Muscular System and Range of motion
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Different names for skeletal muscles
parallel, convergent, pennate, fusiform, spiral, circular
different forms of attachment
tendons, muscle, bones, origin, insertion
tendons
attach muscle to bone
muscle
moves bones toward or away from each other when contracted
bones
movement directed by muscles
origin
point of attachment that does not move
insertion
point of attachment that does move
what is the agonist/prime mover?
the mover that directly performs the movement
what is the antagonist?
muscles that directly oppose agonist, the muscle that is relaxing/lengthening
what is the synergist?
a muscle that contracts with the prime mover to increase efficiency
what is a fixator muscle?
a muscle that stabilizers movement, joint stabilizers
what is the purpose of the arch of foot?
hold up weight, weight distribution, provides spring while walking, medial, lateral, transverse
What is your thumb joint called?
saddle joint, a biaxal synovial joint
Angular Movements
a change in the size of the angle of the joints
flexion
bones are coming closer together so angle is decreasing, lateral flexion- bringing head to shoulder
extension
bones move farther apart so increase in angle, back to anatomical position
hyperextension
extension beyond anatomical position
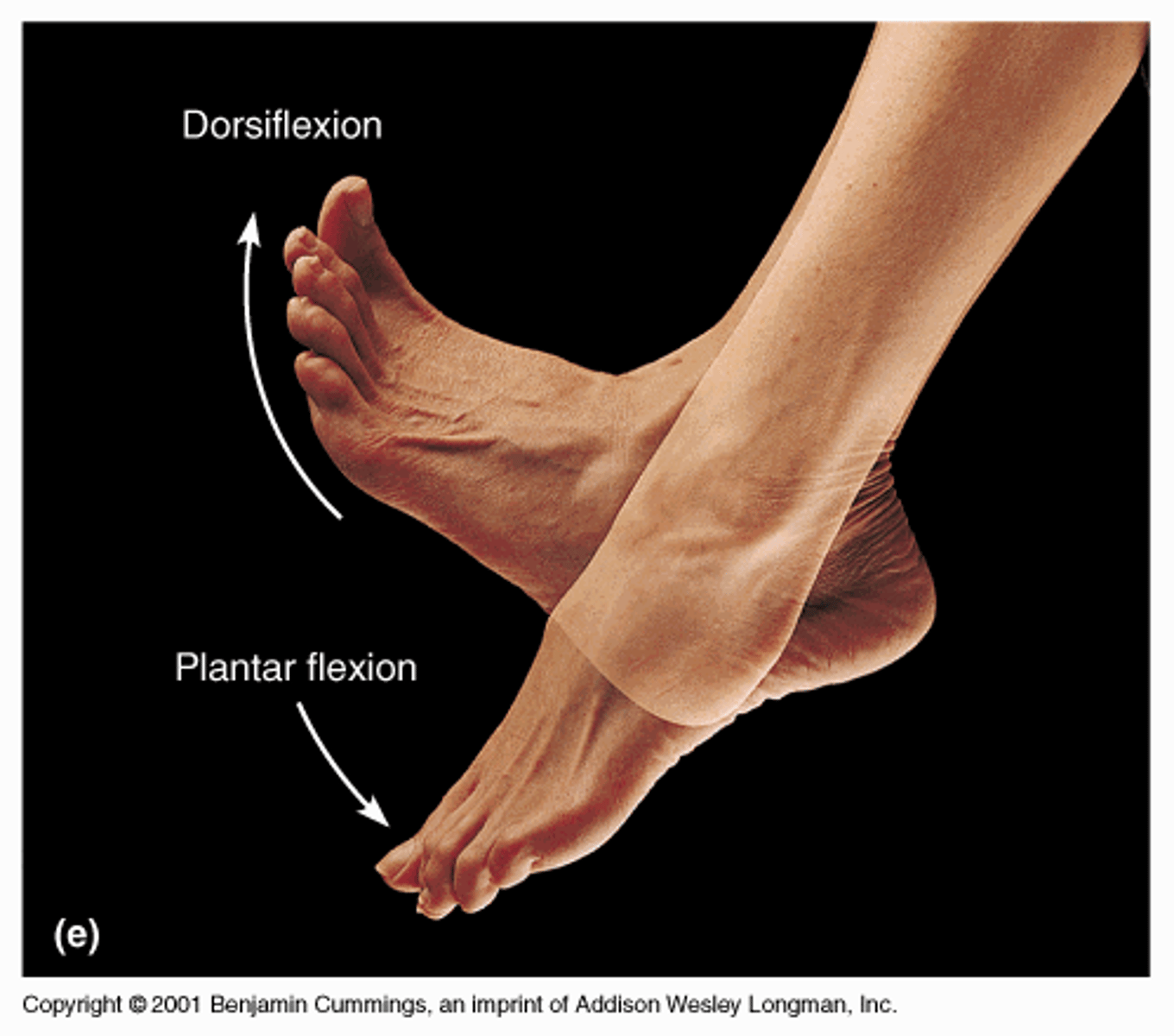
Foot: Plantar Flexion
increase in angle between top of foot and from of leg(pointing foot down)
Foot: dorsi flexion
decrease in angle between top of foot and front of leg (pointing foot up)
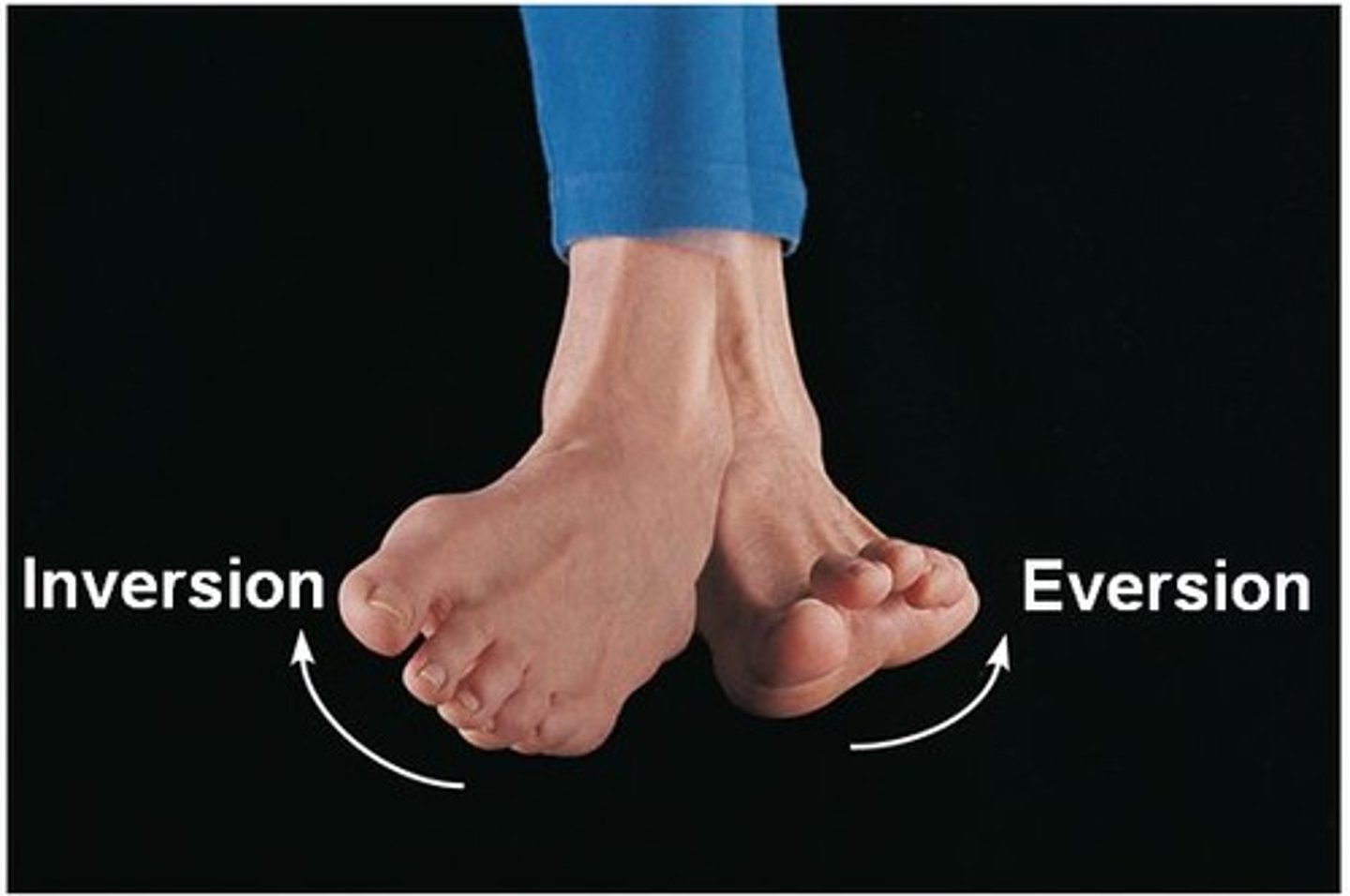
Foot: Inversion
turning foot inward
foot: Eversion
turning foot outward
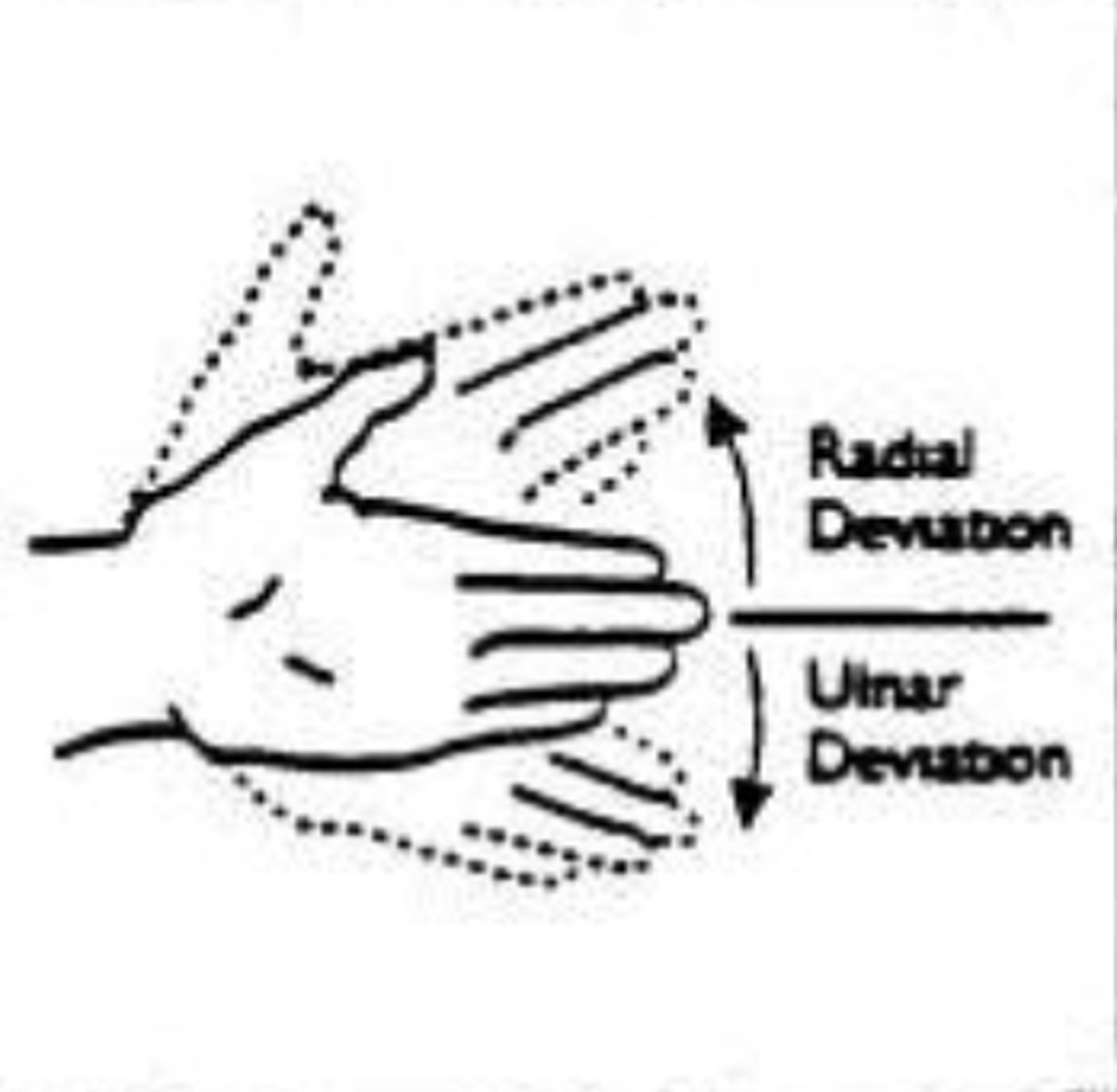
Arm: Ulnar flexion
deviation of hand toward ulnar side
Arm: radial flexion
deviation of hand toward radial side
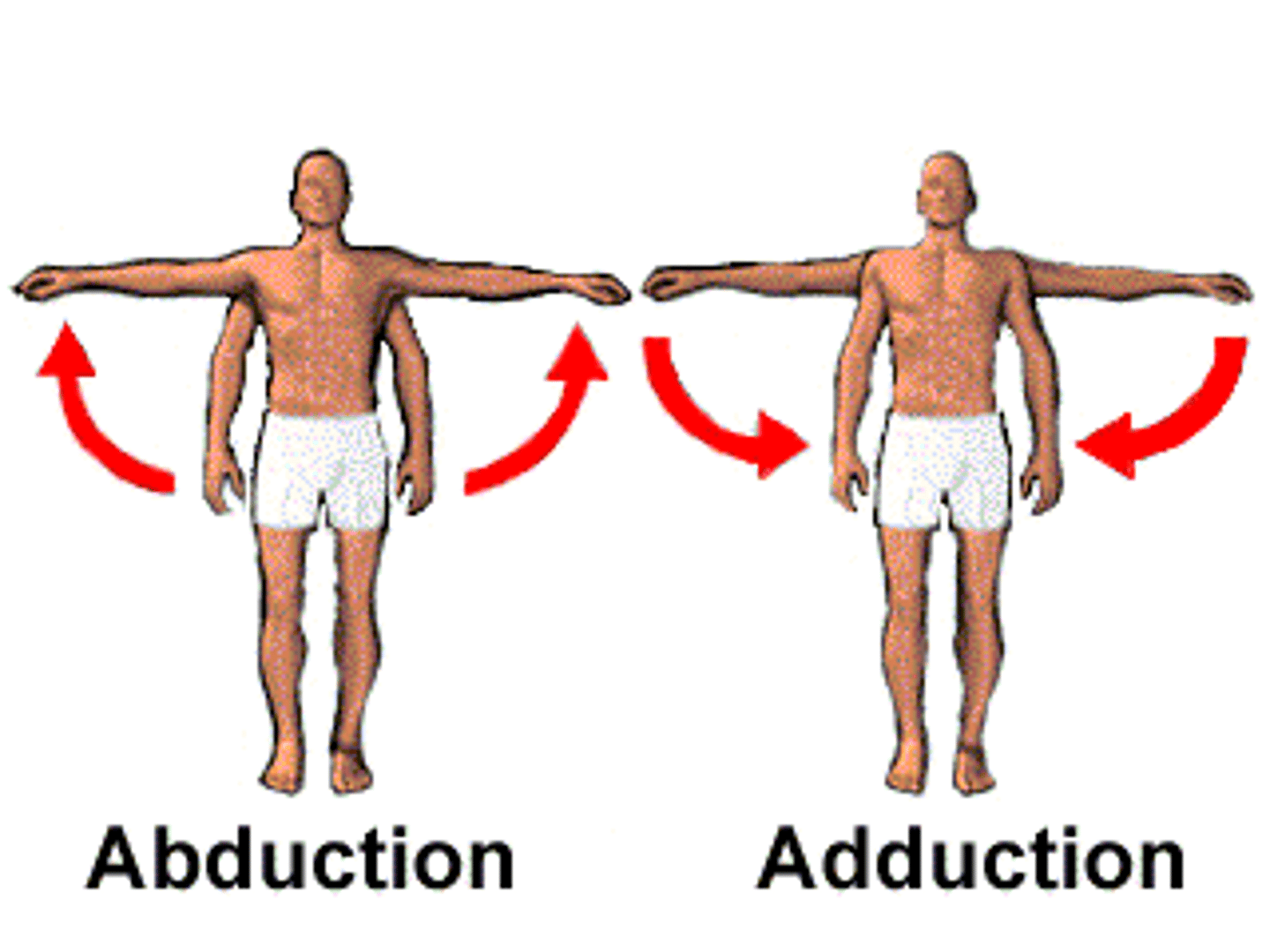
abduction
move body part away from median
adduction
move body part toward median
Circular movement: Rotation
pivoting bone on own axis (shaking head no)
Circular movement: Circumduction
distal end of body part moves in a circle
Circular movement: Supination
turn hand palm side up/thumbs are lateral
Circular movement: pronation
turns hand palm side down/thumbs are medial
What position are your hands, in the anatomical position?
hands are supinated, facing forward or up. if they are turned over than they are pronated
Special Movements
Protraction, retraction: push forward or bring back
Elevation and depression: move body part up and down
Opposition: bringing thumb closer to other fingers