Bio 109 L9 Ecosystems I: Biotic Networks
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
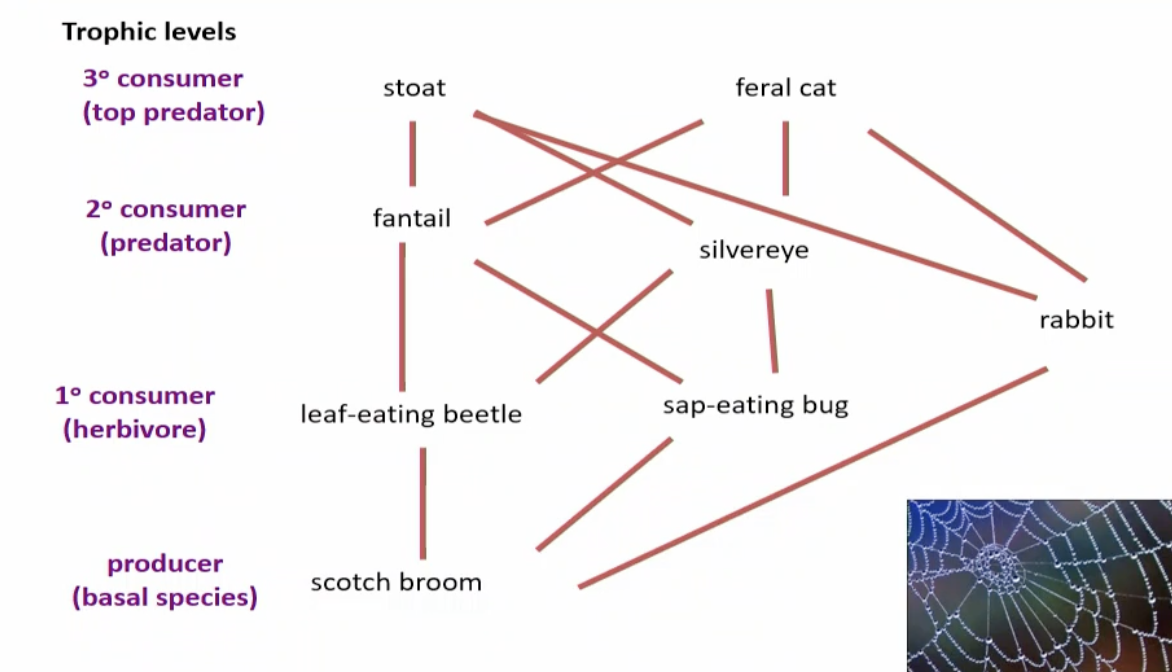
What are food web.
food web is a series of chains
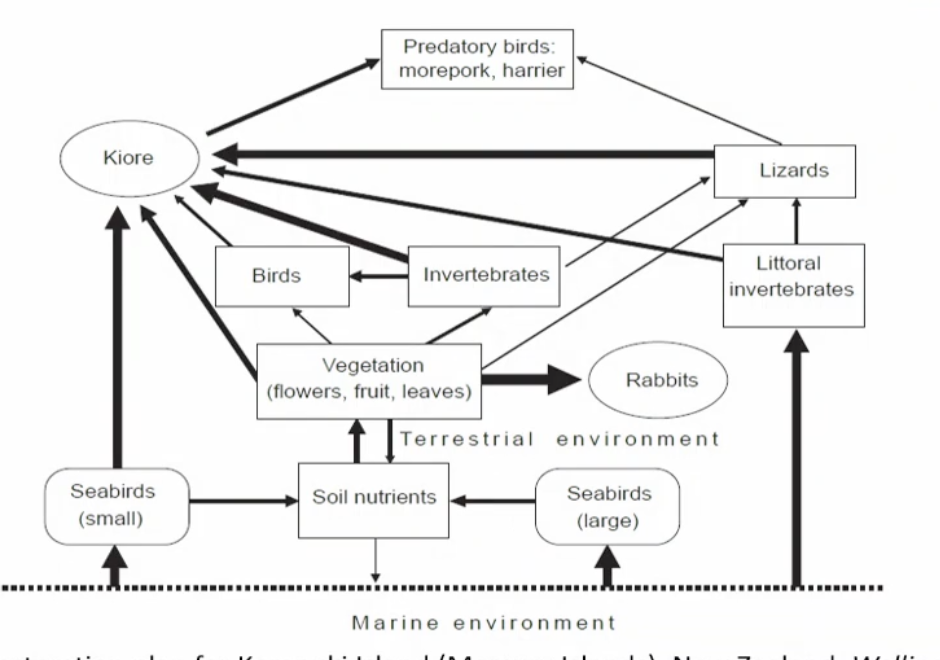
Exaplin this graph
the rapid is the species that eats most of the vegetation (flowers,fruit,leaves) due to thick lign. And most of the spcies are eaten by Kiore. Thick lines = strong interaction.
