Lids III: Infection and inflammation
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is blepharitis?
inflammation of eyelid margins
extremely common
chronic /relapsing
typically bilateral (both eyes)
itis= inflammation
belpharo - lids
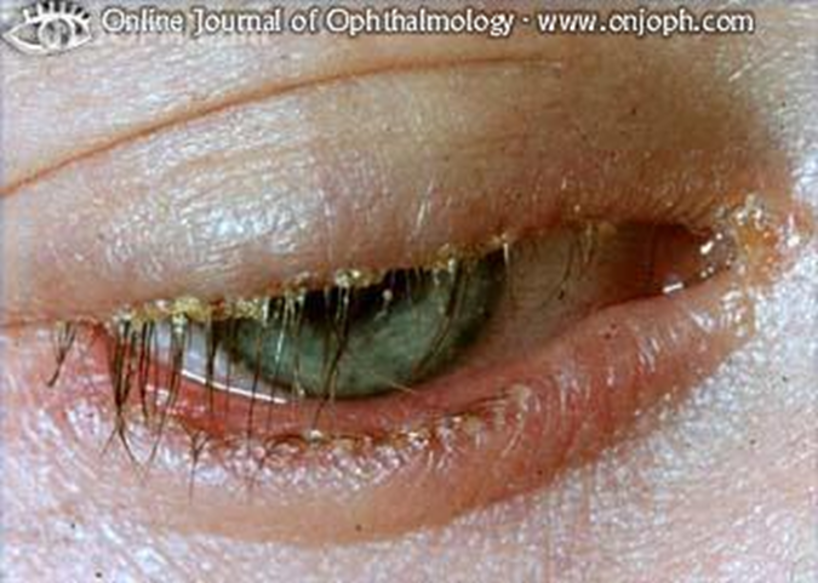
what are the predisposing/risk factors for blepahritis?
seborrheic dermatitits (dandruff)
ocular rosacea —> skin condition effecting checks , nose and eyes
long term Contact lens wear
topical eye medication (glaucoma)
demodex - hair mite follicle
what glands are involved in anterior blepharitis ?
> Zeiss + Moll
anterior blepharitis occurs where eyelash follicles are (base of eyelashes)
what glands are involved in posterior blepharitis?
> meibomian glands
what is the aetiology for anterior blepharitis?
> Bacterial - staphylococcal
> Sebhorrheic —> excess lipid - Gland of Zeiss
> demodex - mite
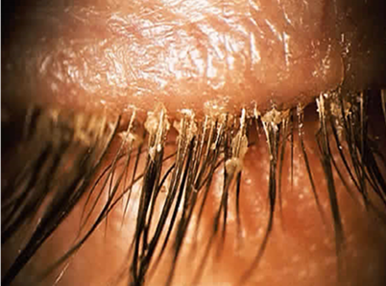
what is the aetiology for posterior blepharitis?
> Meibomian gland Dysfunction
MGD - thickened secretions which block duct
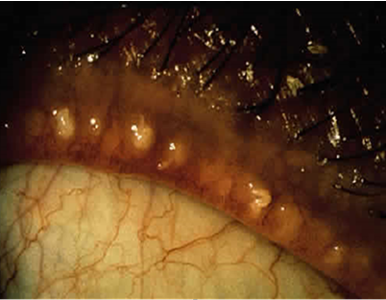
How are the symptoms of blepharitis?
similar in all types
very variable
chronic (months-years)
doesn’t always correspond well with signs
What are the symptoms of blepharitis
ocular discomfort
soreness
burning
itching
grittiness
photophobia
CL intolerance
what are the signs of anterior blepharitis - bacterial ?
Bacterial - staphylococcal —> most common cause of blepharitis
crusting/collarettes/scales - yellow deposits at base of lashes
talengiectasia (dilated blood vessels)
lash misdirection/loss
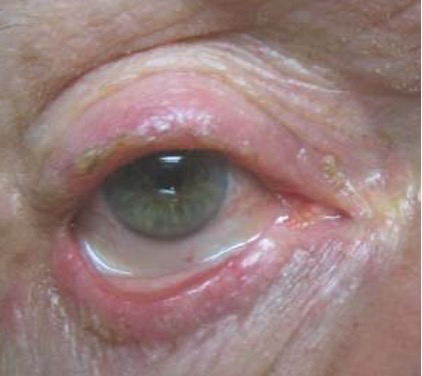
what are the signs of anterior blepharitis - seborrheic ?
