Unit 3 - Nasal Cavity, Oral Cavity, Pharynx
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What are the cartilages of the equine nose?
- Dorsal and ventral lateral cartilages
What are the alae or wings of the equine nose? What are they made up of?
- Lateral: Skin, muscles, fibrous CT
- Medial: Cartilaginous base (Dorsal lamina of alar cartilage and ventral cornu of alar cartilage)
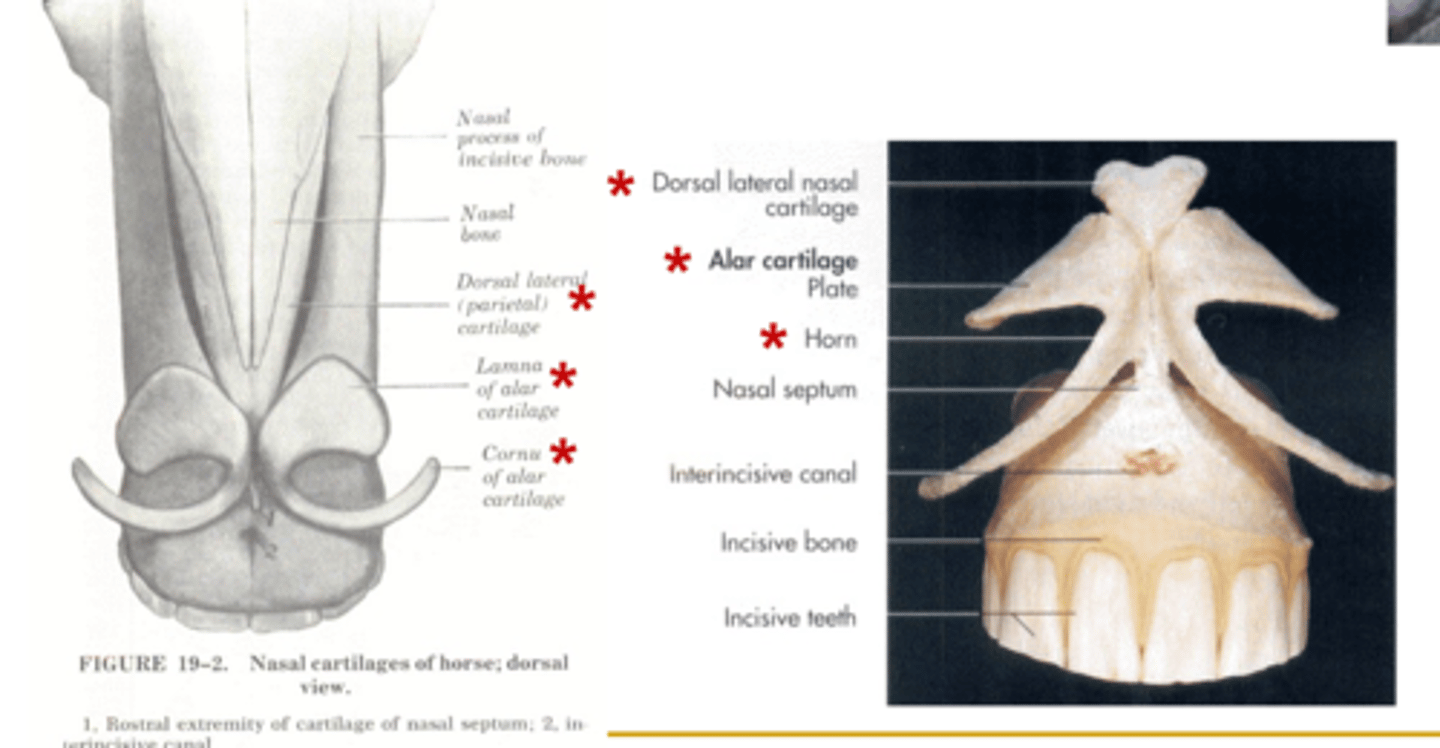
What is the alar fold of the equine nostril?
- Mucous membrane fold continuous rostrally with a fold of skin attached to the lamina of the alar cartilage and caudally with the ventral nasal concha
What is the nasal diverticulum of the equine nostril?
- Blind pocket located dorsal to the alar fold
What is the nasolacrimal duct orifice of the equine nostril? Where is it located?
- External opening of the nasolacrimal duct
- Located on the floor of the vestibule
What are the cartilages of the ruminant nose and nostril?
