Module 9 slides
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
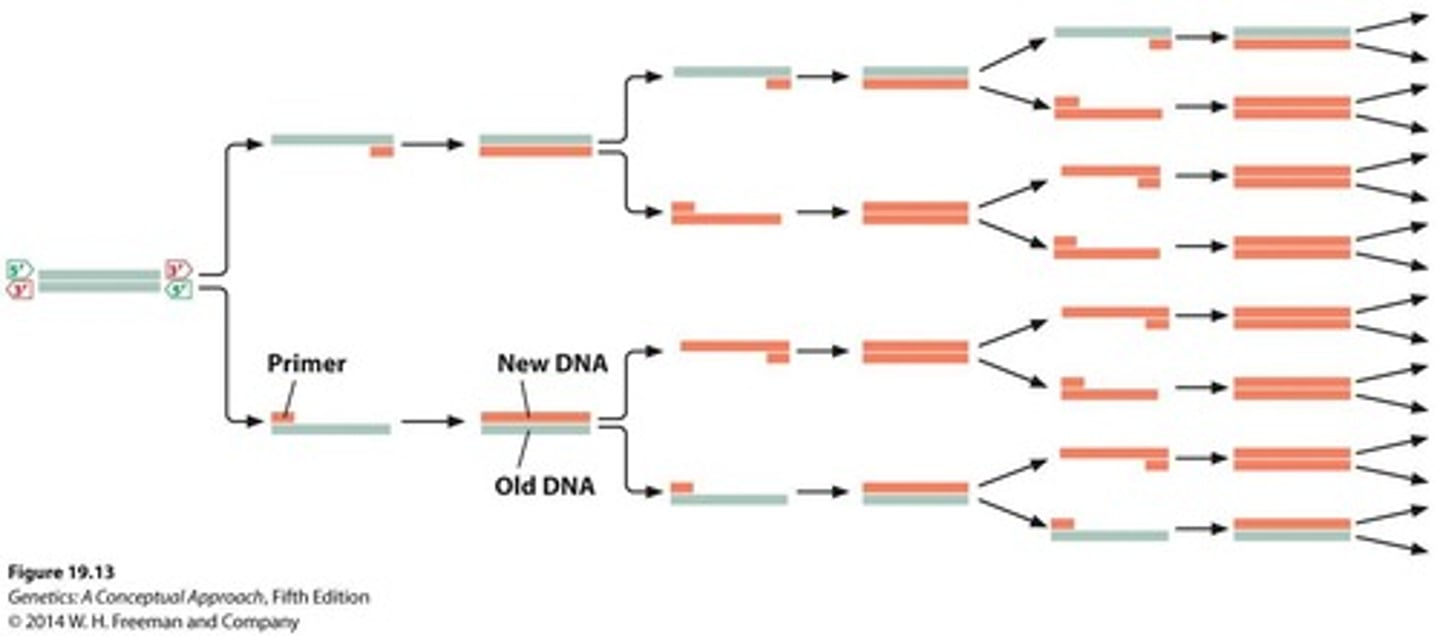
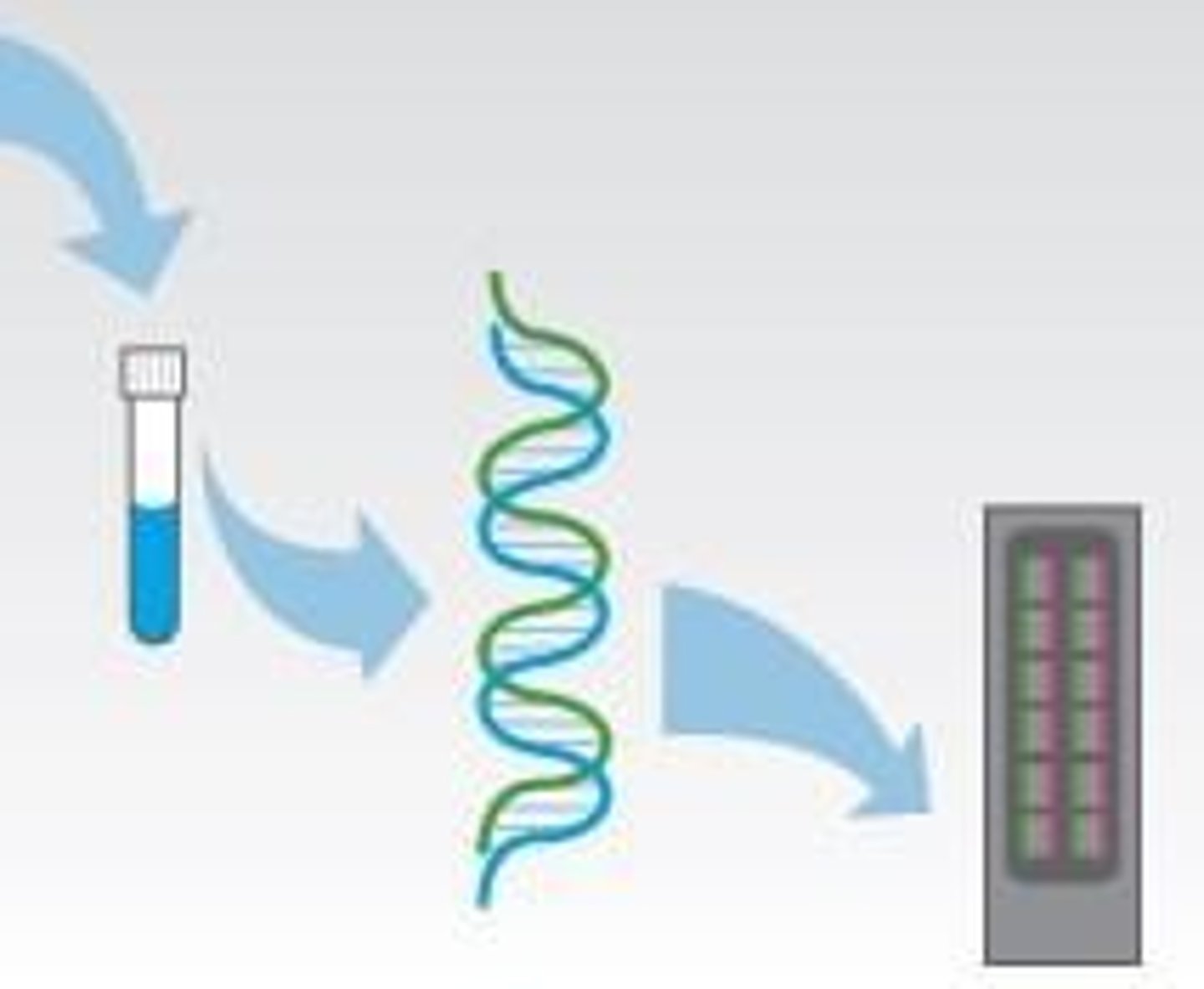
