1.6 - Nucleic Acids
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Nucleic Acids Function
the instructions to constructing a protein
Nucleotides
the monomer that formers the backbone of nucleic acid polymer
Nucleotides Structure
phosphate group, sugar, nitrogenous base
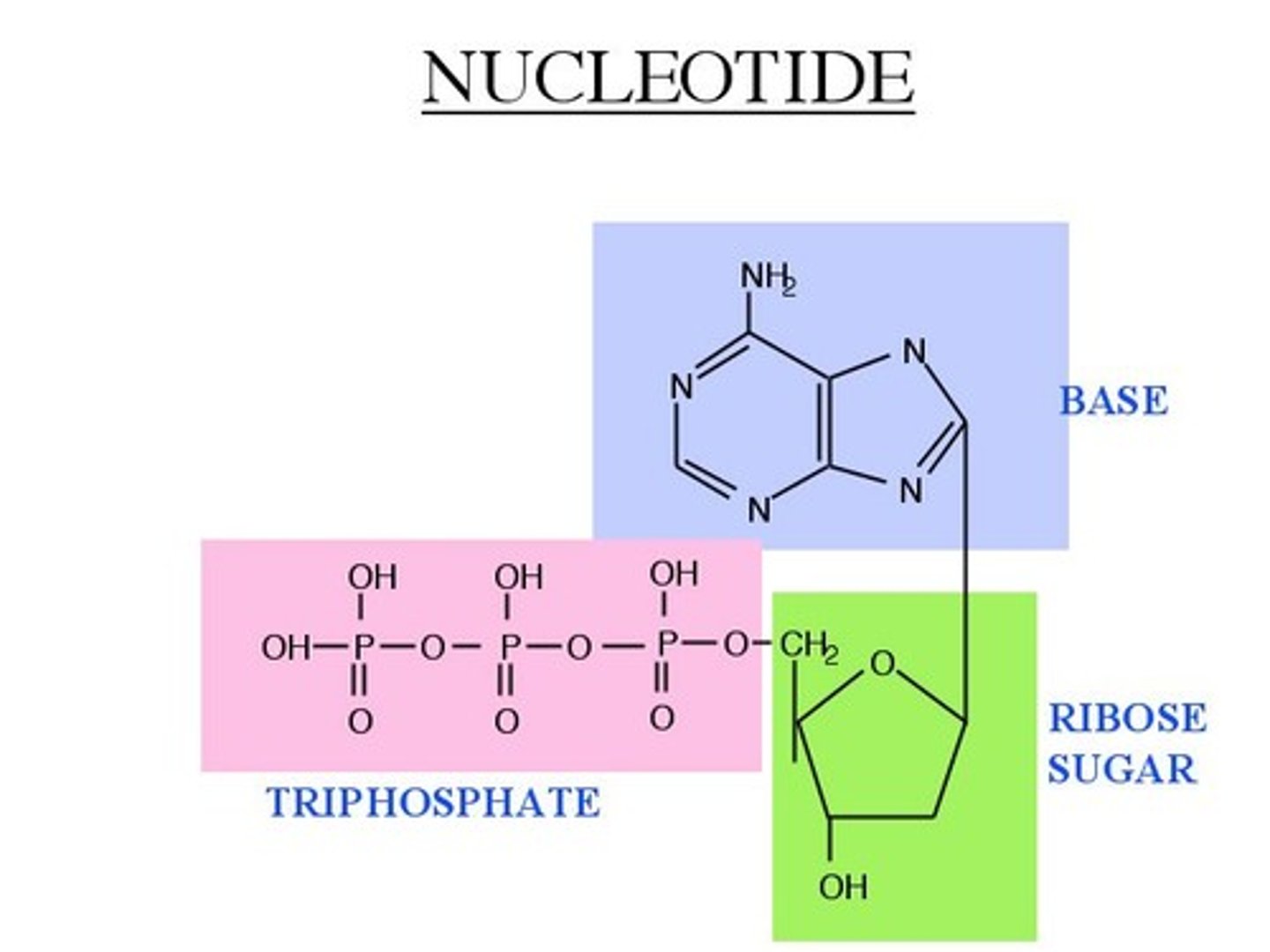
What is connected to carbon 1'?
the nitrogenous base
What is connected to carbon 3'?
a hydroxyl group (important for dehydration synthesis/ bonding)
What is connected to carbon 5'?
the phosphate group (not in the sugar ring)
What bonds nucleotides together?
phosphodiester bond
When bonded together, nucleotides will always have a directionality of what?
