IB Global Politics HL -- 2022-24
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Positive Peace
Attitudes, institutions, and structures that create and sustain peaceful societies
Negative Peace
The absence of violence, war or fear of violence.
War by Proxy
Wars being fought using third-parties
Realism
The belief that world politics is a struggle between states who act out of pure self-interest.
They believe that the only way to peace is through a balanced distribution of power globally across states.
Main focuses: military power, defence, economy
Classical realism
A subtype of realism that believes absolute power is the ultimate goal which states work towards.
Structural realism
A subtype of realism which sees power as a means to an end, the end being survival and outlasting other states.
2 further subtypes:
(1) Offensive: States pursue as much power as possible, they pursue hegemony (dominance)
(2) Defensive: Too much power will be punished, the pursuit of hegemony is selfish and ultimately self-destructive.
Liberalism
A theoretical perspective that emphasises interdependence and cooperation between nations.
Main focuses: soft power, international law, globalisation
Pillars of Positive Peace
- well-functioning government (stability, economic/social growth + development)
- equitable distribution of resources
- free flow of information
- good relations with neighbours
- high levels of human capital
- acceptance of the rights of others
Conflict
The dynamic process of actual or perceived opposition (over positions, interests or values) between individuals and/or groups.
Galtung: 'actors in pursuit of incompatible goals'
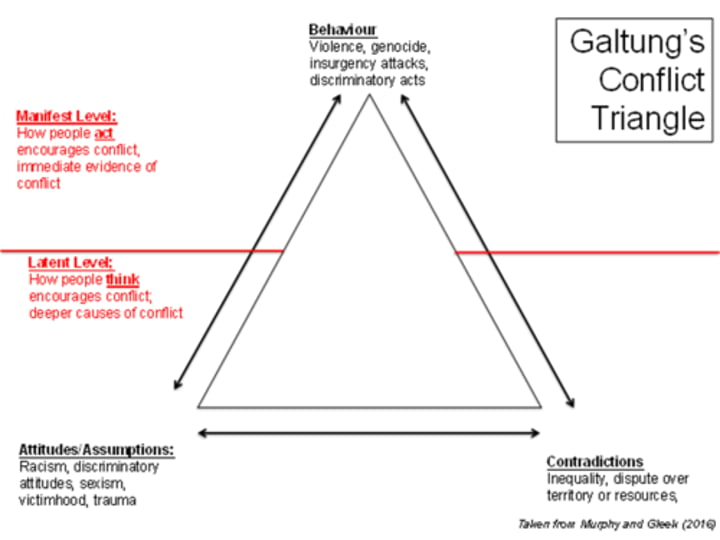
Non-violent conflict
When groups disagree in peaceful ways
- Legit structures are in place for dialogue + communication
- Parties are dependent on each other
- Violence is against the best interests of both parties
Violent conflict
Direct violence i.e war
- Lack of trust on both sides
- No means to peaceful discussion, negotiation
Power
The ability to effect change and, rather than being viewed as a unitary or independent force, is as an aspect of relations among people functioning within a social organization.