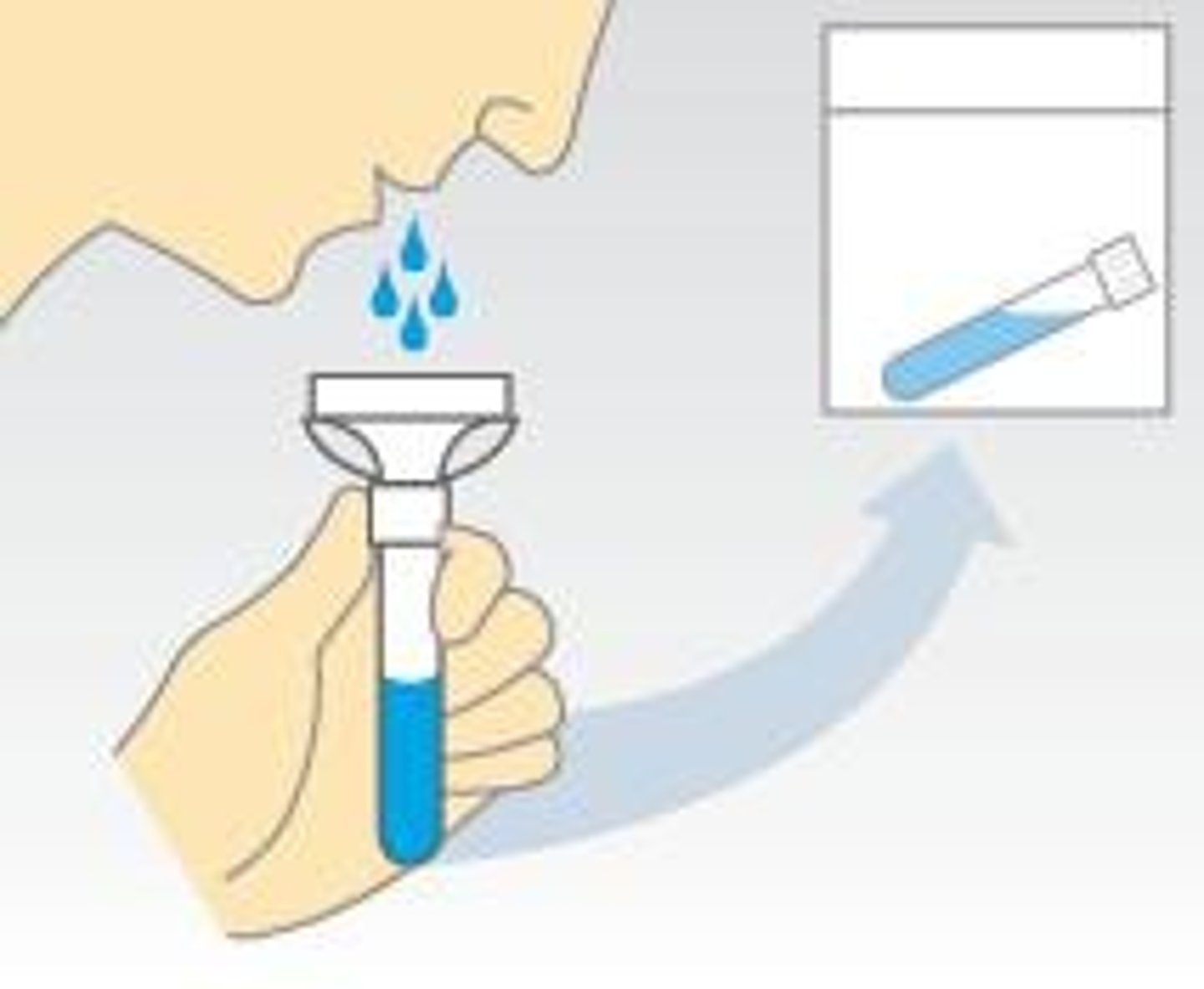
PCR
Polymerase Chain Reaction for DNA amplification.
Electrophoresis
Technique to separate DNA by size.