seborrheic (gland of Zeiss): associated with seborrheic dermatitis - dandruff
→ disease of sebaceous gland
greasy deposits at base of lashes
associated with dermatitis rosacea
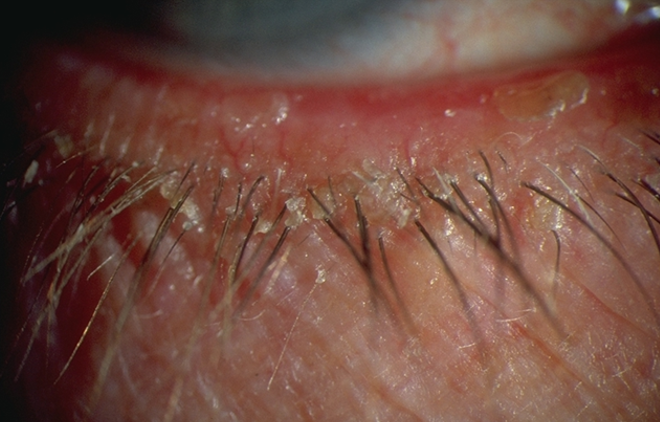
what are the signs for anterior blepharitis - demodex?
less common, very itchy
demodex:
cylindrical deposits extending up lashes
lash misdirection/loss , general redness
itching
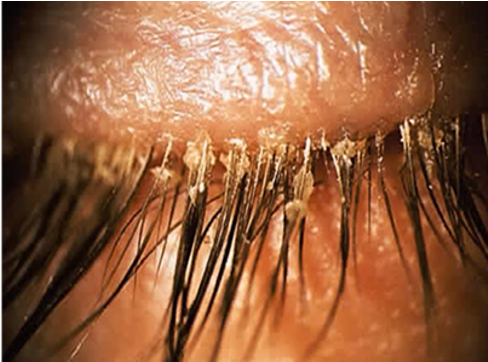
what are the signs of posterior blepharitis?
thickened meibomian secretions
microliths - plaques
meibomianitis - passive retention of secretions (chalazion, styes)
foam in tear meniscus
unstable tear film -evaporative tear deficiency
—> meibomian glands secrete oily lipid layer of tear film so reduced
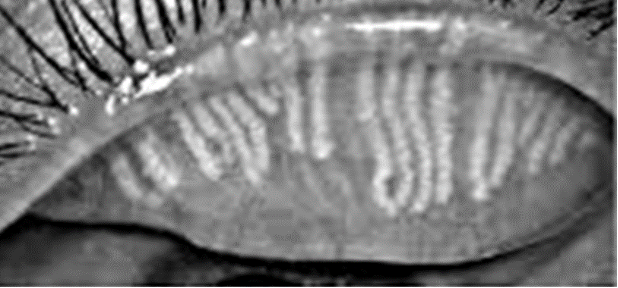
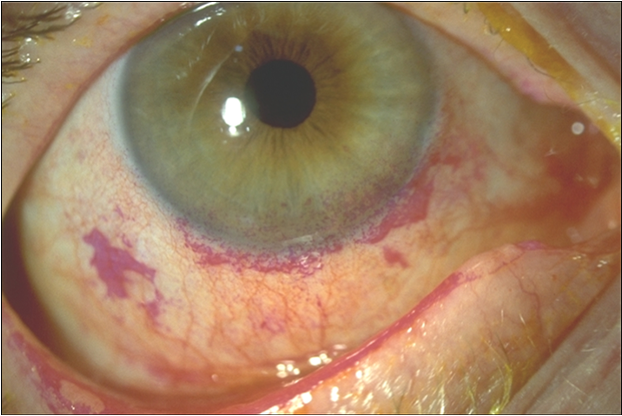
what are the secondary signs of all blepharitis?
chronic red eye - lid margin & conjunctival hyperaemia
punctate epithelial erosion (lower 1/3rd of cornea) →purple dots in image
conjunctival staining - fluorescein etc
marginal keratitis + scarring
neovascularisation —> new blood vessels + pannus (opacification of cornea)
what is the optometric management of blepharitis?