Hard power
Military force, direct aggression, economic sanctions
(Its use will affect one's ability to use soft power)
Smart power
Diplomacy, aid, persuasion, negotiation
Soft power
Outreach, cultural ties, political values, foreign policies
(More attractive to liberal governments, values trust + credibility, easy to break)
Violence
When physical, mental or other types of harm are inflicted by an individual/group unto another
Direct violence
Direct, physical, aggressive violence
i.e killing, raping, torture
Straightforward, possible to investigate and seek justice, most visible
Structural violence
harm inflicted via institutions by government or authority figures
i.e denial of basic human needs, unequal access to opportunities/resources
Conscious choice, denial of basic human rights, widespread but unchallenged, hard to investigate + measure
Cultural violence
violent mindsets/stereotypes present within the beliefs and values of a community
i.e FGM
Embedded in all levels of society, prominent social norms that 'justify' violence, harder to eliminate, government- or society-driven
Misconceptions of conflict
Conflict is caused by a single factor
Conflict parties are (rational) military parties
Conflict is always visible
Conflict is always undesirable
Conflict always needs to be settled
Conflict always requires third-party intervention
Interstate conflict
Conflict between state actors, not necessarily within one's borders i.e WWI, WWII
Intrastate conflict
Conflict between a state and non-state actor within borders i.e civil wars
Extrastate conflict
Conflict between a state and non-state actor outside of borders i.e Afghanistan (NATO v Taliban)
Substate conflict
Conflict between non-state actors not within borders
Types of conflict
TERRITORIAL CLAIMS
IDEOLOGICAL CONFLICT
IDENTITY CONFLICT
INTEREST-BASED
Just War Theory
A doctrine that provides criteria to judge the justifiability of war
(1) RIGHT TO GO TO WAR (JUS AD BELLUM) → purpose of going to war
(2) RIGHT CONDUCT IN WAR (JUS IN BELLO) → moral conduct within war
(3) ENDING WA WAR (JUS POST BELLUM) → post-war settlement & reconstruction
Types of power
MILITARY
Hard power → force, aggression, fear, harm
Soft power → humanitarian aid, rescue efforts
Other factors → GDP, expenditure, army size, nuclear weapons
ECONOMIC
Hard power → economic sanctions, military funding
Soft power → investment, trade
SOCIO-CULTURAL
Soft power → popular culture, foreign/domestic policies, globalisation, public perception
CYBER
Hard power → State secrets, cybersecurity, modern challenge to state power
Ingroup/outgroup theory
(Sears, Huddy & Jervis)
Individuals amplify similarities with ingrou pand differences with outgroup
This phenomenon happens naturally, but has been enhanced with social media
Hostility → discrimination, dehumanisation, conflict, cultural violence
Greed v Grievance
Greed → desire for more (status, power, wealth)
Grievance → rebellion over identity (religion, ethnicity)
Collier-Hoeffler Model (2005): Factors → Availability of finance / Cost of rebellion / Military advantage
(Brown, 1996): Factors → (1) Structural (ethnic groupings, weak states) (2) Economic / social (3) Political factors (4) Cultural, perceptual factors (discrimination, historical context)
Territorial conflict
conflict over possession of natural resources or caused by nationalism
often seen in the aftermath of nationalism
(1) Border disputes (2) Occupied territory
Interest conflict
(Perceived) competitive interests
→ weapons, discrimination, corporate v environmental
Identity conflict
Animosity between groups on grounds of religion, race, gender, etc.
Key variables → different groups, degree of homogeneity (not diverse places) / heterogeneity (diverse places)
(Lipset & Rokkan) state 4 possible causes:
(1) Workers v Owners
(2) Geographic centre v periphery sub-gorups
(3) Urban v rural population
(4) Church v state
Cleavage
Historically determined social or cultural divide
Sovereignty
A state's ability to rule themselves, when an authority has supreme control over what happens within one's borders
Nation
Sovereign acting with the consent of the people
Based on people, culture, history, territory, national identity
State
Sovereignty defined by lines of a map/border
Government and institutions
Nation-state
Where nation and state represent the same thing
Sovereign Nation State
SOVERIEGN NATION STATE
(defined by the 1933 Montevideo Convention)
(1) Permanent population
→ affected by refugees, migration, insurgency
(2) Defined territory & borders
→ affected by oceans, islands, geographical changes
(3) Effective government
→ affected by effectiveness, accountability, inclusiveness
(4) Capacity and legtiimacy to enter relations with other states
→ affected by religion, national history, societal/cultural differences, economy/trade
Internal sovereignty
States governing themselves independently
States having full responsibility and power within one's borders
External sovereignty
How states interact with and respect other states and IGOs
Authoritarianism
Classified by:
Rejection of political plurality
Strong, central power
Reduction in Rule of Law
Reduction in Seperation of Law
No, limited or significantly flawed democratic voting
less civil liberties, more control over media (intimidation, suppression, assassination)
Types of third-party involvement
6 types (Fisher & Keashly, 2011)
(1) Conciliation → 3rd-party provides communication link to identify issue, encouraging direct intervention/negotiation
(2) Consultation → 3rd-party works to problem-solve
(3) Pure mediation → 3rd-party facilitates negotiation (persuasion, reasoning, control of information, suggestion)
(4) Power mediation → Facilitate agreements through use of threat, leverage or coercion, rewards/consequence
(5) Arbitration → 3rd-party considers merits of both parties and imposes what they perceive as 'fair settlement'
(6) Peacekeeping → Monitoring of ceasefire or other agreements, providing military personnel/humanitarian aid/etc.