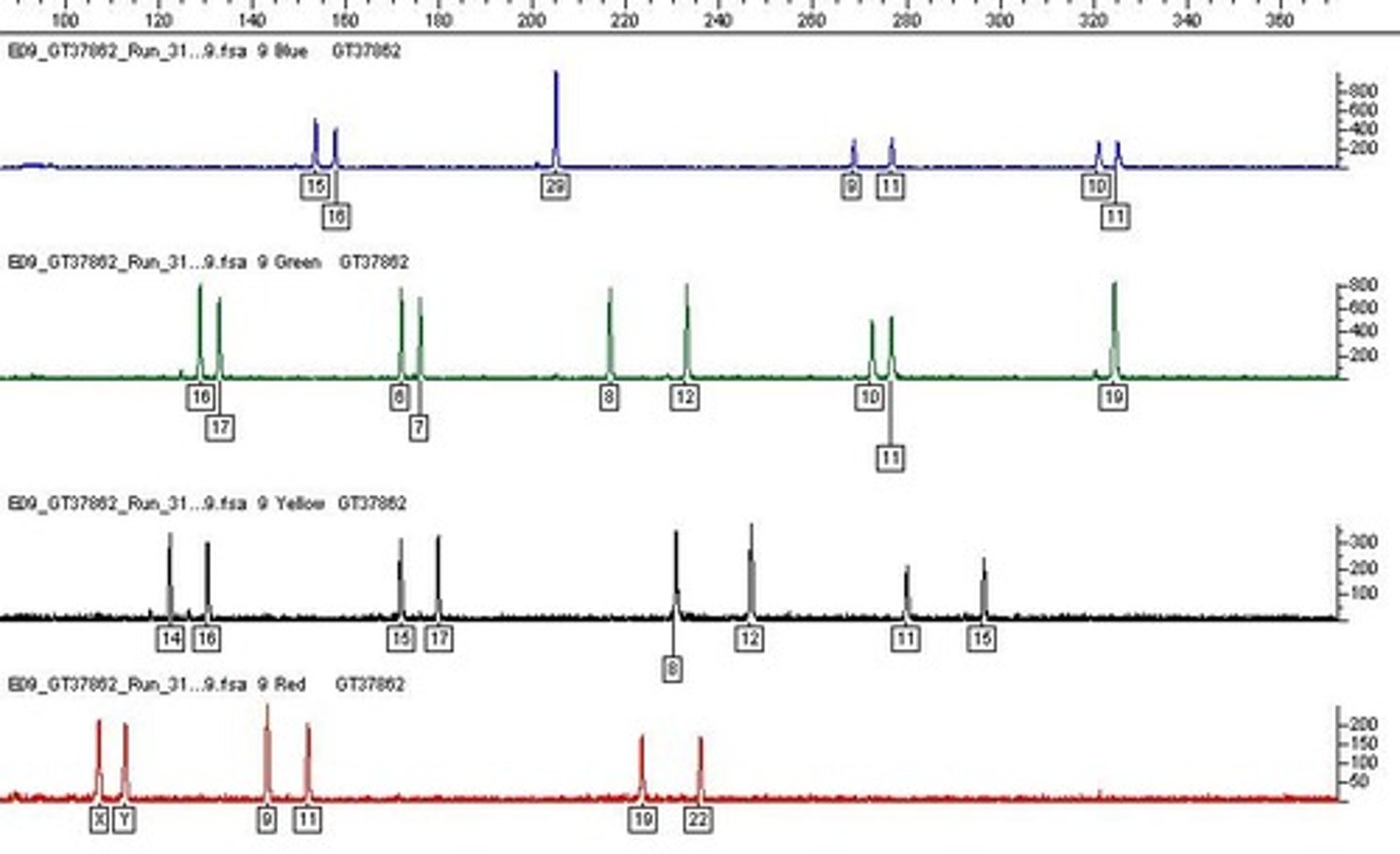
STR
Short Tandem Repeats, useful in forensics and DNA profiling
VNTR
Variable Number of Tandem Repeats in DNA.