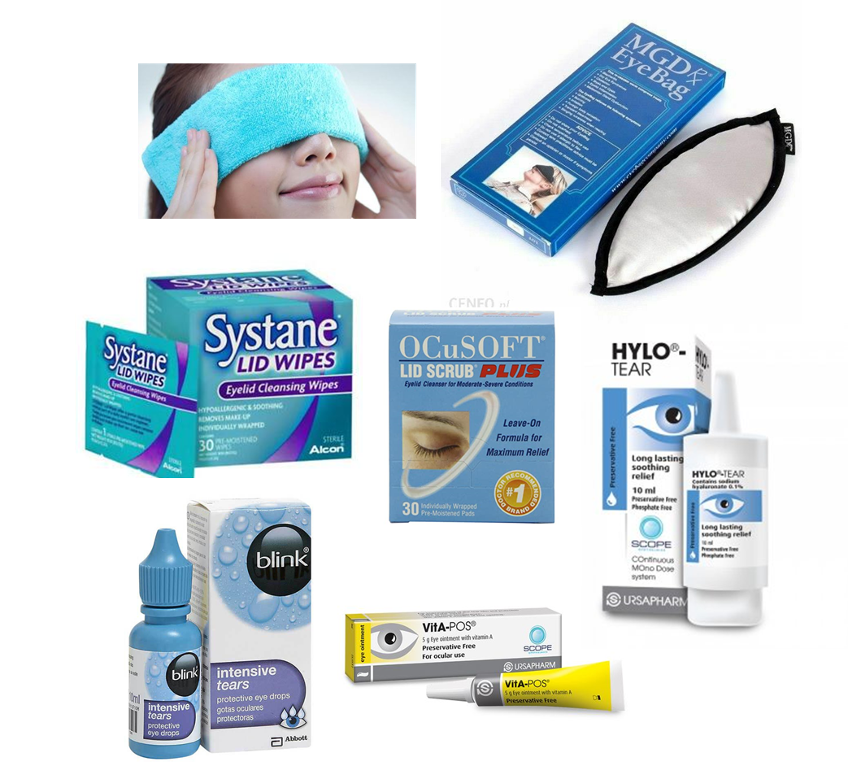
All cases: Lid hygiene
needs to be daily + long term
warm compress, lid massage + clean/wipe
lid scrubs/ wipes , or washes/gels
clean flannel + warm water → hold on closed eyelids for 2 mins so warming up secretions (MG)→ so flow better
eyelid margin massage → help blocked glands express + clean away debris
what other managements are there for blepharitis ?
> ocular lubricants
> drops/ointments
> vitamin supplements
> omega 3/fish oils
BlephEx→ tool
demodex→ tea tree oil (experienced clinician)
what treatments for refractory cases - resistant to treatment ?
topical antibiotic ± steroid
oral tetracycline (3months/12) e.g Doxycycline
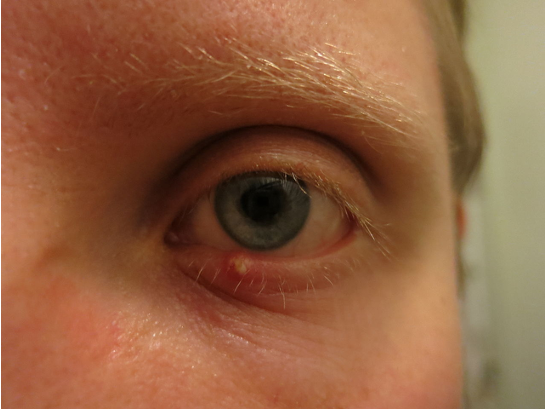
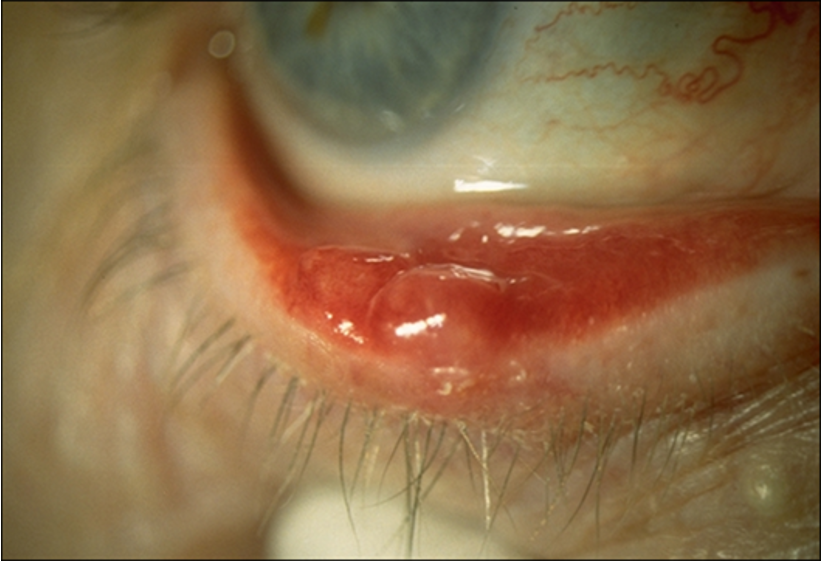
what is hordeolum ?