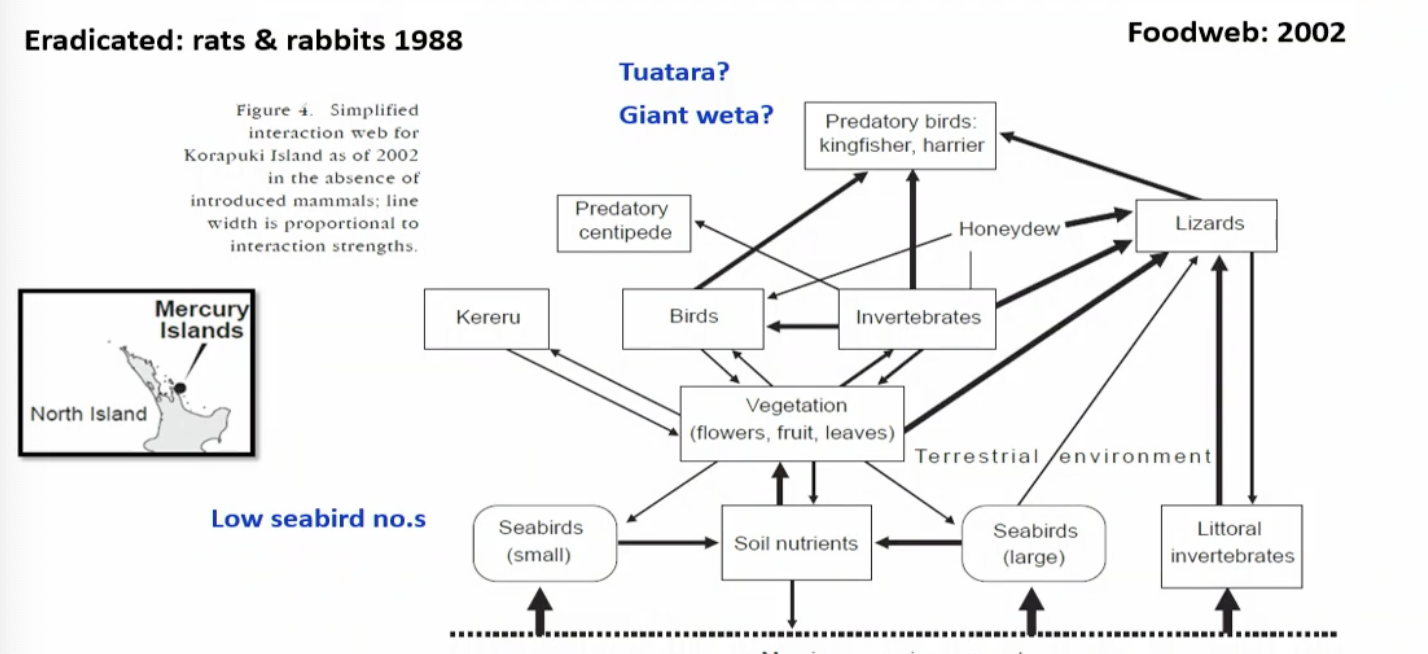
What happened after Kiora erradicated.
Lizard introduction into the habitat. rats and rabbit eradication. lizards eating allot. preditory centipied killing invertebrates they are very dangerous. More predotry birds omming to the fore. seabird levels are low. not only preditory of their food competition.
what is light causing
it pervasive throughout the system impacting all species due to inbuilt biological clock being dirupted.
what does ALAN light at night impact (light polution)
chagnges how and when plants flower and grow
reduces food availability for herbitovurs
helps visual predetors detect prey
reduces nutrient cycling by soil digging nocturnal spp
disrupts circadian cycling and reproducitve cycle
Mutualism
both partener benefit from interaction.