Kary Mullis
Developer of the PCR protocol.

Denaturation
Heating DNA to 95°C to separate strands.
Annealing
Primers bind to DNA at 50-65°C.
Taq polymerase
Enzyme that adds nucleotides during PCR.
Polymorphic loci
Regions with multiple alleles for identification.
Amplification limit
PCR typically amplifies up to 2000 bp.
Contamination risk
PCR susceptible to lab DNA contamination.
Error rate
Taq polymerase has 1 in 20,000 bp errors.
Gel wells
Holes in gel for DNA sample placement.
Negative pole
Electrophoresis end where DNA is loaded.
Positive pole
Electrophoresis end where DNA migrates.
Paternity testing
Determining fatherhood using DNA analysis.
Allele length
Length variations in DNA segments define alleles.
Perfect match
Exact allele match indicates potential identity.
Exclusion criteria
Rules out suspects based on DNA mismatch.
Microsatellite regions
Short repeating sequences in DNA.
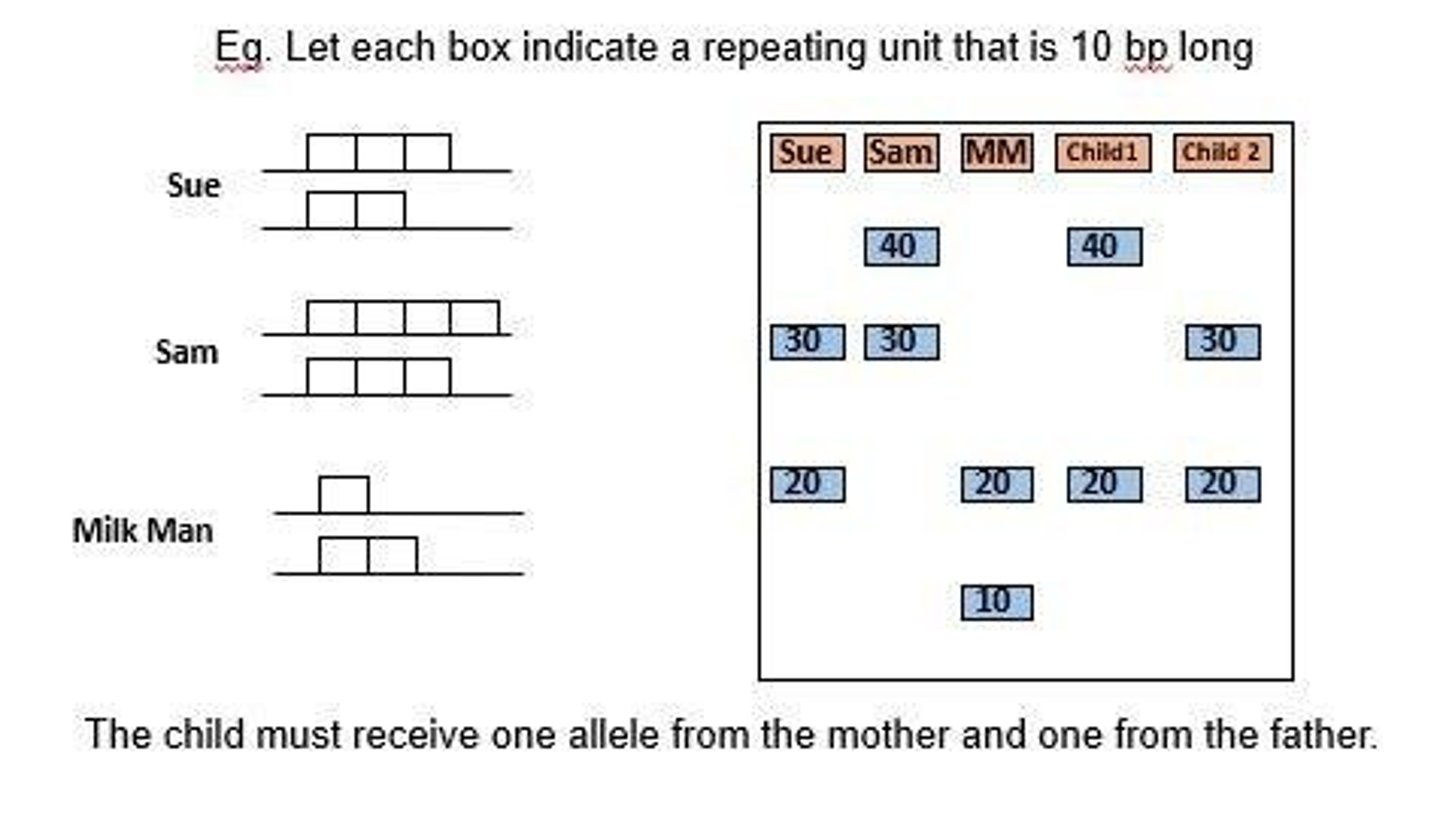
Practice problem
Exercise to determine possible fathers using STRs.