acute bacterial infection (staphylococcal) of an eyelid gland
24-48 hours red swelling
tender eyelid lump
may spontaneously express itself with a purulent material
often associated with blepharitis
image = external hordeolum
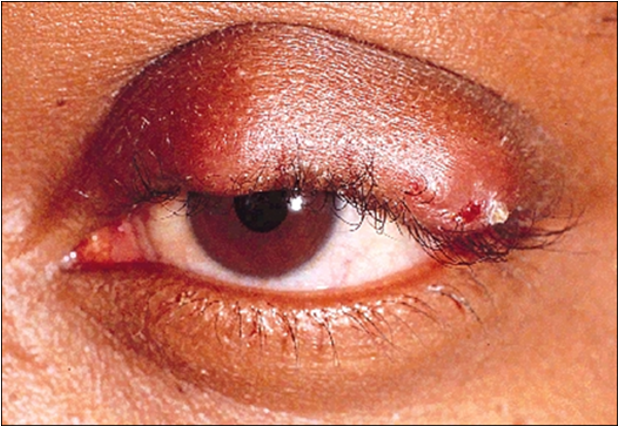
what are the two types of hordeolum ?
External hordeolum (stye)
—> lash follicle + associated with gland of Zeiss or Moll - bass of eyelash
internal hordeolum - further in lid (image)
—> meibomian gland - tarsal plate
treat as per blepharitis
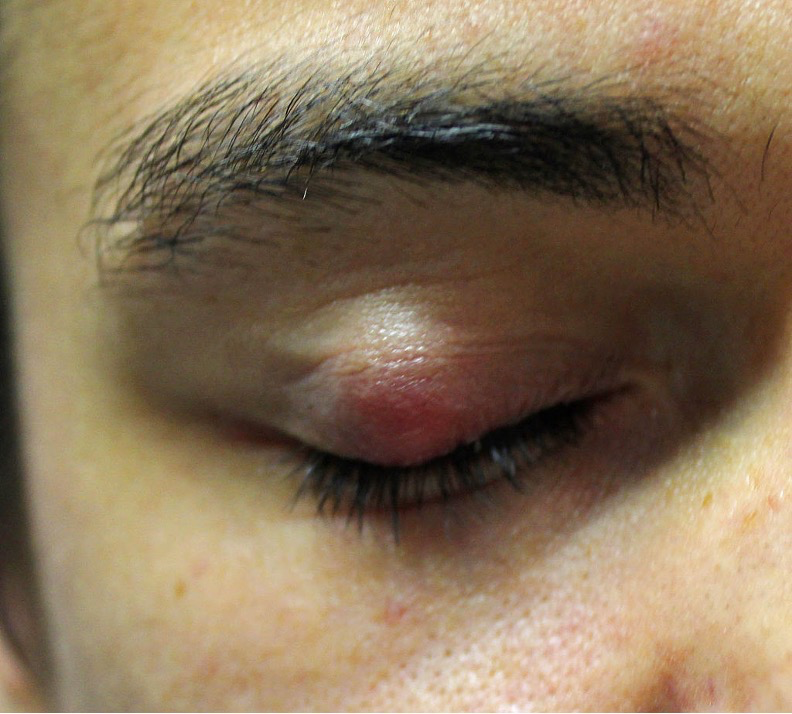
what is the aetiology of a chalazion?
common, chronic lid lump
Blockage of meibomian gland duct
inflammatory response —> stagnate secretions + inflammatory cells
spontaneous or follow hordeolum
typically less acute + occur over a period of weeks
what are the symptoms of a chalazion?
usually painless lid lump
single or multiple, may be recurrent
what are the signs of a chalazion?
