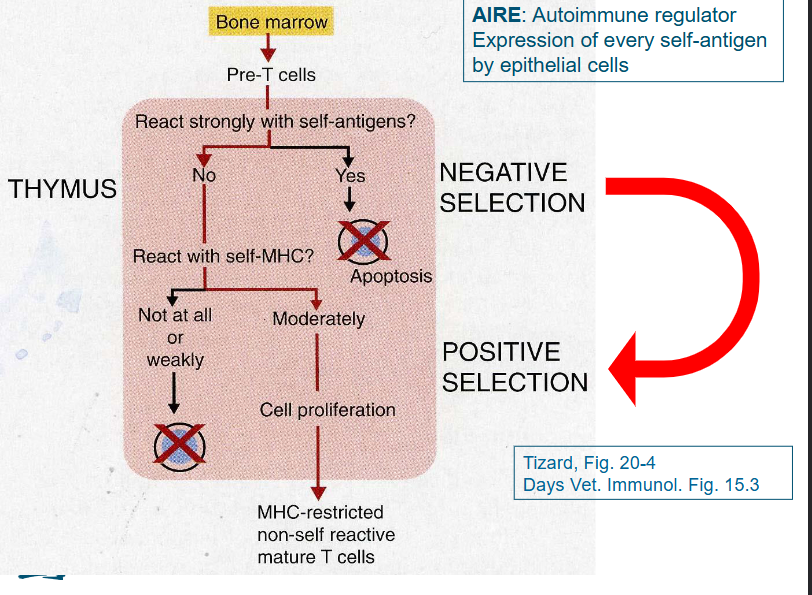
Central tolerance vs peripheral tolerance for the T cell
schematic
pre-T cell → Thymocyte → T-cell
Thymocyte → responses within the thymus → clonal deletion → central tolerance
T cell → low doses of antigen, lack of costimulation → clonal anergy → peripheral tolerance
negative and positive selection in the thymus - schematic overview
T cell - anergy?
schematic overview
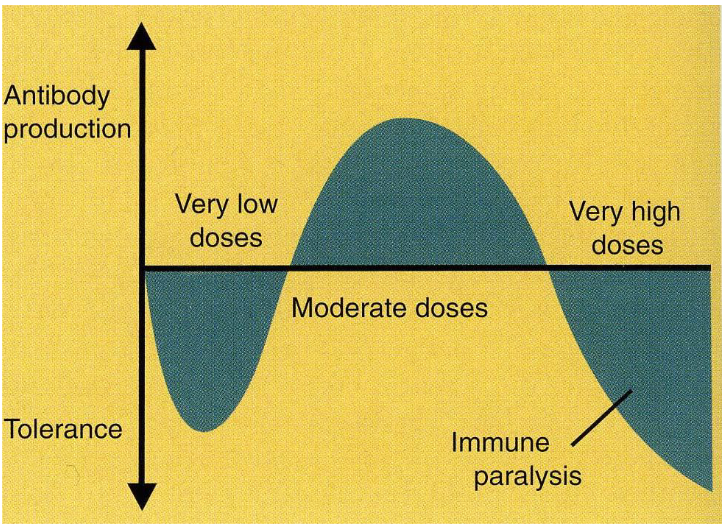
antibody production and tolerance, vs the amount of doses
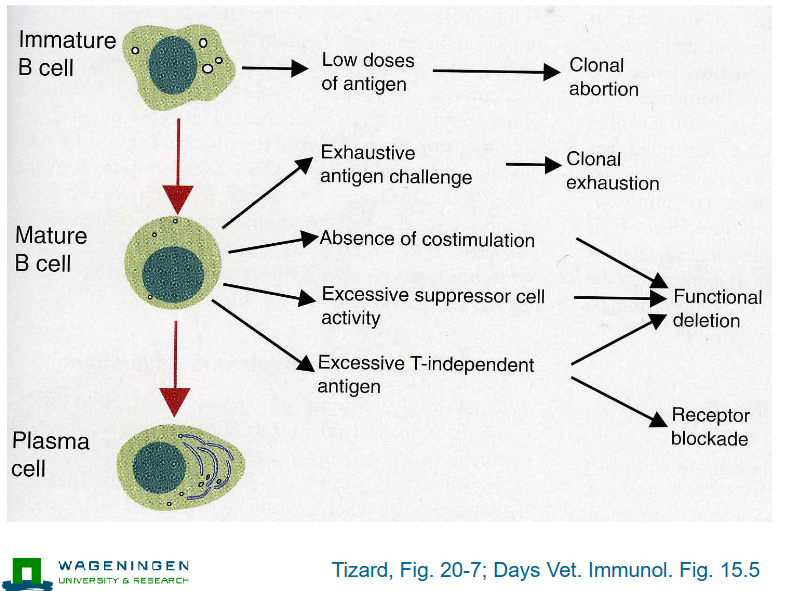
B cell and clonal abortion, clonal exhaustion, functional delection and receptor blockade
schematic overviewS
Immature B cell → Mature B cell → Plasma cell
immature cell → low doses of antigen →clonal abortion