Ethical issues related to forensic testing
Concerns surrounding forensic DNA testing practices.
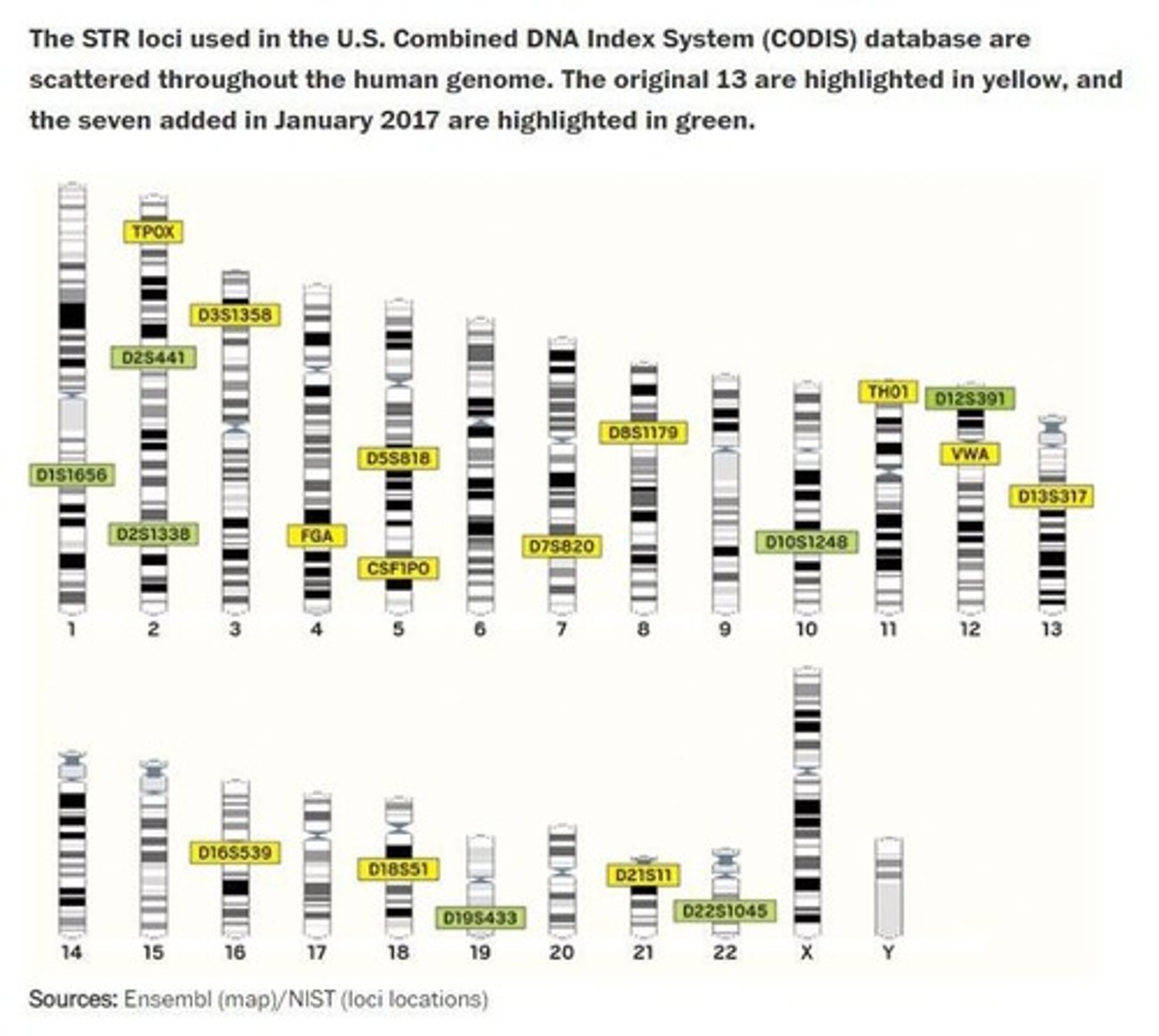
CODIS
Combined DNA Index System for forensic identification.
