Organic Chemistry Unit - Chemistry II
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
CnH2n+2
Alkane Formula
Alkane - single bonds
Contains only single bonds and the first four include methane, ethane, are saturated hydrocarbons that contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms that can bond with the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
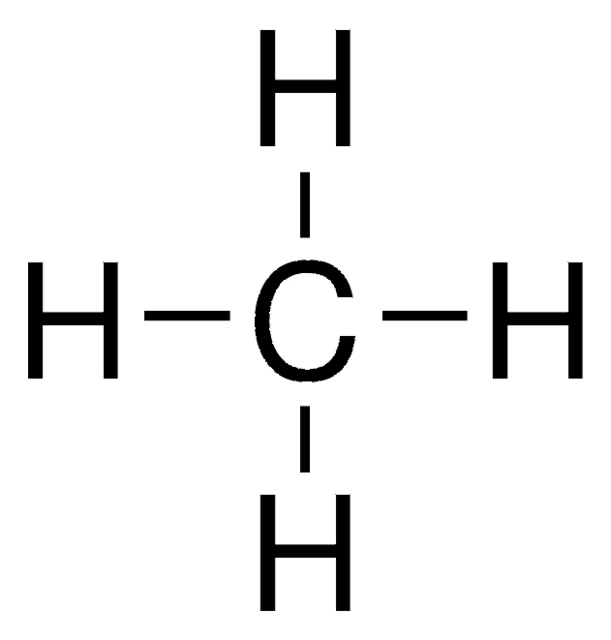
CH4
Methane
C2H6
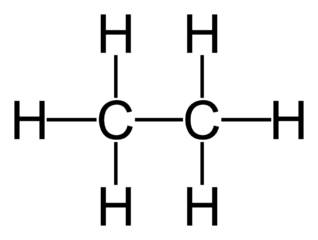
Ethane
C3H8
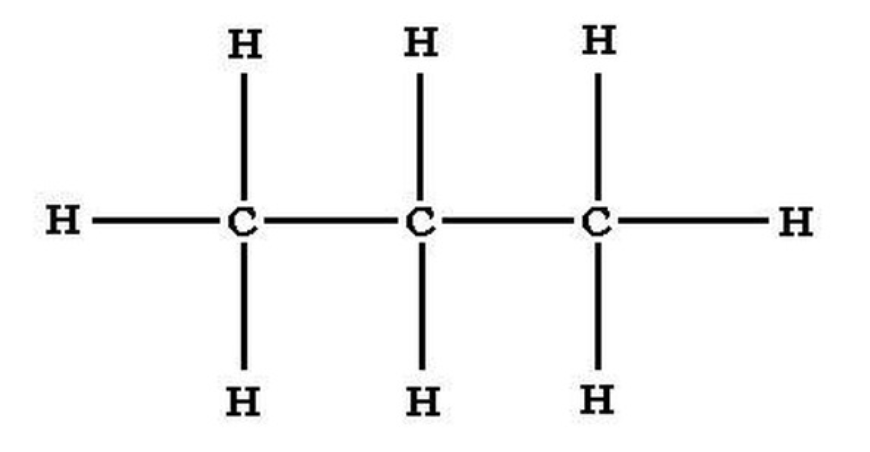
Propane
C4H10
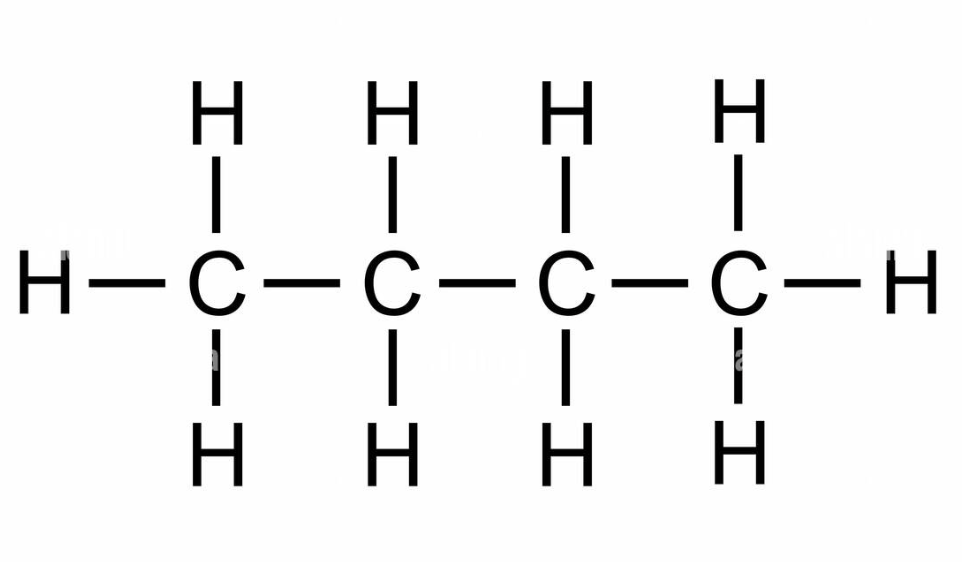
Butane
Closest
Number the carbon atoms in the continuous chain starting with the atom ________ to the branching point and/or double bond
Alkyl group
Alkanes missing a H atom are called what? When two or more of these are present, write them in alphabetical order.