- Dorsal and ventral lateral cartilages?
What is the planum nasolabiale? In which species is it found?
- Highly keratinized region between the nostrils and extending to the upper lip
- Ox
In which LA species is the planum nasale found?
- Small ruminants
In which LA species is the philtrum found?
- Small ruminants
What forms the osseous part of the nasal septum in the horse?
- Perpendicular plate of the ethmoid and vomer bone
In the horse, where does the dorsal nasal concha extend? What is the straight fold?
- Extends from the cribriform plate to the first cheek tooth
- Straight fold: Courses from the dorsal nasal concha to the nostril
In the horse, what are the folds of the ventral nasal concha? Where do they extend/course? Which contains the nasolacrimal duct?
- Alar fold: Courses from the ventral nasal concha to the lamina of the alar cartilage
- Basal fold: Extends rostrally from the ventral nasal concha (contains the nasolacrimal duct)
Where is the middle nasal/ethmoid concha located in the horse?
- Located in the caudodorsal nasal cavity
Where is the dorsal nasal meatus located in the horse? Where does it extend?
- Located between the roof of the nasal cavity and the dorsal nasal concha
- Extends caudally to the junction of the inner plate of the frontal bone with the cribriform plate and lateral mass of ethmoid bone
Where is the middle nasal meatus located in the horse? Where does it extend?
- Located between the dorsal and ventral nasal concha
- Extends caudally to the last cheek tooth
Where is the ventral nasal meatus located in the horse? Where does it extend?
- Located between the ventral nasal concha and floor of the nasal cavity
- Extends/leads into the choana
Where is the common nasal meatus located in the horse? What about the ethmoidal meatuses?
- Between the nasal septum and the conchae
- Between the ethmoturbinates
Which nasal meatus in the horse contains the nasomaxillary opening which communicates with the maxillary sinus?
- Middle nasal meatus
What is particular about the middle nasal meatus in the ruminant?
- Divided into dorsal and ventral passages caudally by the middle nasal concha
Which nasal meatus is largest in the ruminant?
- Ventral nasal meatus
Generally, the oral cavity is made up of which two things?
- Oral cavity proper
- Oral vestibule
In the ruminant oral cavity, buccal papillae are _______________.
- Conical
What is the dental pad composed of in ruminants?
- Thick layer of CT with thick cornified epithelium
Where does the parotid duct drain in the horse? What about the buccal salivary glands?
- Drains into the oral vestibule at the third upper cheek tooth
- Dorsal and ventral buccal salivary glands drain into the oral vestibule
Where does the mandibular salivary gland drain in the horse? Where does the sublingual salivary gland drain?
- Drains at the sublingual caruncle on the floor of the mouth
- Polystomatic only in the horse: Numerous openings drain directly into the floor of the mouth on the sublingual fold
Where does the parotid duct drain in ruminants? What about the buccal salivary glands?
- Drains into the oral vestibule at the level of the upper second molar in the ox, upper fourth premolar or first molar in the small ruminant
- Dorsal, middle, and ventral buccal salivary glands drain into the oral vestibule
Where does the mandibular salivary gland drain in ruminants? What about the sublingual salivary gland?
- Drains at the sublingual caruncle
- The monostomatic portion drains at the sublingual caruncle and is located caudal to the polystomatic portion, which drains directly into the floor of the mouth on the sublingual fold
What are the sections of the pharynx (3)?
- Oropharynx
- Nasopharynx
- Laryngopharynx
What are the tonsils of the oropharynx?
- Palatine tonsil
- Lingual tonsil
In relation to the tonsils, what do ruminants have that horses do not?