Innocence Project
Organization that exonerates wrongfully convicted individuals.
Familial DNA Searching
Identifying relatives of DNA profiles in databases.
Ethical Issues in DNA Testing
Concerns about privacy versus crime-solving effectiveness.
Polymorphic Characteristic
Variability in DNA regions among individuals.
Product Rule
Probability calculation for independent genetic loci.
DNA Database
Collection of DNA profiles for law enforcement.
Capillary Electrophoresis
Technique for separating DNA fragments by size. Uses narrow bone capillary tube instead of gel
STR Assay
Test amplifying multiple STR loci simultaneously.
Partial Match Data
Using incomplete DNA profiles for investigations.
Ethical Conflict in DNA Testing
Balancing crime resolution and individual privacy rights.
SNP
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism, a genetic variation.
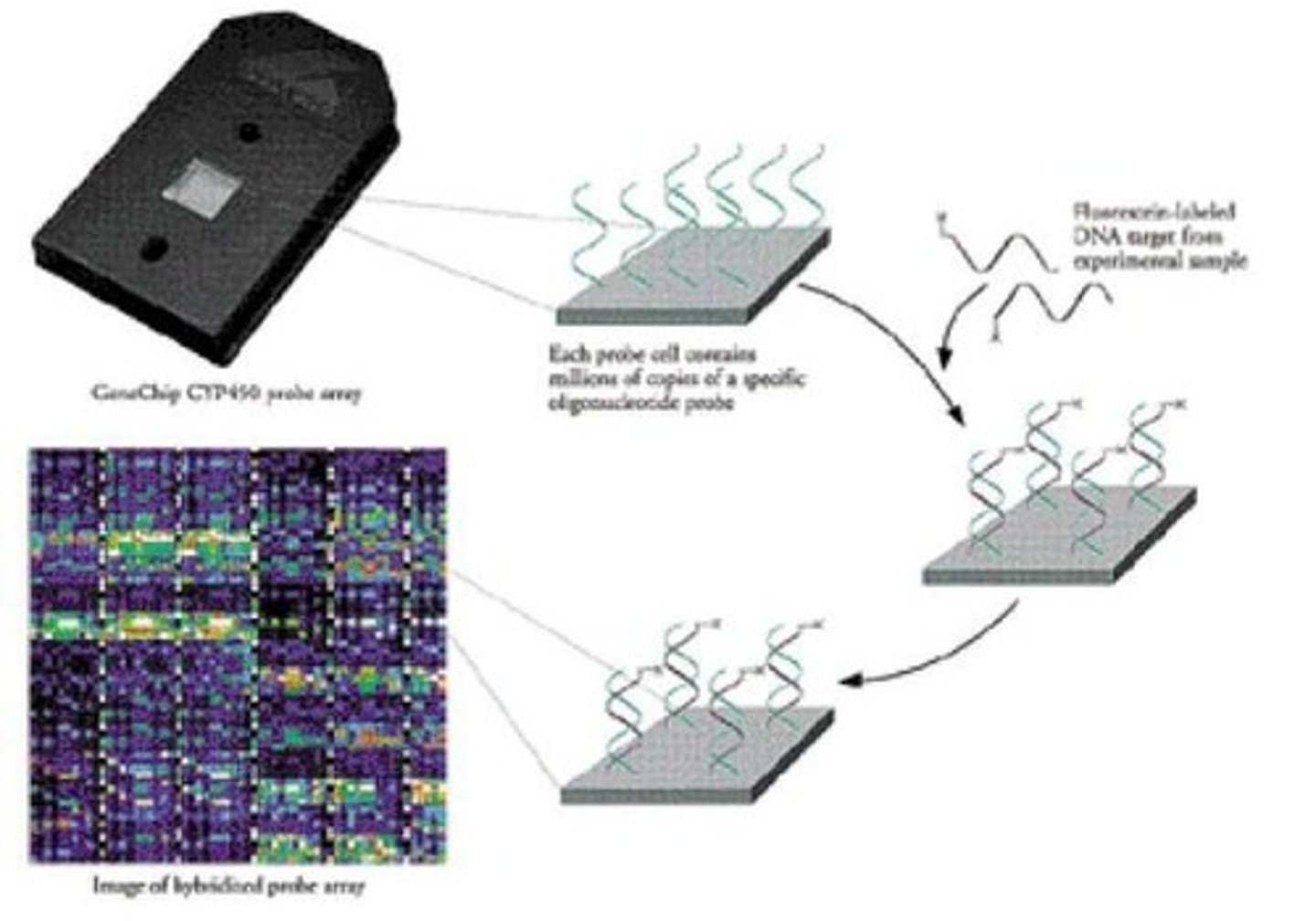
Gene Chips
Microarrays for identifying patient genotypes.