5' - 3' (phosphate group connects to hydroxyl group)
DNA Structure
made up of two strands of nucleotides, double helix

RNA Structure
made up of a singular strand of nucleotides
What type of sugar does the RNA backbone contain
ribose sugar
What type of sugar does the DNA backbone contain
deoxyribose sugar (one less oxygen than ribose)
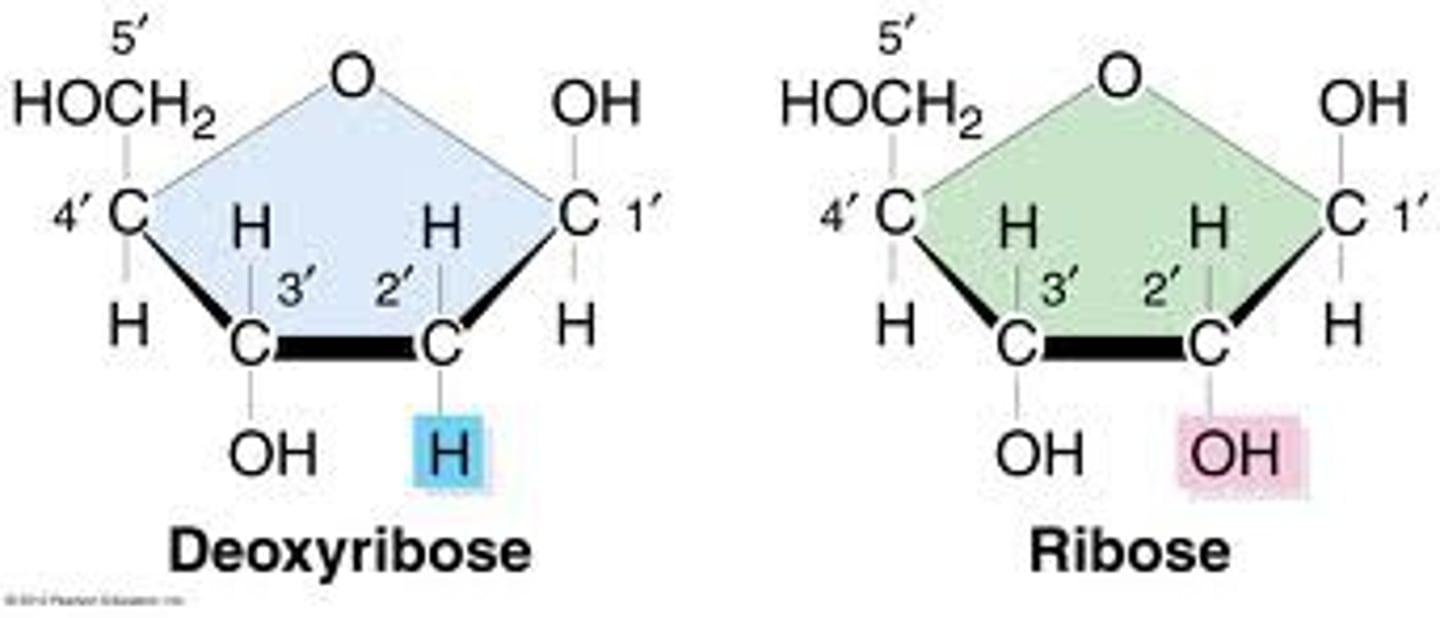
What nitrogenous base can only DNA contain?
Thymine (has a methyl group, makes DNA more stable -> better long term storage)
What nitrogenous base can only RNA contain?
Uracil
Is it possible to have a double helix RNA or a single stranded DNA?
yes, not in organisms. Only founded in viruses