Mature b cell → exhaustive antigen challenge → clonal exhaustion
Mature B cell → absence of costimulation, excessive suppressor cell activity, excessive T-independent antigen → functional deletion
Mature B cell → excessive T-independent antigen → receptor blockade
Antibody mediated suppresion (page 257,258 days vet)
a
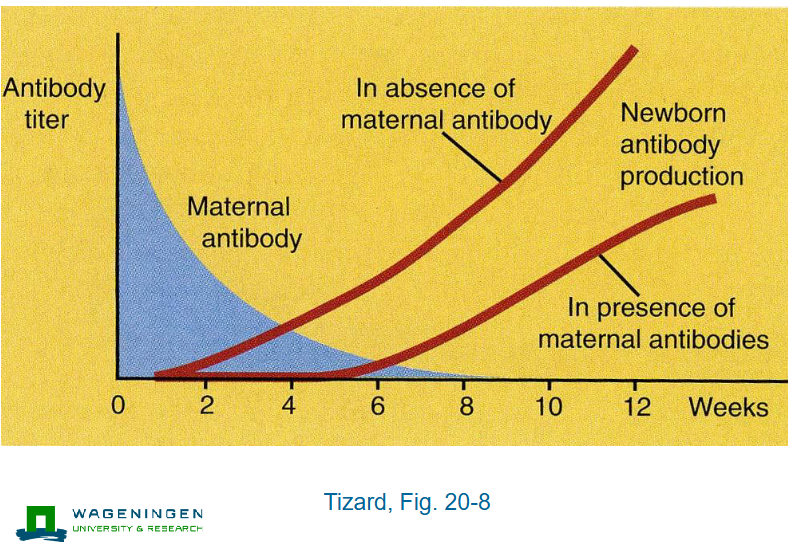
Antibody titer vs maternal antibdoy, newborn antibody production
Schematic overviewS
Negatie feedback mechanism antibodies by FcgammaRIIB(CD32b)
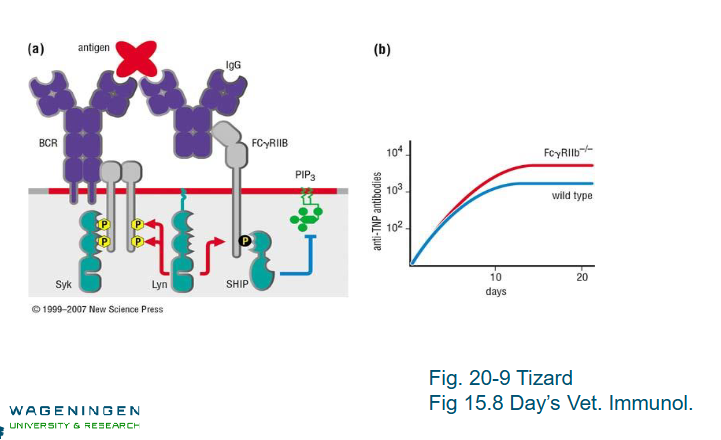
Negative feedback antibodies by FCgammaRIIB
Examples
Maternal antibodies, poor vaccination efficacy
Antibody therapy in rhesus mothers
The effect of stress on the central nervous system