Cycloalkane
Alkanes whose carbon atoms are joined in rings are called ________. The “n” in the formula must be n = 3, 4,….
CnH2n
Cycloalkane formula
Alkene - double bond
Contains at least one carbon-carbon _______ and are typically more reactive than alkanes because they have carbon-carbon double bonds.
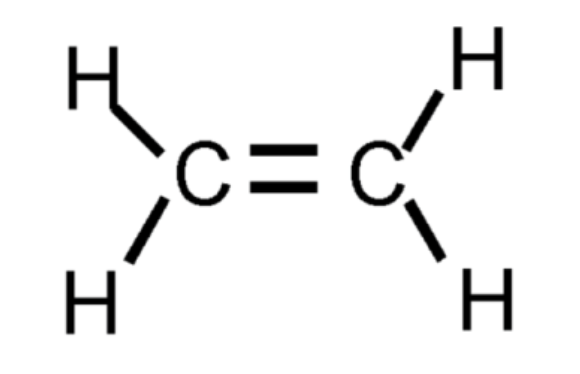
CnH2n
Alkene Formula
C2H4
Ethene
C3H6
Propene
C4H8
1-Butene
Markownikoff's Rule
When a compound HX (such as H-CI , H-Br , or H-OH) is added to an unsymmetrical alkene (or alkyne) the hydrogen gets attached to the carbon with the most hydrogens attached to it already.
Alkyne - triple bond
Contains at least one carbon-carbon _______ and n = 2,3,4,….
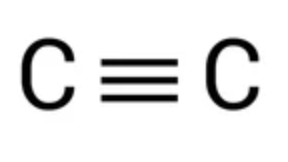
Benzene Rings
Six-membered rings of carbon atoms with alternating carbon-carbon single and carbon-carbon double bonds.