well-defined , 2-8mm subcutaneous nodule in tarsal plate
may be associated with blepharitis and astigmatism
what is the management for a chalazion?
tend to resolve on their own
lid hygiene as per bleph - warm compress, massage + clean lids
resolution may take several weeks
occasionally may be surgically removed → if persistent and hasn’t resolved for 6 months
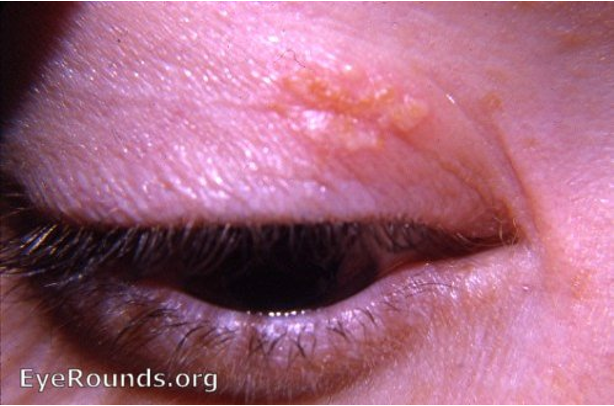
what is herpes simplex virus ?
> swollen lids + conjunctivitis
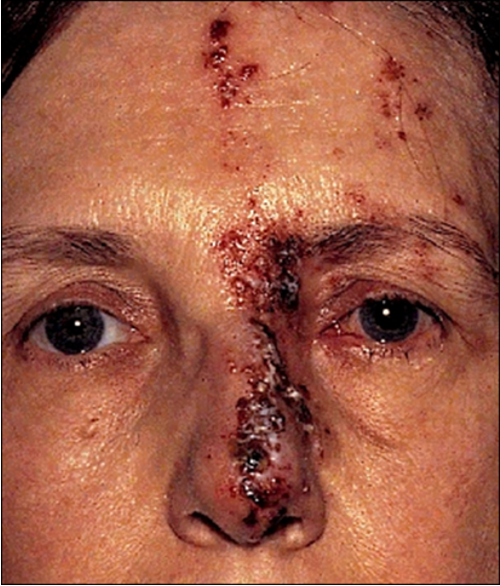
what is herpes zoster virus (shingles)
Varicella (chicken pox vius)
herpesvirus-3
pain/neuralgia (tingling pain) - one sided
vesicular rash
lesion tip on nose (hutchingsons sign)- higher risk of ocular complications
oral acyclovir within 72 hours of vesicles starting ,reduces eye disorders from 50% to 20-30% + reduces pain
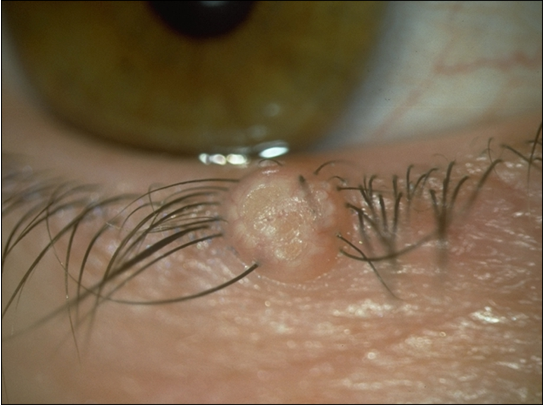
what is molluscum contagiosum?
poxvirus
mildly contagious (skin to skin)
umbilicated skin nodule → 2-3mm
viral toxins may cause follicular conjunctivitis
curette lesions → local or general anaesthetic
—> moluscumi scraped out
what is Tinea faciei ?
fungal infection - Rare
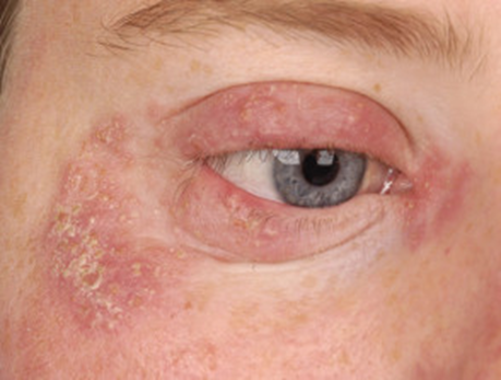
what is impetigo?
Staph infection
rash
occasionally blisters on skin
common in children younger than 14yrs of age
—> can lead to orbital cellulitis