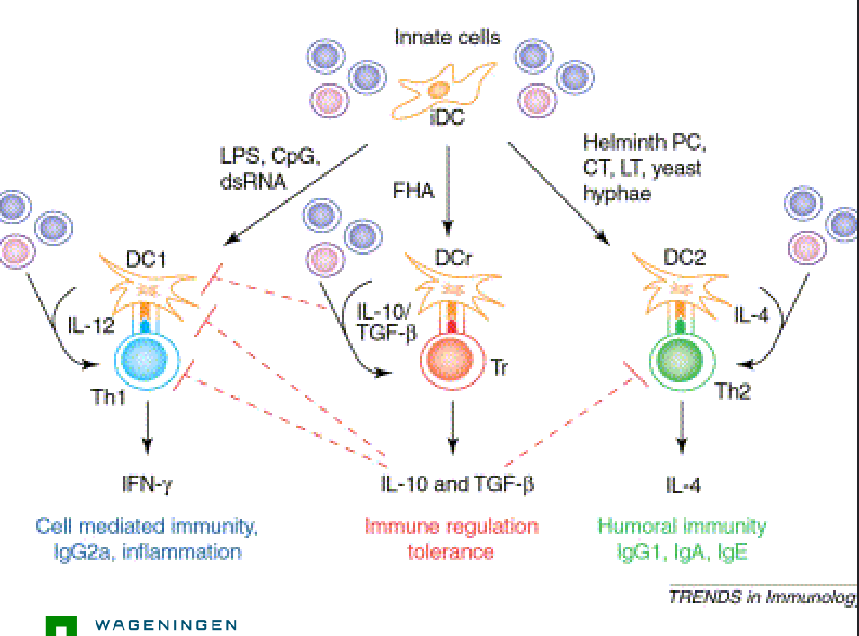
From innate cells to cell mediated immunity, IgG2a, inflamamtion and Immune regulation tolerance and humoral immunity, IgG1, IgA, IgE
Hygiene hypothesis
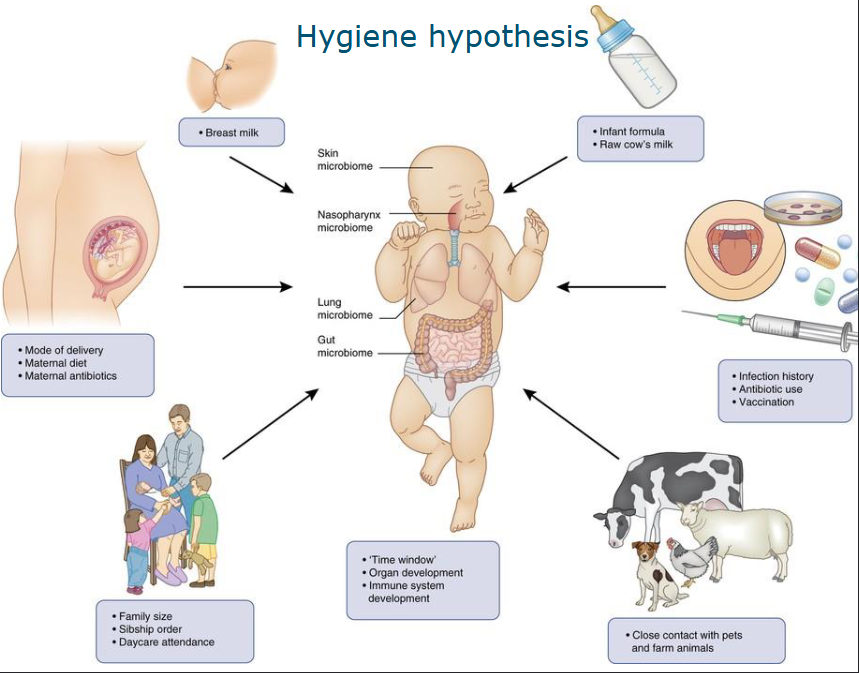
Improved hygiene hypothesis
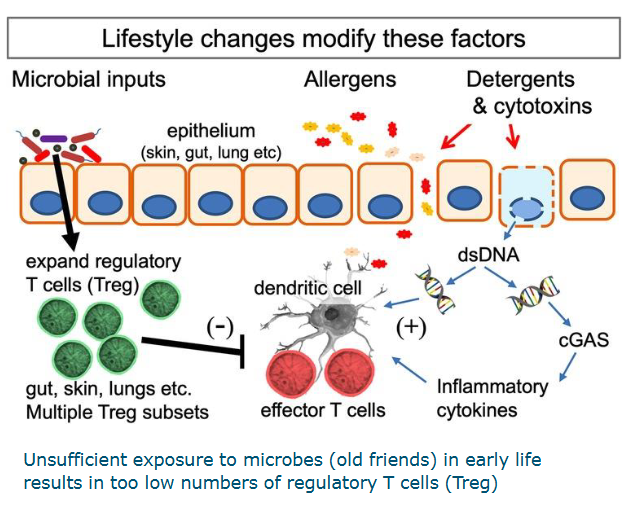
Lifestyle changes modify these factors
microbial inputs, allergesn, detergents and cytotoxins
Treg, dendiritc cells, effector T cells, dsDNA, cGAS, inflammatory cytokine
Unsufficient exposure to microbes (old friends) in early life results in too low numbrs of regulatory T cells (Treg)
Immune reactions influenced by
Environemnt
Hygiene
Genotype
Prenatal experiences
Stress
Nutrition
Physiolgoical status
Age