example
plant seed disperer
plant pollinators
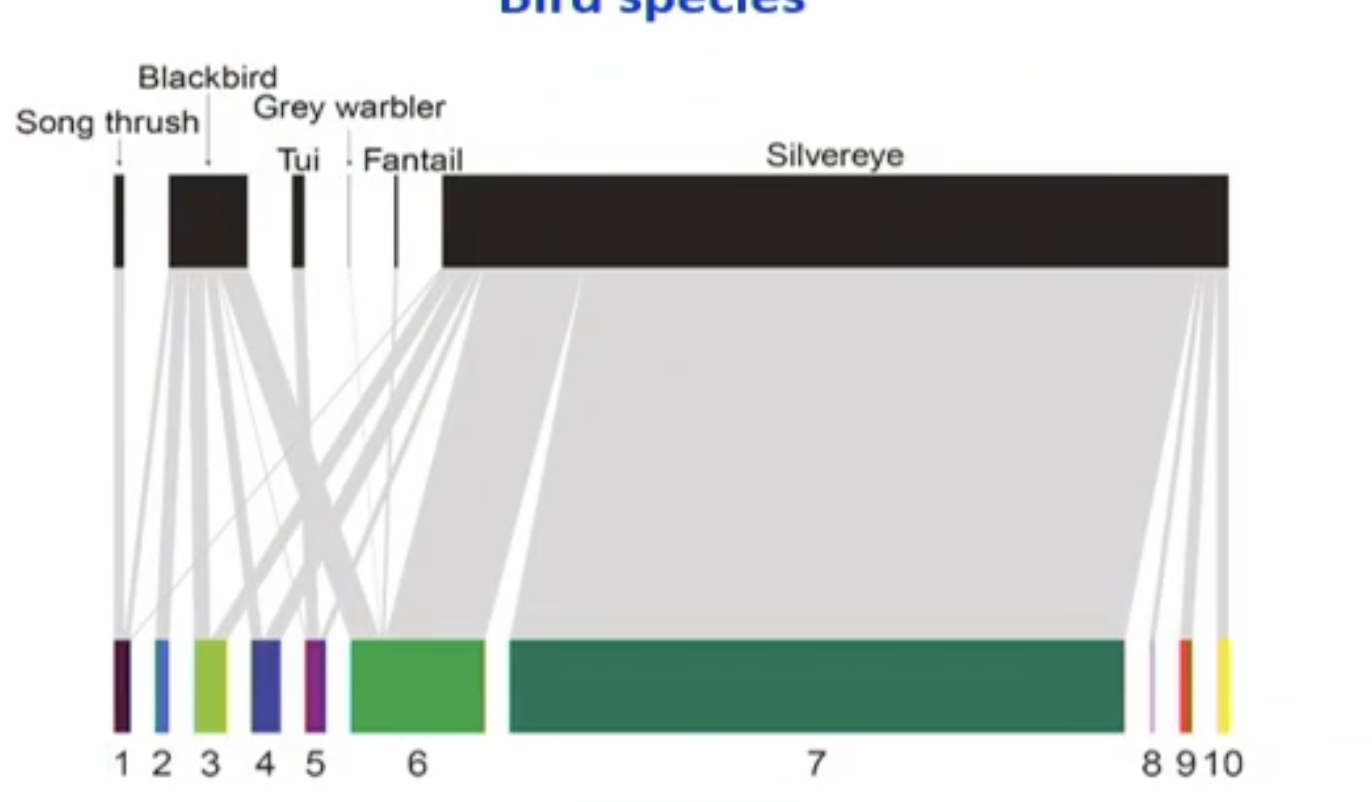
explain this graph
pollination and pollinators hevily dpepndent on one species which is the silverye bird species. much broader than food webs.
What word do we use know rather than food webs
ecological networks
why
because we study not just consumers but pollination aswell.
What are some disrumptions in biotic networks
Trophic cascade
What does it mean
a predator has a positive effect on primary producer species by reducing the abundance of a herbivore.
example
Wolves (top preditor) killing the primary producer (elk) causing fewer elks and increases the willow, aspen trees. Due to this their are more beavers.
another example
otter fur hunting trade.
humans are preditors reduced otters to low numbers and stopped killing kina. the increase in kinna caused kelp to be utterly destroyed.
What is a good anolagy
Some species are more important than others for biotic networks that if you map them around and if you do something with them and remove them, uh, then the system can collapse
What does this anotmy called
A keystone species.
Definition of key stone species
a species whose removal would produce a significant effect (extinction or large change in density) in 1 or more species).
what kan a keystone species be
a species that is a key food resource
top predator
key herbivore or detritivore
seed disperer/pollinator
An example of a bird and how
Kereu feeding on taraire fruit.
birds that can open their mouth wide and only species to disperse seeds. Karaka tare tawa are haavily relient on keraru. Low density of kereu = very low recruitment (seedling) of these species.
anither example
scale insect. kereu pases exess suger out of bum producing pure tree important for kanuka trees. the sugar causes native fornere to have food.
How else does scale insects help.
some trees infested by scale insects not seen before. Now 30 geckos per tree. it was important for food weBs. scale insects important for mainland but onyl in few places. also beenfitical for birds for sugars.
How much percentage of birds does nz and how much breed here.
39% of birds in new zealand and quater breed in nz
what makes seabirds keystone species
they are bringin marine neutrients into land. Burrowed birds dirtupts soil mixing soiling. pooing and regergitation food for kids. nutrients high and nitrogen ending up in these areas.
examples of where seabirds colonies

so main point
seabirds don’t have to be near the sea but inland aswell such as seaward kaikoura rangs birds colonising inland
what is most forests missing
neutrients from the birds system.
summary
pre human were very common - as far inland as mountains of te urewra and seawards kaikora ranges (still present).
Now due to humans largely confined in isalnds.
What are some threats seabirds are facing
Predatation -introcued mammals
Pollution - sea
CLimate change
declining fish stock
fisheries bycatch.
marin input
“new source” of nutrients from marine ecosystems brought into terrestrial ecosystems - energy flow.
seabirds also
result in rare plants and unsual plant communities. These plants can cope with high disturbance (trampling) and are very neutrient rich.
how does poo of seabird Guano prodvide nutrients
sustain invertebrate populations
this in turn supports reptile populations.
How does seabirds impact leaves
Due to seabirds being present it mean leaves has more nitrogen resulting in the survival of the plant.