- Tonsilar sinus
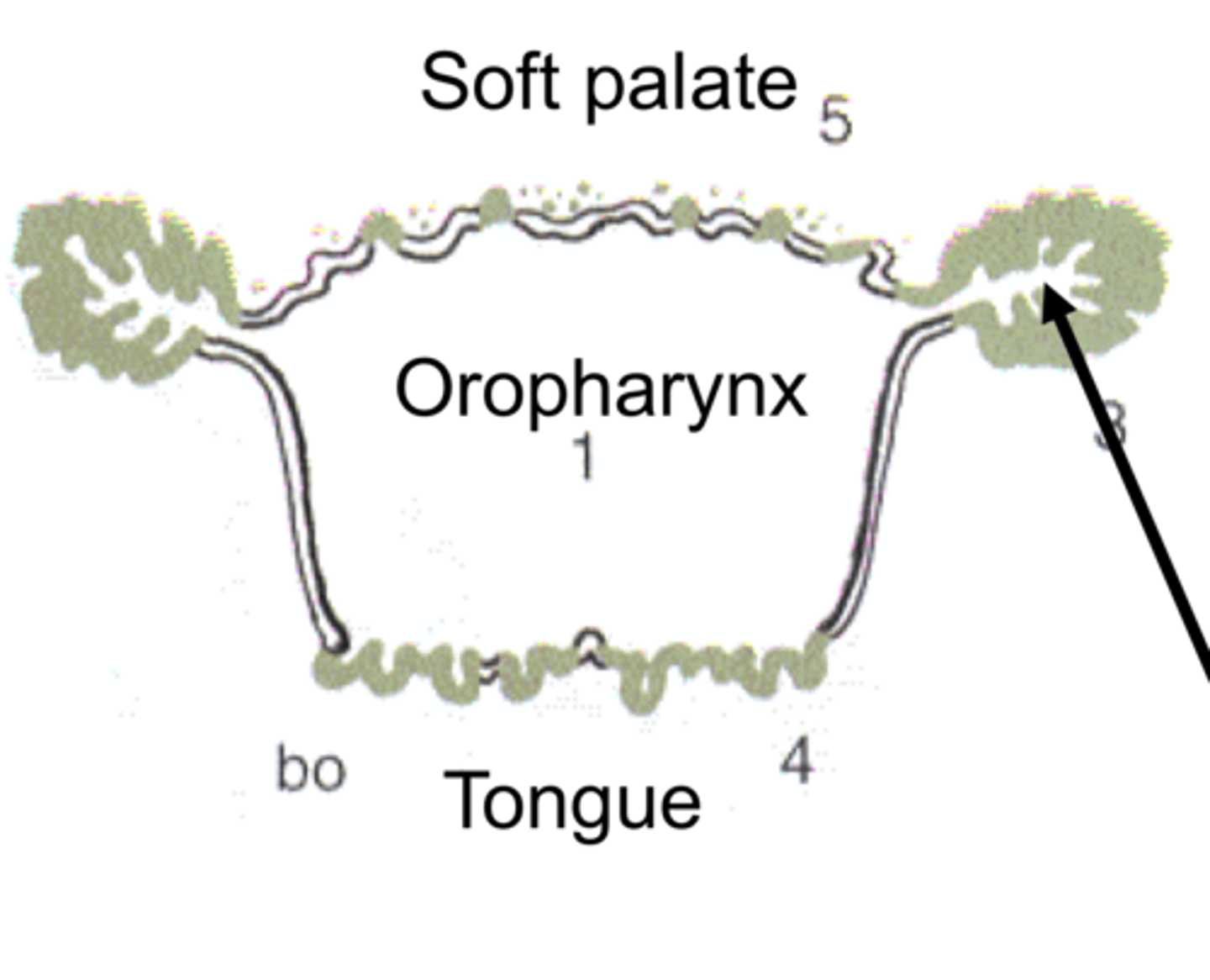
What is the rostral boundary of the equine nasopharynx? The caudal boundary?
- Rostral: Choana
- Caudal: Intrapharyngeal ostium (opening)
Where is the intrapharyngeal ostium located? What is it formed by?
- Located between the nasopharynx and the laryngopharynx
- Formed by the palatopharyngeal arch and the free border of the soft palate
What four structures can be found in the equine nasopharynx?
- Pharyngeal tonsils
- (Dorsal) pharyngeal recess
- Pharyngeal opening of auditory tube
- Tubal tonsils
What four structures can be found in the bovine nasopharynx?