Arms embargoes
Restriction or sanction on arms
USE: to show disapproval of certain actions, maintain neutrality by not escalating conflict
ENFORCEMENT: control on transport/trade, restrictions on licensing
EFFECTIVENESS: can be restricted completely or selectively, may worsen conflict if one party gains upper hand
Financial freeze
Restrictive measures or sanctions against entities so that funds are not directly accessible
ENFORCEMENT: Monitored by special committees, blocking of trade routes, interpol intervention
EFFECTIVENESS: Can block access to funds required within conflict party
Trade limitations
Restrictions on trade of goods/services
USE: coercion, punitive action, persuasion, show of disapproval, political message
ENFORCEMENT: UN or other IGO resolutions, blocking of trade
EFFECTIVENESS: could affect citizens
Responsibility-to-protect (R2P)
Commitment made by states to UN (2005)
States forego the right to 'full sovereignty' should they fail to protect rights from genocide, ethnic cleansing, etc.
Advantages of R2P
Moral → creates moral obligation, respects human rights
Legal → justification of 3rd party intervention
Disadvantages of R2P
Can be abused
May be misinterpreted
Legal basis is lacking
Traditional legitimacy
Legitimacy derived from historically-accepted, traditional system
Charismatic legitimacy
Legitimacy derive from charisma, popularity and pscyhologically-dominating leader
Generally reliant and centered around leader, weak politically and in administrative instutions
Rational-legal legitimacy
Public trust in government to act with respect to public interest and societal laws
Peacekeeping
Negative peace → allows for further negotiation, discussion
Aim: create space for negotiotion, discsusion over violence
Methods: ceasefires, treaties, armistices
At this stage, the original cause is not yet resolved
Organs of UN for peacekeeping → Sec-Gen, UNSC, GA
Peacemaking
May require 3rd party involvement
Negotiation stage for truce
Aim: prevent escalation, sustain negative peace to create positive peace
Methods: mediators, task forces
Ideal mediator
impartial, has more influence relative to conflict parties, focus on underlying needs, has incentive to reach an agreement, creative approaches
Peacebuilding
Building of long-term, sustainable, positive peace
Aim: resolve injustice in nonviolent ways
Methods
- Conflict management
- Disarmamament
- Demobilisation
- Reintegration
- Preventing visible extremism
Truth and Reconciliation Commissions (TRCs)
Expose + investigate crimes of those involved in conflict
Promotes forgiveness and understanding over punishment and recrimination
Restorative rather than retributive
Successful TRCs: South Africa, Sierra Leone
Success came from reliance on religion, strong belief in forgiveness, total rehaul of government, conscious rebuilding
Social movements
An organised effort by a large group of people to achieve a goal, typically social or political
A collective group of people bonded by a socio-political issue against another group of people
Causes of social movements
Political; changes in government (elections, agenda), new legislations, landmark cases
Economic; recessions, media
Social; case-by-case
Psychological; influence by foreign groups/entities
Stages of social movmenets
emerge → coalesce → bureaucratise → success/failure/repression/mainstream/cooptation → decline
Alternative social movements
Movements advocating for self-improvement of individuals i.e Alcoholics Anonymous, MADD, Planned Parenthood
Redemptive social movements
Movements advocating for total change of individuals i.e Civil Rights
Reformative social movements
Movements advocating for changes to specific aspects of society i.e Buy Nothing Day, environmentalism
Revolutionary social movements
Movements calling for complete overhaul of society
Mass Society Theory
With industrialization and subsequent social changes, people have become isolated and alienated (Kornhauser)
Relative Deprivation Theory
People satisfied in their current lives are less inclined to participate in social movements
Resource Mobilisation Theory
Success of social movements rely on capacity and competency in utilising resources
Rational Choice Theory
assumes that all individuals have preferences and will pursue their best interests
Informal forums
Platform for world leaders to meet and discuss matters of global importance outside of institutions i.e G7, G20, BRICs
Global Governance
A coordinated effort of state, regional, int'l actors to manage global affairs. The process comprises of discussion and consensus-forming between actors in order to produce guidelines that encompass all involved and better the situation