Alcohol
Derivatives of hydrocarbons in which an OH group has replaced a hydrogen atom
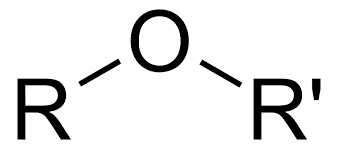
Ethers
Contains the functional group R-0-R' where R represents an alkyl group and R' represents a second alkyl group that may or may not be identical to the first alkyl group
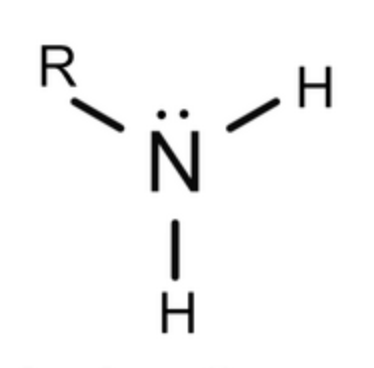
Amines
Occurs when one or more hydrogen atoms of NH3 are replaced with an alkyl group
Aldehyde
These have at least one H atom attached to the carbonyl group uses the suffix “al”
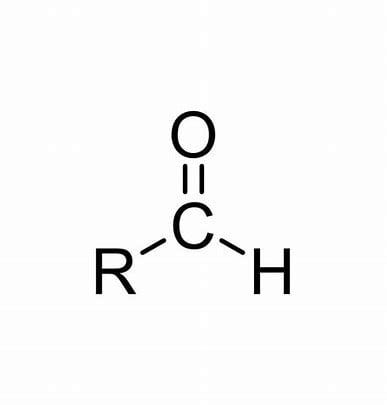
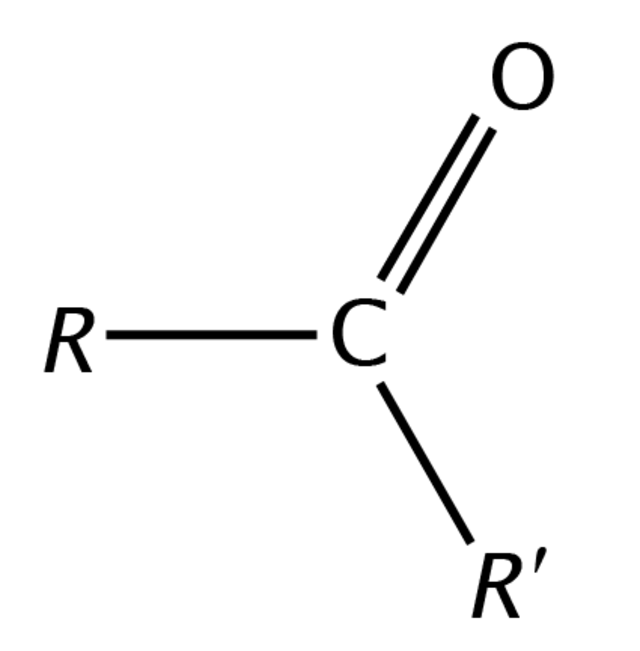
Ketones
Must have two carbon atoms attached to the carbonyl group, uses the suffix “one”
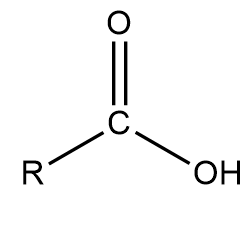
Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids contain the functional group R-COOH where R represents an alkyl group, uses the suffix “anoic acid”
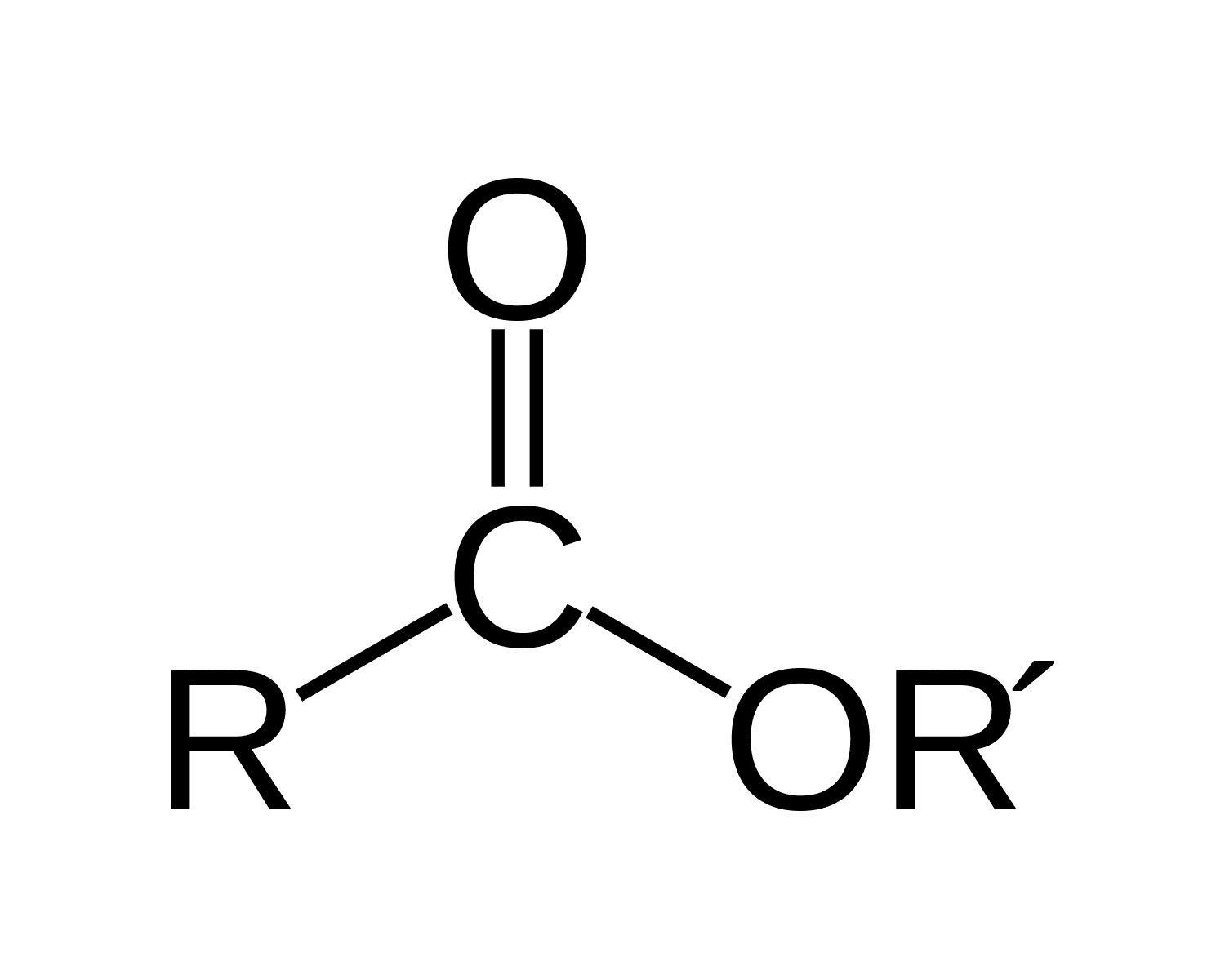
Ester
Contains the functional group R-COOR' where R represents an alkyl group and R' represents a second alkyl group that may or may not be identical to the first alkyl group.
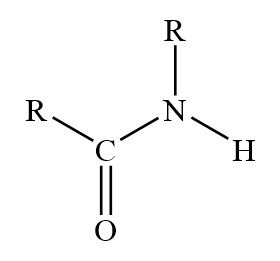
Amide
Molecules that contain nitrogen atoms connected to the carbon atom of a carbonyl group
Right
Adding more of a product or removal of a reactant shifts the equation to the _______. “Add to the left, shift to the ______”
Left
Adding more of a reactant or removal of a product shifts the equation to the ______. “Add to the right, shift to the _____.”
Less
When volume is decreased/pressure is increased, it causes the reaction to shift to whichever side has _____ moles of gas.
More
When volume is increased/pressure is decreased, it causes the reaction to shift to whichever side has _______ moles of gas.
Right
In an endothermic reaction (delta h +), adding heat causes the reaction to shift to the _____.
Left
In an exothermic reaction (delta H -), adding heat causes the reaction to shift to the _____.
Catalyst
Increases the rate of the reaction but does not effect the position of equilibrium.
Slowest Step
The rate determining step is the __________ _______.
Spontaneous
ΔSuniverse > 0
Nonspontaneous
ΔSuniverse < 0
Equilibrium
ΔSuniverse = 0
Spontaneous
ΔG < 0
Nonspontaneous
ΔG > 0
Equilibrium
ΔG = 0
CnH 2n-2
Alkyne