3.2.6 (Coordination of the cardiac cycle)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is an electrocardiogram?
A trace that records the electrical activity of the heart
What is myogenic muscle?
Muscle that can initiate it’s own contraction
What is Purkyne tissue?
Consists of specially adapted muscle fibres that conduct the wave of excitation from the AVN down the septum to the ventricles
What is the Sino-atrial node(SAN)?
The hearts natural pacemaker. It is a small patch of tissue that sends out the waves of electrical excitation at regular intervals in order to initiate contractions
What is Tachycardia?
A rapid heart rhythm
Describe where the electrical nodes and fibres are located in the heart?
The Sino-atrial node is in the left atrium
The atrioventricular node is in the septum
The bundle of hiss travels down the septum and connects further down
The Purkyne fibres connect from the bundle of hiss and are throughout the layer of muscle around the ventricles
Describe how electrical Impulses are generated and travel through the heart and cause contraction of the heart?
The Sino-atrial node generates an electrical wave of excitation
The wave travels across the atria and causes the atria to contract
The wave then reaches the AVN and the base of the atria
The base of the atria has tissue which doesn’t conduct the wave and means that the wave doesn’t travel down to the ventricles
When the wave reaches the atrioventricular node, it absorbs the wave of excitation and causes a delay of the wave which means the wave travels after about 0.1 seconds later
The wave travels down the bundle of Hiss and to the Purkyne fibres, which causes the heart to contract from the apex of the heart upwards which then
Draw and label the ECG of a healthy heart beat
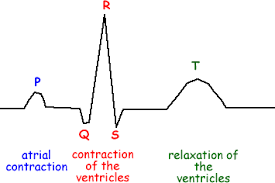
What are the 6 ECGs that we need to recognise?
Sinus rhythm(normal)
Bradycardia
Tachycardia
Atrial fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation
Ectopic heartbeat:
Premature ventricular contraction(PVC)
Premature Atrial contraction
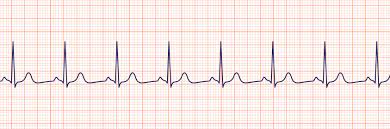
What ECG trace is this
Normal(sinus rhythm)
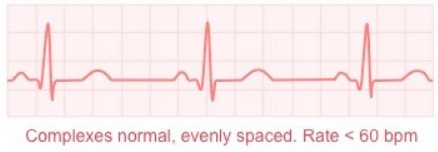
What ECG trace is this?
Bradycardia
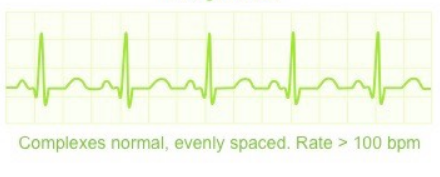
What ECG trace is this?
Tachycardia
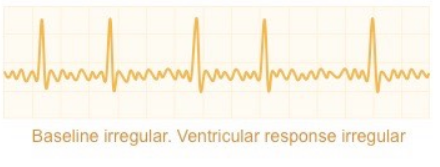
What ECG trace is this?
Atrial fibrillation
What ECG trace is this?
Ventricular fibrillation
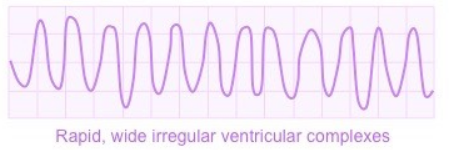
What ECG trace is this?
Ectopic heart beat: PVC
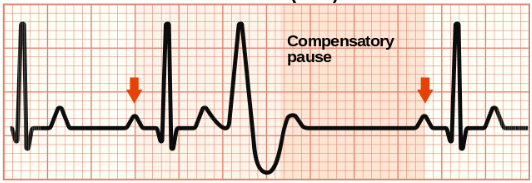
What ECG trace is this?
Ectopic heart beach: PAC
What is bradycardia, what could it be caused by and what could it cause?
It is a pattern of electrical activity that is normal but slow
It could be caused :
Good aerobic fitness
Drugs such as:
tranquilisers
Beta-blockers
It could cause:
Stagnation
Risk of blood clots
What is Tachycardia, what could it cause and what is treatment for it?
It is normal electrical activity but faster than usual
It could cause:
Little blood filling the ventricles due to short filling time leading to lack of blood reaching the body
Treatment:
Relaxation therapy
Beta-blockers
What is fibrillation, what does it cause the heart to do and what is treatment?
Fibrillation is when there is uncoordinated contraction of the atria and ventricles
It causes the heart to:
Flutter
Pump little blood
Treatment:
Defibrillator
how does a defibrillator work?
The heart is shocked with electrical signals which causes the heart to stop and stops for 5 seconds then it restarts:
It could restart with normal rhythm, fibrillation again or not restart
Is Ventricular or atrial fibrillation more serious and why?
ventricular fibrillation, this is because it causes the ventricles to quiver therefore not contracting normally leading to to the heart not pumping enough blood, which causes collapse after about 6 minutes and cardiac arrest
What is an ectopic heart beat?
This is when there is an extra or a missed heart beat