- Pharyngeal septum
- Pharyngeal tonsil
- Medial retropharyngeal lymph node
- Pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube
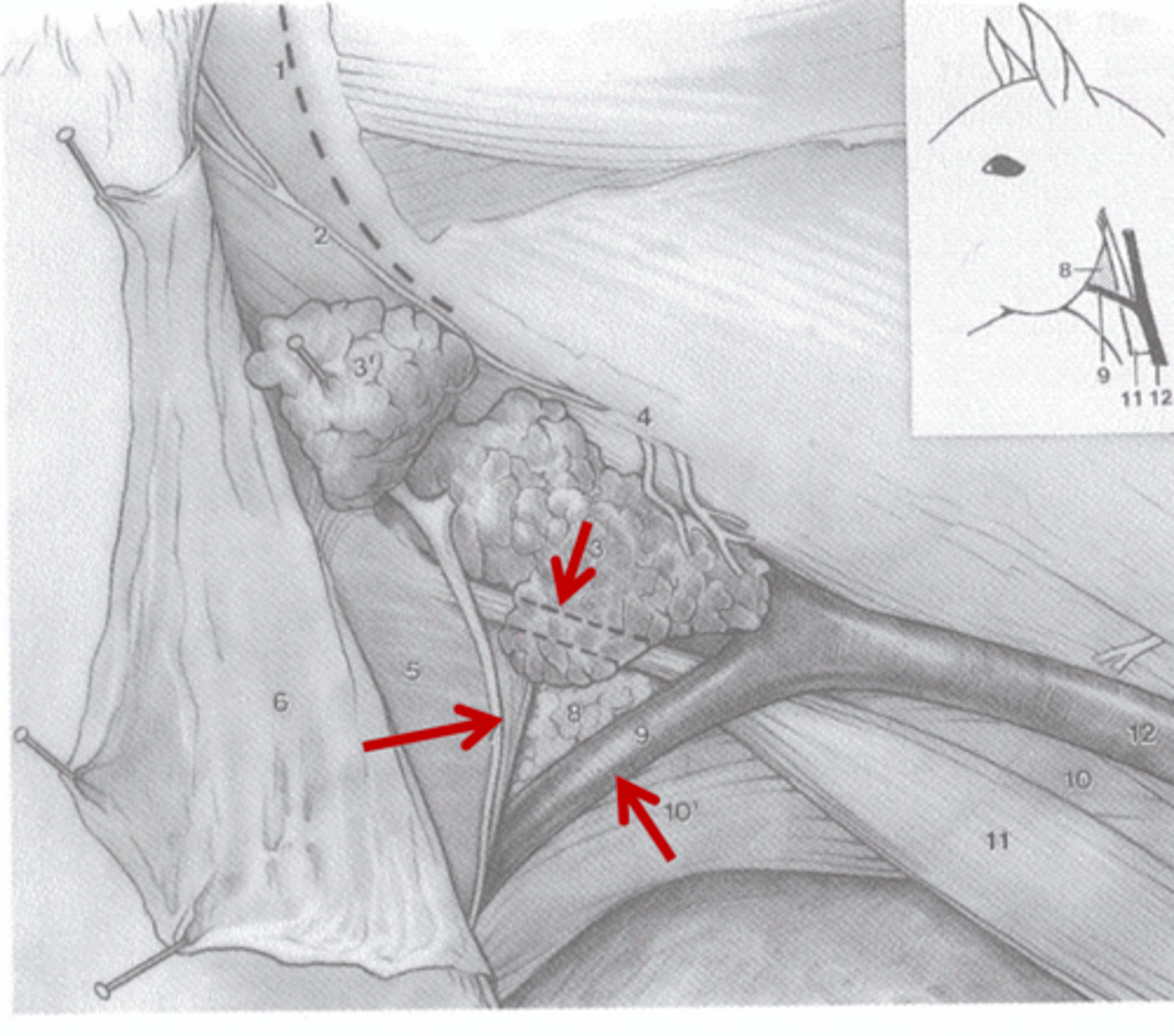
Found in the horse, what is the guttural pouch? What are its dorsal and ventral boundaries?
- A ventral diverticulum of the auditory tube
- Dorsal boundary: Base of cranium and atlas
- Ventral boundary: Pharynx and beginning of esophagus
The guttural pouch is "draped" over what? What does this form?
