11.1- Economic Growth
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Define short run economic growth
What can cause SR economic growth
An increase in the amount of goods and services produced stemming from something other than more FOP
Could occur from SRAS increasing (Reduction in costs or Increase in productivity)
Could occur from an AD increase
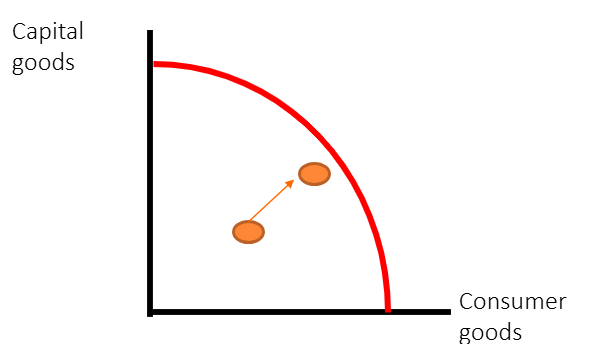
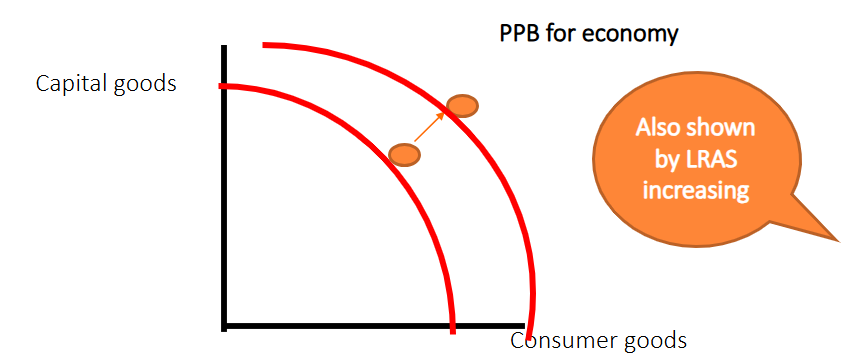
Define long run economic growth
An increase in an economies productive capacity after increased FOP
This is can be also explained by LRAS increasing
Will economic growth always cause an increase in living standards`
No - if population increases faster living standard will fall
No - If there is a large income/ wealth inequality then living standards will not increase
What will cause supply side growth
Changes in SRAS or LRAS (costs falling, productivity improvements, better FOP (quality and quantity)
Non-inflationary
What will cause demand side growth
Factors of AD increasing (C + I + G + (X - M))
Will be inflationary unless economy is operating below full capacity before the growth
Name each section of the Business/ Economic cycle
Boom, Recession, Slump, Recovery
Describe what occurs in an recovery - 4 main details
Output and employment begin to increase
Consumption increases as consumers have more disposable income - Multiplier
Firms begin to use their spare capacity
Business confidence increases, increase investment - accelerator starts
3 Advantages of a boom
Business and consumer confidence is very high
Very high levels of demand
Increased levels and production and output
Investment is high due to high confidence in the economy
3 Drawbacks of a boom
Skilled workers already employed and so there is a lack of skilled workers in the labour market so to attract more firms increase wages - this leads to inflation
Goods and services are in higher demand and so become scarce - inflation
Interest rates are increased to keep down inflation - more saving less spending
Wage price spiral
UK goods are not competitive with alternatives
Purchasing power diminishes as imports increase - due to more income
What does it mean for a countries goods to be competitive
A countries ability to produce and sell goods and services in international markets
What can increase a countries competitiveness
Price competitiveness - lower inflation will increase competitiveness, Higher productivity lower costs per unit lower price, Better infrastructure lowers production and distribution costs - lower prices
Non-price competitiveness - Focuses on quality, brand reputation and innovation
Benefits of competitiveness
Higher Exports: Competitive goods are more likely to be exported
Increased standard of living - increased consumer choice, lower prices
Characteristics of a recession
Increased FoP costs from Boom eats into profit so firms invest less
Income and output starts to fall as firms can’t keep on employing expensive workers leads to high levels of spare capacity. Leads to businesses closing as costs too high or mergers/ takeovers
Confidence falls
Wealth falls - wealth effect further decreases consumption
Inflationary pressure falls as there is less demand and spending
Characteristics of a slump
Low production, so lots of spare capacity
Unemployment rises as firms close or cut back on workforce due to small demand
Low inflation - possibly deflation as goods and services are in low demand
Low interest rates to get spending going
As confidence is low, investment is low (Low demand for capital, capital price falls) however low price of capital will encourage investment due to potential for returns - brings around recovery
Prices falls so goods become price-competitive with foreign goods - higher demand, higher exports
What is an output gap
Where GDP differs from Capacity or trend level of GDP
Can be shown in classical by equilibrium being different to LRAS
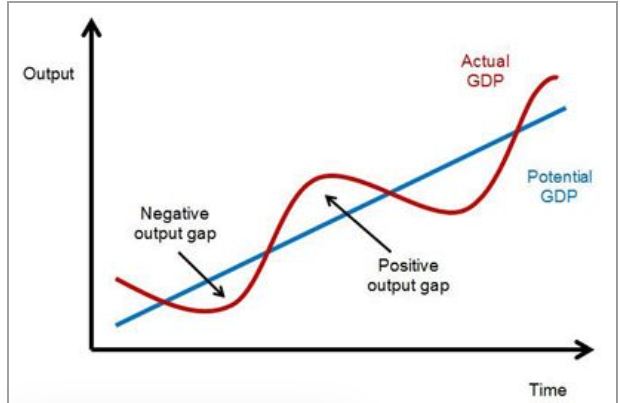
What effects does a negative output gaps have on the economy
Downward pressure on inflation,