Ecogenetics
Study of genetic variation affecting chemical responses.
Safety/ guideline Standards in Genomics
Guidelines for diverse genetic backgrounds in medicine.
GINA defintion
Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act protecting genetic data.
Loci
Specific locations on chromosomes for genetic markers.
Alleles
Different forms of a gene at a locus.
DNA Sampling Warrant
Legal requirement for collecting DNA samples.
Genetic Testing Importance for helping with
Crucial for personalized medicine and health assessments.
Crime Scene DNA
DNA collected from locations of criminal activity.
DNA Profile Hits
Matches found between DNA profiles in databases.
SNPs
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms, genetic variations at one base.
Haplotype
A sequence of SNP patterns on a chromosome.
tagSNPs
Few SNPs identifying a larger haplotype.
SNP density
100,000 SNPs can identify most human haplotypes.
Gene Chip
Microarray technology for SNP detection.
SNP probes
Short DNA sequences on a chip for matching.
Association Studies
Correlate SNP presence with genetic disorders.
Correlation vs. Causation
Correlation does not imply direct cause.
risk of exposure to a chemical depends on the genetics involved in
transport of chemicals influenced by genetics, metabolism of the chemical, and excretion of the chemical
parathion
common pesticide is broken down into a toxic chemical paraoxan.
Paraoxonase
Enzyme detoxifying paraoxan from pesticides.
RR genotype for paraoxan
Detoxifies paraoxan 10 times faster than QQ. Since RR is dominant.
Pesticide Sensitivity
Varied responses to pesticides based on genetics.
Genotype Frequency
Distribution of genotypes within a population.
African Americans QQ frequency for pesticides
Approximately 10% have QQ genotype.
Latino Americans QQ frequency for pesticides
Approximately 35% have QQ genotype.
Caucasian Americans QQ frequency for pesticides
Approximately 47% have QQ genotype.
Safety Testing Implications
Genetic differences affect safety testing outcomes.
Drug Sensitivity
Variability in drug metabolism among individuals.
Suxamethonium
Short-acting muscle relaxant; recovery varies by genetics.
Autosomal Recessive Condition
Requires two copies of mutated gene to express.
Precision Medicine Initiative
2015 effort to personalize medical treatment based on genetics.
Patient Privacy
Confidentiality of patient data in medical research.
Tamoxifen
Breast cancer drug reducing recurrence and mortality.
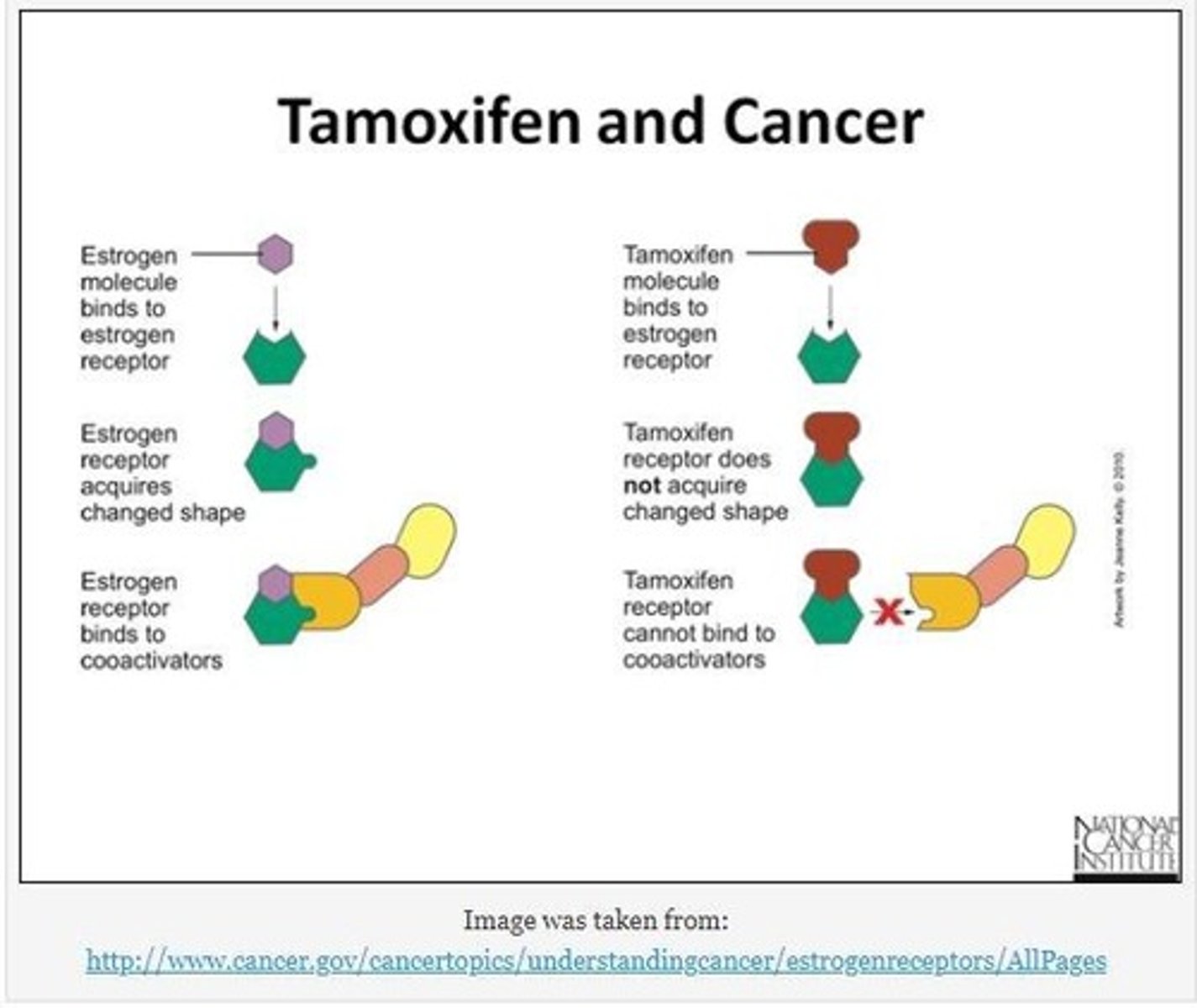