- "Draped" over the stylohyoid bone
- Forms medial and lateral compartments
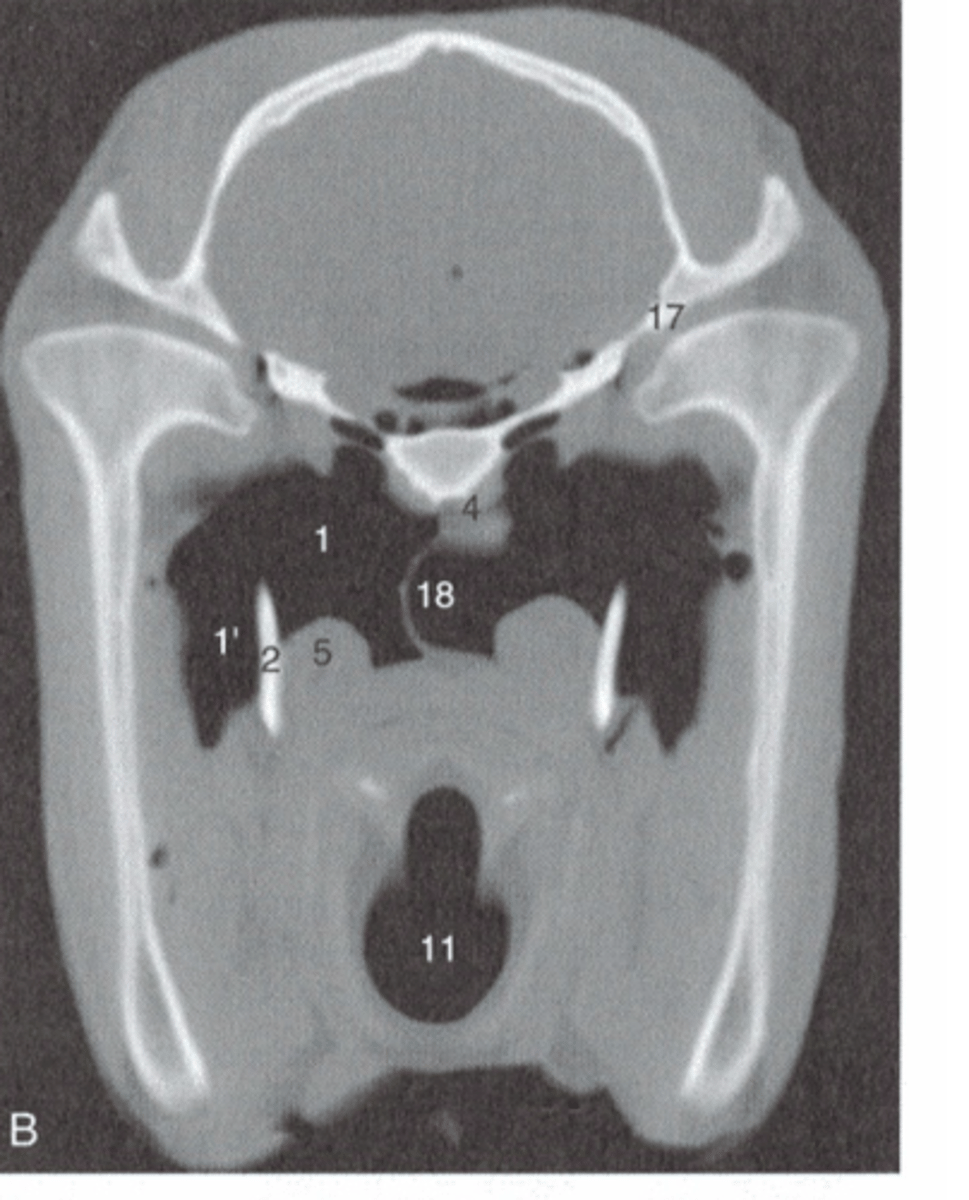
Which compartment of the guttural pouch is larger? Ventrally, what is the medial compartment in contact with? What other structures is it in contact with?
- Medial compartment is larger
- In contact with the medial retropharyngeal lymph node
- The medial compartment is also in contact with the internal carotid artery, the ventral cerebral vein (from the occipital vein), the glossopharyngeal nerve, the vagus nerve, the accessory nerve, the hypoglossal nerve, and the cranial cervical ganglion, and sympathetic trunk
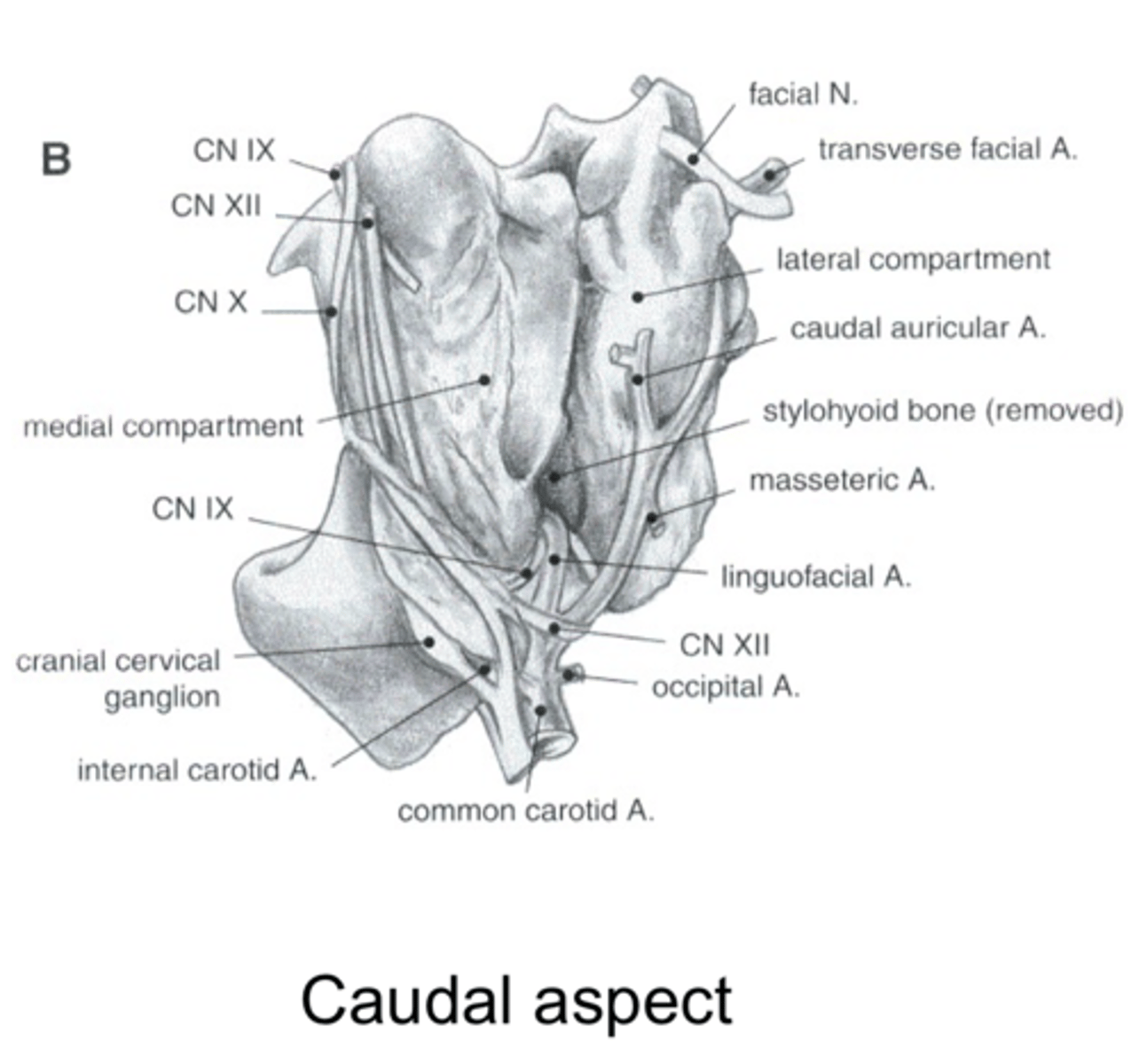
What courses along the lateral surface of the lateral compartment of the guttural pouch?
- The facial n., external carotid artery, and maxillary a. + v.
The pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube in the horse is found where? When is it open?
- Is it found in the guttural pouch, positioned approximately at the level of the lateral canthus of the eye
- Open during expiration and swallowing
In the horse, found in the guttural pouch, the pharyngeal opening is a __________ slit.
- Vertical
What is the plica salpingopharyngea? Where is it found?
- Mucosal fold
- Found in the guttural pouch, attached to the lateral wall of pharynx and medial wall of auditory tube; Located ventrally
What are the four surgical approaches to the guttural pouch?
- Hyovertebrotomy incision
- Viborg's triangle incision
- Modified whitehouse incision
- Whitehouse incision
What are the boundaries for Viborg's triangle incision? What is particular about these boundaries?
- Linguofacial v., caudal border of the mandible, and the sternocephalicus tendon (sternomandibularis)
- Surgical landmark for access to an enlarged guttural pouch, normal guttural pouches do not extend this far ventrally