CYP2D6 Gene
Gene affecting tamoxifen metabolism rates.
Tamoxifen Metabolism
Varies among women, influencing treatment effectiveness.
Alleles and drug use
Different forms of a gene, affecting drug metabolism.
Phenotypes
Observable characteristics resulting from genetic variations.
Warfarin
Blood thinner with significant dose variability.

CYP2C9 Gene
Gene encoding enzyme for warfarin metabolism.
VKORC1 Gene
Gene influencing warfarin's therapeutic dose.
Direct to Consumer Testing
Genetic tests marketed directly to consumers and how Genetic tests available without physician involvement.
SNP Probes
Used to identify genetic variations in testing.
Ancestry.com and 23 and Me
DTC testing service costing approximately $99.
DTC testing for ancestry and limited health info.
Genotype
Individual's genetic makeup influencing treatment response.
Informed Consent
Patient's agreement after understanding risks and benefits to test outcomes.
Healthcare Provider Education
Training necessary for understanding precision medicine.
Data Analysis Tools
Developed for managing large medical datasets.
FDA Oversight
Regulation ensuring safety of drugs and tests.
Recurrence Risk
Increased likelihood of cancer returning post-treatment.
SNP Patterns
Common genetic variations in specific populations.
BRCA1 Mutation
A genetic alteration increasing cancer risk.
Ethical Questions in Genomics (genetic info)
Concerns about genetic information usage and access.
GINA
Protects against genetic discrimination in health insurance.
GINA Provisions
Insurance cannot alter coverage based on genetic tests.
GINA Employment Protections
Employers cannot discriminate based on genetic test results.
Genetic Testing Requirements
No mandatory genetic testing by insurers or employers.
Racial Disparities in DNA Databases
Concerns about bias in genetic data collection.
Genetic Counseling
Support for understanding genetic diseases and risks.
Genetic Counselor Responsibilities/ role. what do they do
Gathering medical histories and assessing genetic risks.
Patient Education
Informing patients about disorders and inheritance patterns.
Informed Decision Making
Empowering patients to make choices about their care.
Non-Directive Counseling
Counselors provide options without imposing decisions.
Psychological Support
Emotional assistance during genetic counseling sessions.
Screening Test
Identifies potential genetic disorders in asymptomatic individuals. estimates risk of genetic disorder.
Diagnostic Test
Confirms the presence of a genetic disorder.